L2 - Spatial learning and Long term potentiation 1
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Neural basis of learning - how do we go about searching for the neural basis of learning?
Learning = change in behaviour that results from experience
Corresponding physical change in the brain
Criteria for learning to occur, should be the same as neural condition
Pavlovian conditioning…
Neural basis of learning - how do we go about searching for the neural basis of learning? - Pavlovian conditioning overview
behaviour is learned process, occurs through association
2 stimuli become linked, generate a new behavioural response to a previously neutral stimulus
Neural basis of learning - how do we go about searching for the neural basis of learning? - Pavlovian conditioning - Stimuli
NS paired with US, trigger an UR
NS becomes a CS, trigger now a CR
e.g. light and shock, eventually light will trigger prepatory response
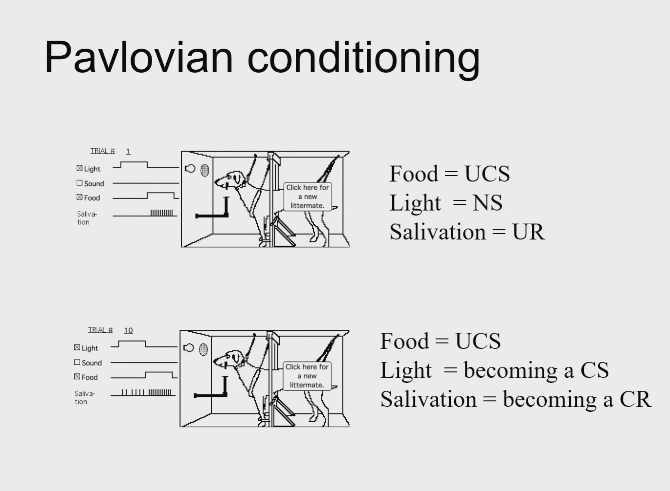
Pavlovian conditioning - picture e.g. light (cs) = salivation (cr)
Leaning is a psychological process….
of pairing events together, of association formation
looking for a neural mechanism that would allow associations to be formed…. how can events be linked biologically in the brain…. hippo
hippocampus is in the
temporal lobe
Hippocampus processes multimodal sensory and
spatial information; ‘loop of synaptic connections’
hippocampus - enthorhinal cortex
main input
CA1 - main output
Contiguity is important for
learning (C= the principle that ideas, memories, and experiences are linked when they occur close together in time or space)
Pre discovery of LTP - kindling, a model of epilepsy in which…
prior stimulation increases the likelihood of neurons firing (logic applies whether one stimulates and measures single neurones or thousands of neurones)
In 1973 - Bliss and Lomo applied this experimental design to hippo
Pre discovery of LTP - kindling … pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neurones must be…
be segregated and readily identifiable - stimulate one neuroens and see what happens in the other neurone, see responses of different populations.
Pre discovery of LTP - Suitable circuity of the hipppo for measuring LTP
Pre-synaptic and post-synaptic populations must be segregated and readily identifiable
The anatomy of the hippocampus fits the bill
why is the hippocampus so good for research of LTP
loop of connections; distinct populations of cells; we can use these different populations of cells to stimulate the cell bodies in one areas and the we can measure the effects of those on another area.
