Reduction + Aldol Condensation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Reduction
basic type of chemical reaction and is the opposite of oxidation. The process of gaining electrons.
results in a decrease in oxidation number of a carbon atom
Reducing agents (LiAlH4 and NaBH4) produce H-
LiAlH4 is larger and has more electrons further from nucleus, more reactive
look at electronegativity differences to see strength, NaBH4 weaker but safer
must be performed in aprotic anhydrous solvents
catalytic hydrogenation
used in ochem to reduce pi bonds in a variety of functional groups, involves addition of a molecule of dihydrogen across a carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom double or triple bond in the presence of a metal catalyst such as platinum, palladium, nickel, or rhodium that is often adsorbed on an inert solid support like carbon.
nickel and palladium expensive
H2 gas and high temperature unsafe
very little waste so ideal for industry but not lab
Chemical reduction
metal hydride reducing agents that are used in the latter have differing reactivities toward specific functional groups
LiAlH4 is very reactive
NaBH4 is less reactive and more selective
can reduce up to 4 mole of fluorenone due ot 4 H’s present
will react with water, don’t get on skin and rinse if contacted.
nitro (NO2) is reduced to amino (NH2) group
reduction of aldehydes leads to primary alcohols and reduction of ketones leads to secondary alcohols
Carbonyl group
a rich source of many important reactions in organic chemistry
polarization of the carbon-oxygen pi bond, owing to relatively high electronegativity of oxygen atom
increases the acidity of the alpha hydrogen atoms (alpha carbon atoms can become nucleophilic through deprotonation to form an enolate ion).
nucleophiles
lewis bases, oxygen atom in the carbonyl group.
electrophiles
lewis acids
tautomerization
keto-enol equilibrium to switch between enolate and enols.
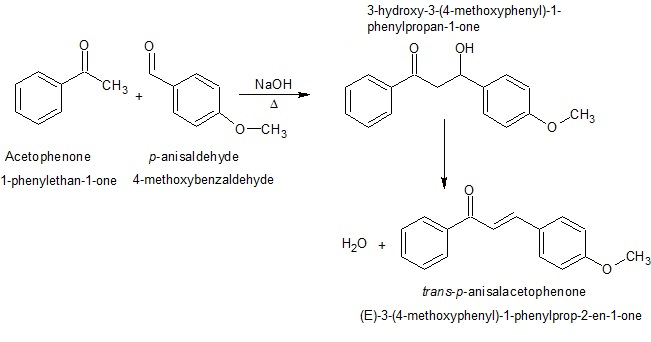
Reduction of 9-Fluorenone, synthesis
Look for disappearance of carbonyl peak and there will not be a large OH peak due to hydrogen bonding
Initial product is salt formation: R-C(=O)-R → (R-C(-O-B(-)-Na(+))-R) (4 moles of this)
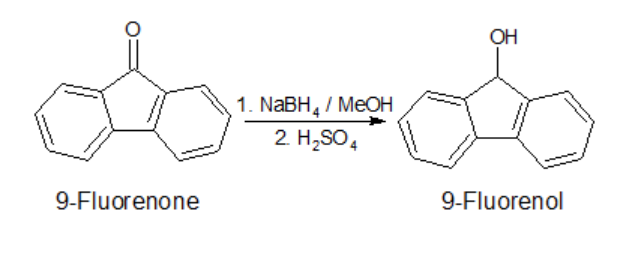
Mechanism of Aldol condensation
multiple enolates can form
multiple electrophilic carbons, can control to make enolate first
typical reaction favors reactants but we can use a stronger base like LDA to shift to products.
should see a carbonyl peak in the ketone position and no alkene or C-H stretch
works with weaker base due to only one possible enolate because aldehyde reacts faster
extended conjugation of product is energetically favorable
9-fluorenone color
yellow
Fluorenol color
white
Specific mechanism for aldol condensation