SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY - PSYC002
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Intrapersonal topics
emotions
attitudes
self
social cognition
Interpersonal topics
helping behavior
agression
prejudice
discrimination
attraction
close relationships
group processes
intergroup relationships
Situationism
view that our behavior and actions are determined by our immediate environment and surroundings
Dispositionism
view that out behavior is determined by internal factors such as personality traits and temperament
Quizmaster study
Participants randomly assigned to role
of either the questioner or participant.
• Questioners developed difficult
questions to which they knew the
answers.
• Participants answered questions
correctly 4/10 times.
• Participants tended to disregard the
influence of the situation and wrongly
concluded that a questioner’s
knowledge was greater than their own.
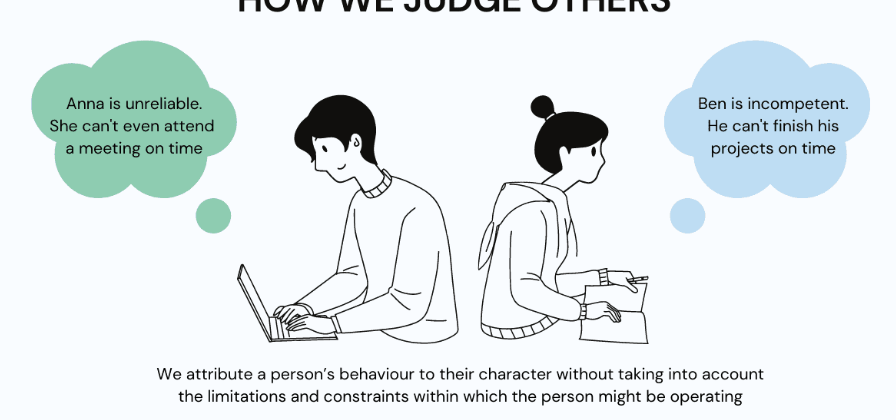
Fundamental Attribution Error
tendency to overemphasize internal factors as explanations for the behavior of other people and underestimate the power of the situation
HOW WE JUDGE OTHERS
Fundamental Attribution Error Differences
people form an individualistic culture more likely to commit the fundamental attribution error
people from collectivistic cultures are more likely to emphasize relationships with others
provides broader perspective including both situation and cultural influences
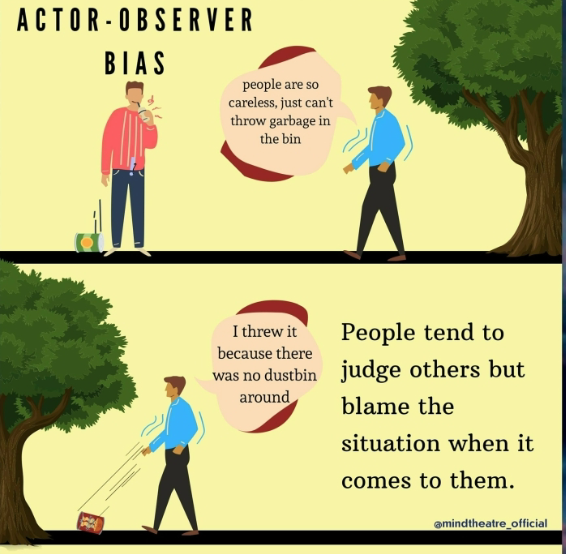
Actor-Observer Bias
tendency of attributing behaviors of others to internal factors BUT our own to situational forces
Attribution
Belief about the cause of a result
Locus of control - internal vs external
Stability - extent to which the circumstances are changeable
Controllability - extent to which the circumstances can be controlled
Our team wins : its talented (internal), works hard (stable), and used effective strategies (controllable)
Our team loses : the other team has more experienced players (external), played at home (unstable), and the weather affected our teams performance (uncontrollable)
Self-Serving Bias
tendency of an individual to take credit by making dispositional or internal attributions for positive outcomes but situational or external attributions for negative outcomes.
