4.3: Facets of Experimental Design
The Placebo Effect
- Placebo: a pill/drug that looks and tastes like the real thing, but has no actual effect on the individual taking it
- Placebo effect: when the patient’s belief that a treatment will have an effect causes an actual change to take place
- Placebos are often, but not always, given as a control group
- If a placebo is given and all other factors in the control group and treatment group are held constant, any differences in the results can be attributed to the treatment
Blind Studies
- Single-blind study: the subjects do not know which group/treatment they are in/receiving, but the doctors/individuals measuring and interacting with the subjects do know which treatment the subject received
- Or the subjects know, but the people interacting with them don’t
- Double-blind study: when neither the subjects nor those interacting with them and measure the response variable know which treatment the subject received
- Whenever possible, experiments with human subjects should be double-blind
- Sometimes, however, double-blind studies are not possible
- Major advantage — limits unconscious/subconscious bias by the researcher administrating the treatments
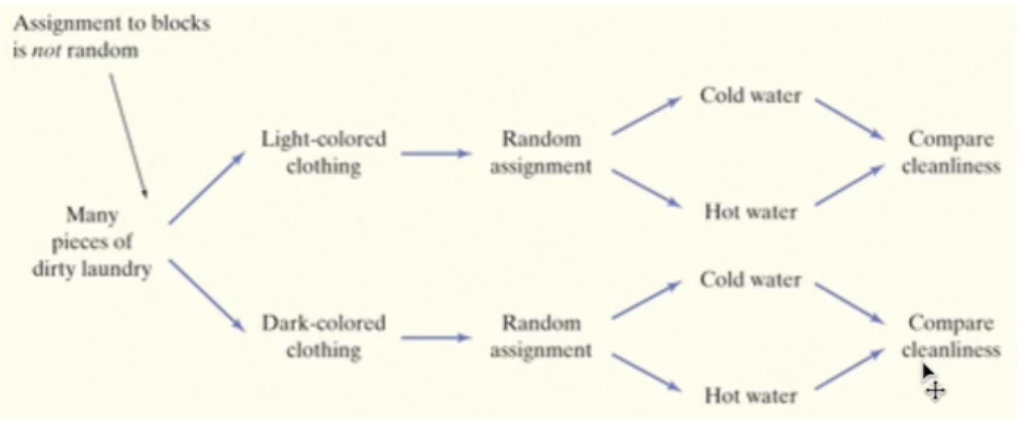
Block Design
Randomized block design: used when groups of experimental units are known to differ from each other and may respond differently to treatment as a group; to avoid confounding, the groups are separated into blocks and the assignment of experimental units to treatments is carried out separately within each block
- Eg. females vs. males
Block: a group of experimental units that are known before the experiment to be similar in some way that is expected to affect the response to the treatment
- Not formed at random (experimenter assigns experimental units to blocks)
- The differences from block to block should be as significant as possible, but within each block, subjects should be similar
- A good experimenter will form blocks based on the most important, unavoidable sources of variety among subjects
- Randomization will then average out the effects of remaining lurking variables
Block design helps us obtain more precise conclusions
Blocks vs. Strata
- Major difference: stratifying is used for sampling before an experiment is started; how subjects are identified/gathered, whereas block is the design of the experiment itself
- One major similarity is that both designs divide subjects into groups based on similar features
- Matched pairs design
- Match pairs of similar subjects
- Use random assignment to decide which member of each pair gets each treatment
- Helps reduce the effect of variation among subjects
- Can also be one individual that receives two treatments, and the order of treatments is randomized
- Observed effects are statistically significant if the probability is larger than what would be expected if the effect was just by chance
- If the principles of experimental design are followed and a statistically significant result is reached, it is good evidence that the treatment caused the effect