free scored fl psych/soch
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Which is a plausible reason why participants with the attachment style investigated are less likely to seek support from others in times of stress?
Results revealed that an avoidant attachment style was significantly associated with distress and symptoms of burnout, depression, and somatic complaints following exposure to a critical incident
A.
Participants think that others are reluctant to get close to them.
B.
Participants find it difficult to trust and depend on others.
C.
Participants do not worry that they will be abandoned by others.
D.
Participants want to merge completely with others and this desire pushes people away.
B, a key characteristic of avoidant attachment style
As infants, what type of parent-infant interaction most likely occurred for the participants?
Results revealed that an avoidant attachment style was significantly associated with distress and symptoms of burnout, depression, and somatic complaints following exposure to a critical incident. This attachment style was also significantly associated with few social contacts, low satisfaction with social support, and maladaptive coping strategies.
A.
A confused infant-parent bond that is characterized by mixed separation anxiety and a tendency for the infant to resist and have a dazed behavior
B.
An infant-parent bond that is characterized by some separation anxiety and a tendency for the infant to seek contact with the parent after separation
C.
An infant-parent bond that is characterized by strong separation anxiety and a tendency for the infant to resist contact with the parent after separation
D.
An insecure infant-parent bond that is characterized by little separation anxiety and a tendency for the infant to resist contact with the parent
D, avoidant attachment style pretty much means you want to stay away from everyone which is further reinforced with the statement of “few social contacts” so the only answer that aligns with this would be D because “little separation anxiety”
Assume that participants in the study were divided into high and low avoidant attachment groups. The graph represents the percentage of ambulance workers with high and low avoidant attachment styles by the time to recover from social withdrawal following a critical incident.
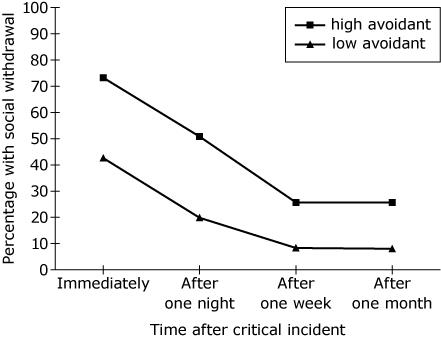
Which conclusion is accurate based on the results of the graph?
A.
The largest percentage difference of social withdrawal between levels of avoidant attachment occurred one week following exposure to a critical incident.
B.
More than half of the ambulance workers with low avoidant attachment withdrew from social contacts immediately following exposure to a critical incident.
C.
Ambulance workers with high avoidant attachment were more likely than those with low avoidant attachment to report greater occurrence of social withdrawal following exposure to a critical incident.
D.
Social withdrawal was the same for high and low avoidant attachment one month following exposure to a critical incident.
C
The internal working model that sets expectations about self and others described in the study is an example of:
Early experiences with caregivers become internalized into a working model of expectations about self and others that can provide the basis for subsequent responses to stressful experiences. Attachment theory research has explored how this internalized working model influences the way in which individuals respond to stress and utilize coping resources.
A.
an insight.
B.
a critical period.
C.
a cognitive schema.
D.
a heuristic.
the internalization aspect can be looked at like this a child who grew up spoiled always getting what they want and was never told no grow up become adults and expect to get their way still its a preset mindset which aligns with answer choice C
cognitive schema
knowledge structures that determines ones expectations in diff contexts such as social interactions
Assume that the researchers wanted to measure a behavioral component of ambulance workers' emotion regulation following exposure to a critical incident. Based on the study, which component is most likely to be assessed?
A.
Journal entries of ambulance workers' emotional reactions following the critical incident
B.
Ambulance workers' heart rates following the critical incident
C.
Ratings of likeability from coworkers following the critical incident
D.
Observations of workers' social interactions with others following the critical incident
D
Which brain region will be LEAST activated when participants are completing the tasks in the study?
Ambulance workers were then asked to identify a critical incident they encountered in the past. Use of coping strategies and support seeking within 24 hours of responding to a critical incident were measured. Additionally, somatic complaints, symptoms of burnout, depression, and distress, including recalling physical and emotional stress responses, were measured.
