9. somatic nervous system
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what is a neurone
nerve cell
- functional unit of nervous system
neurone structure
dendrites
soma
axon
axon terminal
types of neurones
bipolar
pseudonipolar
multipolar
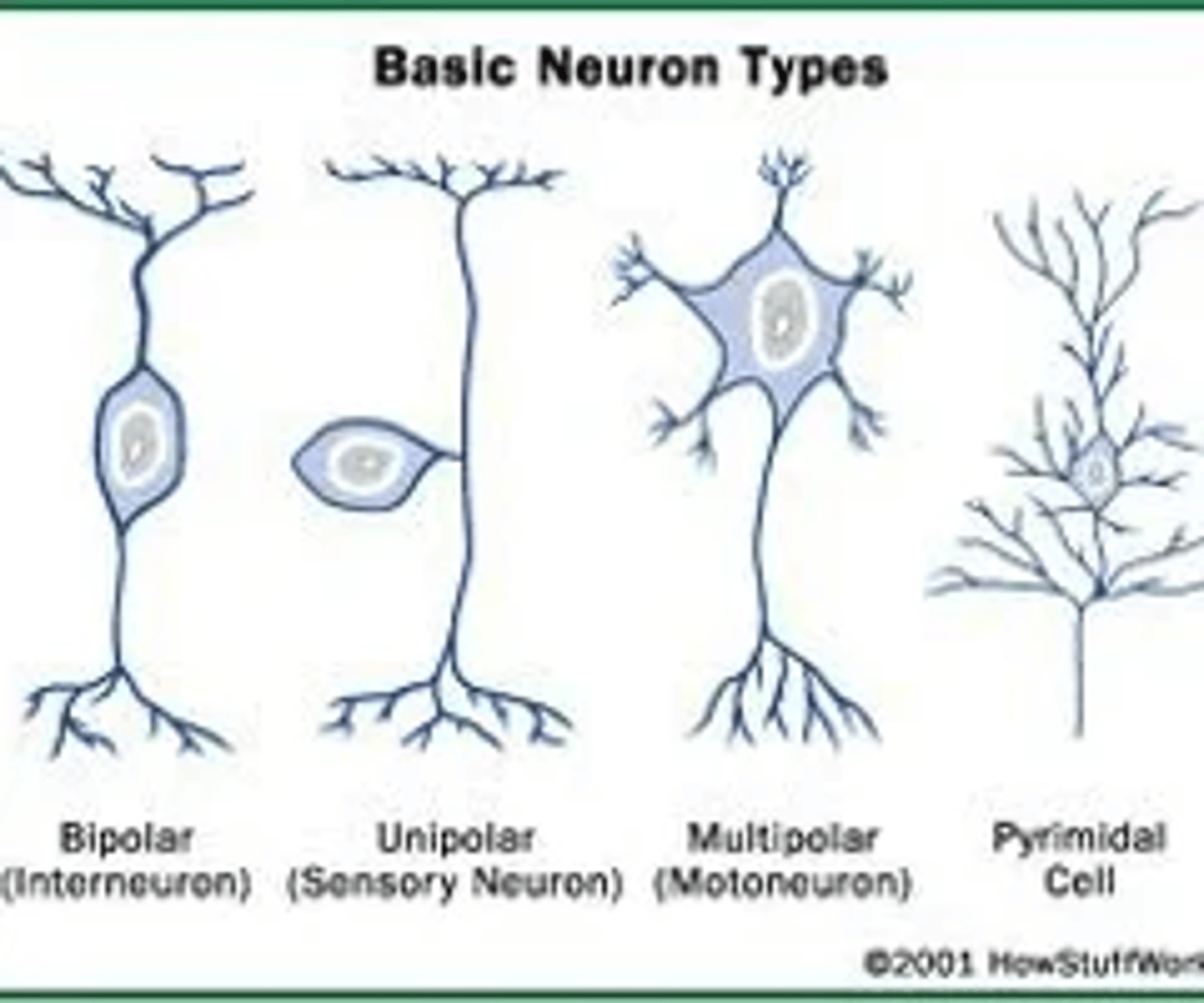
types of neuroglial cells in CNS
astrocytes
microglial cells
ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
myelin sheath
surrounds axon
lipid and protein layer
increases velocity of impulse conduction
whats the important thing about myotomes
one muscle myotome may include several spinal segments
clinical relevance of dermatomes and myotomes
to test for motor and/or sensory loss of one or more spinal nerves/segments by testing joint movements or an area of skin in neuro disorders
