L3 - DNA replication
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
On a DNA melting curve what is Tm
Tm= half DNA is single stranded and half DNA double stranded
the higher the Tm value the more G-C bonds you have as have more H bonds
DNA replictaion is ( 2 things)
semi-conservative (half parental half newly synthesized stand)
happen bidirectionally
where does replication start
At the point of origin
DNA replictaion ends at
termination site
what is replicosome
all the machinery involved in DNA replication
how many replication forks are there
2 as replication is bidorectional
where replication begins in prokaryotes
1 orgin of replication called OricC site (euk have many orgins)
form 1 replicon (as1 site of origin)
have termination sites
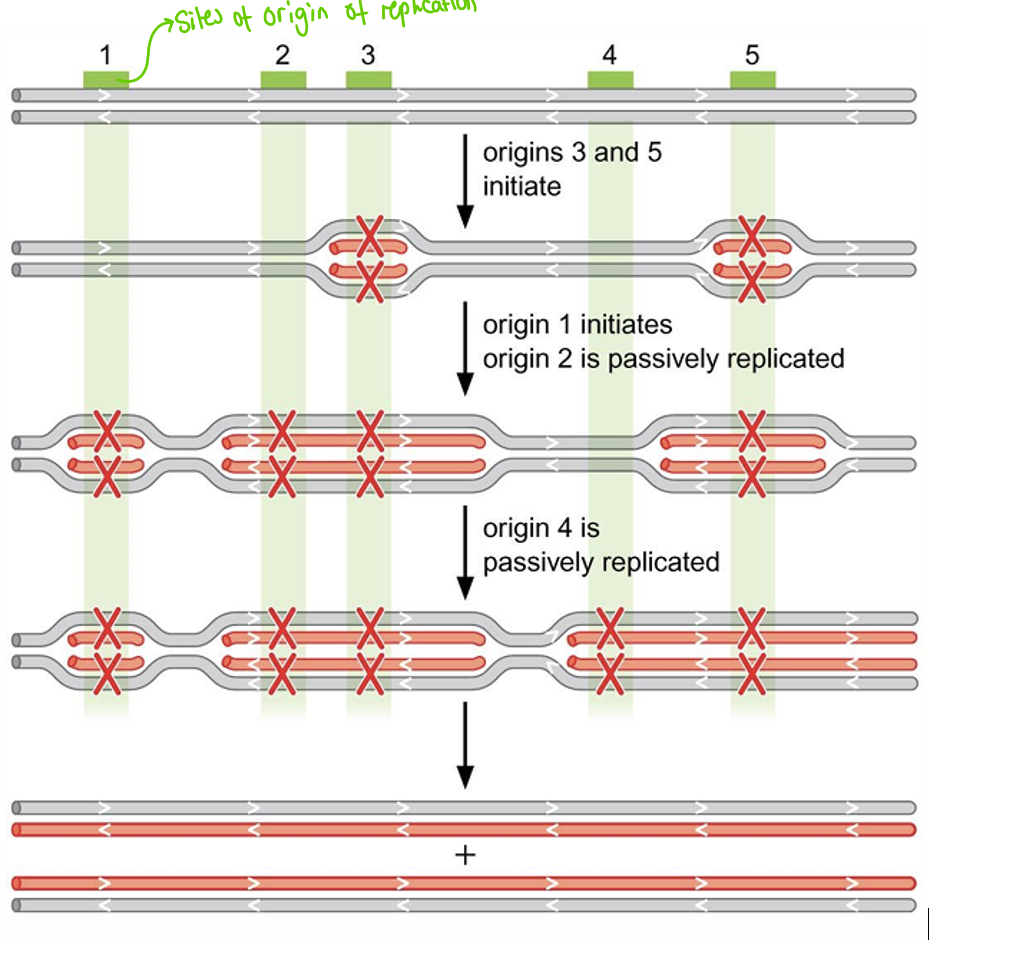
DNA replication in Euk
have multiple sites of orgin
not all orgins of replication are activated at the same time (way to regulate DNA replication)
form multiple repicons due to many sites of orgin
picture shows how it works
Replication model for replication initiation in prok..
