CARDIAC RHYTHYMS
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Sinus Bradycardia
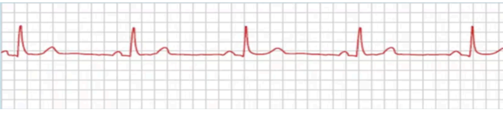
Identify the rhythm
Calcium Channel Blockers, Beta blockers

What is the cause of this?
NO cardiac compressions
Atropine (only if symtomatic: showing low perfusion, pale, cool, clammy)
Atropine, Dopamine (Infusion), Epinephrine (infusion)

What is the treatment?
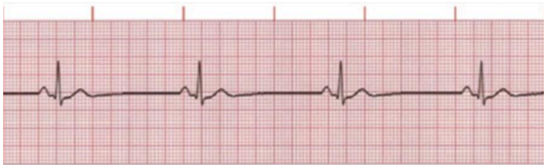
SINUS TACHYCARDIA
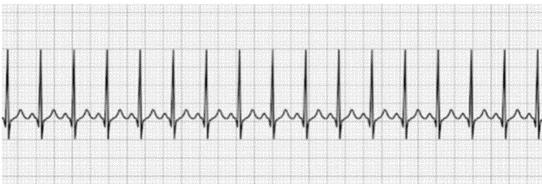
Identify the rhythm
Normal P-Wave, QRS Complex, T-wave
HR >100 BPM (at rest)
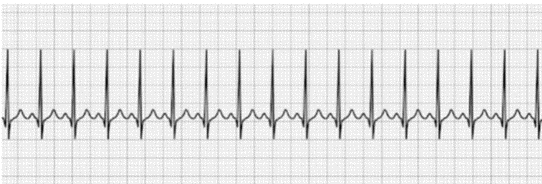
Give its characteristics
Reverse underlying conditions (fever, anxiety, exercise)
Beta-blockers (metoprolol, sotalol)
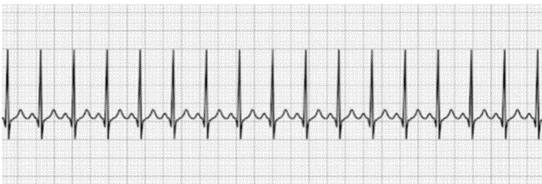
What is the treatment for this?
ASYSTOLE
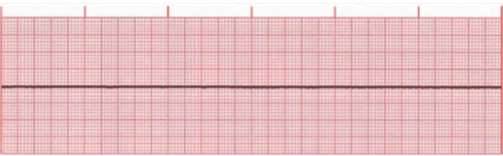
Identify the rhythm
Identified by absence of palpable pulse
Systole is reflected by a flatline in the ECG
Electrical activity in the ventricles is completely absent
No BP, no cardiac output, or breathing is detected. Clinical death has occured.
Give its characteristics
Begin immediate CPR with high-flow oxygen
Intubate and establish IV
If unchanged, begin transcutaneous pacing
Epinephrine (1mg IVP per 10 ml solution, every 3-5mins)
Atropine (1mg IVP, repeat every 3-5mins to a total dose of 0.003-0.004 mg/kg). May be given by ET tube at 2-3 mg diluted in 10 mL normal saline
If no response, sodium bicarbonate (1 mEq/kg IVP) may repeat 0.5 mEq/kg every 10min
If asystole persists, consider quality of resuscitation, identification of reversible causes, and support for termination protocols.

Give its treatment
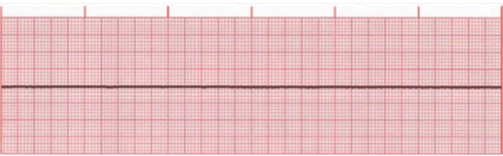
PULSELESS ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY
Identify the rhythm
Monitor shows an identifiable electrical rhythm, but no pulse is detected
Rhythm may be sinus, junctional, or ventricular in origin
PEA is also called Electromechanical dissociation
Unresponsive, no respiration/pulse/BP

Give its characteristics
Begin immediate CPR with high-flow oxygen
Intubate and establish IV
If unchanged, begin transcutaneous pacing
Epinephrine (1mg IVP per 10 ml solution, every 3-5mins)
Atropine, if ECG HR<60 bmp (1 mg IVP, repeat every 3-5 mins to total doese of 0.03-0.04 mg/kg). May be given by ET tube at 2-3 mg diluted in 10 mL normal saline
Consider fluid challenge of 500 mL normal saline, especially in suspected hypovolemia
If no response, sodium bicarbonate (1 mEq/kg IVP) may repeat 0.5 mEq/kg every 10min

Give its treatment
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION
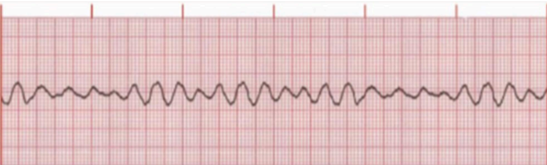
Identify the rhythm
Chaotic electrical activity occurs with no ventricular depolarization or contraction
The amplitude and frequency of the fibrillatory activity can be used to define the type of fibrillation as coarse, medium, or fine

