Chem 107 Final Review
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
VBT
starts by hybridizing atomic orbitals on a central atom, and uses these hybrids to form bonds to nearby substituents
Fine Structure
refers to the splitting of spectral lines of atoms due to electron spin and relativistic effects. Due to vibronic coupling
Diamagnetic
characterized by paired electrons that are not attracted to a magnetic field
Paramagnetic
characterized by unpaired electrons that are attracted to a magnetic field.
Molecular Orbital Theory
assumes that the valence elctrons of atoms within a molecule will form orbital overlaps and become delocalized as allowed by symmetry rules
Three Conditions for AOs to interact and form MOs
Same symmetry, similar energy, spatial overlap
Non-bonding Combinations
Orbitals with differing numbers of internuclear nodes cannot form overlaps, and result in non-bonding combinations
Gerada
symmetrical with respect to inversion
Ungerada
unsymmetrical with respect to inversion
sp Mixing
When orbitals of the same symmetry (sigma or pi, g or u) are of a similar energy, they can undergo a further interaction. The more stable orbital is further stabilized, while the less stable orbital is further destabilized
Effective Nuclear Charge
the positive charge experienced by the valence electrons of an atom or molecule. As you move right on periodic table, Zeff increases because there are more protons in the nucleus. s-type orbitals are more sensitive to increases in Zeff because they have more electron density
Molecules with sp-mixing
Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2
Molecules without sp mixing
O2, F2, Ne2
Crystal Field Theory
a simple explanation for how d-electrons are perturbed by the ligands that surround a metal. the point charges are the ligands themselves, which function as repulsive electron clouds
