ORAD800: Inflammatory Lesions of the Jaws
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Common Sources of Inflammatory Lesion
Infection from pulpal tissue
periodontal disease
tooth extraction wound
compound fractures
hematogenous spread
sterile trauma
What are the two common ways of infection from pulpal tissue?
caries
coronal fracture
Acute
recent onset
Chronic
prolonged course
Osteitis
inflammation in the bone
osteomyelitis
inflammation in the bone or bone marrow
Mediators of inflammation tip the normal bone metabolism to favor either bone ___ or ___
formation
resorption
T/F: there is radiographic evidence for acute inflammation
FALSE - clinical signs and symptoms
T/F: there is widening of the PDL space in acute inflammation
TRUE
T/F: there may be a reduction in bone radiopacity in acute inflammation
TRUE
Chronic inflammation often has increased ___ and ___
radiopacity
radiolucency
Chronic inflammation has the same __ but change in bony pattern
density
Where are inflammatory lesions often seen?
apex of the teeth
What is the periphery of inflammatory lesions?
ill defined
well-defined
long areas of transition
What is the internal structure of inflammatory lesions?
spectrum of appearances
resorption
bone formation
mixed
What are the effects of the inflammatory lesion?
widened PDL
root resorption
periosteum
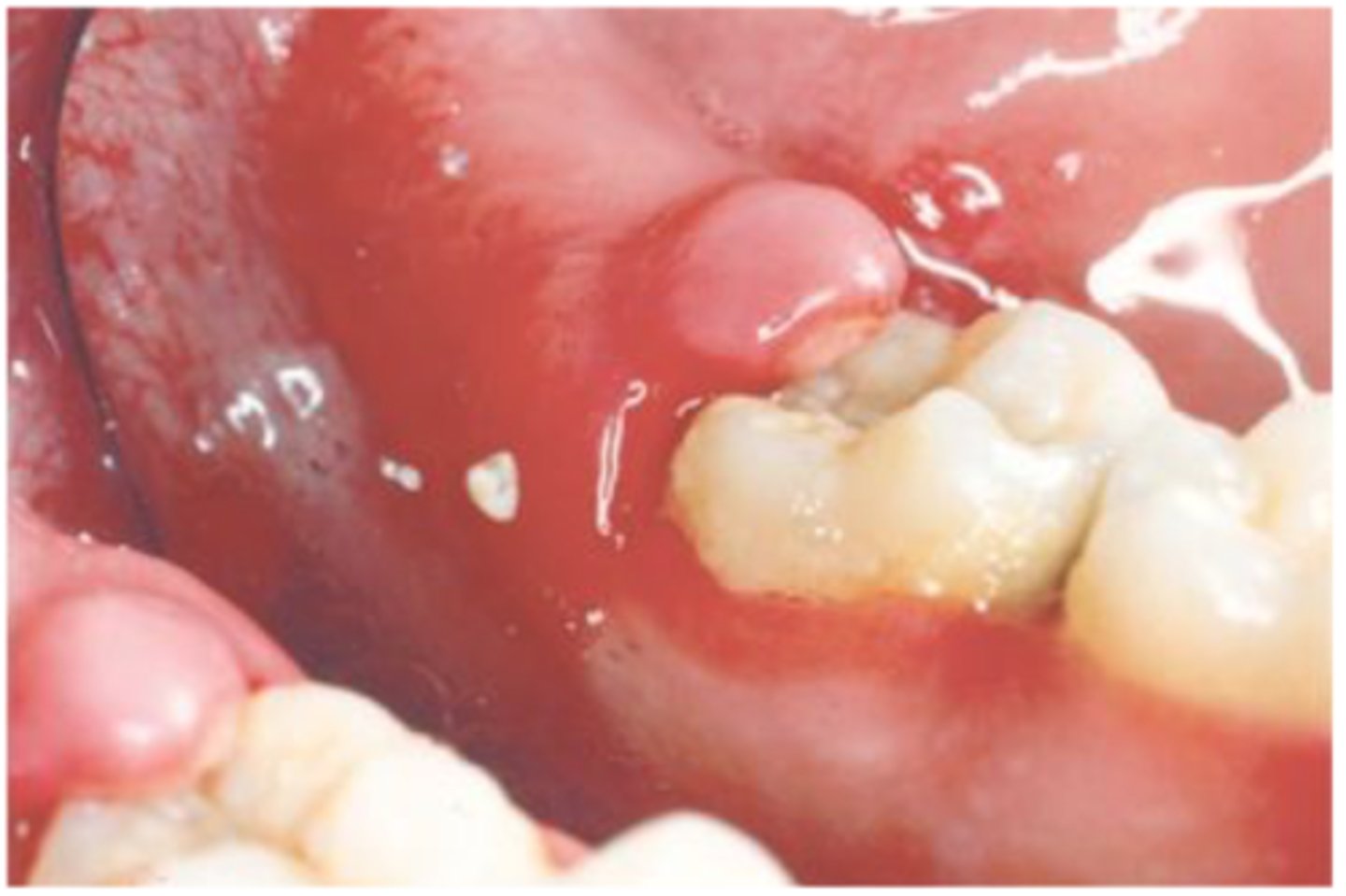
Apical Periodontitis
minimal inflammatory reaction, non-vital teeth, spontaneous, edema, localized to the apical-PDL
T/F: apical periodontitis is spontaneous and non-vital teeth
TRUE
Radiographic features of apical periodontitis
