Lecture 4: Immunoserology techniques
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
contributing factors to immunoserology techniques
affinity
avidity
affinity
initial force of attraction between a FAB site on an Ab and an EPITOPE on an antigen
avidity
overall strength of antigen/antibody binding. All of the affinities put together
precipitation general information
start with both antigen and antibody in soluble form. When they come together they become insoluble.
precipitation graph issues
prozone
zone of equivalence
postzone
prozone is when
too much Ab in patient serum means no PPT. dilute to fix false neg
postzone is when
too much antigen means no PPT
zone of equivalence is when
we can readily and accurately see PPT
techniques to measure precipitation in fluid
turbidimetry
nephelometry
turbidimetry measures
how much light comes through. How turbid?
nephelometry measures
how much light is scattered. Measured at 90 degree angle
techniques to measure precipitations in gel
radial immunodiffusion
ouchterlony immunodiffusion
basic premise of precipitation reaction in gel
antibody and antigen interaction. If they meet there is a visible line of PPT. Agarose stabilizes the reaction so we can visualize.
what is radial immunodiffusion
a single passive diffusion precipitation technique
what is the goal of radial immunodiffusion
look for patient Ag. gel contains Ab
how does radial diffusion work
Antibody incorporated into the gel itself
Punch holes in the gel and add Ag to the hole. Antigen diffuses into the gel
As the Ag diffuses it reaches the zone of equivalence and makes a PPT ring
how can we measure PPT in radial diffusion
Based on standards with known concentration Ag. create standard curve
Measure diameter and square. Compare to standard curve
pro of radial diffusion
can quantitate
con of radial diffusion
takes 3 days
what is the ouchterlony immunodiffusion
double passive diffusion technique
what is the purpose of ouchterlony immunodiffusion
compare the similarity of antigens
possible results of ouchterlony immunodiffusion
identity
non identity
partial identity
identity ouchterlony immunodiffusion looks like this
arc
non identity ouchterlony immunodiffusion looks like this
cross
partial identity ouchterlony immunodiffusion looks like this
spur
in a partial identity the middle antigen is ____________ similar to the underlined antigen
more similar to the underlined
methods of electrophoresis to measure precipitation
immunoelectrophoresis
immunofixation electrophoresis
purpose of immunoelectrophoresis
looks for antigen in patient serum
information about immunoelectrophoresis
double diffusion technique.
both Ag and Ab are being sent out
what does it mean when we see lines of PPT on immunoelectrophoresis
it means the patient has the target antigen
purpose of immunofixation electrophoresis
determination of identity of monoclonal gammopathy
could be used to diagnose multiple myeloma and waldenstrom's
immunofixation electrophoresis picture
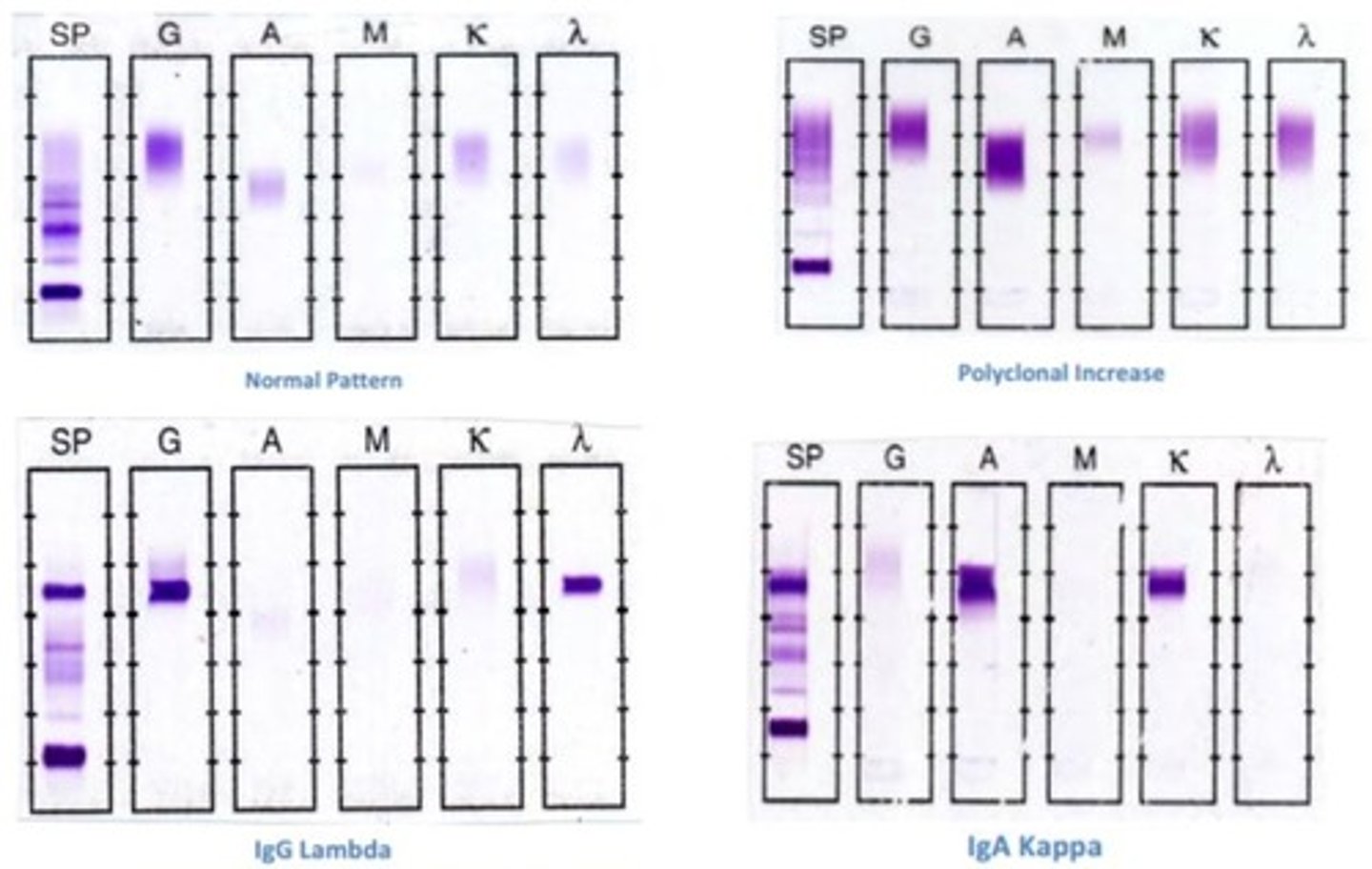
nephelometry application
Immunoglobulins, complement, CRP, serum proteins
nephelometry principle
Light that is scattered is measured. ABS informs how much Ag/Ab is present
radial immunodiffusion application
Immunoglobulins and complement
radial immunodiffusion principle
Antigen diffuses out into the gel that is infused with Ab. measurement of diameter determines the amount of antigen present.