A.
Parietal lobe
B.
Hippocampus
C.
Prefrontal cortex
D.
Amygdala
A
parietal lobe function
integration of sensory information like smelling burnt bread
hippocampus
memory encoding, needed for recall of critical incident
prefrontal cortex
executive functioning and decision making
Which statement is NOT a plausible application of psychodynamic theory to explain psychological responses to upward comparison?
A.
The superego demands that the individual should either match or surpass the partner on the dimension of comparison.
B.
The ego fails to satisfy the demands of the superego, and the individual experiences anxiety.
C.
The id attempts to use the pleasure principle to resolve the subconscious conflict caused by the superego.
D.
The ego uses rationalization by suggesting that the dimension of comparison is unimportant.
C, lowkey everything else was about ego so i just went with something that firstly was different as the rest was pointed towards the same thing
super ego
demands one to perform their highest possible standard, an upward comparison
ego
structure of personality for balancing the conflicting demands of ID and superego when equilibrium isnt reached/resolving subconscious conflict caused by superego, it induces anxiety which is an upward comparison in the sense you experience anxiety bc you are comparing yourself to something of higher stature and failing
ID
basic drives (hunger, sex, aggression, survival urges).
In psychodynamic models, the id is often emphasized less as a literal “thing” in the brain and more as a conceptual source of unconscious motivations and conflicts.
The patient described in the passage is most likely using which defense mechanism?
He has stopped attending social events with his partner because such events elevate his feelings of inferiority. However, despite his feelings of inferiority and envy, the patient also reports having extreme admiration and love for his partner
A.
Projection
B.
Rationalization
C.
Reaction formation
D.
Emotional displacement
C
Was the independent variable in the study manipulated by the researchers?
Then, the participants were told that they were going to be paired with potential dates and were given information on their potential dates’ scores on the same personality dimensions. The dates’ scores were made up by the researchers to be either similar to or different from each participant’s actual self or ideal scores. The study showed that participants reported greater interest in dates who were similar to their ideal selves than in dates who were similar to their actual selves. The therapist finds the study relevant to the patient’s case but is reluctant to make direct inferences because she suspects that the participants’ ratings of actual self may have been influenced by social desirability.
A.
Yes; the researchers obtained specific measures of the actual self and the ideal self from the participants.
B.
Yes; the researchers controlled the similarity of the potential date to the participant's ratings of themselves.
C.
No; the researchers have no control over whether or not the participants prefer dates who are similar to them.
D.
No; the researchers cannot manipulate the difference between the participants' actual selves and their ideal selves.
B
Which statement best explains the patient's behavior in terms of operant conditioning?
The patient describes his current partner as being highly successful and competent and reports feeling inferior to his partner. He reports that he “hates feeling that way.” He has stopped attending social events with his partner because such events elevate his feelings of inferiority. However, despite his feelings of inferiority and envy, the patient also reports having extreme admiration and love for his partner.
A.
Feelings of inferiority function as a positive reinforcer for attending social events with partner.
B.
Feelings of inferiority function as a negative reinforcer for attending social events with partner.
C.
Feelings of inferiority function as a positive punisher for attending social events with partner.
D.
Feelings of inferiority function as a negative punisher for attending social events with partner.
C, attending the events made his feelings of inferiority elevate which is a positive punisher, an additional thing was added onto making him feel worse about the situation
Weber's characteristics of an ideal bureaucracy suggest that most formal organizations will:
A.
train employees to conduct a variety of tasks.
B.
select employees based on technical qualifications.
C.
require employees to seek consensus in decisions.
D.
evaluate employees based on individualized criteria.
B
whats webers ideal bureaucracy in a nutshell
a organization thats based off merit so following those with higher status, hiring those based on technical qualifications over race
whats mcdonalidzation of society created by George Ritzer
extreme rationalization —> streamlined but dehumanized
more focus on speed and efficiency, making everything the same across the platform using non human stuff when possible
A 34-year-old man has had a series of brief relationships with several romantic partners, but has never established a close, intimate relationship with a partner. According to Erikson's theory of psychosocial development, which outcome best describes this example?
