PSY B110 EXAM 2 CHAPTER 3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are neurons responsible for?
Sending messages to and within the brain.
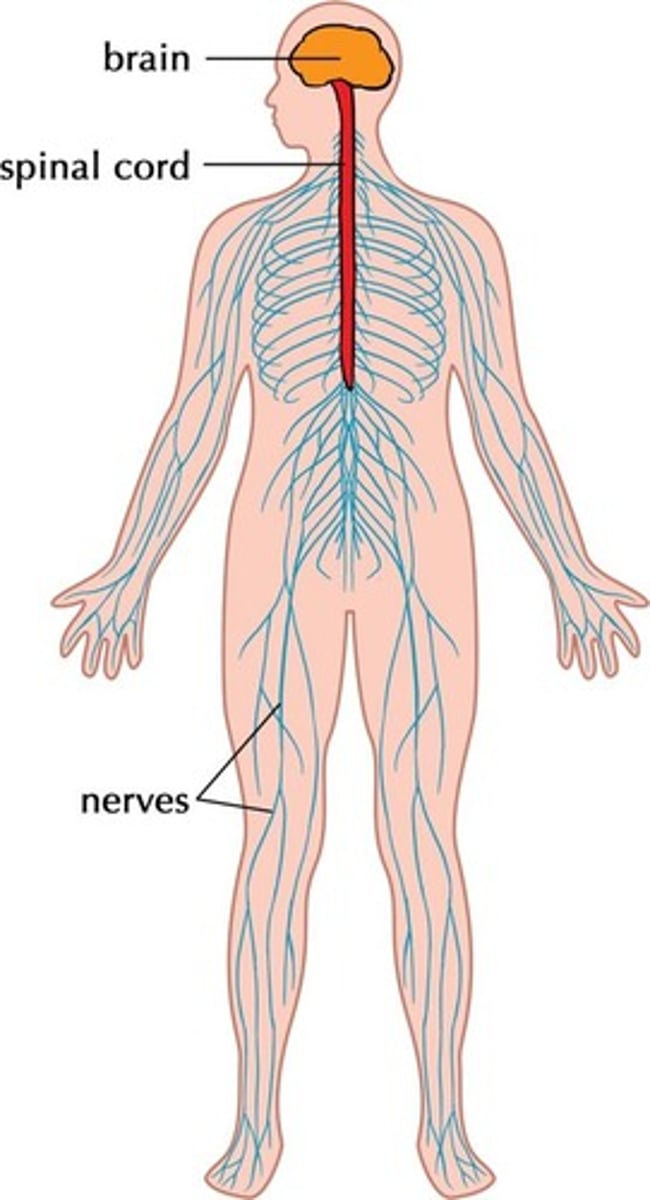
What does the central nervous system consist of?
The brain and spinal cord.
What is a unique feature of the spinal cord's functioning?
It can activate a motor response without sending sensory input to the brain, as seen in cat-like reflexes.
What is the peripheral nervous system?
Neurons outside the CNS that allow communication between the brain, spine, and the rest of the body.
