Chapter 2 Flashcards - Principles of Economics
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Which of the following sayings best reflects the concept of opportunity cost?
a. "You can't teach an old dog new tricks."
b. "Time is money."
c. "I have a baker's dozen."
d. "There's no business like show business."
b
Suppose the price of an airline ticket from Dallas to Boston costs $600. A bus ticket costs $150. Traveling by plane takes 6 hours compared with 51 hours by bus. Other things constant, an individual would gain by choosing air travel if, and only if, his time were valued at more than
a. $6 per hour.
b. $8 per hour.
c. $10 per hour.
d. $15 per hour.
c
The opportunity cost of an option
a. measures the undesirable aspects of the option.
b. includes only the monetary cost of the option
c. is the highest-valued alternative that must be given up as the result of choosing the option.
d. is objective, and it will be the same for all individuals.
c
Which of the following will most likely occur under a system of clearly defined and enforced private property rights?
a. Resource owners will fail to conserve vital resources, even if they expect their supply to be highly limited in the future.
b. Resource owners will ignore the wishes of others, including others who would like to use the resource that is privately owned.
c. Resource owners will fail to consider the wishes of potential future buyers when they decide how to employ privately owned resources.
d. Resource owners will gain by discovering and employing their resources in ways that are highly valued by others.
d
If an economy is operating at a point inside the production possibilities curve,
a. its resources are not being used efficiently.
b. the curve will begin to shift inward.
c. the curve will begin to shift outward.
d. This is a trick question because an economy cannot produce at a point inside the curve.
a
The primary benefit that results when a nation employs its resources in accordance with the principle of comparative advantage is
a. an expansion in investment resulting from a reallocation of resources away from consumption.
b. a larger output resulting from a more efficient use of resources.
c. greater equality of income resulting from an increase in the number of workers.
d. an increase in the profitability of business enterprises resulting from an increase in investment.
b
"Now that Terrance paints the broad surfaces and I do the trim work, we can paint a house in three-fourths the time that it took for each of us to do both." This statement most clearly reflects
a. the importance of secondary effects.
b. the fallacy of composition.
c. the law of comparative advantage.
d. behavior inconsistent with economizing.
c
Suppose Country A and Country B can only make two products, milk and bread. The table below describes their different production possibilities:
Country A |
| Country B | ||
Milk | Bread |
| Milk | Bread |
0 | 100 |
| 0 | 120 |
75 | 0 |
| 60 | 0 |
Which of the following is true?
a. Country A has an absolute advantage in milk production
b. Country B has an absolute advantage in milk production.
c. Country A has a comparative advantage in bread production.
d. Country B has a comparative advantage in milk production.
a
If Country A and B do not engage in specialization and trade and each split their resources equally to produce milk and bread, the total or combined amount of bread produced in Country A and Country B is _______ units. Instead, if Country A and Country B each specialize in the good in which they have a comparative advantage, the total or combined amount of bread is _________ units.
a. 110; 120
b. 100; 120
c. 120; 100
d. 50; 120
a
With voluntary exchange,
a. both the buyer and seller will be made better off.
b. the buyer will be made better off, while the seller will be made worse off.
c. the seller will be made better off, while the buyer will be made worse off.
d. both the buyer and the seller will be made worse off.
a
Three basic decisions must be made by all economies. What are they?
a. how much will be produced, when it will be produced, and how much it will cost
b. what the price of each good will be, who will produce each good, and who will consume each good
c. what will be produced, how goods will be produced, and for whom goods will be produced
d. how the opportunity cost principle will be applied, if and how the law of comparative advantage will be utilized, and whether the production possibilities constraint will apply
c
If a firm or a nation desires to maximize its output, each productive assignment should be carried out by those persons who
a. have the highest opportunity cost.
b. have a comparative advantage in the productive activity.
c. can complete the productive activity most rapidly.
d. least enjoy performing the productive activity.
b
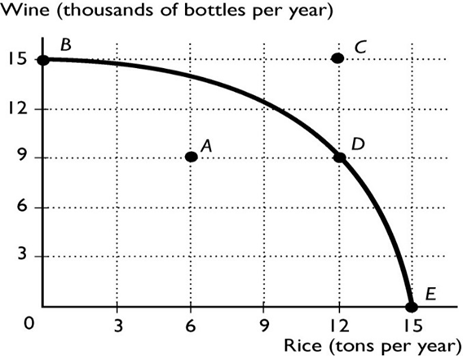
The above figure shows the production possibility frontier for a country. What is the opportunity cost per ton of rice to move from point D to E?
a. 9 bottles of wine
b. 1/9 of a bottle of wine
c. 3 bottles of wine
d. 1/3 of a bottle of wine
c