A.
Despair
B.
Isolation
C.
Role confusion
D.
Stagnation
B
Which statement best describes the sociological conceptualization of race and ethnicity?
Racial and ethnic identities are:
A.
consistent across time periods and geography
B.
composed of mutually exclusive categories.
C.
based primarily on physical characteristics.
D.
institutionalized in major social structures.
D
Which construct best describes the process in which an immigrant group comes to express the cultural values and norms of a new country?
A.
Cultural transmission
B.
Cultural relativism
C.
Cultural diffusion
D.
Cultural assimilation
D
Which conclusion demonstrates a fundamental attribution error when interpreting the results of the study?
A.
Dispositional attributions of others' behavior are weaker when attitude ratings are influenced by the presence of others than when alone.
B.
Dispositional attributions of others' behavior are stronger when attitude ratings are influenced by the presence of others than when alone.
C.
Situational attributions of others' behavior are weaker when attitude ratings are influenced when alone than when in the presence of others.
D.
Situational attributions of others' behavior are stronger when attitude ratings are influenced by the presence of others than when alone.
B, overestimated dispositional cannot be C because even though its underestimating it they switched to it alone than presence of others invalidating it
dispositional attribution (internal)
-assume its about the person
exp: she failed the exam because shes lazy
situational attribution (external)
-assume its because of an external cause
exp: she failed the exam because she was sick that day
what is dispositional and situational attribution correlation with fundamental attribution error
overestimate dispositional and underestimate situational
If participants in the study rated the administrator's attitude more inconsistently in the "Alone" condition than in the "With Others" condition, then:
A.
the mean in the "Alone" condition would be higher than in the "With Others" condition.
B.
the mode in the "Alone" condition would be higher than in the "With Others" condition.
C.
the median in the "Alone" condition would be higher than in the "With Others" condition.
D.
the standard deviation in the "Alone" condition would be higher than in the "With Others" condition.
D
In the study, what is the most likely outcome if participants exhibited social facilitation?
A.
Participants who are with others will look at others' card-sorting strategies and use a similar strategy to complete the task.
B.
Participants who are alone will perform better on the card-sorting task than those who are with others.
C.
Participants who are with others will perform better on the card-sorting task than those alone.
D.
Participants who are with others will exert less effort to complete the card-sorting task since they are pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal.
C
Based on the elaboration likelihood model, which type of processing was most likely induced by the administrator when interacting with the participants?
‘The administrator of the card-sorting task displayed a positive (smiling, consistent eye contact, and pleasant tone of voice) or negative (scowling, poor eye contact, impatient foot tapping) attitude by using a variety of nonverbal cues toward half of the participants in each condition”
A.
High elaboration processing
B.
Central route processing
C.
Careful processing
D.
Peripheral route processing
D
elaboration likelihood model
explains how people are persuaded depending on how much they think about a message
what are the two routes of elaboration likelihood persuasion
central route
peripheral route
central route
Content: logic, facts, strong arguments
peripheral route
presentation: facial expressions, appearance, emotions, superficial cues
Which construct is most relevant to the description in paragraph 2 about the comparison of two wines with different levels of sweetness?
“Sommeliers are under a great deal of pressure to perform the difficult task of describing wines correctly. The ability to pick out specific flavor notes from the overall wine flavor and name them accurately requires considerable practice. As more sugar is added, subtle changes in the sweetness of wine can be detected by both experts and novices. However, the lowest level of an odor that can be detected does not seem to be improved with training.”
A.
Weber's law
B.
Perceptual constancy
C.
Natural selection
D.
Absolute threshold
A, most aligned with the last sentence about not improved with training
Which factor is most likely a potential confounding variable in the study described in the final paragraph?
“To examine whether visual information was more relevant than a flavor profile in eliciting an accurate description of the wine’s flavor, researchers had 54 novices—students training to become sommeliers—perform two different wine comparison sessions. In each individual testing session, people tasted two different wines, one red and one white, and described the two wines. In the second session, one week after the first, both of the wines were actually the same; the white wine had been colored red and substituted for the red wine. The results are shown in Figure 1.”