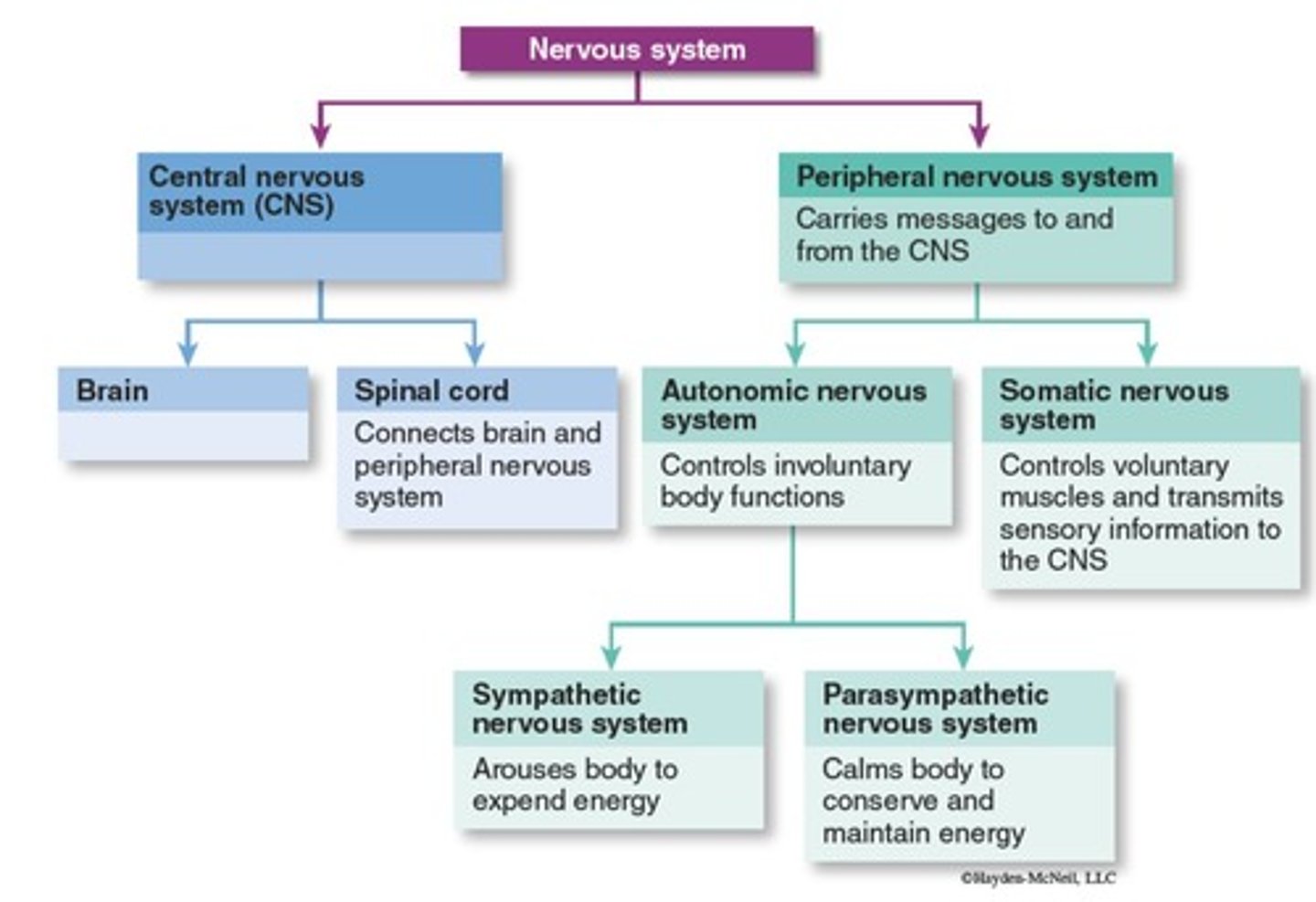
What are the two main divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Somatic and Autonomic nervous systems.
What does the somatic nervous system control?
Voluntary muscles and sensory information to the CNS.
What functions does the autonomic nervous system regulate?
Involuntary body functions, such as those of internal organs.
What is the role of the sympathetic nervous system?
To arouse the body to expend energy and mediate the fight-or-flight response.
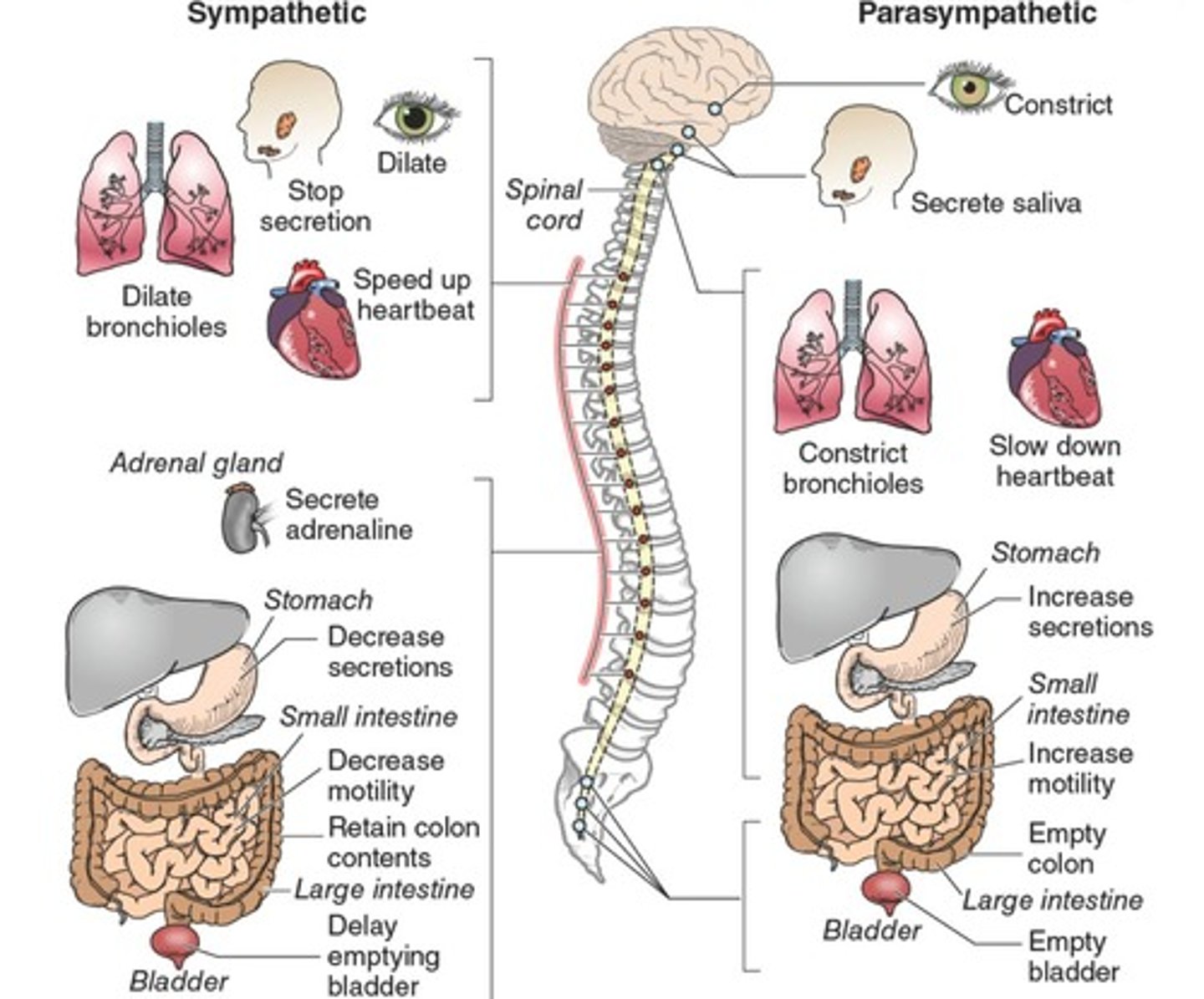
What does the parasympathetic nervous system do?