Ligand Field Theory
combines ideas of CFT and MO theory to describe the interactions of metal valence orbitals with frontier MOs of the ligands
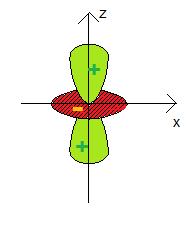
3dz²
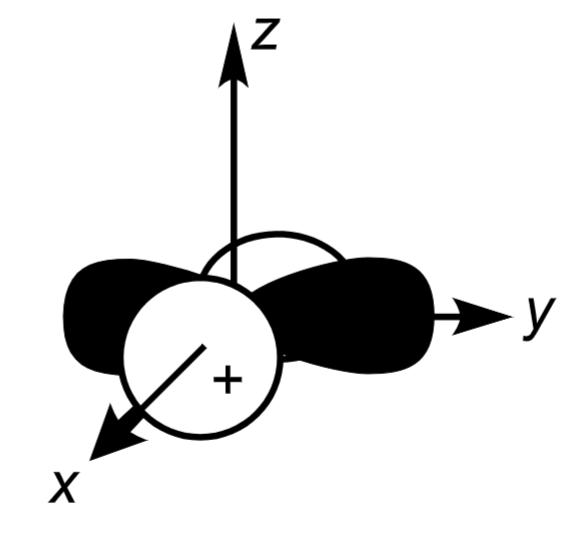
3dx²-y²
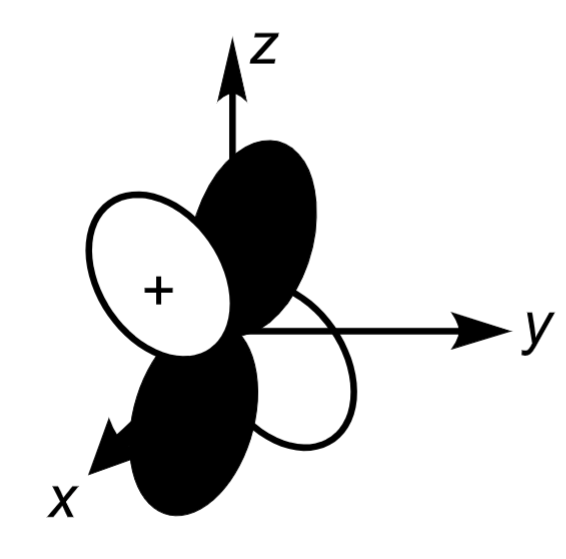
3dyz
3dxz
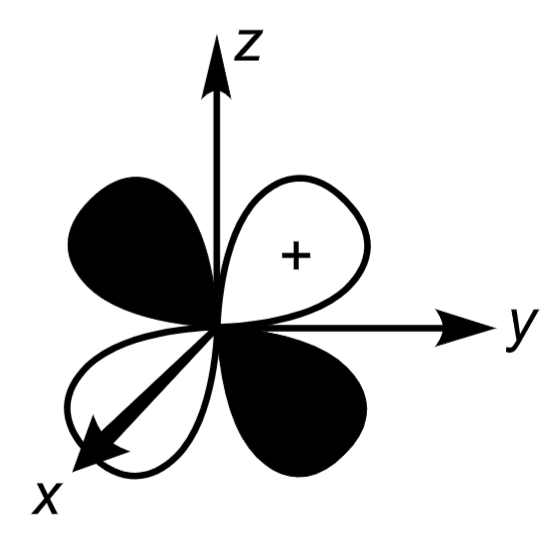
3dxy
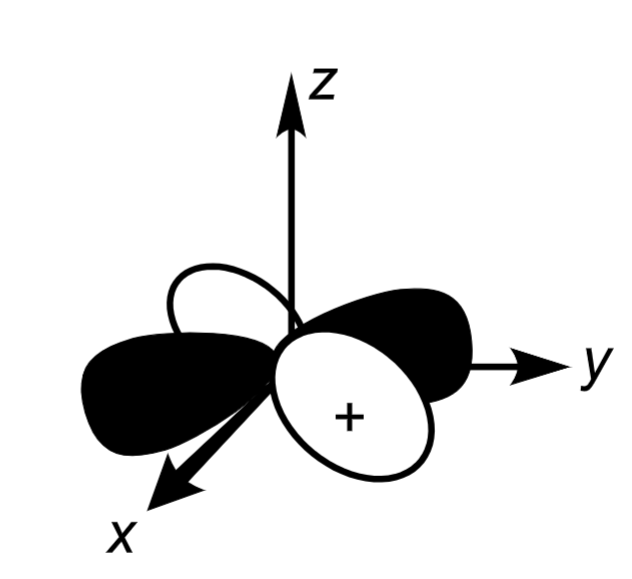
Octahedral crystal field splitting
From top to bottom: (dz²,dx²-y²), (dxy,dyz,dxz)
Tetrahedral crystal field splitting
From top to bottom: (dxy,dyz,dxz), (dz²,dx²-y²)
Square planar crystal field splitting
From top to bottom: (dx²-y²), (dxy), (dz²), (dxz,dyz)
ML5, D3h crystal field splitting
From top to bottom: (dxy, dx²-y²), (dz²) higher energy, (dxz,dyz)
D3h, ML3 crystal field splitting
From top to bottom: (dxy, dx²-y²), (dz²) lower energy, (dxz, dyz)
Order of crystal field splitting energies
Delta sp > Delta O > Delta T
Tetrahedral splitting, high or low spin
high spin
Square planar, high or low spin
low spin
Octahedral, high or low spin
either or, depends on ligand
Multiplicity
count unpaired electrons, add one
Noble d8 metal compounds are usually tetrahedral or square planar?
Square planar; if tetrahedral, more electrons placed in higher energy level compared to square planar diagram
Pi donor or acceptors: Cl-, Br-, I-
Pi donors
Pi donor or acceptors: OR-, SR-
Pi donors
Pi donor or acceptor: NR2-
Pi donor
Pi donor or acceptor: O2-
Pi donor
Pi donor or acceptors: NR2 -
Pi donor
N3-
Pi donor
Pi donor or acceptor: H2O
regular sigma donor!
Pi donor or acceptors: NH3
regular sigma donor!
Pi donor or acceptors: en (ethylenediamine)
regular sigma donor!
Pi donor or acceptors: PMe3
regular sigma donor!
