Abnormal psychology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
The four Ds Bennett 2005 for abnormality
Deviance from the norm
Distress
Dysfunctional
Dangerous
Psychological disorder
set of symptoms of thoughts, feelings and behaviour that are ‘out of ordeR
Psychological dysfunction.
an individual cannot complete typical daily tasks, cannot socialise or maintain relationships, or is unable to work effectively for psychological reasons
Psychological deviance
People acting in contrary to what is considered societally normal
It may cause them no stress at all to deviate
Psychological distress
experience of psychological disorder or dysfunction, which may be brief or transient, or may become chronic, depending on what is being experienced
Two major guides to diagnosing mental illnesses and disorders in children and adults
The International Classification of Diseases – Version Eleven (ICD-11).
– The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Version Five (DSM-V).
Diagnostic methods
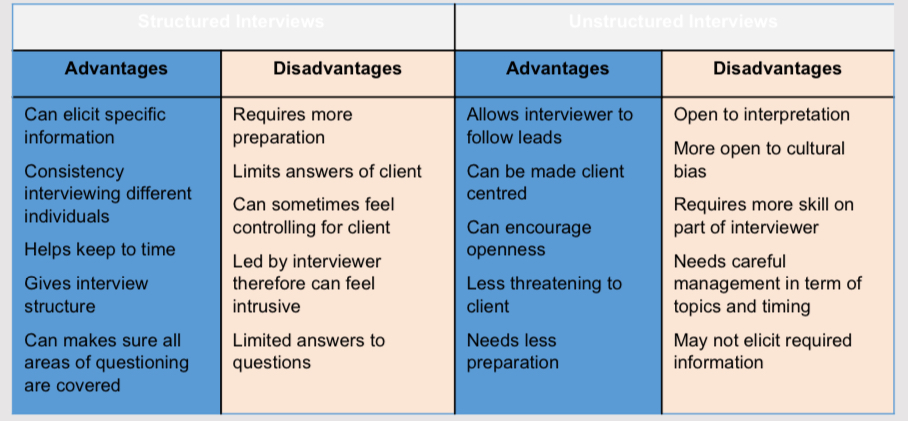
Clinical interviews are part of any diagnostic assessment
Self report is a form of clinical observation, but it is where the individual monitors their own thoughts, feelings and behaviours.
Psychometric tests and measurements are tools that can be used to gather information about a person’s mental functioning.
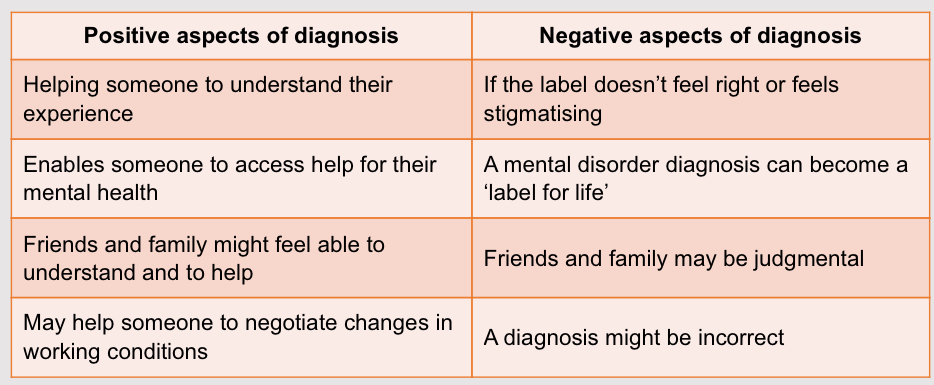
Positives and negatives of diagnosis
Formulation
a piece of writing, a diagram, a letter or some other kind of document that provides the story of an individual’s journey to their current mental health state
Butler 1998 list of features of a good formulation
– Grounded in an appropriate level and breadth of assessment.
– Culturally sensitive.
– Expressed in accessible language.
– Considers the possible role of trauma and abuse.
– Considers the possible role of services in compounding problems.
– Includes the impact and meaning of medical and healthcare interventions.
The superego
the part of our personality that contains all the rules we have been taught or that are followed by the culture and society we inhabit.
• The Superego can clash with the Id, and the Ego has to act as the judge and mediator between the two.
The attachment/developmental model
Developmental psychology is truly biopsychosocial, drawing on genetics, neurobiology, family and peer relationships, environmental influences and many other factors.
• Attachment theory seeks to explain how most individuals tend to have a consistent way of forming and maintaining relationships.
explore an individual’s early life relationships and see how these relate to current behaviours and thoughts about other people.
Sociocultural approaches and Ideas
Help a therapist to remember to consider wider factors
Used with community to to assess individuals environment to see where sources of stress may be maintaining
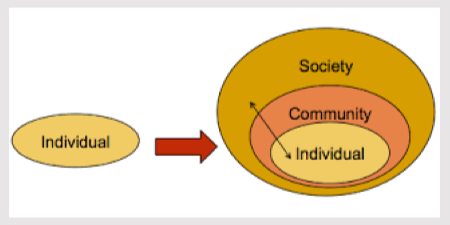
The power threat meaning (PTM) framework (2018)
attempt to outline a conceptual alternative to psychiatric diagnosis, starting from first principles in order to identify non-medical patterns in distress and troubled or troubling behaviour.
• The PTM framework requires psychologists conducting assessments to consider the following questions in assessment:
– Impact of POWER: ‘what has happened to you?’
– Impact of a sense of THREAT: ‘how has this affected you?’ and ‘what did you do to get through it?’
generalised anxiety disorder GAD
people feel anxious across a whole range of daily experiences and relationships
They can be constantly looking out for danger or something going wrong, and they might avoid doing things they believe will turn out badly.
• Physical symptoms include sweating, shaking, raised heart rate, breathing quickly and tensing or clenching up – this can lead to severe fatigue
Has a strong genetic component
Schizophrenia
experiences that are perceived as unusual by others in society, these are often referred to by mental health professionals as symptoms.
• ‘Positive’ symptoms are unusual and bizarre experiences in relation to thinking, feeling, talking, memory and behaviour:
Schizophrenia characteristics
Delusions are unusual beliefs that would seem bizarre and outside of reality to others.
– Hallucinations are sounds, sights and other sensory events that are not experienced by others.
disorganised thinking and speech
Inappropriate emotion display
Avolition is a lack of energy or interest in goals or life
Withdrawal from external interests entirely to thier own issues
Catonia - stops responding to their environment, remaining motionless and silent for prolonged periods
Schizophrenia approaches
• The dopamine hypothesis model suggests that the disorder is due to an excess of the neurotransmitter dopamine and antipsychotic medication is used to manage this
• The diathesis stress model suggests that although there may be a biological underpinning for schizophrenia, it needs external environmental stressors for the symptoms to be triggered (Holmes, 2010).
• Psychological approaches emphasise the impact of trauma, abuse and deprivation on an individual’s thinking, feeling and behaviour (BPS, 2017), and may advocate psychological treatments to manage the distress associated with having these stressful experiences
Bulimia nervosa
episodes of binge eating that occur at least once a week for at least three months, and then attempts to purge themselves to avoid gaining weight
• In a psychodynamic model, BN might be thought to be the result of an individual not developing a sense of their own hunger cues at an early age, possibly as a result of inconsistent or neglectful parenting around eating
Fairburn’s Transdiagnostic Model (Fairburn, Cooper & Shafran, 2003) sees The thoughts, feelings and behaviours of a person with BN are focused on in four areas: mood intolerance, perfectionism, interpersonal problems, and low self- esteem.