The excretory system
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are the functions of the kidneys
primary excretory organs
Work to:
ride body of wastes, especially nitrogenous wastes such as urea,Uric acid and creatine
Maintain constant concentration of materials in body fluids
Regulate the balance of fluid, salt & pH
How does the Kidney achieve those functions?
Filtering through blood as it passes through
Waste substances removed by process of filtration and tubular secretion
Useful substances returned to body by process of selective reabsorptiom
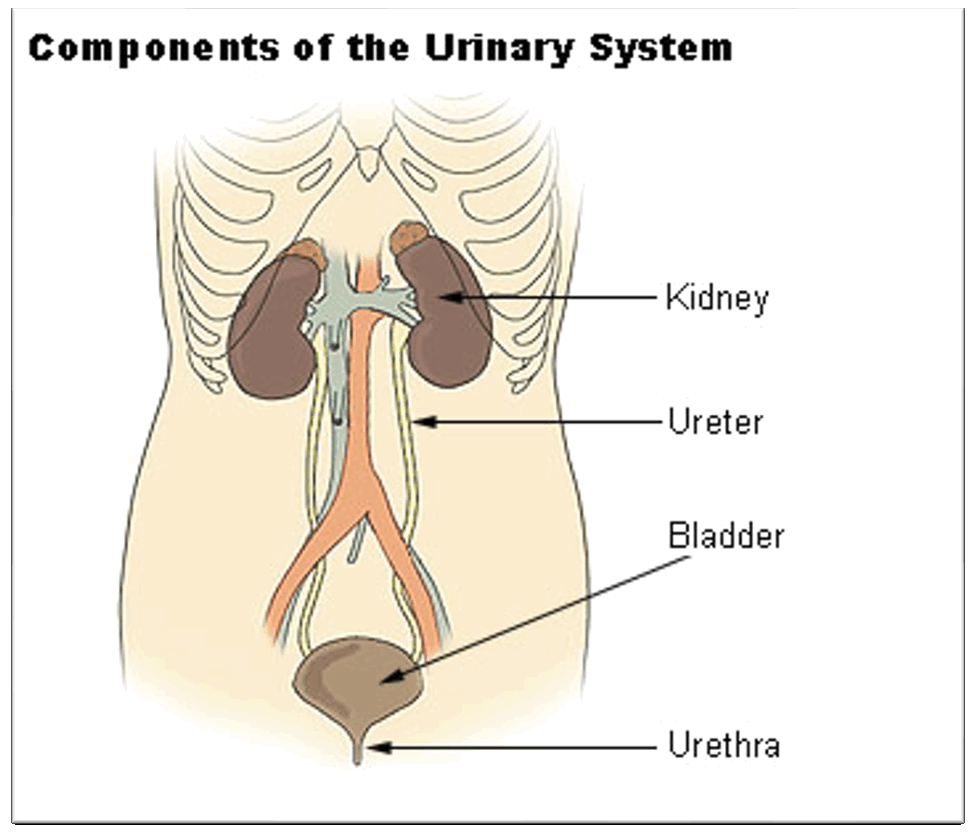
What is the structure of the excretory system?
Kidney 2x
Urinary bladed 1x
Ureters 2x
Urethra 1x
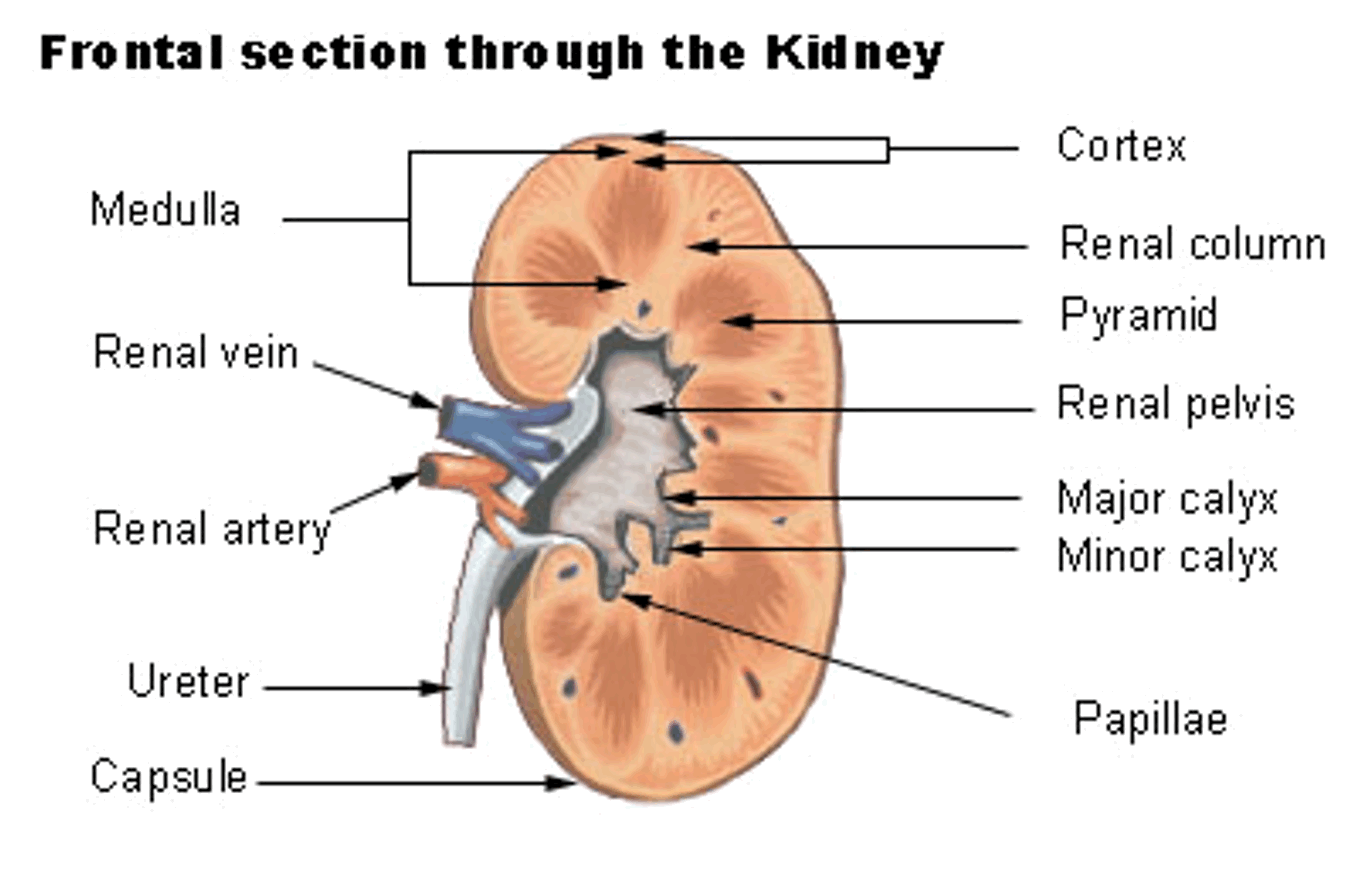
What is the structure of the kidney?
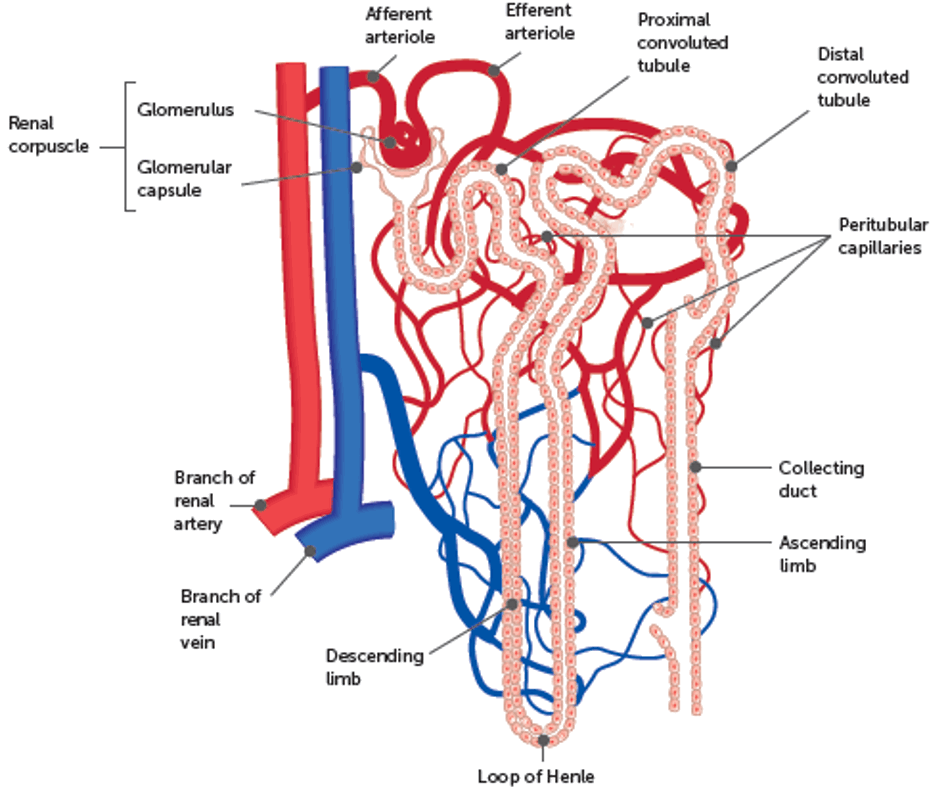
What is the Nephron?
functional unit of the Kidney’s
Make urine
~ 1.2 million nephrons in each kidney
What does ghe Nephron consist of?
renal corpuscle (made of bowman’s capsule and glomerulus)
Real tubule (divided into proximal convoluted tubule, loop of henle, and distal convoluted tubule)
Associated blood supply