initiator DNA binding proteins Recognize OriC site
downstream have 5 regions of 9 mer and 3 regions of 13 mers
these are also recognized by specific DNA binding proteins to then start DNA replication
What are the DNA binding proteins involved
DnaA
DnaB
DnaC
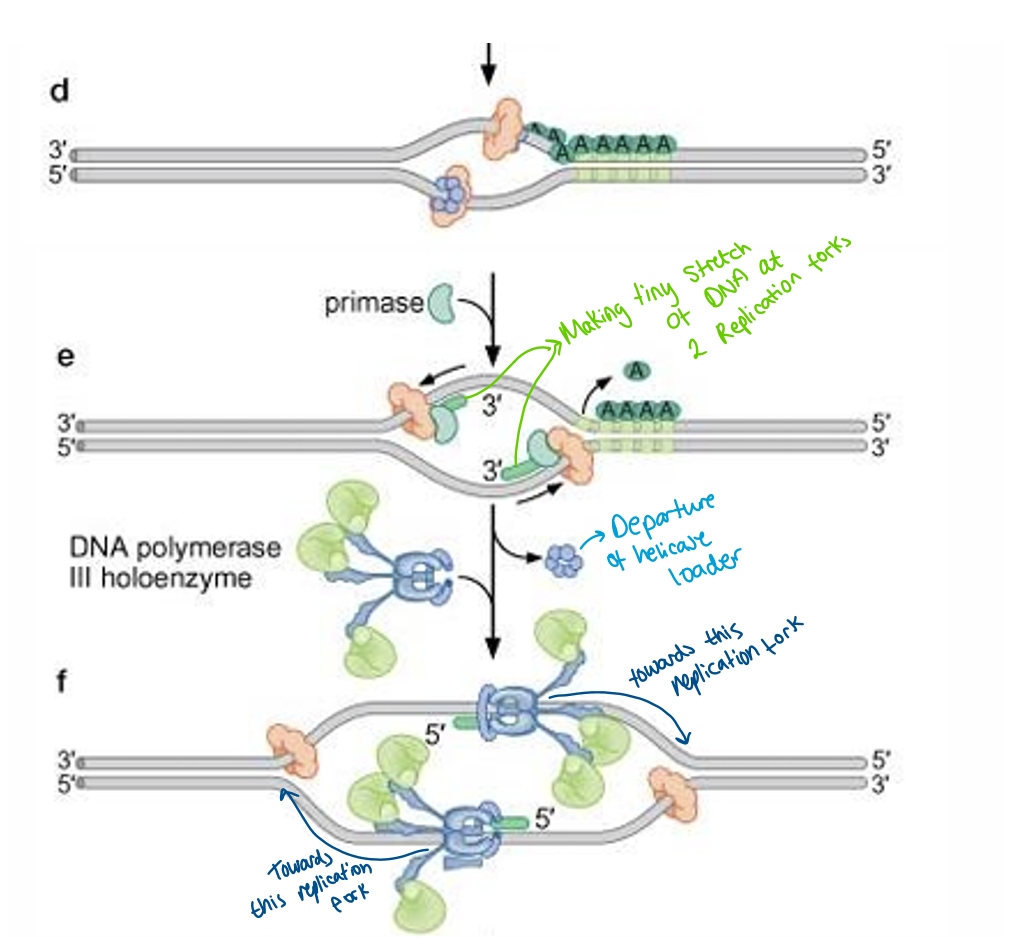
what does DnaA do?
DnaA binds to the 5 9mer regions (each 9mer bound with 1 DnaA = so 5 DnaA bound)
DnaA has ATP bound which interacts with 13mer regions to open up DNA creating replication bubble
what does DnaB do ?
it is a helicase
a hexametric protein and has a ring structure
it is inactive when bound to helicase loader
what id DnaC?