Calms the body to conserve and maintain energy under normal conditions.
What is the function of the amygdala?
Involved in emotional reactions to the environment and emotional memories.
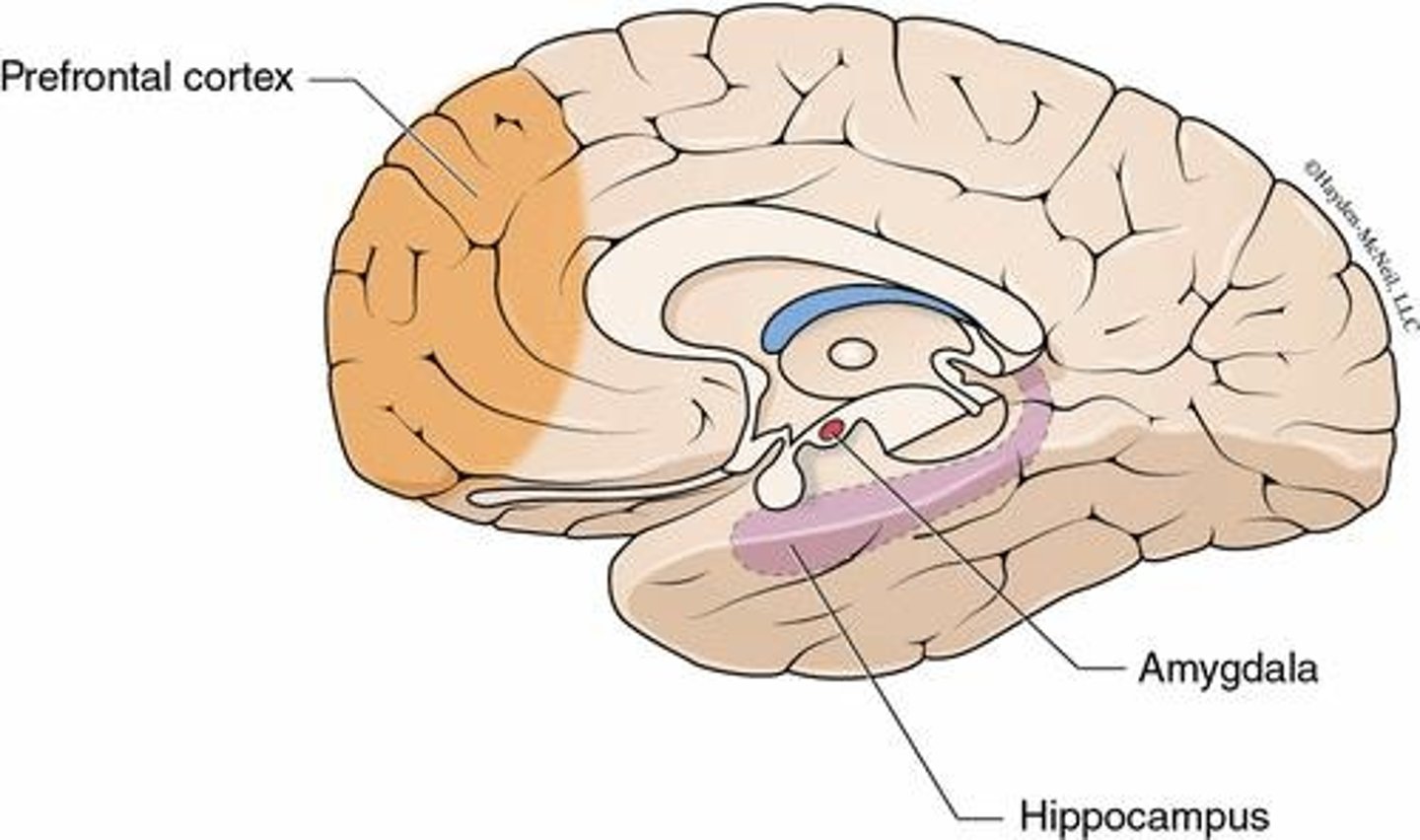
What is the hippocampus primarily responsible for?
Memory acquisition and retention.
What is the function of Broca's area?
Critical for the production of language.