What is the renal corpuscle and what does it do? + it’s divisions
filtration takes place in renal corpuscle
Consists of bowman’s capsule ad mass of blood capillaries (called glomerulus)
renal arteries delivering blood to kidneys are large, approximately 1.2L passes through the pair
Renal corpuscle has afferent (in) and efferent (out) arterials
Efferent arteriole then divide into network of pertubular capillaries surrounding Renal tubule

What are podocytes and what do they do?
specialness cells that line bowman’s capsule
Cells have finger-like extensions that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus
Spaces between the ‘fingers’ are filtration slits

How does filtration occur in the Kidney? stage 1
occurs in glomerulus, where fluid is forced out of the blood, into bowman’s capsule
Blood pressure within glomerulus high, aiding movement of fluid
How does filtration occur in the Kidney? stage 2
Afferent (in) arteriole wider diameter than efferent (out) arteriole = increases resistance to blood flow and increases blood pressure, forcing water and s dissolved blood components out of the capillary
How does filtration occur in the Kidney? stage 3
walls of glomerular capillaries ans the glomerular capsule are only 1 cell thick (and flat)
Filtrate consists of the materials in the blood except red and white blood cells and plasma proteins (too large)
Filtration as a diagram

How does reabsorption occur in the Kidney?
selective reabsorption of materials from the filtrate, required by body, takes place in renal tubule
Returned to blood in pertibular capillaries
Convolutions of renal tubule, and high number of nephrons in Kidneys provide large surface area for reabsorption to take place
Depending on body’s needs, permeability of cells of the tubule can be altered (facultative reabsorption)
What is inside the proximal tubule?
microvilli line proximal tubule and create bush border
Greatly increases surface area for reabsorption
What is tubular secretion?
tubular secretion adds materials from the blood to filtrate
Tubular secretion aims to:
maintain blood pH (7.4-7.5) by removing excess hydrogen and ammonium ions
Maintain ruin pH (6)
Active transport, through PCT and DCT
Reabsorption with structures and how they transport across
Structure | Substance | Active/passive |
PCT | Water (60-70%) Salts (60-70%) Glucose (100%) Amino acids (100%) Vitamins (100%) | Passive (osmosis) All active |
Loop of Henle | Water (25%) Na+/Cl- (25%) | Passive (osmosis) Active |
DCT | Water (5%) Na+/Cl- (5%) | Passive (osmosis) Active |
Collecting duct | Water (5%) | Passive (osmosis) |
What is Urine?
clear, transparent fluid. Normally amber colour
Collected in bladder, eliminated through urethra
Average amt of urine in 24 hrs os ~1,200 cm³
Where is Urine stored?
Water and other substances not reabsorbed drain into collecting ducts, then renal pelvis
Urine drains into ureters and is pushed y waves of muscle contractions
Urethra carries urine from bladder to exterior of body
What is the Composition of Urine?
varies according to diet/warter intake/ health
Typically:
~96% water
~4% other solutes, organic molecules, ions, and other metabolic wastes:
~ 2% urea
Creatinine
Uric acid
Sodium, chloride, other irons (1,5%)
Does not contain glucose or significant amt of protein
What is Uric acid created from?
Uric acid created from metabolism of purines
Purines come from the breakdown of Nucleic acids, when cells die, and also occur in many foods
What is creatinine created from?
produced in muscle from the breakdown of creating phosphate. (Phosphatecreatine. An energy-rich molecule
What is delamination?
How does the liver play a role in the excretory system?
Ammonia into urea
Create bile for waste excretion
The liver processes and metabolizes various harmful substances
What is protein like in the excretory system and deamination?
excess protein in diet cannot be stored in cells of the body
Body needs to break it down to remove it
What happens to unused protein in deamination?
Protein can come from:
worn out/broken cells, and broken down into amino acids to make new proteins
Can be lost from body via urine, skin, hair and fingernails
Protein helps form cell structures, enzymes, antibodies, and glandular secretions
How is Protein used for Energy?
initially body uses carbohydrates and fats for energy
When carbohydrates are depleted, fats in food and stored fats are used to release energy
Protein NOT utilised in energy-releasing reactions, MAJORITY of the time
To use Protein for energy, body can metabolise large amounts of protein
What is deamination?
Deamination is the removal of the amino group from an amino acid molecule
It occurs in the liver with the aid of enzymes
What is the equation for Deamination?

What do the two equations for deamination mean?
It shows how amino acid, turns into ammonia, and some energy, and from ammonia turn into urea, which can then be excreted in urine.
It shows how we can excrete excess waste and protein. ?
What is the purpose of deamination?
crucial process for:
balancing protein metabolism
ensuring the proper excretion of nitrogenous waste
allowing body to utilize amino acids for energy
other metabolic needs.
What is ammonia? Ands it’s features
soluble in water, highly toxic to cells
Urea much safer for body
Excreted by kidneys and eliminated from body in urine
Also last in sweat
What is the whole structure of the Nephron’s (including capillaries)