Pi donor or acceptors: CO
pi acceptor
Pi donor or acceptors: CN-
pi acceptor
Pi donor or acceptors: NO+
pi acceptor
Pi donor or acceptors: pyridine
pi acceptor
High or low spin for pi acceptor
low spin
high or low spin for pi donor
high spin
Geometries for 3-coordinate complexes
t-shaped, pyramidal, trigonal planar
Geometries for 5-coordinate complexes
trigonal bipyramidal, square pyramidal
Geometries for 6-coordinate complexes
tetragonally distorted, octahedral, trigonal prisms
Seven coordinate geometry
Pentagonal bipyramid
Eight coordinate geometry
square antiprismatic, bicapped trigonal prismatic
Coordinate covalent bond
a bond in which both electrons are donated from one of the atoms/groups. AKA dative bond. ONLY applies to neutral ligands
Nomenclature: H2O
aquo
Nomenclature: NH3
ammine
Nomenclature: OH-
hydroxo
Nomenclature: H
hydrido
Nomenclature: CN-
cyano
Nomenclature: NO2-
nitro
Nomenclature: O2-
oxo
Nomenclature: —SCN-
thiocyano
Nomenclature: —NCS-
isothiocyano
Nomenclature: anionic complexes
get -ate suffix to metal.
Some use greek name, ex:
Fe: ferrate Ag: Argenate Pb: Plumbate
Au: Aurate Sn: Stanate