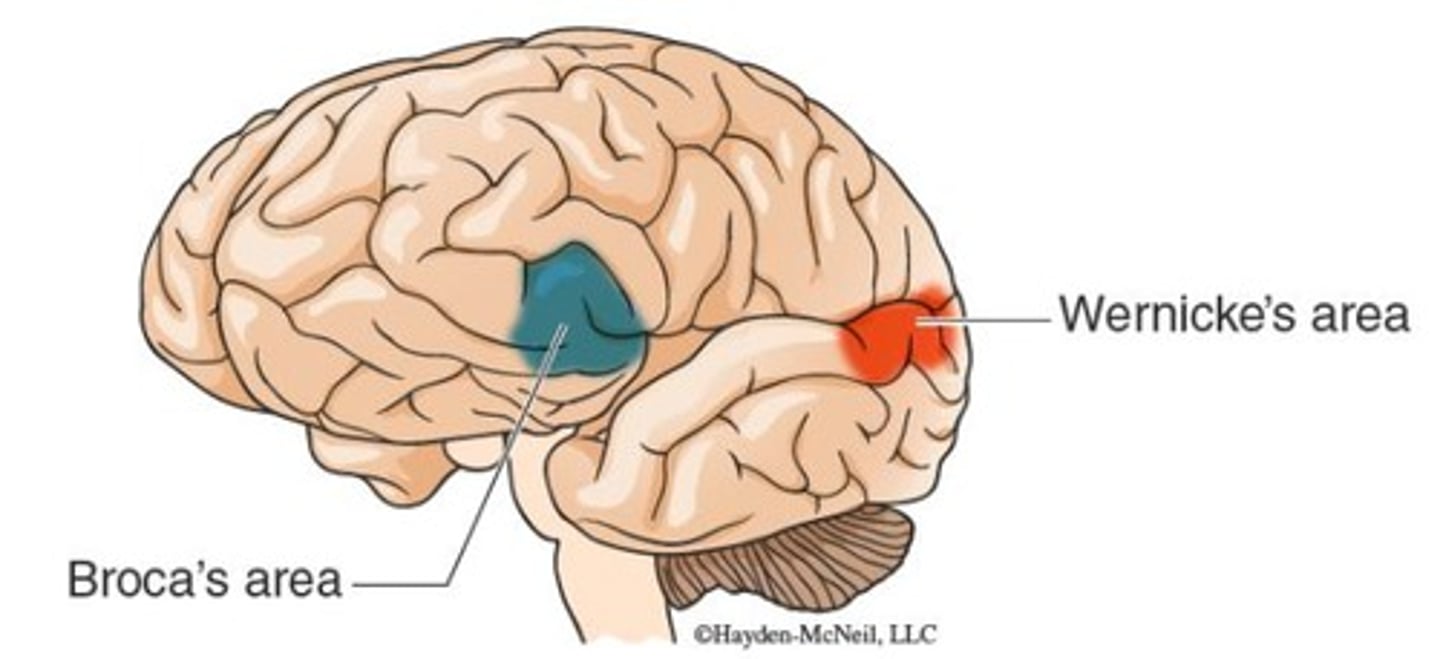
What does Wernicke's area do?
Critical for the understanding of language.
What happens if Broca's area is damaged?
It can lead to difficulties in language production, known as Broca's aphasia.
What occurs if Wernicke's area is damaged?
It can result in Wernicke's aphasia, characterized by impaired language comprehension.
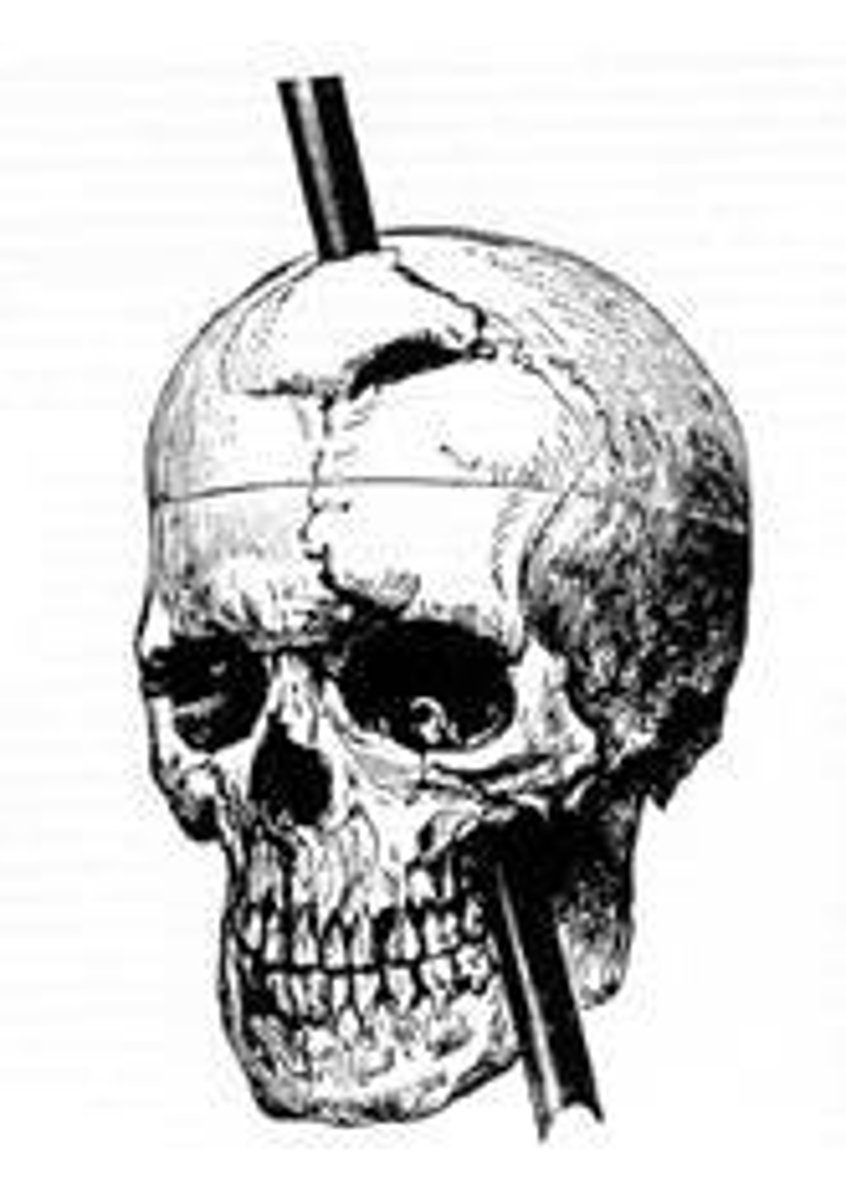