A.
The presence of the red food coloring in the second session
B.
Number of red wine words successfully produced
C.
Whether the food coloring can be tasted by subjects
D.
The obesity levels of the subjects
C
confounding variable
factor that isn’t independent nor dependent it could affect results and give false association , it provides a different reasoning that isn’t fully related to the experiment
Which receptors are responsible for the color vision necessary to detect the food coloring described in the passage?
A.
Rods, found mainly in the fovea of the eye
B.
Rods, found mainly in the periphery of the eye
C.
Cones, found mainly in the fovea of the eye
D.
Cones, found mainly in the periphery of the eye
C
A student sommelier who correctly describes a wine explains his or her success by saying "I just got lucky." Which factor best explains the student's attribution?
A.
Conformity
B.
External locus of control
C.
Social facilitation
D.
Social inhibition
B
In Study 2, the primary function of donepezil is to:
“Participants with AD were on daily drug treatments of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AchEI) donepezil”
A.
increase the antagonistic effects of acetylcholine.
B.
increase the duration of acetylcholine action.
C.
inhibit the release of acetylcholine.
D.
inhibit the formation of acetylcholine.
Donepzeil is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor meaning it prevents the breakage of acetylcholine since it is inhibiting an esterase of acetylcholine, esterase breaks stuff down degrades them so answer is B by preventing the breakage of acetylcholine it increases the duration of its action
Which conclusion CANNOT be made based on the design of Study 2?
The benefits of pharmacological mono- and combination therapy show differential effects and:
The effects of pharmacological treatment on brain atrophy (A), cognitive scores (B), and daily living scores (C) in AD patients were compared to CONT participants (Figure 1). The cognitive score was determined by word recall, word recognition, comprehension of spoken language, and word naming tasks. The daily living score was determined by the ability to do routine tasks such as grooming, eating, and walking independently.
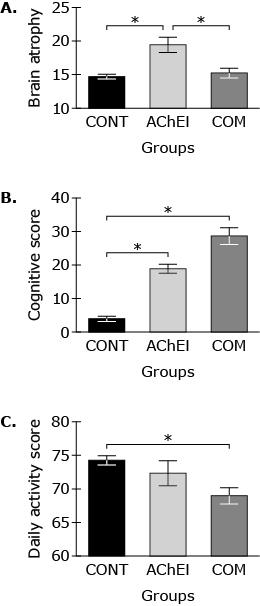
Figure 1 Effects of drug treatment in AD patients compared to controls on brain atrophy (A), cognitive score (B), and daily living scores (C) (Note: * indicates a significant difference as indicated from the other group.)
A.
donepezil provides better results than memantine.
B.
combination therapy with memantine does not always provide better results.
C.
monotherapy does not always provide better results.
D.
the results depend on the type of neurobiological test.
A
Which statement is supported by the results of Study 2?

Figure 1 Effects of drug treatment in AD patients compared to controls on brain atrophy (A), cognitive score (B), and daily living scores (C) (Note: * indicates a significant difference as indicated from the other group.)
Participants treated with:
A.
AchEI showed significantly better protection from brain atrophy compared to those treated with combination therapy.
B.
combination therapy showed significantly better cognitive ability compared to those in the AchEI group.
C.
combination therapy showed significant behavioral impairment compared to participants in the CONT group
D.
AchEI showed significant cognitive and behavioral improvement compared to those in the COM group.
C
The results of the Study 1 and(or) Study 2 suggest that patients with AD show:
“The results showed that for AD patients, there was a spatial shift in cortical activity that was independent of latency or strength of the electrical current, compared to controls. The cortical shift was located at a posterior region of the somatosensory cortex and was determined not to be a result of brain atrophy known to occur in AD.”

Figure 1 Effects of drug treatment in AD patients compared to controls on brain atrophy (A), cognitive score (B), and daily living scores (C) (Note: * indicates a significant difference as indicated from the other group.)
A.
significant structural loss of brain cells that can be prevented by pharmacological treatment.
B.
structural loss due to atrophy, but reorganization may preserve functional activity in some brain regions.