widened PDL space
Thickening of the lamina dura
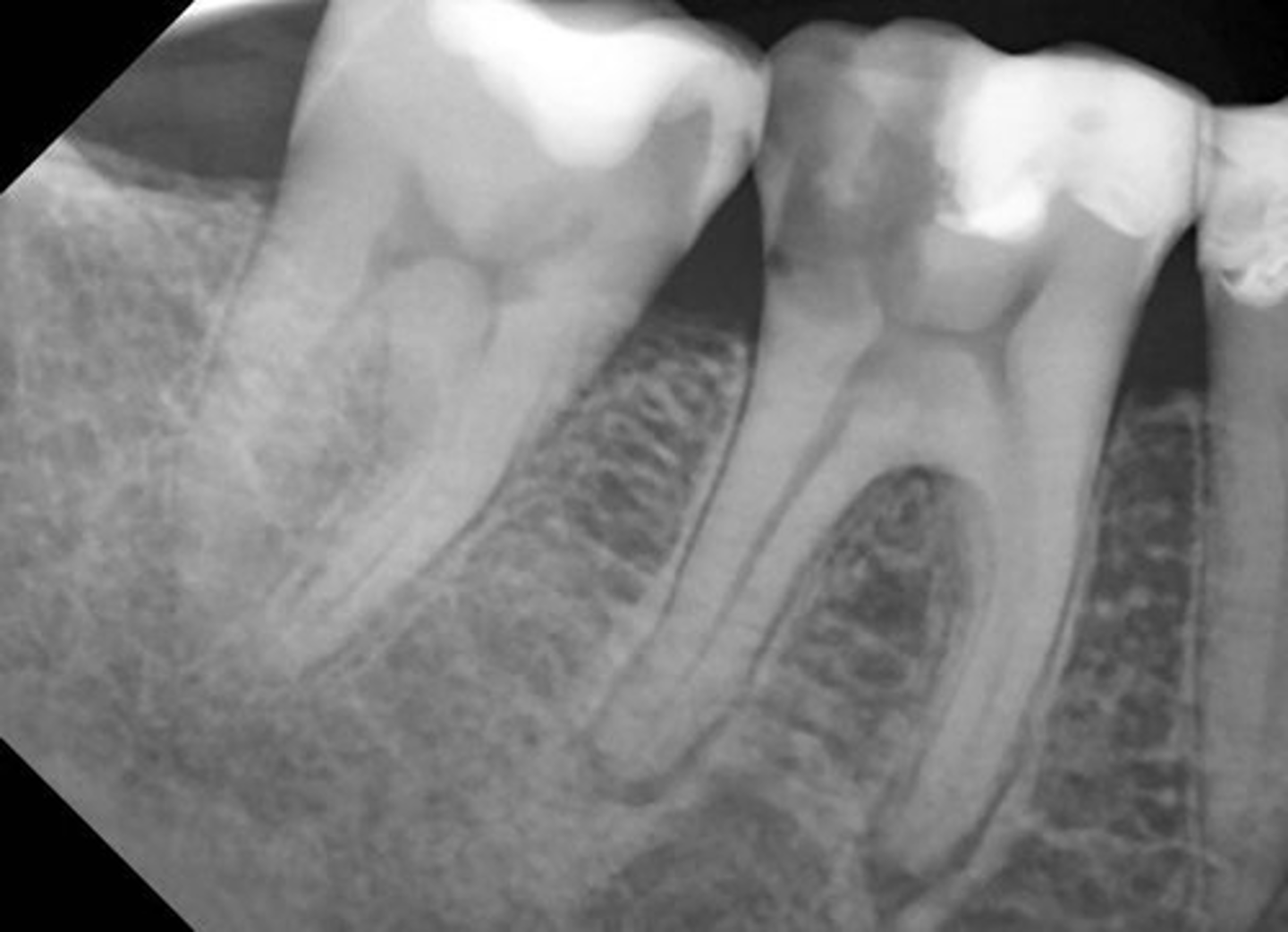
Apical Rarefying Osteitis
chronic inflammation, low grade rxn, low virulence, sequela of acute episodes
Rarefying
black
Radiographic features of Apical Rarefying Osteitis
radiolucent lesion
LOSS of lamina dura
margins either ill/well defined
corticated/non corticated
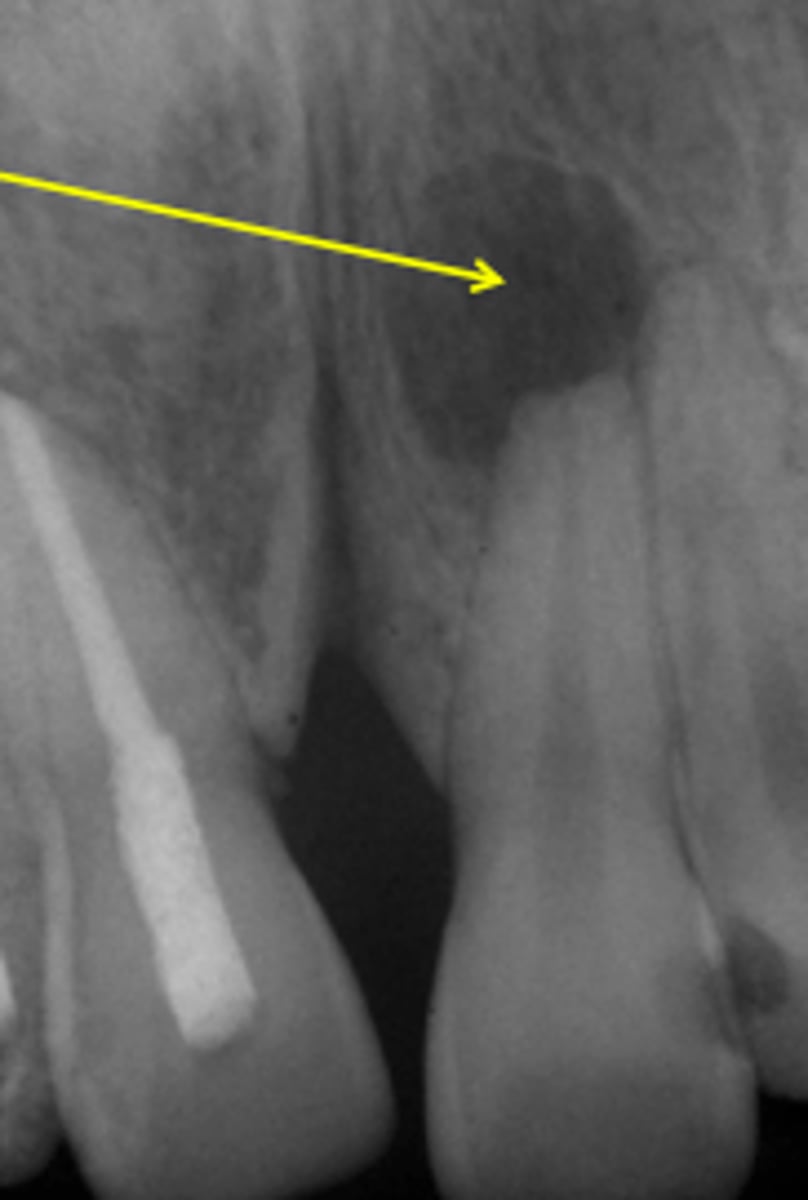
Which periapical Inflammatory Lesion has LOSS of the lamina dura
apical rarefying osteitis
Which periapical inflammatory lesion has THICKENIGN of the lamina dura
apical periodontitis
Sclerosing
white
Apical Sclerosing Osteitis
circumscribed proliferation of periapical bone, exudate of low toxicity, long standing infection, nonvital/degenerating pulp, mandible
Where is Apical Sclerosing Osteitis commonly found?