Give its characteristics
Immediate defibrillation
Epinephrine (1mg IV every 3-5 mins)
Amiodarone (300 mg IV diluted to 20-30ml NSS as loading dose, followed by 150 mg IV once in 3-5 mins)
Check adequacy of the high-quality CPR being performed: 100 compression/minute at 2” to 2.4” depth

What is the treatment?
PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
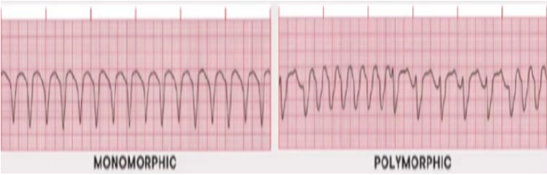
Identify the rhythm
If the patient becomes hemodynamically unstable, prepare for synchronized cardioversion with 200 joules of biphasic electrical current
If the patient is pulseless, defibrillation is recommended with 200 joules of biphasic electrical current
Epinephrine (1 mg IV every 3-5mins)
Amiodarone (300 mg IV diluted to 20-30 ml NSS as loading dose, followed by 150 mg IV once in 3-5 mins)

Give its treatment
TORSADES DE POINTES
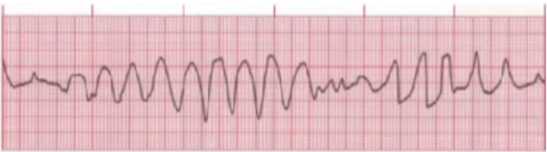
Identify the rhythm
Magnesium sulfate (1-2 g IV mixed with 50-100 ml NSS for 5-60mins)
If the patient loss consciousness and pulse, defibrillate with 120 to 200 joules of biphasic electrical current
Ventricular pacing to override the ventricular rate and, thus, capture the rhythm is also acceptable treatment
Procainamide should be avoided because its effect is to prolong the QT interval

Identify the treatment
An atypical form of VT, also referred to as polymorphous VT.
It can result as a consequence of drug therapy (eg. quinidine therapy) or electrolyte imbalance such as hypomagnesemia (due to malnutrition and alcohism)
The phrase translates to “twisting of points” in French

Give its characteristics
BRADYCARDIA WITH PULSE (SYMPTOMATIC BRADYCARDIA)
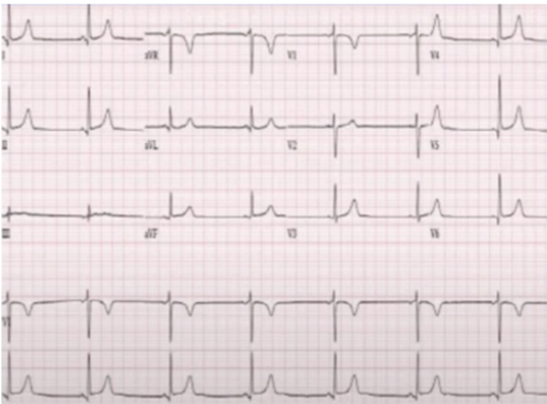
identify the rhythm
Atropine (1 mg IV bolus every 3-5mins; max of 3mg)
If atropine is ineffective, transcutaneous pacing or dopamine infusion (5-20 mcg/kg/min)
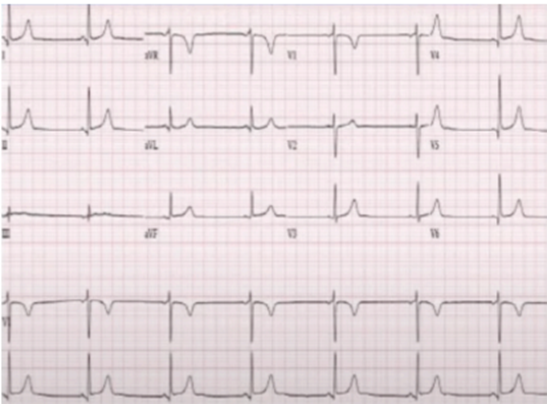
Give its treatment
<60 bpm with symptoms like low bp, altered mental status, syncope, signs of shock, ischemic heart disease, heart failure
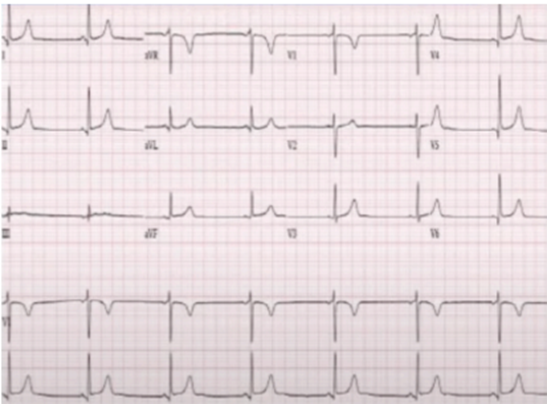
Give its characteristics