C.
functional loss in memory and structural loss due to atrophy that can be reversed through pharmacological treatment.
D.
functional loss in motor skills required for daily living without significant structural loss due to atrophy.
B
A woman loses her job, finds that she is unable to pay her bills, and accumulates debt. She must sell her home and move into an apartment. This woman has experienced which type of social mobility?
A.
Horizontal mobility
B.
Vertical mobility
C.
Intergenerational mobility
D.
Structural mobility
B
A researcher interested in cultural differences regarding happiness designs a cross-cultural study in which happiness is measured relative to a nation's gross domestic product. Which is a dependent variable in this study?
A.
Cultural differences
B.
Nations
C.
Gross domestic product
D.
Happiness
D
Which condition provides the best example of medicalization?
A.
Cancer
B.
Diabetes
C.
Alcoholism
D.
Hypertension
C
People tend to form social and romantic relationships with individuals that they see frequently. Which construct is most likely to explain this tendency?
A.
Looking-glass self
B.
Mere exposure effect
C.
Social comparison
D.
Social facilitation
B
The results of the study support which correlation?
“Results indicated that living in a highly segregated neighborhood was associated with an elevated rate of premarital births, regardless of neighborhood SES.”
A.
A positive correlation between degree of neighborhood segregation and neighborhood SES
B.
A positive correlation between degree of neighborhood segregation and rate of premarital births
C.
A negative correlation between neighborhood SES and neighborhood poverty level
D.
A negative correlation between neighborhood poverty level and rate of premarital births
B
Which combination of theories from the passage is most likely to share assumptions with the life course approach?
‘Structural explanation 1 posits that the shift of industrial production away from urban centers led to an outmigration of middle-class African American families and a subsequent concentration of poverty in some African American neighborhoods. Structural explanation 2 posits that residential segregation in urban areas concentrates poverty and contributes to neighborhood decline.”
“The ecological perspective includes a potentiator model, which refers to correspondence between risks from the environment and those from the family, as well as a protective model, which describes how more affluent families tend to protect their adolescents from risks in the environment.”
A.
Structural explanation 1 and structural explanation 2
B.
Structural explanation 1 and potentiator model
C.
Structural explanation 2 and protective model
D.
Potentiator model and protective model
D, since we are asking about life course approach we need to focus in on micro reasonings as life course pertains to individuals this kicks out structural explanation 1 and 2 as both affect a group of people
Due to the assertion that the local environment influences adolescents' norms and values, the ecological perspective is most similar to which sociological theory?
A.
Social strain theory
B.
Disengagement theory
C.
Differential association theory
D.
Labeling theory
values and norms are affected aka the way they think is affected, answer C is right
In subsequent research, the study is expanded to examine how high-SES African American adolescents adapt to predominantly white neighborhoods. Which concept would be LEAST applicable to this follow-up study?
A.
Front stage self
B.
Intersectionality
C.
Social role conflict
D.
Demographic transition
D
front stage self
individuals impression managment thats consistent with expectations of ones social role
intersectionality
indicates different aspects of someone’s social background thats linked to privileges or disadvantages due to ones race, ethnicity, age etc
social role conflict
conflicting demands of two different social roles in someones life
demographic transistion
balance between fertility and mortality rates in society
The participants in Study 1 ignore information that suggests that negative events are more likely than they think. This is best characterized as an example of:
A.
conforming to information provided by a credible source.
B.
discounting information that causes cognitive dissonance.
C.
experiencing group polarization regarding negative information.
D.
using the representativeness heuristic to evaluate negative information.
B
Based on the findings from Study 1, which outcome is most likely for Study 2?
In Study 2, another group of participants watched a short clip depicting a car accident. A week later, the participants were presented with a written summary of the clip they viewed previously. For Group A, the written summary contained small errors that made the car accident in the video appear more serious than it really was. For Group B, the written summary contained small errors that made the car accident appear less serious than it really was. For the control group, the written summary contained no errors. After a delay of one more week, the participants were asked to retrieve their memory of the original video as accurately as they could. The researchers were interested in the participants’ likelihood of creating false memories for the car accident.
Source monitoring errors:
A.
are more likely to be made by Group A.