protects self-esteem-allows people to feel good about their accomplishments

Just World Hypothesis
belief that people get the outcomes they deserve
the world is a fair place, therefore good people experience positive outcomes, and bad people experience negative outcomes
Social Roles
pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group
defined by culturally shared knowledge
expected behavior varies across situations
Social Norm
group expectation of what is appropriate and acceptable behavior for its members
Script
a persons knowledge about the sequence pf events expected in a specific setting
Obedience
behavior change to comply with demand by an authority figure
Milgram obedience study
participants told to shock “learners” for giving wrong answer
65% continued to administer shocks to an unresponsive learner
The Stanford Prison Experiment (Philip Zimbardo) 1971
mock prison was constructed and male college students were randomly assigned to play the role of prisoners or guards
the two week study had to be ended after six days
guards became increasingly sadistic
prisoners began showing signs of severe anxiety and hopelessness
Attitude
our evaluation of a person, idea, object
can be positive or negative
Affective Component
feelings
Behavioral Component
effect on behavior
Cognitive Component
belief and knowledge
Cognitive Dissonance
psychological discomfort arising from holding two or more inconsistent attitudes, behaviors, or cognitions
to reduce cognitive dissonance, individuals can…
change behavior
change beliefs through rationalization/denial
add new cognition
The Effect of Initiation
A difficult initiation into a group influences us to like the group more.
Arson and Mills Experiment (1959)
college students volunteered to join a group that would meet regularly to discuss the psychology of sex
3 conditions - no initiation, easy initiation, difficult initiation
students in the difficult initiation condition liked the group more than students in other conditions due to the justification of effort.
Persuasion
process of changing attitudes toward something based on some kind of communication
we encounter attempts at persuasion attempts everywhere. Persuasion is not limited to formal advertising; we are confronted with it throughout our everyday world
Elaboration Likelihood Model
Petty & Cacioppo 1986
persuasion can take one one of two paths, and the durability of the end result depends on the path
Central Route
logic driven
date and facts
direct route to persuasion focusing on the quality of information
works best when audience is analytical and willing to engage in processing of the information
Peripheral Route
indirect route
uses peripheral cues to associate positivity with the message
uses characteristics such as positive emotion or celebrity endorsement
results in less permanent attitude change
Foot-in-the-Door Technique
get someone to agree to small favors only to request a larger favor
Door-in-the-Face Technique
Make a larger request that you know will not be accepted then follow with a more moderate request
Conformity
change in persons behavior to go along with the group, even if they do not agree with the group
Asch Effect
76% of participants conformed to group pressure at least once
Motivation to Conform
Normative social influence
conform to group norm to fit in, feel goof, and be accepted
Informational social influence
conform because they believe the group is competent and has the correct information
The greater the majority the more an individual will conform
Presence of another dissenter causes conformity rates to drop to near zero
Public responses cause more conformity than private
Effects of Conformity on Groups
Groupthink
modification of the opinions of members of a group to align with what they believe is the group consensus
groups often take action that individuals would not perform outside the group setting because groups make more extreme decisions than individuals do
Group Polarization
strengthening of an attitude after discussion of views within a group
Social Facilitation
An individual performs better when an audience is watching than when the individual performs the behavior alone
occurs when performing a task for which they are skilled or an easy task
when nervous or less skilled an audience may hinder rather than help
Social Loafing
exertion of less effort by a person working together with a group
occurs when individual performance cannot be evaluated separately from the group
Group performance declines on easy tasks
when task is difficult ppl feel more motivated and believe that their group needs their input to do well on a challenging project
Prejudice & Discrimination
Prejudice
negative attitude and feeling toward an individual based on their group member ship
Stereotype
specific belief or assumption about individuals based on their group membership
