Anatomy of Joints: Types, Movements, and Key Structures
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Joint (articulation)
A point where two bones meet; allows movement and provides stability depending on structure.
Arthrology
Study of joints
Biomechanics
Study of movement and mechanical processes in the body
Kinesiology
Study of body movement
Bony joint (synostosis)
An immovable joint formed when two bones fuse, as in the frontal bone of the skull or the epiphyseal line in adults.
Fibrous joint (synarthrosis)
A joint where bones are connected by dense connective tissue, allowing little or no movement (e.g., skull sutures).
Suture
Immovable joint between skull bones
Serrate suture
Interlocking, saw-like edges between bones
Lap suture
Overlapping bones with beveled edges
Plane (butt) suture
Straight, non-overlapping edges
Gomphosis
Attachment of a tooth to its socket
Periodontal ligament
Connective tissue holding tooth in place
Syndesmosis
Joint bound by longer collagen fibers allowing some movement
Cartilaginous joint (amphiarthrosis)
A slightly movable joint where bones are joined by cartilage, such as in the pubic symphysis or intervertebral discs.
Synchondrosis
Bones joined by hyaline cartilage
Symphysis
Bones joined by fibrocartilage
Synovial joint (diarthrosis)
A freely movable joint enclosed by a capsule and filled with lubricating synovial fluid, such as the shoulder or knee.
Articular cartilage
Smooth covering on bone ends in a joint
Synovial fluid
Lubricating fluid in joint cavity
Joint capsule
Encloses joint cavity; includes fibrous capsule and synovial membrane
Articular disc
Pad of fibrocartilage in some synovial joints
Meniscus
C-shaped fibrocartilage pad in the knee that cushions and stabilizes the joint.
Tendon
A tough, fibrous cord connecting muscle to bone, transmitting the force of muscle contraction.
Ligament
A band of connective tissue connecting bone to bone, providing joint stability.
Bursa
A fluid-filled sac that cushions and reduces friction between tissues such as tendons and bones.
Tendon sheath
Elongated bursa surrounding a tendon
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Compression of median nerve in wrist
Lever system
Mechanical structure to move a load using force and fulcrum
Fulcrum
Fixed point a lever pivots on
Effort
Applied force to move a load
Load
Object being moved by the lever
Mechanical advantage (MA)
Ratio of output force to input force
Power lever
Lever with MA > 1, gives force advantage
Speed lever
Lever with MA < 1, gives speed advantage
First-class lever
Fulcrum in the middle (e.g., scissors)
Second-class lever
Load in the middle (e.g., wheelbarrow)
Third-class lever
Effort in the middle (e.g., tweezers)
Range of motion (ROM)
Extent of movement of a joint
ROM-limiting factors
Articular fit, ligaments, and muscle tone
Axis of rotation
Line around which movement occurs
Degrees of freedom
Number of axes a joint can move around
Monaxial
Movement in one plane
Biaxial
Movement in two planes
Multiaxial
Movement in three planes
Ball-and-socket joint
A multiaxial synovial joint allowing movement in all directions, such as the shoulder and hip joints.
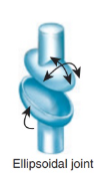
Condylar (ellipsoid) joint
Biaxial joint; oval surface fits into depression
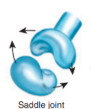
Saddle joint
Biaxial joint; both bones have concave and convex surfaces
Plane joint
Gliding, flat surfaces between bones

Hinge joint
A monaxial joint that permits movement in one plane, like the elbow or knee.
Pivot joint
A joint that allows rotation around one axis, such as the joint between the atlas and axis vertebrae.
Gliding movement
Bones slide past each other
Angular movement
Change in angle between bones
Rotation
Movement of a bone around its own axis, such as turning the head left or right.
Flexion
Decreases the angle between two bones, bringing them closer together (e.g., bending the elbow).
Extension
Increases the angle between two bones, moving them farther apart (e.g., straightening the knee).
Hyperextension
Extension beyond normal range
Abduction
Movement away from the body's midline, as when lifting the arm sideways from the body.
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body, such as bringing the arms down to the sides.
Elevation
Raises a body part
Depression
Lowers a body part
Protraction
Moves part forward
Retraction
Moves part backward
Circumduction
Circular movement of a limb
Medial rotation
Turns bone inward
Lateral rotation
Turns bone outward
Supination
Rotating the forearm so the palm faces upward or forward.
Pronation
Rotating the forearm so the palm faces downward or backward.
Lateral flexion
Side bending of head or waist
Right/left rotation
Turning head or trunk to side
Lateral excursion
Side-to-side movement of mandible
Medial excursion
Movement of mandible to midline
Ulnar flexion
Tilts hand toward little finger
Radial flexion
Tilts hand toward thumb
Dorsiflexion
Movement that raises the foot upward toward the shin.
Plantar flexion
Movement that points the toes downward, as when standing on tiptoe.
Inversion
Turns sole inward
Eversion
Turns sole outward
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Jaw joint
Articular disc (TMJ)
Fibrocartilage pad in TMJ
TMJ disorder
Pain or dysfunction in jaw joint
Shoulder (glenohumeral) joint
Ball-and-socket joint of shoulder
Glenoid labrum
Fibrocartilage ring around glenoid cavity
Rotator cuff
Group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and assist with rotation and lifting.
Shoulder dislocation
Humerus displaced from glenoid cavity
Elbow joint
Hinge joint between humerus and ulna
Radial & ulnar collateral ligaments
Stabilize the elbow joint
Knee joint
The largest joint in the body; a hinge joint that includes menisci and ligaments like the ACL and PCL.
Menisci (knee)
Fibrocartilage pads between femur and tibia
Patellar ligament
Connects patella to tibia
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament)
Prevents the tibia from sliding forward relative to the femur; crucial for knee stability.
PCL (posterior cruciate ligament)
Prevents the tibia from sliding backward relative to the femur.
Locked knee
Knee fully extended and stable
Lateral-impact knee injury
Damage from side blow to knee
Talocrural (ankle) joint
Joint between tibia, fibula, and talus
Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon
Attaches calf muscles to heel
Sprain
Torn ligament or tendon
Dislocation
Displacement of a bone from its joint, often caused by trauma.
Bursitis
Inflammation of a bursa, often due to overuse or repetitive motion.
Tendonitis
Inflammation of a tendon, commonly caused by repetitive stress.
Arthritis
Inflammation of a joint causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.