3.1 Surface area to volume ratio
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Describe the relationship between the size and structure of an organism and its surface area to volume ratio (SA:V)
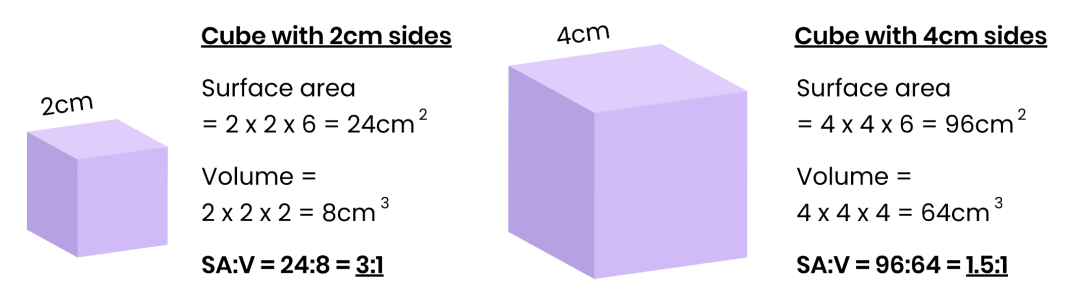
As size increases, SA:V tends to decrease.
More thin/ flat/ folded/ elongated structures increase SA:V.
How is SA:V calculated?
Divide surface area (size length x side width x number of sides) by volume (length x width x depth).
Suggest an advantage of calculating SA:mass for organisms instead of SA:V
Easier/ quicker to find/ more accurate because of irregular shapes.
What is metabolic rate? Suggest how it can be measured
Metabolic rate = amount of energy used up by an organism within a given period of time.
Often measured by oxygen uptake → as used in aerobic respiration to make ATP for energy release.
Explain the relationship between SA:V and metabolic rate
As SA:V increases (smaller organisms), metabolic rate increases because:
rate of heat loss per unit body mass increases
so organisms need a higher rate of respiration
to release enough heat to maintain a constant body temperature i.e. replace lost heat.
Explain the adaptions that facilitate exchange as SA:V reduces in larger organisms
Changes to body shape (e.g. long/ thin)
Increases SA:V and overcomes (reduces) long diffusion distance.
Development of systems, such as a specialised surface/ organ for gaseous exchange e.g. lungs.
Increases (internal) SA:V and overcomes (reduces) long diffusion distance.
Maintains a concentration gradient for diffusion e.g. by ventilation/ good blood supply.