mandible
Apical Sclerosing Osteitis is also known as
condensing osteitis
focal sclerosing osteitis
Apical Rarefying Osteitis is also known as
chronic apical abscess
apical granuloma
apical cyst
Radiographic features of Apical Sclerosing Osteitis
increased radiopacity
well-defined margins
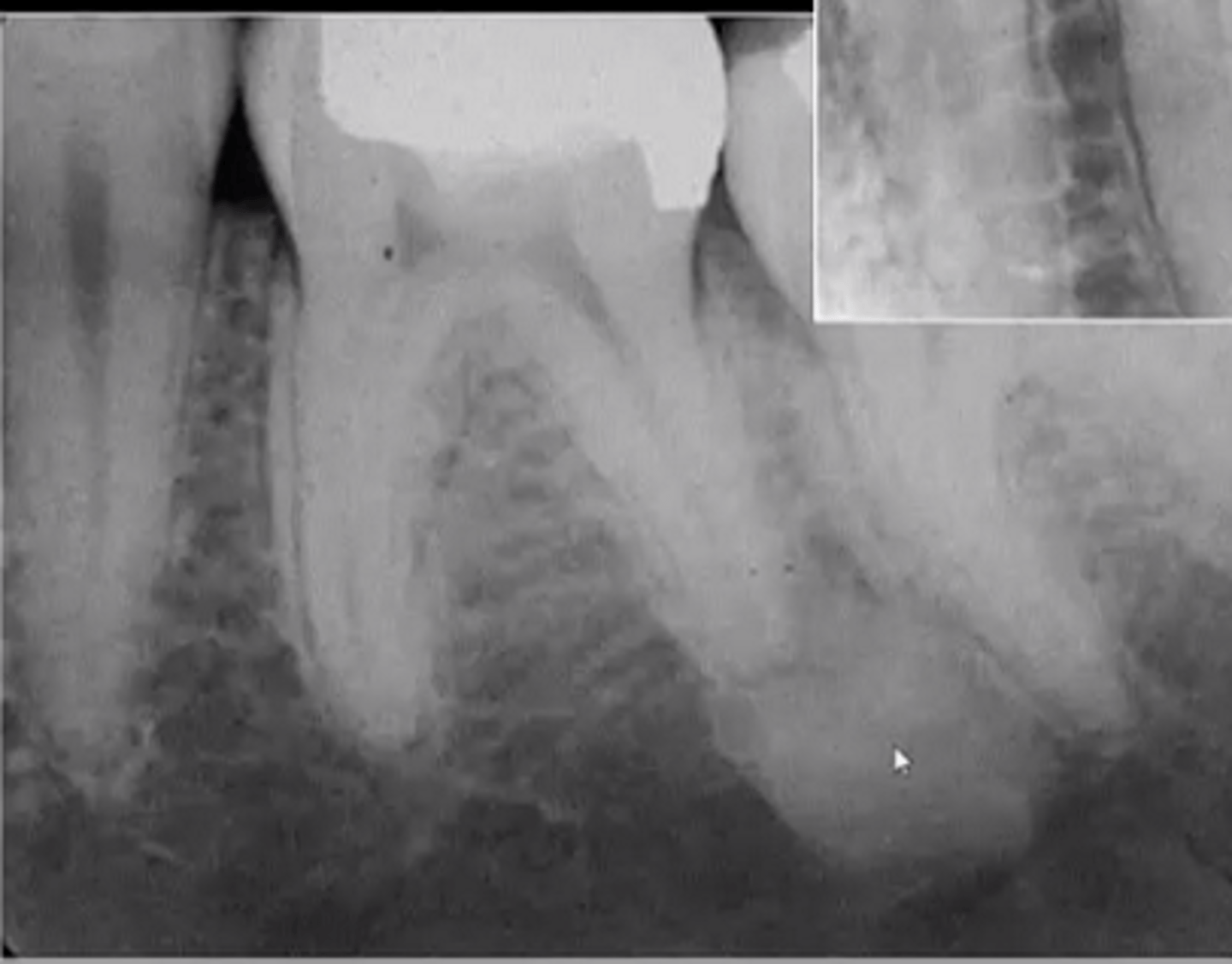
Osteomyelitis
inflammation of bone or bone marrow
predisposing conditions for osteomyelitis
malnutrition
diabetes
leukemia
anemia
alcoholism
What is a MAJOR predisposing factor for osteomyelitis
Hypovascularity
Which has less blood supply, mandible or maxilla?