Nomenclature: bridging ligands
prefix µn-
(where n is # of metals bridged)
Nomenclature: PR3
phosphine
Nomenclature: NR2-
amido
Nomenclature: NR2-
imido
Denticity
number of donor atoms on a ligand
ex.
monodentate: phosphine
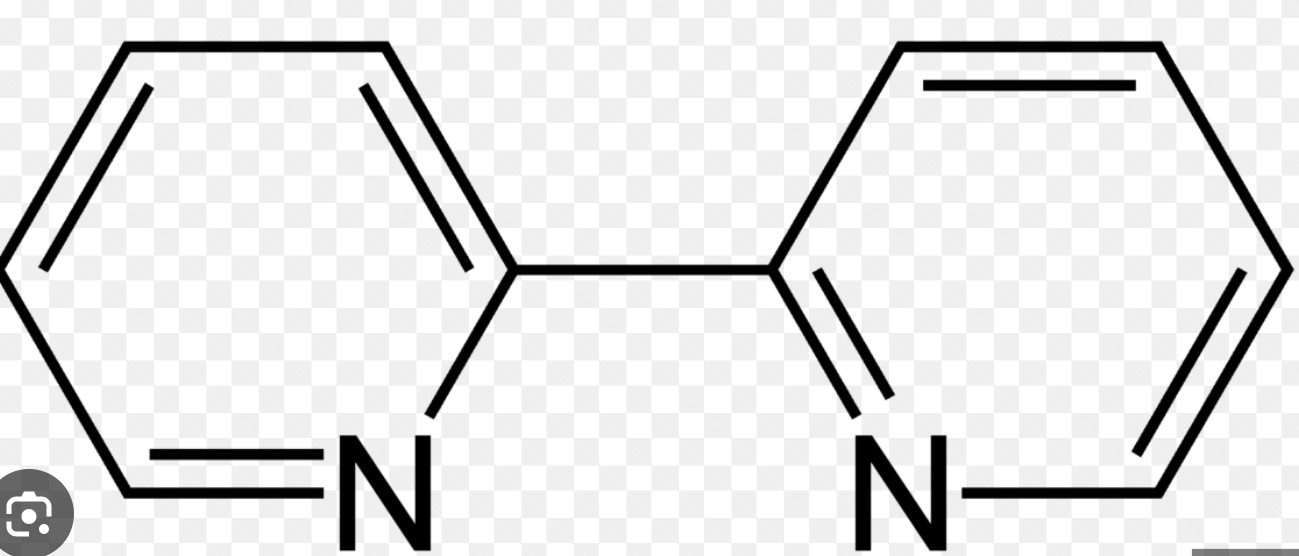
bidentate: bipy
bipy
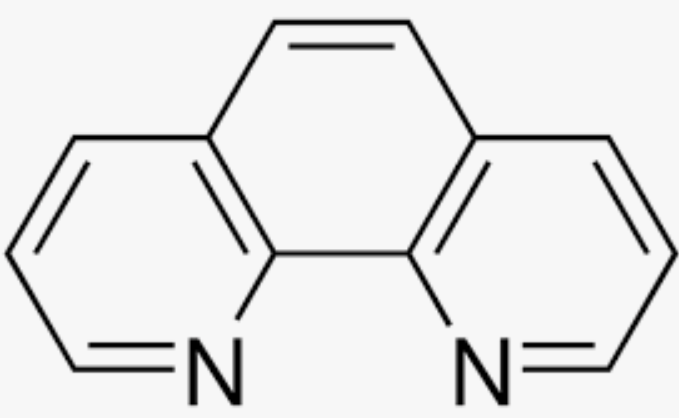
ortho-phenanthroline (ophen)
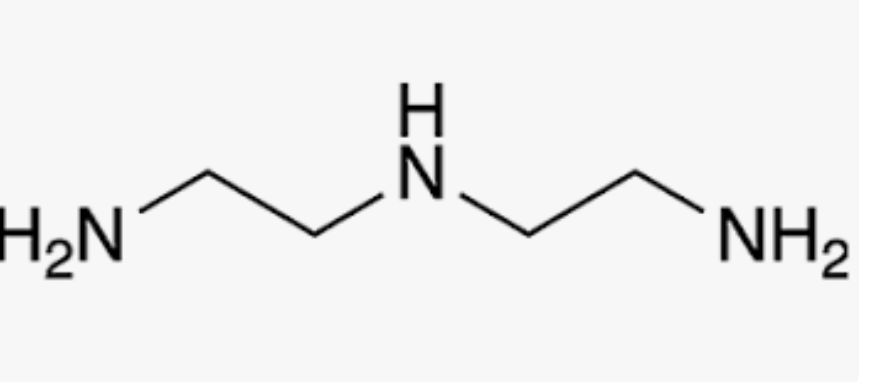
diethylenetriamine (dien)
triethylenetetraamine (trien)
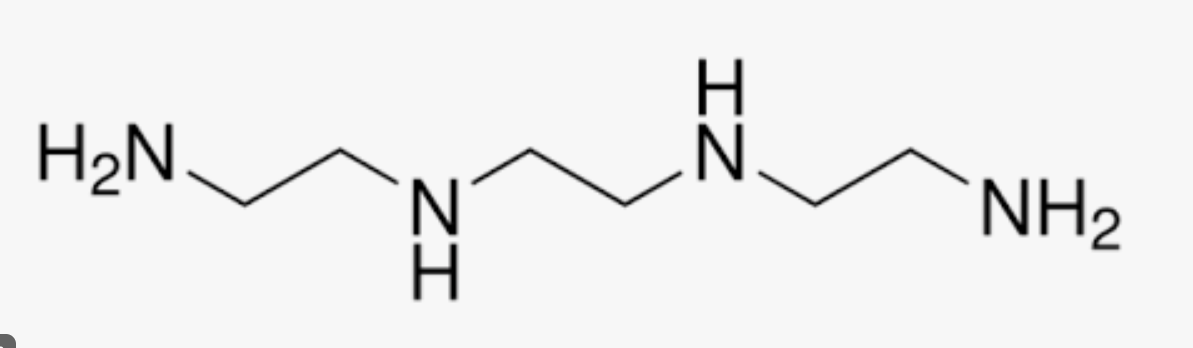
tris-(2-aminoethyl)amine (tren)
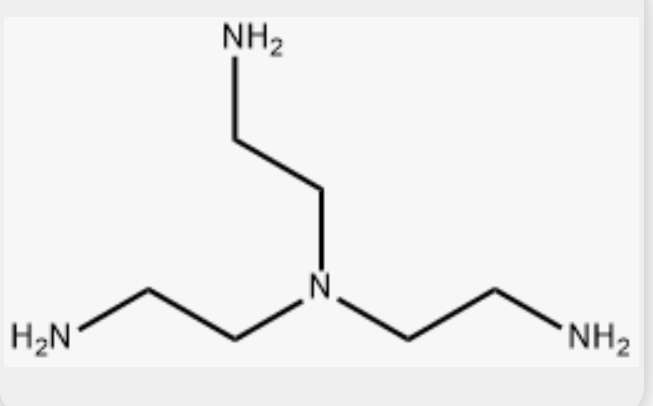
terpy
terpyridine (bipy + another pyridine)
Chelation
binding of a metal by a ligand through 2 or more donor atoms, forming a ring(s)
Thermodynaic Chelate effect
chelating ligands form more thermodynamically stable complexes than with non-chelating ligands. it’s primarily an entropic effect
Kinetic chelate effect
the probability of a dissociated ligand binding back to the metal is increased when that ligand is held on by a “tether”. if the chelated ligand partially dissociates, reassociation is facile because it remains partially bound.