B.
are more likely to be made by Group B.
C.
are not likely to be made by either group.
D.
are equally likely to be made by both groups.
B
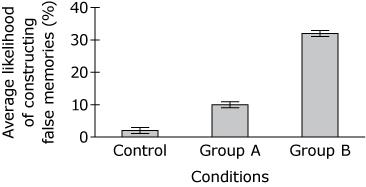
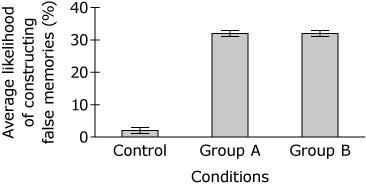
Based on the findings from Study 1, which graph shows the most likely outcome for Study 2?
“The results showed that people were more likely to update their beliefs when the new information suggested that negative events were less likely than they expected.”
‘For Group A, the written summary contained small errors that made the car accident in the video appear more serious than it really was. For Group B, the written summary contained small errors that made the car accident appear less serious than it really was.”
A.
B.
C.
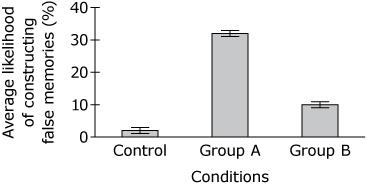
D.
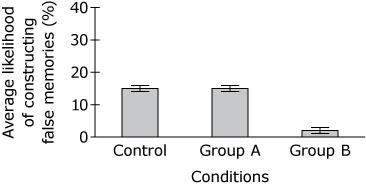
A
The researchers who conducted Study 1 were interested in the individual differences between the participants in terms of how they update their beliefs. The participants' scores on which variable would be most likely to predict how they update their beliefs?
‘The results showed that people were more likely to update their beliefs when the new information suggested that negative events were less likely than they expected.”
A.
Optimism
B.
Self-esteem
C.
Impression management
D.
Self-efficacy
A
When caring for a family member with advanced cancer, caregivers are often faced with the demands of completing many tasks for the patient while maintaining employment and other personal responsibilities. This situation describes which role dynamic?
A.
Role conflict
B.
Role adjustment
C.
Role strain
D.
Role engulfment
A
Which statement best explains the variation in caregiver distress by gender?
A.
Gender identity theories state that women are more likely than men to provide beneficial care.
B.
Contemporary gender roles assign shared responsibility for family caregiving between women and men.
C.
Gender socialization theories state that men are less likely than women to respond to the needs of others.
D.
Traditional gender roles assign more responsibility for family caregiving to women than to men.
D
The future research described at the end of the passage is LEAST likely to be designed with which type of method?
“More research is still needed, such as studies that determine how support for caregivers could be improved and how providers can help caregivers manage their new roles.’
A.
Survey methods
B.
Ethnographic methods
C.
Experimental methods
D.
Comparative methods
C
In operant conditioning, partial reinforcement, rather than continuous reinforcement, leads to a response that is:
A.
slower to acquire and more resistant to extinction.
B.
faster to acquire and less resistant to extinction.
C.
faster to acquire and more resistant to extinction.
D.
slower to acquire and less resistant to extinction.
A
A woman's manufacturing job is unexpectedly outsourced to a factory in Country A. She responds with hostility and anger towards all people from Country A and accuses them of taking her job. Which concept best describes her response?
A.
Xenophobia
B.
Scapegoating
C.
Prejudice
D.
Ethnocentrism
B
xenophobia
fear and suspicion towards cultures perceived to be foreign
scapegoating
erroneously assigning blame to an identifiable source
prejudice
preconceived negative judgment about certain individuals and groups due to their social background
ethnocentrism
values and practices of other cultures are evaluated by someone’s own cultural lenses and considered inferior
Based on the animal studies described in the passage, elevated levels of which hormone are most likely to affect hippocampal volume?
‘Studies on humans show that people who have experienced posttraumatic stress disorder have reduced hippocampal volume. In contrast to stress, exercise has been shown to benefit learning and memory functioning in aged animals.”
A.
Melatonin
B.
Cortisol
C.
Prolactin
D.
