SM 143 Statically indeterminate & Compatibility equations
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Statically indeterminate objects
Object is “restrained”
More unknowns than equil equations, which means compatibility conditions need to be considered.
Superposition requirements
The load must be linearly related to the stress and displacements
No significant displacement or changes in geometry are allowed
“Compatibility conditions”
Logical equations developed by using equil equations & ΔL (δ) equations in context, then solved simultaneously.
ΔL is written as δ, because change is small.
Make sure δ > gap in stress questions
Examples:
Global equil to relate forces to each other, then a comp equation that sets total δ = 0. Simultaneously solve to find values of forces.
Global equil to relate forces, then comp equation that sets δ of both objects of interest equal to each other. Solve simultaneously.
Increase in temperature of restrained object
↑ in temp results in displacement
Displacement is retrained so thermal stress occurs
ΔLT = 0
ΔL due to ΔT
α is coefficient of thermal expansion which is given.
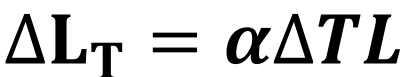
Thermal stress
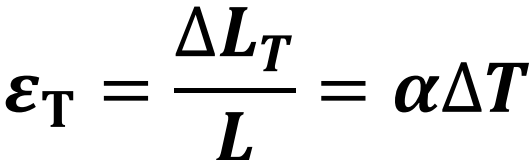
Force exerted back onto object due to elongation
Find total δ, then subtract gap size from it. Use difference as δ in δ = PL/AE to find P exerted by wall.
If >1 segment on object, account for it by adding more terms to δ equation for each segment. eg. δdiff = δAB + δBC, where P are equal in each term