Discrimination
negative action toward an individual based on their group membership
Examples: Racism, Ageism, Homophobia, Sexism
Dual Attitudes Model
Explicit
conscious and controllable
Implicit
unconscious and uncontrollable
Confirmation Bias
tendency to seek out information that supports our beliefs and ignore information that is inconsistent with our beliefs
Self-fulfilling Prophecy
an expectation held by a person that alters his or her behavior sin a way that tends to make it true

The Pygmalion Effect
Rosenthal & Jacobson (1968)
disadvantaged students with teachers that expected them to perform well had higher grades than those with teachers who expected them to do poorly
Group Dynamics
In-groups
a group that we identify with or see ourselves as belonging to
Out-groups
a group that we view as fundamentally different from us
In-group bias
prejudice & discrimination because the out-group is perceived as different and less preferred than out in-group
Scapegoating
act of blaming an out-group when the in-group experiences frustration or is blocked from obtaining a goal
Forces that promote reconciliation between groups
expression of empath
acknowledgment of past suffering on both sides
halt of destructive behaviors
Agression
Behavior intended to cause pain or harm to others
Hormones and Aggressive Behavior
Male aggressive behavior heavily depends on testosterone
young men = high rates of aggressive behaviors & violent crimes
testosterone levels are higher for men convicted of murder or rape than for burglary or drug offenses
Testosterone
increasing testosterone in women
increased time looking at angry faces
more arguing during collaborative tasks
Intermale aggression
observed in most vertebrates, including humans
adaptive for gaining access to food and mates
seasonal fluctuations
Serotonin Levels and Aggression
normally inhibits aggression
lower levels in more aggressive monkeys
Testosterone, Serotonin, Cortisol
growing consensus that aggressive behavior does not correlate strongly with any one chemical because it depends on a combination
testosterone = aggressive, assertive, dominant behavior
Serotonin = impulsive behaviors
Cortisol = aggression
Aggressive behavoirs dépends on ratio of testerons to cortisol
Bullying
Attempt to inflict harm, injury, humiliation
Gender differences…
Boys
direct, physical aggression
Girls
indirect, social forms of aggression
Victim:
decreased mental health + anxiety & depression
The Bystander Effect
Latane & Darley Phenomenon in which a witness/bystander does not volunteer to help a victim or person in distress
diffusion of responsibility - tendency for no one in a group to help because the responsibility to help is spread throughout the group
Kitty Genovese - attacked and killed outside her apartment building
residents heard her screams for help numbers times but did nothing (bystander effect)
Cooperation
Cooperation and Fairness (monkeys trying to work together to get nuts)
Criminal Behavior (Penguin stealing rocks from other penguins nests in order to make his own)
Game theory: study of strategic decision making (focused on whether a rational player should cooperate)
Prisoners Dilemma (cooperate to betray partner in crime for jail release)
Numbers- Ultimatum (Game Theory)
decide how much money is distributed between two individuals with the receiver being able to accept or reject money leaving them with something or nothing (Giver $8 → Receiver $2)
Prosocial Behavior
voluntary behavior with the intent to help other people
Altruism
peoples desires to help others even if the cost outweighs the benefits of helping
Motivation to Help
Empathy
Capacity to underwent another persons perspectives
empathetic ppl make emotional connections with others and feel compelled to help
Altruism
form of selfless helping (not motivated by benefits)
feeling good after helping is a consequence not a cause
Helping is SELF SERVING because our EGOS are involved and we receive benefits
Forming Relationships
Proximity
the people with whom you have the most contact
Similarity
people who are similar to us in background, attitudes, lifestyles
Homophily
tendency for ppl to form social networks with others who are similar
Reciprocity
give and take in relationships
Self-disclosure
sharing of personal information
leads to intimate connections
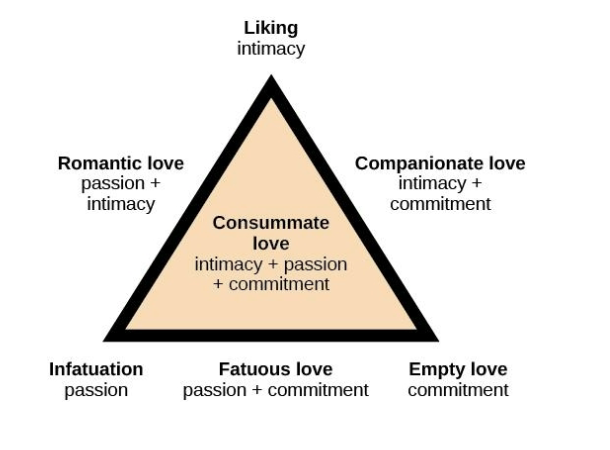
Sternberg’s Triangular Theory of Love
Seven types of love described from combinations of three components:
Intimacy - sharing details and intimate thoughts and emotions
Passion - physical attraction
Commitment - standing by the person
Social Exchange Theory
people may keep track of the costs and benefits of forming and maintaining a relationship
typically only those relationships in which the benefits outweigh the costs will be maintained