What did the case of Phineas Gage teach us?
The frontal lobe is responsible for personality and higher executive functioning.
What was the outcome of H.M.'s surgery?
He suffered severe anterograde amnesia after his hippocampus was removed.
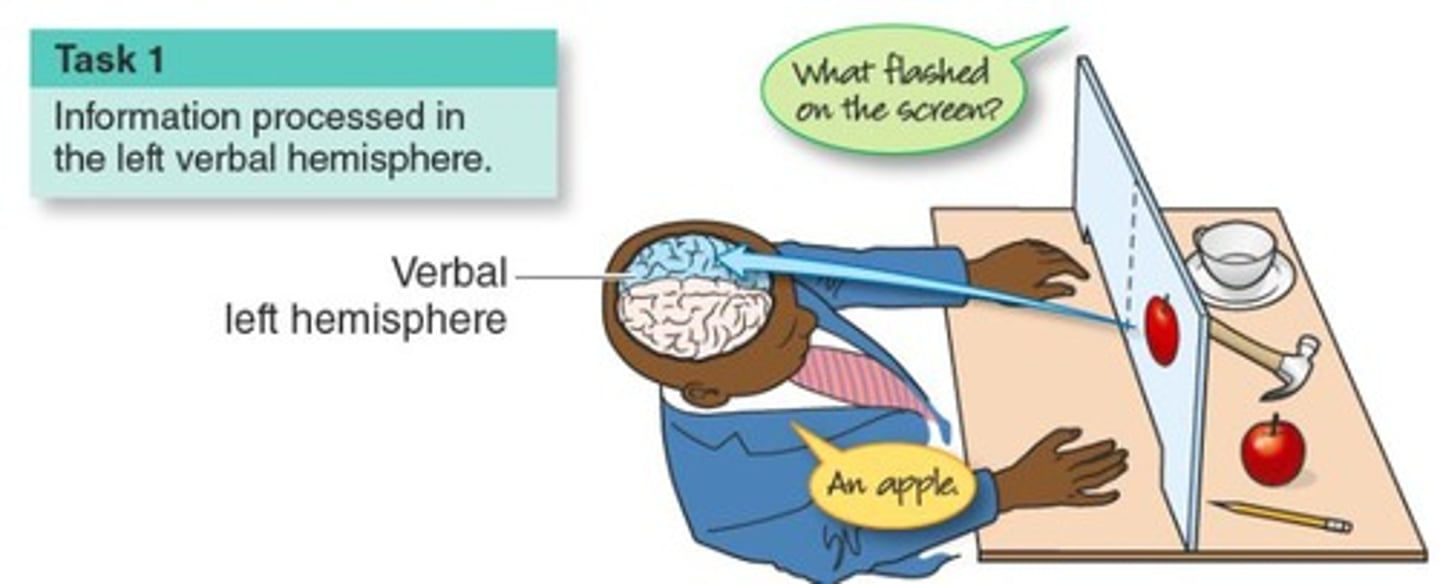
What is the significance of split-brain studies?
They demonstrate that information from the visual field is processed contralaterally in the brain.