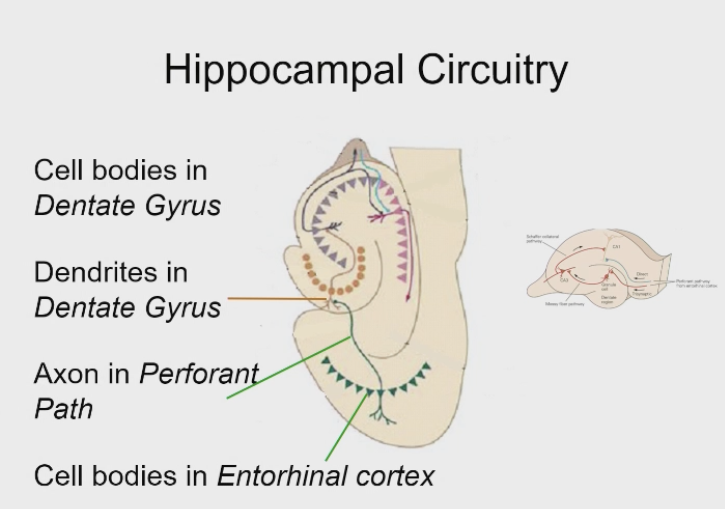
Pre discovery of LTP - Suitable circuity of the hipppo for measuring LTP - anatomy
Hippo has the dentate gyrus and entorhinal cortex, loop of connections - so distinct populations of cells
use the different populations of cells - by stimulating cell bodies in one area, and then measure the effect of those on another area
Stimulate axons of one population of cells, and record activity in the post-synapticly in a different population of cells
Can test the idea that if you repeatedly activate one type of cell, what impact does that have on other populations of cells
Pre discovery of LTP - Bliss and lomo in segregating post and pre synaptic populations
conducted their experiments on anastheitized rabbits hippocampus , later work in isolated slices
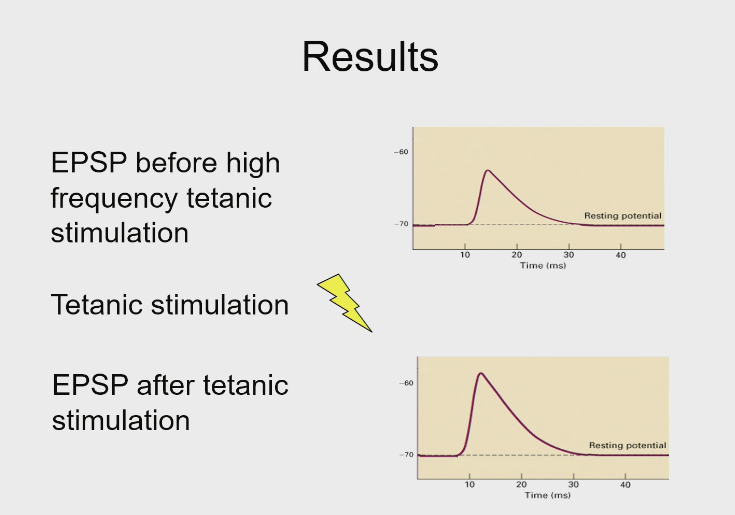
Pre discovery of LTP - Bliss and lomo in segregating post and pre synaptic populations - found that
EPSP before high frequency tetanic stimulation,
if you repeatedly stimulate the presynaptic neurone, lots of high level activity
The EPSP increases massively in the post synaptic cell
This is a lasting process - one week or one month later - same increase seen
EPSP =
excitatory post synaptic potential
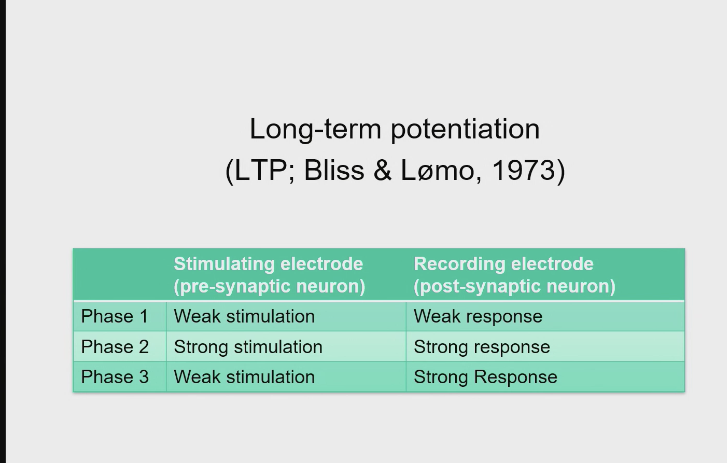
Bliss and Lomo found that by
that providing strong stimulation to cells in the entorhinal cortex, which synapse with cells in the dentate gyrus results in a long-term increase in the ability of the entorhinal cells to increase activity in the dentate gyrus cells. The synaptic connection between the cells was potentiated (long-term potentiation, LTP)
after repeated stimulation of presynaptic synapse - the post synaptic neurone will fire more strongly with weak stimulation, easier to fire.