Oxytocin
B
The categorization aspect of the cognitive functioning assessment involves which type of memory?
A.
Sensory memory
B.
Short-term memory
C.
Episodic memory
D.
Semantic memory
D
sensory memory
holds memory for half a second no recall correlation
short term memory
very short lived memory unless actively reproduce it doesnt aid in recall
episodic memory
personal connection memories long term
semantic memory
linked to categorization and categorizing task
The morphological changes associated with elevated stress or exercise are examples of:
‘Studies on animals have shown that chronic increases in stress-related hormones are associated with reduced dendritic spines, decreased long-term potentiation, and reduced neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Studies on humans show that people who have experienced posttraumatic stress disorder have reduced hippocampal volume. In contrast to stress, exercise has been shown to benefit learning and memory functioning in aged animals.”
A.
lesions.
B.
maturation.
C.
neural transmission.
D.
neural plasticity.
First isolate whats been altered
-reduced dendritic spines
-increases learning and memory both ties with answer choice D
Which process most likely accounts for the effect of the peer group's response, described in paragraph 4, on a teenager's drug experimentation?
“Novice users are typically adolescents or young adults who view drug use as a means of gaining social acceptance from a peer group. The novelty of the sensory, motor, or emotional experiences produced by the drug high is another important factor for new users. Certain personality traits, such as impulse control and sensation seeking, have been found to be associated with drug use in adolescents.”
A.
Central route persuasion
B.
Peripheral route persuasion
C.
Informational social influence
D.
Normative social influence
D
Participants' scores on the antagonism scale are most likely associated with scores on which personality trait?
“In a study designed to determine whether specific traits could predict drug use, high school seniors completed a questionnaire regarding their past use of tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs. To assess personality, the researchers developed a brief inventory (the HP5) based on the Five-Factor Model of personality. Participants responded to 20 self-statements on a four-point response scale, where higher scores indicate that the individual has the trait being assessed. The researchers found that scores on the HP5 “antagonism” and “impulsivity” scales were the most closely associated with initial drug experimentation.”
A.
Agreeableness
B.
Conscientiousness
C.
Sensation seeking
D.
Openness
answer is A because agreeableness is one of the 5 personality
Participants' responses to the self-statements on the inventory described in the passage could be affected by each of the following confounds EXCEPT:
A.
Hawthorne effect.
B.
demand characteristics.
C.
self-serving bias.
D.
confirmation bias.
D
hawthorne effect
change in participants behavior when they know they are being watched even occurs in self reports
demand characteristics
research design provides cures to participant regarding the study hypothesis and casues them to respond in specific manner
confirmation bias
tendency to put more weight on information that confirms ones preexisting attitudes doesn’t affect self statements
If a researcher defines the concept of religiosity as the frequency an individual engages in religious meetings, rituals, or practices, that researcher has created a(n):
A.
hypothetical definition.
B.
conceptual definition.
C.
thematic definition.
D.
operational definition.
D
Some medical conditions, such as HIV/AIDS, are met with shame and disapproval by segments of society. Public health interventions, such as HIV testing campaigns, are often conceived as efforts to counteract the negative attitudes associated with those conditions. Based on this description, such interventions are specifically targeting:
A.
the stereotype threat associated with conditions such as HIV/AIDS.
B.
social segregation of those with conditions such as HIV/AIDS.
C.
the social stigma associated with conditions such as HIV/AIDS.
D.
discrimination against those with conditions such as HIV/AIDS.
C
A postsynaptic cell has a resting membrane potential of -65mV with a threshold potential of -55mV. Will an action potential be generated by a single stimulus that lowers the membrane potential of the postsynaptic cell by 15mV?
A.
Yes, because the stimulus caused the membrane potential to exceed the threshold potential
B.
No, because the stimulus hyperpolarized the membrane, producing an inhibitory effect
C.
Yes, because the stimulus had an excitatory effect on the postsynaptic membrane
D.
No, because the depolarizing effect of the stimulus did not exceed the threshold potential
B, because if it lowers membrane by 15 the -65 will become -80 pushing it further from threshold which is hyperpolarizing and inhibits potentials