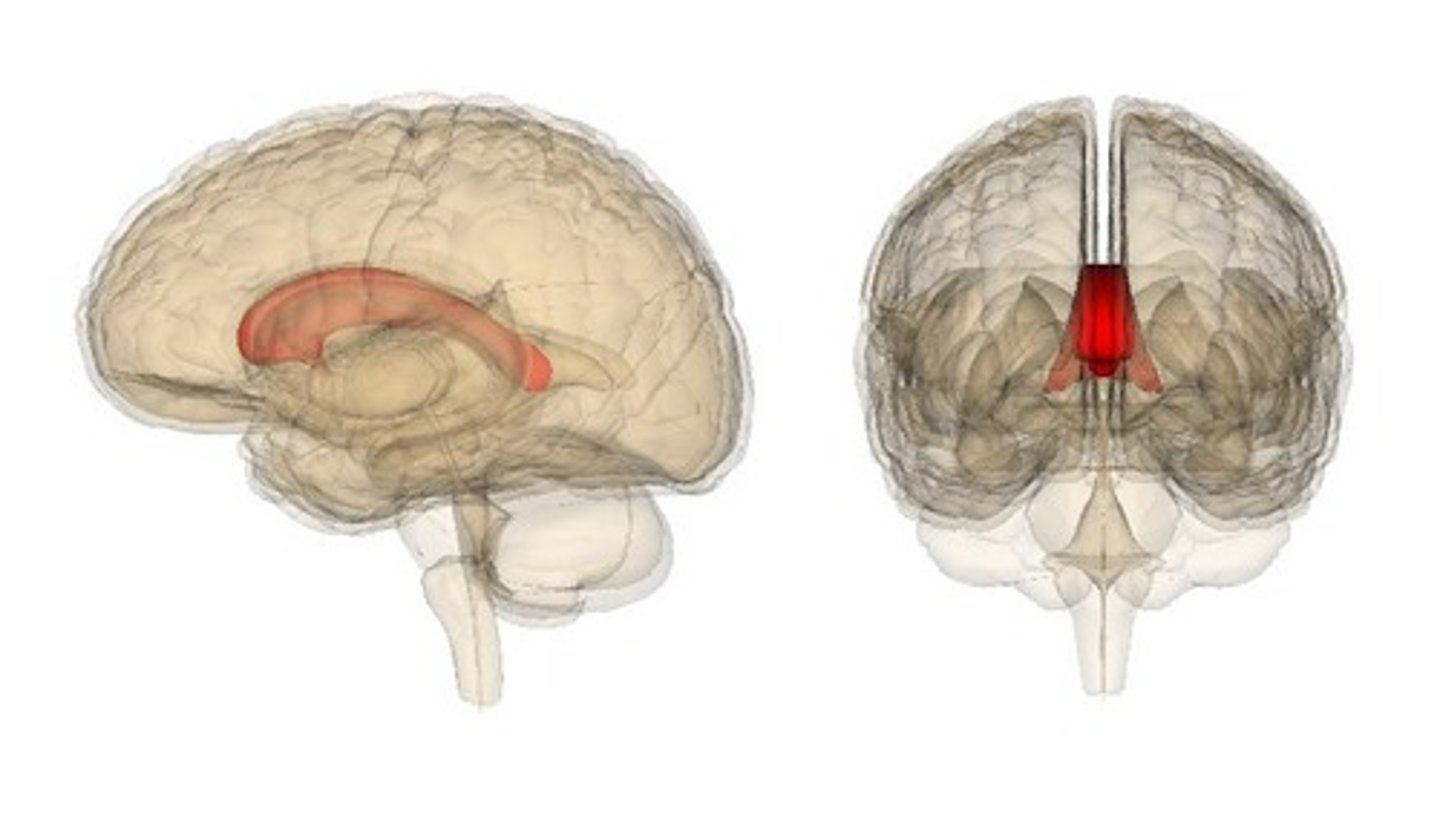
What is the function of the corpus callosum?
It allows for the transfer of information between the left and right sides of the brain.
What does an electroencephalograph (EEG) measure?
Changes in electrical activity in the brain.