motor end plate
neuromuscular junction
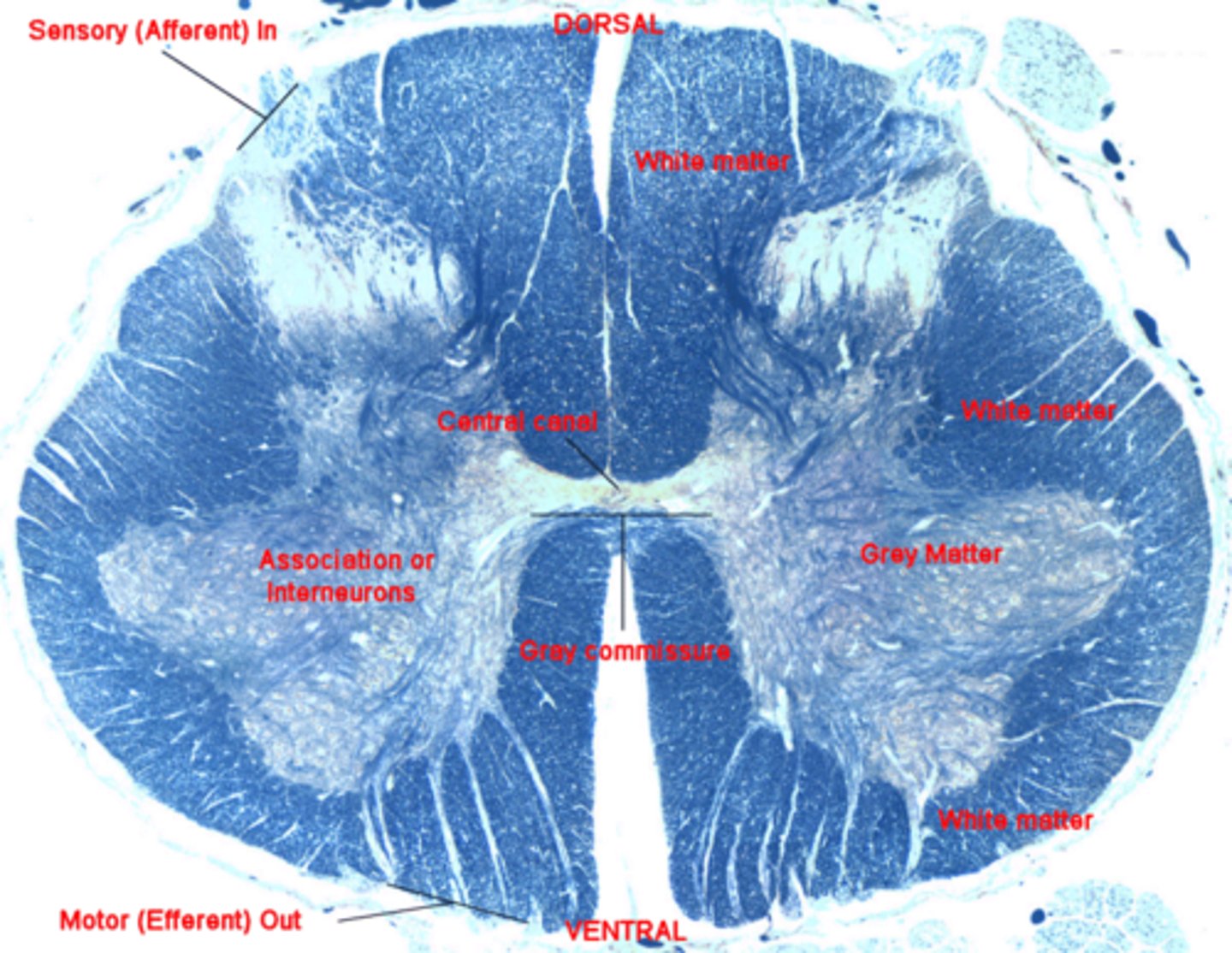
histology of spinal cord
Includes central canal, dorsal horn, ventral horn, site of ventral root, and ventral fissure
histology of peripheral nerve
looks like a finger print
somatic nervous system
motor
- voluntary control
- skeletal muscle
sensory
- pain, touch, temperature, proprioception (SKIN)
visceral nervous system
motor
- involuntary - ANS
sensory
- visceral pain, chemoreception, stretch receptors (ORGANS)
somatic motor fibre
regulates voluntary control of body movements via skeletal muscle
somatic sensory fibre
transmits general sensation - pain, touch temperature, proprioception - to CNS
spinal cord injury
- roots
sensory OR motor loss