it is helicase loader helps helicase attach to DNA
Intercation between DnaB and DnaC
once bound to DNA helicase is still inactive becuase still bound to helicase
primase synthesis a short RNA primer at BOTH replication forks which causes helicase loader to dissociate and so activating helicase
what are SSB’s
single stranded DNA binding proteins which keep DNA open - stop it from reanealing back together
bind to single stranded Dna after helicase has opened it
what ahppens after primer formation form primase enzyme
RNA primer formed at BOTH replication forks get helicase loader to dissociate
DNA polymerase to come and attach to primers (to the 3’ hydroxyl group)
have 2 DNA polymerases moving towards replication fork while DNA helicase still working
types of tropoiomerases
type I —> nicks one stand of DNA, relasing a few of those stands then rejoing it
type II —> makes break in both double stands of DNA and rejoins them after
they stop DNA for becoming too coiled
difference between positive and negative super coiling
negative —> that region of DNA is opened, so less coils there
positive —> more coils and turns in that region
At end of DNA replication what happens to that RNA primer
gets degraded and replaced by DNA joined to strand using DNA ligase
Formation of the phophodiester bond
the complementary base pair gets close enough to stand so that
3’ Hydroxyl group initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate group (alpha phosphate) of the complementary base pair
this forms a phosphodiester bond
remaining 2 phophates are called pyrophosphates and are broken down by pyrophosphotase which releases energy for this whole recation to take place
usually non comp bases do not join together as do not get close enough for nucleophilic attack to happen
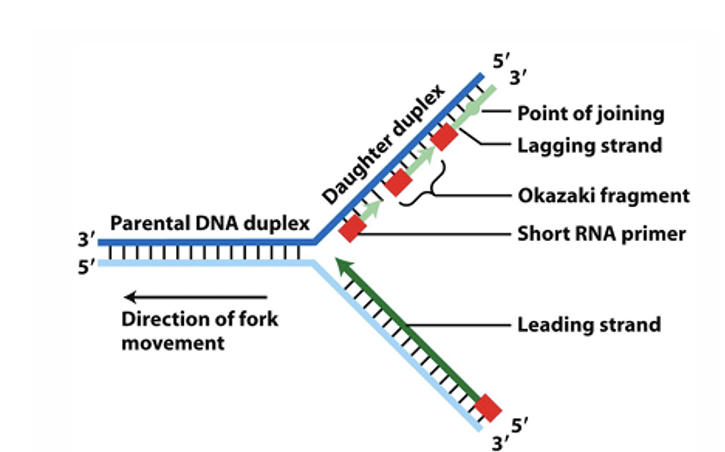
how does synthesis of new stand actually happen
Synthesis occurs from 5’ - 3’ direction
on the leading stand synthesis easily happens
as lagging strand is anti-parallel harder for this to occur
what happens is small RNA primer binds and then get small epice of DNA syntheises in 5’ -3’ diection
RNA primer then detached and moves backwards and retached then get DNA synthesie form 5’ to 3’
this contously happens fomring olkazaki fragments which are joined using different DNA polymerase 1 (in prokaryotes)
there are 3 parts to DNA polymerase one used in leading stand other two used in lagging strand
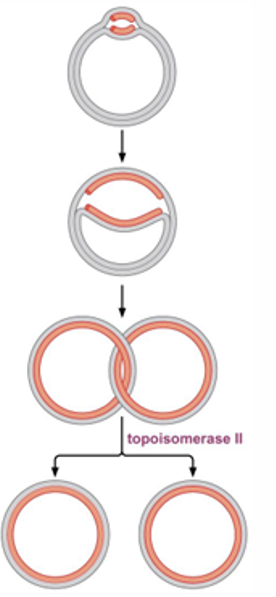
what problem occurs in prok after DNA replication and how is this solved ?
Circular DNA will be joined together
in order to separate them tropoiosomerase 2 makes a cut in one DNA and loops it out of the other
then have 2 separate circular DNA
how DNA polymerase works
shaped like a hand
the palm of hand is the active site for polymerization reaction
if incorrect base is detected hand closes and catalytic activity is paused
Incorrect base moved ot exonuclease domain to then be removed (3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity)
then hand relaxes and DNA moves back to polymerase domain when recation is unoaused and picks up speed
why do mistakes not happen often?
complementary base pairing
DNA polymerase proof reading
post replication repair system (Miss-match repair)
What are the steps in PCR
Denaturing
Annealing
Elongation/ Extension