2 key properties of LTP….
long term
LTP only occurs when firing of presynaptic neurone is followed by firing of post synaptic neurone - this co-occuance is sen as the critical factor in LTP, analogous to pavlov’s dogs
CO-OCCURANCE …..if the post synaptic cell is active but doens’t
depolarise, the post synaptic cell doens’t get active and you won’t get LTP
If post synaptic cell is depolarised and the presynaptic cell isn’t - don’t get LTP
How does co-occurance link to pavlov’s dogs - assumption that co-occurence is…..
a physiological necessity for learning and memory is often names Hebb’s postulate for leanring
The Hebbian basis of memory?
if the synapse is active as the same time as the post-synaptic neurones fires, physical changes to the synapse will take place that strengthen it
Nuerone’s that fire together wire together
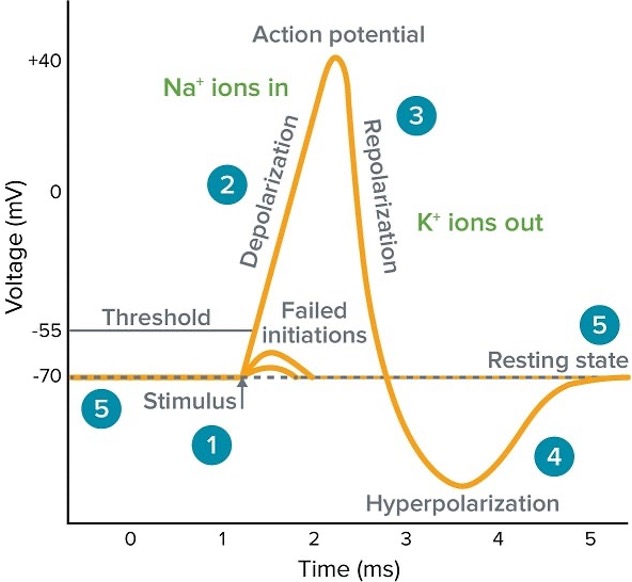
An action potential is …
a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane, caused by the positive flow of ions into the cell – which rapidly depolarises the cell; you then get a brief period of hyperpolarisation – then it reaches the resting state.
Action potential - recap - cell firing - in relation to glutamate
Glutamate - primary excitatory neurotransmitter - causes depolarisation
The normal glutamate receptor is known as the - AMPA receptor
AMPA receptors and glutamate
When glutamate binds on the post-synaoptic cell the AMPA receptor opens membrane channels leading to depolarisation (allows positive ions into the cell) carry’s on excitation in the brain.
LTP is most widely studied at synapses with…
lots of NMDA receptors
Induction of LTP - NMDA receptors
- NMDA receptors are also glutamate receptors
AMPA receptors are non-fussy – no co-occurrence needed; but NMDA receptor fussy – only work well when the post synaptic neurone is partially or already depolarised!
Induction of LTP - Nmda receptors-linked channels: coincidence detectors
Only open in the presence of NT and when post-synaptic membrane is depolarised
Therefore, they act as pre & post synaptic activity coincidence detector
Only when post synaptic cell has been depolarised through stimulation, AND glutamate has been released (by another event) from the synapse can NMDA function
AMP receptors…
non fussy, if glutamate is present in the synapse, glutamate will bind and receptor opens
NMDA receptor voltage sensitivity
The ion channel associated with the NMDA receptor is normally blocked by a positively charged magnesium ion, when depolarisation occurs mg ion is released and channel opens
This ion is no longer attracted to the cell once the membrane is sufficiently depolarised
overview of LTP process and NMDA receptor
NMDA recpertor, magnesium is attached to the receptor blocking the channel, resting state at -70 mv
cell starts too depolarise - e.g. the AMPA receptors allow glutamate to bind, + ions enter - depolarise - -40mv - when action potentials start occurring, the magnesium ions detach from the NMDA receptor (no longer has the charge it needs to stay in place)
Glutamate binds to the NMDA receptor, and opens the channel, calcium is allowed to enter.
Ampa receptors will not allow
calcium into the cell, but NMDA receptor are selective to calcium
How is the synapse more efficient?
the induction mechanism (NMDA receptor) is post synaptic
what evidence is there for changes in the post-synaptic dendrites
is there evidence for pre-synaptic changes?
How is the synapse more efficient? - what evidence is there for changes in post synaptic cells - changes 1 - AMPA receptors increase for LTP
after calcium has entered the cell through NMDA receptors (when both post and pre synapse are active), is that the number of AMPA receptors increases – AMPA cell trafficking – AMPA cells are trafficked to the cell membrane – cell becomes more responsive to glutamate – more ions enter and easier to depolarise the cell.