However, if ring is too large, effect is reduced.
Hydrate (solvent) isomerism
occurs when water (or another solvent) can appear within the primary or secondary coordinate sphere of a metal ion; e.g. [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 vs. [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2 . H2O
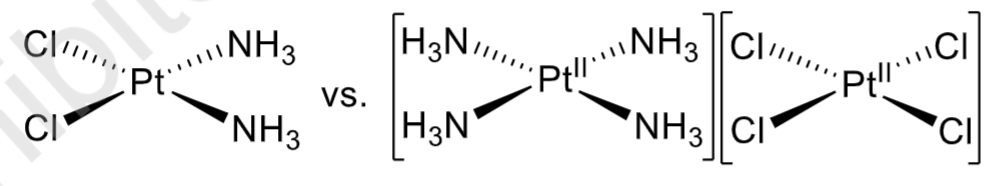
Ionization isomers
the same formulae, but differ in which ions are present in the primary and secondary coordination spheres; e.g. [Co(NH3)5(SO4)][NO3] vs. [Co(NH3)5(NO3)][SO4]
Coordination isomerism
occurs when ligands can be distributed differently between two or more metals
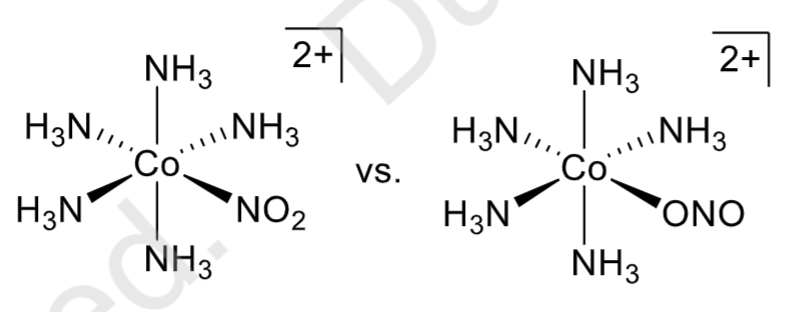
Linkage isomerism
occurs when ligands use different donor atoms to bind to a metal center
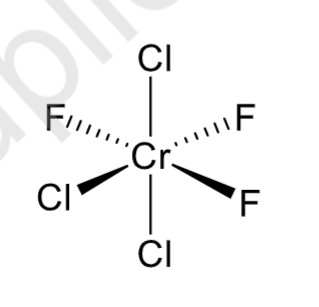
fac or mer?
mer
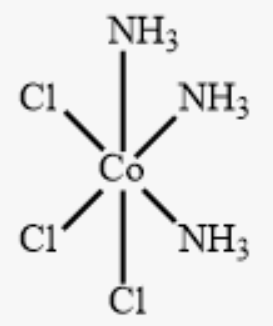
fac or mer?
fac
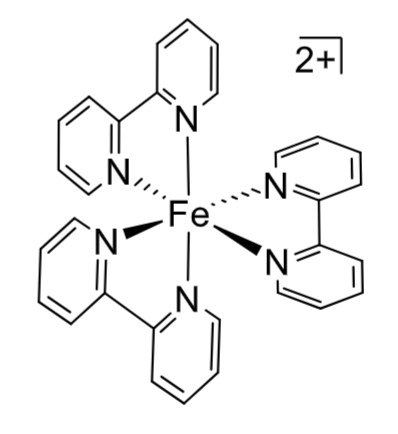
Λ or ∆?