- ventral root = MOTOR loss
- dorsal root = SENSORY loss
spinal cord injury
- spinal nerve
motor AND sensory loss
spinal cord injury
- rami
motor AND sensory loss
- ventral ramus - motor and sensory loss of anterolateral trunk and limbs
- dorsal ramus - motor and sensory loss of back
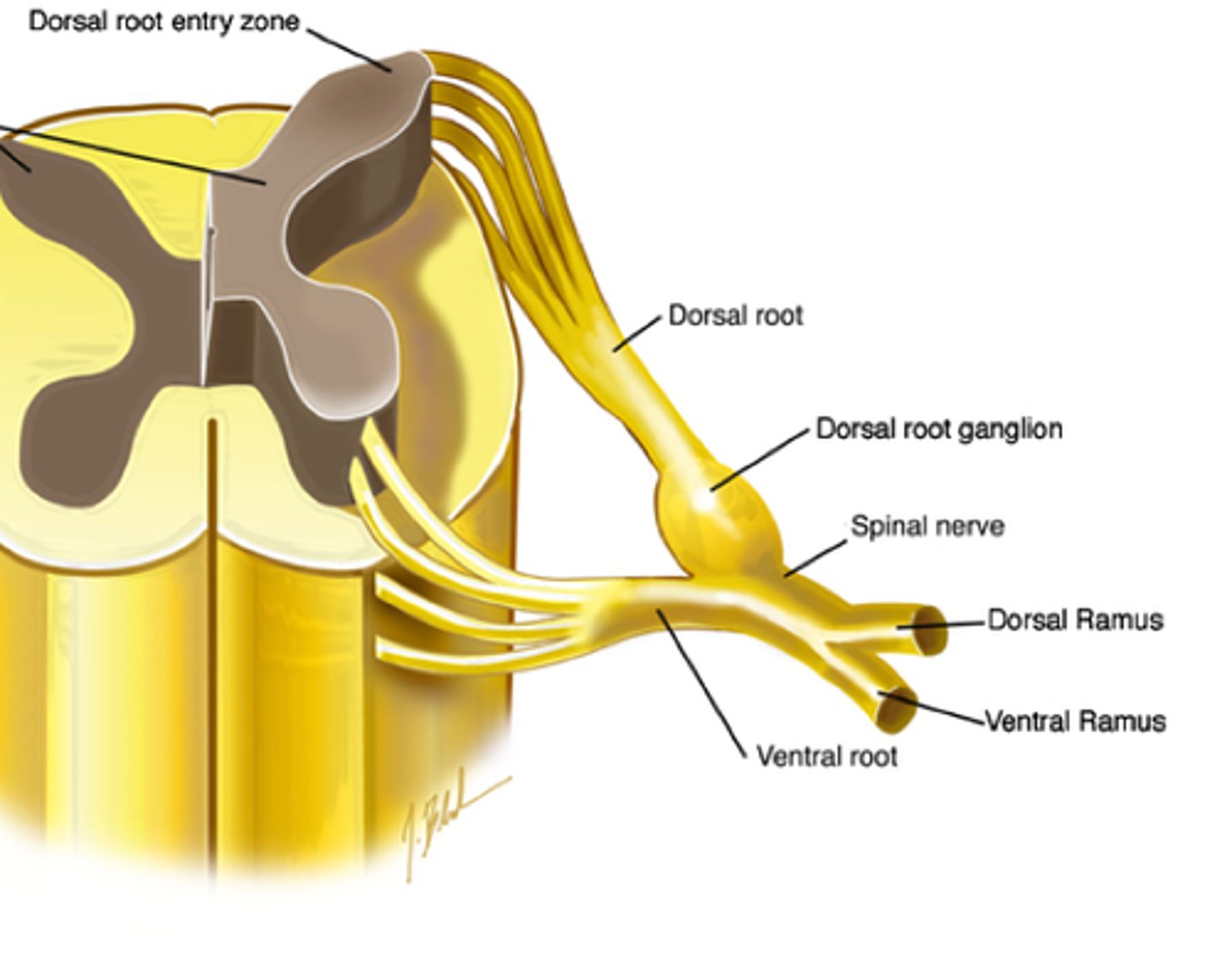
what does the spinal nerve carry
sympathetic fibres
where does the spinal nerve exit
intervertebral foramen
spinal nerve compression
back pain
Where does the spinal cord end?
L1-L2
5 components of somatic reflex arc
1) receptor responds to stimuli
2) afferent neurone carries signal to CNS
3) integrating centre in CNS initiates response
4) efferent neurone carries signal to effector
5) response from effector
wrist drop
damage to radial nerve