How is the synapse more efficient? - what evidence is there for changes in post synaptic cells - changes 1 - AMPA receptors increase for LTP - Muller, July and Lynch (1988)
- AMPA receptor antagonist, prevented LTP expression.
How is the synapse more efficient? - what evidence is there for changes in post synaptic cells - AMPA receptors increase for LTP - Tocco et al (1992)
measured the number of AMPA and NMDA receptors. LTP changed AMPA, but not NMDA receptor numbers.
How is the synapse more efficient? - what evidence is there for changes in post synaptic cells - changes 2 - protein synthesis (nyguyen, Abel and Kandel, 1994)
blocking protein synthesis, though inhibiting transcription after stimulation, prevents LTP
How is the synapse more efficient? - what evidence is there for changes in post synaptic cells - changes 2 - protein synthesis - the structure of the cell may change
calcium triggers the calcium signalling cascade, it triggers protein kinases that activate protein transcription factors – meaning we have the generation of new proteins – changing the fundamental structuring of the cell
How is the synapse more efficient? - what evidence is there for changes in post synaptic cells - changes 2 - protein synthesis - the structure of the cell may change - what ways does it change?
- Long term increase in AMPAR’s
- Growth of new spines - more synapses
- Enlargement of spines – more synapses; increased SA
- Splitting of spines
- Enlarged postsynaptic areas
This all means that the surface area of the post synaptic cell is larger and more receptive to glutamate.
LTP results in post synaptic changes - overview
increased number of glutamate receptors (AMPA receptors), also know that the synaptic area enlarges (more responsive to glutamate)
LTP results in pre-synaptic changes
these changes occur as a direct consequence of post-synaptic changes. The post-synaptic cell releases nitric oxide, which acts as a second messenger causing greater glutamate production in the presynaptic cell.
How is the synapse more efficient? - what evidence is there for changes in pre-synaptic effects
•Radioactively label glutamate precursors
•Measure synaptic radio-activity before and after LTP
More radioactivity in synapse after LTP (Dolphin, Errington, & Bliss, 1982; Skrede & Malthe-Sørenssen, 1981)
More glutamate is being released Fromm the pre-synaptic cell
How can the presynaptic cell know?
The induction mechanism (the NMDA receptor) is in the post-synaptic cell
After NMDA receptor activation the signal must be sent from the post-synaptic to the pre-synaptic cell
When calcium enters the post-synaptic cell it activates second messengers within the cell (kinase enzymes)
One consequence is that the post-synaptic cell releases nitrous oxide (NO)
This acts as a retrograde transmitter being detected by, and inducing changes in, the pre-synaptic cell (through action on pre-synaptic cyclic GMP (guanosine monophosphate) glutamate production is increased)
So what does LTP have to do with leanring and memory?
•Associative learning requires the formation of links between the memories of different stimuli (e.g. bell and food, Pavlov’s dogs)
•Long-term potentiation is a mechanism for the formation of links between neurons
•Maybe LTP is the neural basis of learning and memory?
NMDA receptor dependent LTP - The NMDA receptor is a coincidence detector + lTP only binds if 2 things happen:
glutamate binds to NMDA receptor
The cell is depolarised
Why would coincidence detection be important for associative learning? Pavlovian conditioning - longer version
- - When the food neurones are depolarised, they will not only form synaptic connections with CS neurons that are concurrently firing and releasing glutamate.
- If CS neurones fire and the food neurons are not depolarised, no synaptic connections will form.
- You will only form associations between things that are concurrently happening.