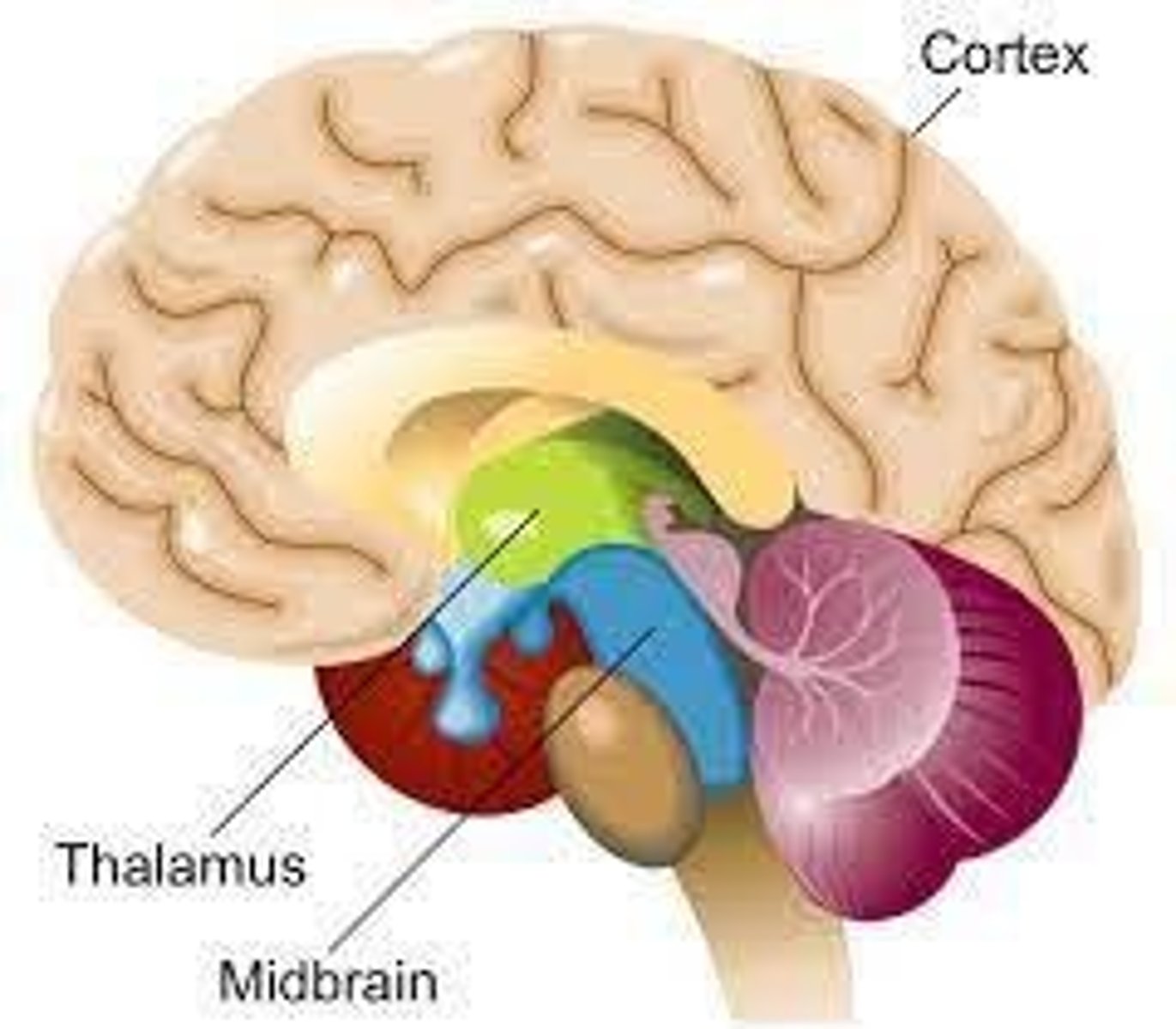
What is the purpose of neuroimaging techniques?
To study the human brain using minimally invasive methods.
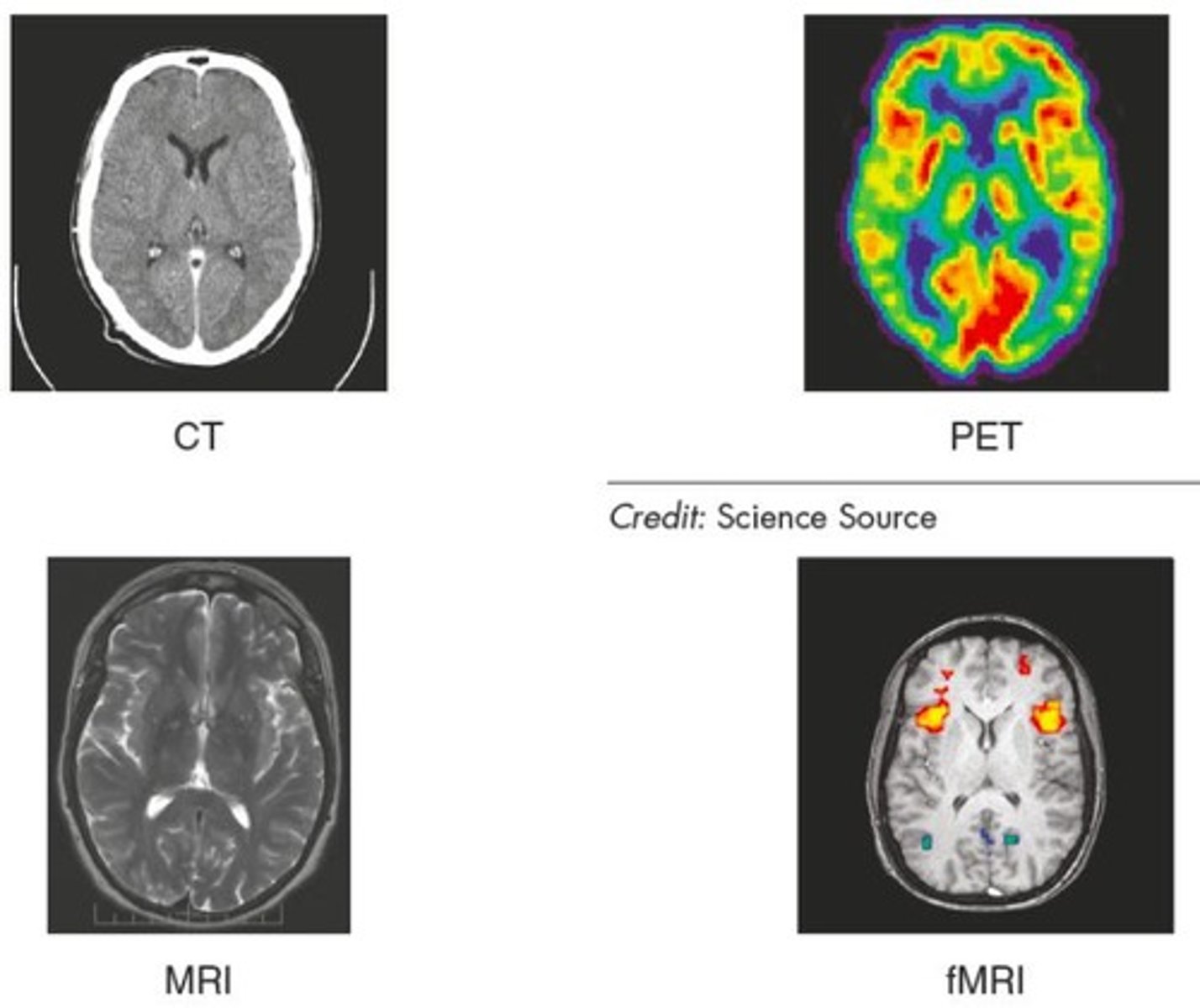
What does a CT scan provide?