ouchterlony double diffusion application
complex antigens. compares which antigens are most similar
ouchterlony double diffusion principle
Both antigen and antibody diffuse out from wells in gel. Lines of PPT form and indicate the similarities between antigens
immunoelectrophoresis application
Differentiation of serum proteins
immunoelectrophoresis principle
Electrophoresis of serum is followed by diffusion of antibody into wells
immunofixation electrophoresis application
over or underproduction of antibodies
immunofixation electrophoresis principle
Electrophoresis of serum is followed by direct application of antibody to the gel. Tells us the identity of the Ab
what is agglutination
soluble + insoluble = looks for agglutination
what is the two step process for agglutination
sensitization
lattice formation
what is sensitization in relation to agglutination
coating particle/cell with something to help in agglutination
what is lattice formation in relation to agglutination
visualization of the agglutination reaction which is a product of crosslinking.
how much more effective is IgM than IgG
igM is 700X more effective than igG
why is IgM more effective than IgG
igM is a pentamer
what temp does igM work best at
room temp
what is coombs reagent
anti-human immunoglobulin. Helps IgG bind even though it is a monomer
techniques to measure agglutination
direct agglutination
passive/indirect agglutination
reverse passive agglutination
definition of direct agglutination
using known antigen attached to a particle to test for Ab in a patient.
what kind of test is a Wisal test
direct agglutination
describe the wisal test
detects antibody to salmonella typhi. All you need is the serum to test
hemagglutination
Involves RBC (sialic acid on RBC) binds viruses to form crosslinking agglutination
positive hemagglutination result
lattice
solid color
negative hemagglutination result
button
how should we read hemagglutination (titer)
the well where a positive reaction last happened
hemagglutination inhibition looks for _____________
patient antibody
steps for hemagglutination inhibition
Make dilutions of Pt serum and add to wells
Add virus to well
Incubate for 30 min
Add RBC
Incubate RBC for 30 min and interpret
what does the positive result for Hemagglutination inhibition look like
button
what does the negative result for Hemagglutination inhibition look like
solid color
lattice
when should Hemagglutination inhibition be used
Acute and convalescent serology example. Used for Rickettsia
hemagglutination inhibition assay is a type of
reverse passive agglutination
what is passive/indirect agglutination
employs particles coated with antigen not normally on the particle.
what is the use for passive/indirect agglutination
looks for virus ab in patient sample. Usually IgM
what is a common use for passive/indirect agglutination
cross reactivity
how can we fix cross reactivity for passive/indirect agglutination.
use as a screening test and do a confirmatory test after
what is a reverse passive agglutination
Uses carrier particles. Attached manufacturer Ab so we are looking for the patient Ag.
what is an example of reverse passive agglutination
rapid strep test
labeled immunoassays
competitive
non competitive
in competitive immunoassays everything is added _________________
everything is added at the same time
what is the goal of competitive immunoassays
look for patient antigen
competitive immunoassays
POS result _____________
NEG result _____________
POS result less color
NEG result more color
what is the goal for non competitive immunoassays
look for patient antigen
non competitive immunoassay
POS result________________________
NEG result _______________________
POS result more color
NEG result less color
formats of labeled immunoassays
radioimmunoassay
enzyme immunoassay
fluorescence immunoassay
chemiluminescence immunoassay
historical information about ratioimmunoassay
First kind of immunoassay developed in the 1950s
Radioactive labeled 125iodine
things needed for complement reaction
Pathogen/antigen
Antibody
Complement
complement fixation is a test where we add _____________ and ______________ and looks for __________ in a patient sample
adds RBC and C'
looks for antibody in pt
positive complement fixation reaction
button
intact RBC
negative complement fixation reaction
solid color
lysed RBCs
how do we quantitate complement fixation
titer
what is the common use for complement fixation
virology and dimorphic fungi
examples of dimorphic fungi
Coccidioides
Histoplasma
Penicillium marnefii
Paracoccidioides
Sporothrix