intro to human anatomy
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
anatomy
The study of structure of the body parts and their relationships to eachother
Physiology
Study of the function of the body
3 subdivisions
Gross anatomy, microscopic, developmental
Gross anatomy
When you are able to see the structure with naked eye
Microscopic
Need a microscope (cells)
Developmental
Structure you see over time (fertility)
principal of complementary
Function always reflects structure
Bones (structure) can support (function) and protect (function) body organs because they contain hard mineral destroying
6 levels of structural organization
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Chemical level
Simplest level, atoms that combine to form molecules
Cellular level
Cells are made up of molecules
Tissue level
Tissue has similar types of cell
Organ system level
System has different organs that work together closely
Organismal level
The human organism is made up of many organ system
Tissue
A group of similar cells that have common functions
What is the relationship between 6 structural organizations
They all build off of eachother
Tissue
Group of similar cells that have common functions
Organ
Contain two or more types of tissues
Organ systems
12 major
Integumentary system
Protects
Skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs
Muscular system
Fast acting control system
Endocrine system
Produce hormones
Cardiovascular system
Blood vessels transport blood
Lymphatic system
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns them to blood
Immune system
attacks against forging substance
Respiratory system
Supplied with oxygen and removes CO2
Digestive system
Breaks down food to absorbable units
Urinary system
Eliminates nitrogenous waste from the body, regulates water, electrolytes, acid base balance
Reproduction
Production of offspring
Homeostasis
Maintains a relatively stable internal condition despite continuous changes in the environment
Basic elements of homeostatic
Stimuli, receptors, control Centre, effort, variable, response
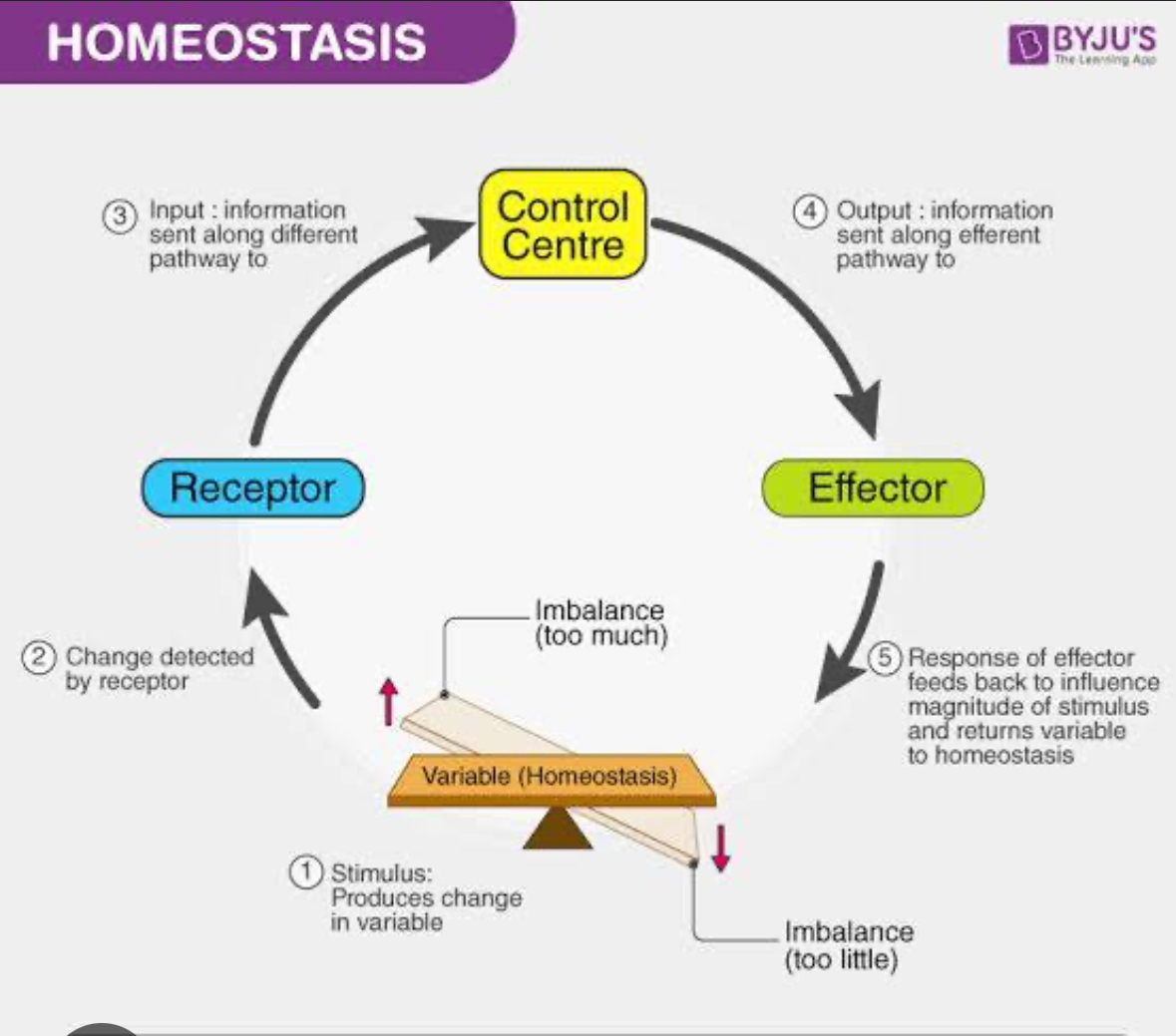
In order
Stimulus, receptor, input, output,response,
Stimuli
Cause change in a variable
Receptor
Monitors for change in a variable
Control center
Determines the set point at which variable is maintained
Effector
Receives output from control center, reduces or enhances stimuli
Response
Either reduces(negative) or enhances stimulus( positive)
Variable
Something we can monitor
Positive feedback
to amplify a signal and drive a process to completion
Ex: childbirth (contractions)
Negative feedback
To maintain stability and equilibrium by reducing or reversing a stimulus
Ex cold (shivering)
How many tissues do you need to be an organ
2 or more
Describe anatomical postion
Body erect, feet are slightly apart, palms facing forwards, thumbs facing away from the body
Superior
Towards the head/ upper part of the body/structure (above)
Inferior
Away from the head or toward the lower part of the body(below)
anterior
Towards or at the front of the body ( in front of)
Posterior
Towards or at the back of body (behind)
Medial
Towards or at the midline of the body (on the inner side of)
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body (on the outer side)
proximal
Closer to the origin of the body parts or the point of attachment to the body truck
Distal
Farther from the origin of the body parts or the point of attachment of a limb to the body truck
Superficial
Towards or at body surface
Deep
Away from the body surface more internal
Major body cavities
Dorsal, ventral body cavity
Dorsal cavity
cranial cavity, vertebral cavity
Cranial cavity
Brain
Ventral cavity
Spinal cord
Ventral cavity
Thoracic cavity, abdominopelvic cavity,
Thoracic cavity
Heart, lungs
Abdominopelvic
Liver, stomach, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, bladder reproductive organs
Serous membrane or serosa
Thin double layered membranes, included parietal serosa and visceral serosa
Parietal serosa
Lines internal body cavity walls
Visceral serosa
Covers internal organs
Serous fluid
Decreases friction as layers move over one another
Pericardium
Heart
Pleurae
Lungs
Peritoneum
Abdominopelvic cavities