Newton's Laws of Motion
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is Newton’s First Law?
An object remains at rest or moves with a constant velocity provided no resultant external force is applied.
Inertia - The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion.
What is Newton’s Second Law?
Def 1 - For a constant mass, the acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force applied to it.
Def 2 - The force is equal to the rate of change of momentum.
Equation: F = ma
F - Resultant Force / N m - Mass / kg a - Acceleration / ms-2
What is Newton’s Third Law?
If object A exerts a force on object B, then object B will exert a force on object A which is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
F = ma Problem 1: Two forces in opposite directions.
Where F1 > F2 , F1 - F2 = ma
If F2 is unknown, F2 would be equal to Ma where M is the second mass.
This is then rearranged F1 - Ma = ma , F1 = ma + Ma , F1 = (M+m)a
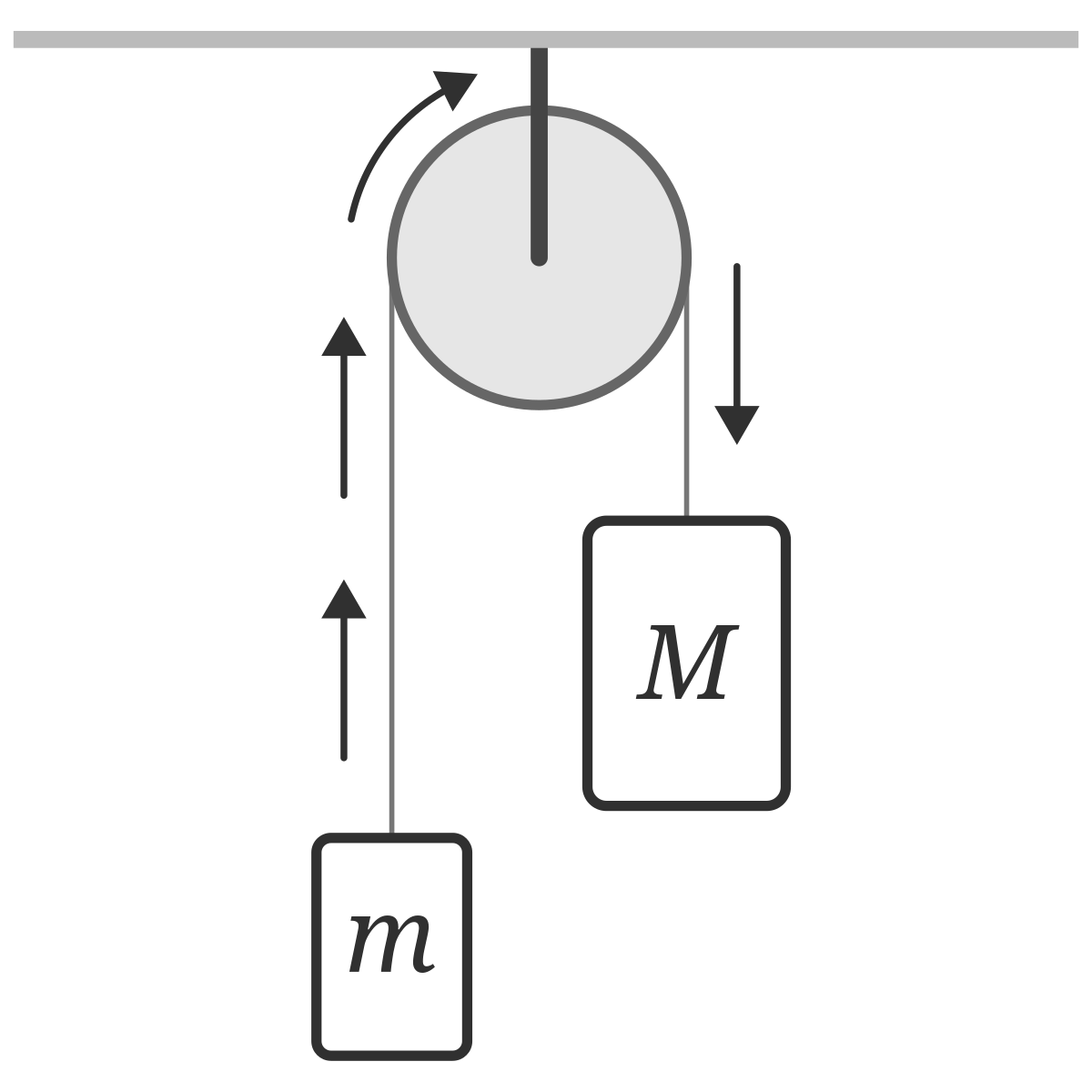
F = ma Problem 2: Forces in a pulley.
There are two masses M and m where M > m.
The resultant force on mass M is Mg - T = Ma
The resultant force on mass m is T - mg = ma
You can add the two equations together to get Mg - mg = (M + m)a
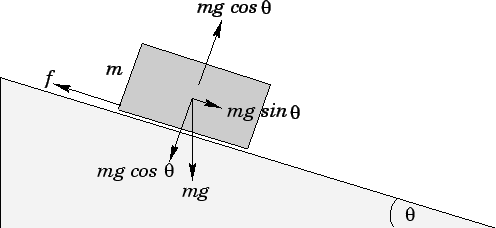
F = ma Problem 3: A mass on a slope.
The component of the block’s weight = mg sin(θ), where θ is the angle of the slope.
Set the force of Friction to F0 then the resultant force = mg sin(θ) - F0
Therefore mg sin(θ) - F0 = ma , where a is the acceleration of the block.
If there is an addition of a engine force FE then the equation would become FE + mg sin(θ) - F0 = ma
What is a Drag Force and what does it depend on?
Drag force is the force of fluid resistance on an object moving through a fluid.
It is dependent on the shape of the object, its speed, and the viscosity of the fluid.
What is Terminal Speed?
The maximum speed reached by an object when the drag force in it is equal and opposite to the force causing the motion of the object.
At this point, the object no longer accelerates and moves at a constant speed. The resultant force at this point is then zero.
What is the Motive Force of a object?
The driving force of an object. The resultant force on an object liks this is = FE - FR where FE is the motive force and FR is the resistive force (Sum of drag forces).
What is Thinking, Breaking and Stopping Distance?
Thinking Distance - The distance travelled by a vehicle in the time it takes the driver to react. It is equal to speed x reaction time.
Braking Distance - The distance travelled by a car in the time it takes to stop safely.
Stopping Distance - The total distance travelled in the time it takes to react and stop. It is equal to Thinking + Braking.
What is Collision Time and what are car features that affect it.?
Collision Time - The amount of time two objects are in contact with each other during a collision. A greater Collision Time results in a reduced force experienced during impact.
Car Safety Features:
Airbags - They reduce the force on a person by increasing the collision time.
Seat Belts - They restrain the occupant where the restraining force is much less that the impact force.
Crumple Zones - They are designed to absorb energy during a collision, increasing the time over which the impact occurs.