LTP - it looks like it could be involved in leanring, but is it learning? Hypothesis - manipulations that impair LTP impair learning -
e.g. hippocampus and spatial learning e.g. HM, cog map theory
LTP is observed in the hippo
The hippo has long been associated with learning and memory
The Hippo is known to be especially important in spatial learning
Prediction: LTP in the hippo is necessary for spatial learning
LTP - it looks like it could be involved in leanring, but is it learning? Hypothesis - manipulations that impair LTP impair learning - Morris water maze stimuli
circular walls
learn the location vis extra-maze cues (distance from edge)
Test navigation with a probe test with the platform removed
Hidden platform
LTP - it looks like it could be involved in leanring, but is it learning? Hypothesis - manipulations that impair LTP impair learning - Morris water maze test
test navigation with a probe test with the platform removed
training - latencies (time to escape), distance travelled
Test - percent of rime in correct quadrant
LTP - it looks like it could be involved in leanring, but is it learning? Hypothesis - manipulations that impair LTP impair learning - Morris water maze experiment (1982)
Rats trained on water maze task, at end of training, a probe trial was conducted in which the platform was removed from the pool
Sham lesioned rats showed a strong preference for the quadrant of the pool which previously contained the platform
Hippocampal lesioned rats did not show preference
Lesioned rates not impaired on a visual person
LTP - it looks like it could be involved in leanring, but is it learning? Hypothesis - manipulations that impair LTP impair learning - Morris water maze experiment (1989) - second study - using AP5
AP5 (an NMDA receptor antagnoist) was infused into the brain of rats
Rats then tested on water maze task
Rats given control showed a strong preference for the training quadrant, AP5 rats failed to show a preference
AP5 did not impair visual discrimination or retention of previously learned spatial info
LTP - it looks like it could be involved in leanring, but is it learning? Hypothesis - manipulations that impair LTP impair learning - Morris water maze experiment (1989) - second study - conclusion
AP5 impaired spatial learning
This may suggest that LTP is necessary for spatial learning
LTP - it looks like it could be involved in leanring, but is it learning? Hypothesis - manipulations that impair LTP impair learning - Morris water maze experiment (1989) - second study - BUT rats treated with AP5 …
- showed sensorimotor impairments, It is possible that AP5 impaired performance (e.g., swimming, climbing on the platform) rather than learning.
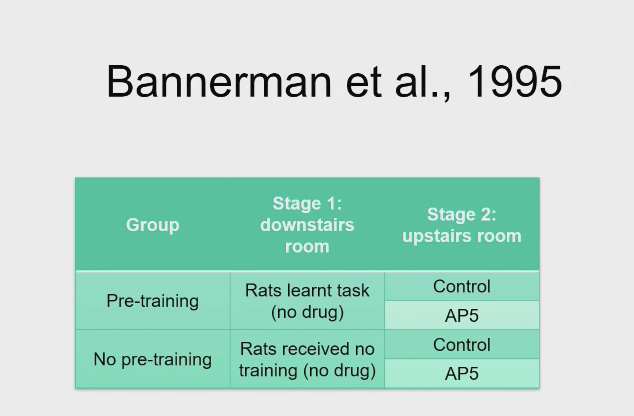
AP5 and spatial leanring, follow on from morris 1989 - is there a way of dissociating a performance deficit from a learning deficit? - Bannerman et al., (1995) - Maze task
2 water mazes, one upstairs, one downstairs
Unique extra maze cues, learning in one would not help navigate in the other.
Trained rats on swimming so AP5, did not impair motor performance.
AP5 and spatial leanring, follow on from morris 1989 - is there a way of dissociating a performance deficit from a learning deficit? - Bannerman et al., (1995) - Method
- Prior to testing the effects of AP5 on spatial learning (in the upstairs room) rats were trained on the water maze task ( in the downstairs room)
- Should become proficient at swimming, before ap5
AP5 and spatial leanring, follow on from morris 1989 - is there a way of dissociating a performance deficit from a learning deficit? - Bannerman et al., (1995) - hypothesis
prior training will make rats more proficient at the task, and will reduce the effects of AP5 on sensorimotor performance
AP5 and spatial leanring, follow on from morris 1989 0- is there a way of dissociating a performance deficit from a learning deficit? - Bannerman et al., (1995) - results
AP5 impaired performance when there was no pretraining
But AP5 did not impair performance when rats had pretrianing
Hippocampal lesions impaired performance even when rats had pretraining
AP5 and spatial leanring, follow on from morris 1989 0- is there a way of dissociating a performance deficit from a learning deficit? - Bannerman et al., (1995) - conc
when rats had pretraining on the water maze, AP5 failed to impair hippocampus dependent spatial leanring. This suggests that LTP in the hippocampus may not be necessary for spatial learning
LTP in spatial learning
NMDA dependent LTP in the hippocampus maybe not always necessary for spatial leanring?
Role may be more complex….. next lecture