Images of brain structure.
What does an MRI scan show?
Detailed images of brain structure.
What does an fMRI measure?
Brain function by assessing oxygenated blood flow.
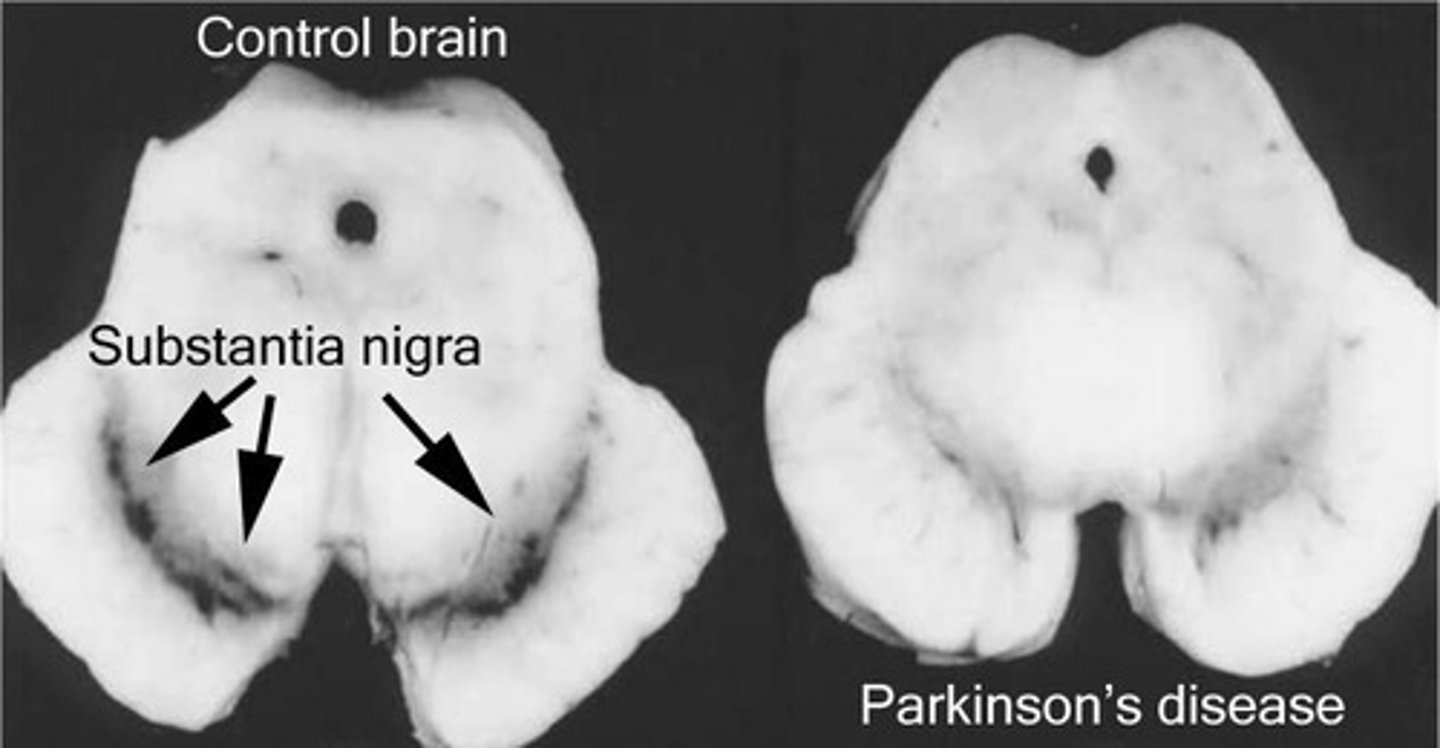
What is the role of the basal ganglia?
Involved in the control of movement.
What are mirror neurons?
Active when preparing to make a movement and when watching others perform a movement.
Still learning (24)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!