lambda
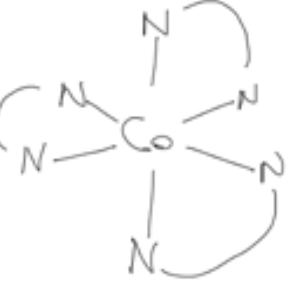
Λ or ∆?
delta
Symmetry of p-orbital
C∞v
Symmetry of d-orbitals (not z2)
D2h
Symmetry of f-orbitals
Td
Chiral or achiral?: C1, Cn, Dn
chiral
How to determine point group
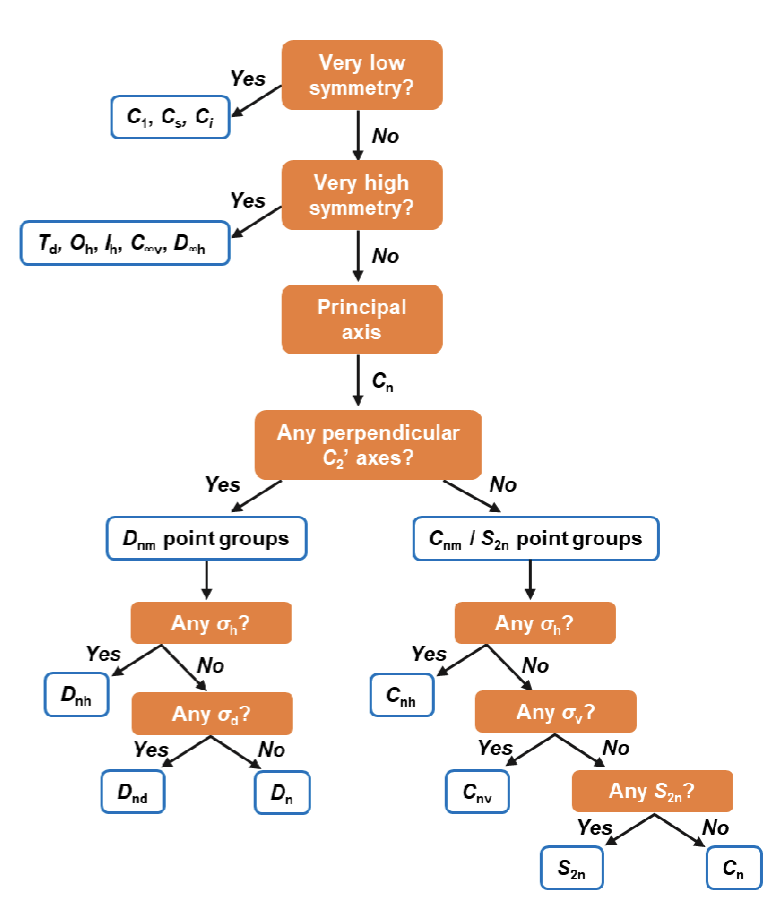
what is ∆E approximately equal to
∆o. Therefore, incresing ∆o, decreases wavelength (lambda) absorbed
Laporte selection rule
selection rule explaining transitions between different orbitals (d→p allowed, d→d not allowed)
(can also think of g→u allowed, g→g not allowed)
spin selection rule
A transition is allowed if the starting and final states have the same multiplicity (∆S=0)
(Basically can’t pair spin up and spin up, gotta be up and down pairing)
strongly colored, somewhat colored, or colorless: spin and laporte allowed
strongly colored
strongly colored, somewhat colored, or colorless: spin forbidden, laporte allowed (or vice versa)
somewhat colored
strongly colored, somewhat colored, or colorless: spin and laporte forbidden
colorless
Jahn-Teller Theorem
a system with unequal occupation of degenerate electronic states will undergo a structural distortion, removing that degeneracy
Weak or strong Jahn Teller: high spin d4
strong
Weak or strong Jahn Teller: low spin d7
strong
Weak or strong Jahn Teller: d9
strong