mandible
Clinical features of osteomyelitis
pain
swelling
redness
fever
purulent discharge
Acute Osteomyelitis
severe pain
swelling/redness
lymphadenopathy
T/F: there is radiographic manifestation for acute osteomyelitis
FALSE
After 10 days, there is a decrease in __ of the trabeculae, blurred outline for acute osteomyelitis
density
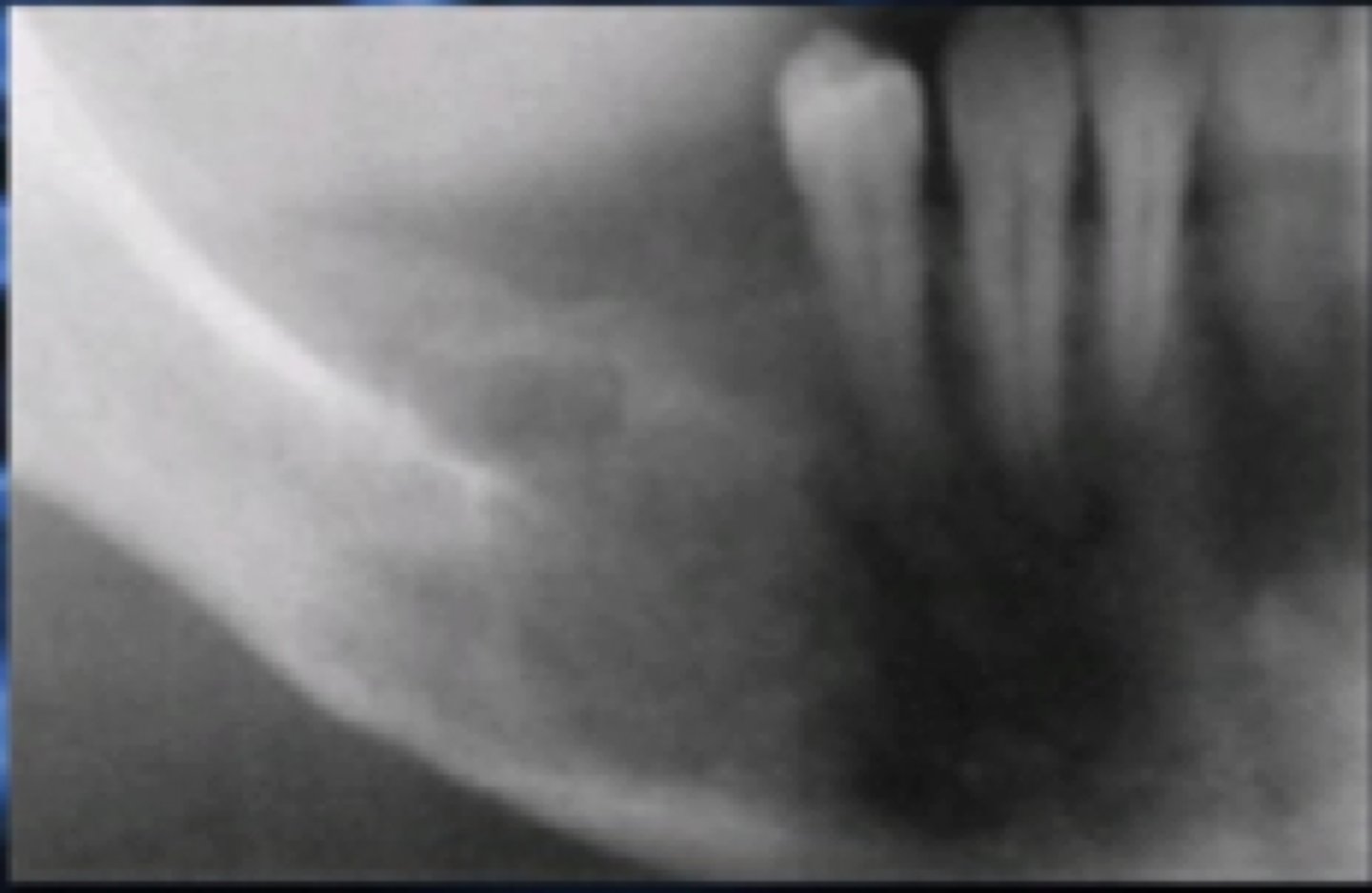
Chronic Osteomyelitis
milder symptoms
low virulent agent
effective host resistance
sinus tract
intermittent exacerbation
Chronic Osteomyelitis has ___ development
sinus tract
Radiographic features of chronic osteomyelitis
radiolucency
mixed radiolucent-radiopaque
sequestration, fistula, fracture
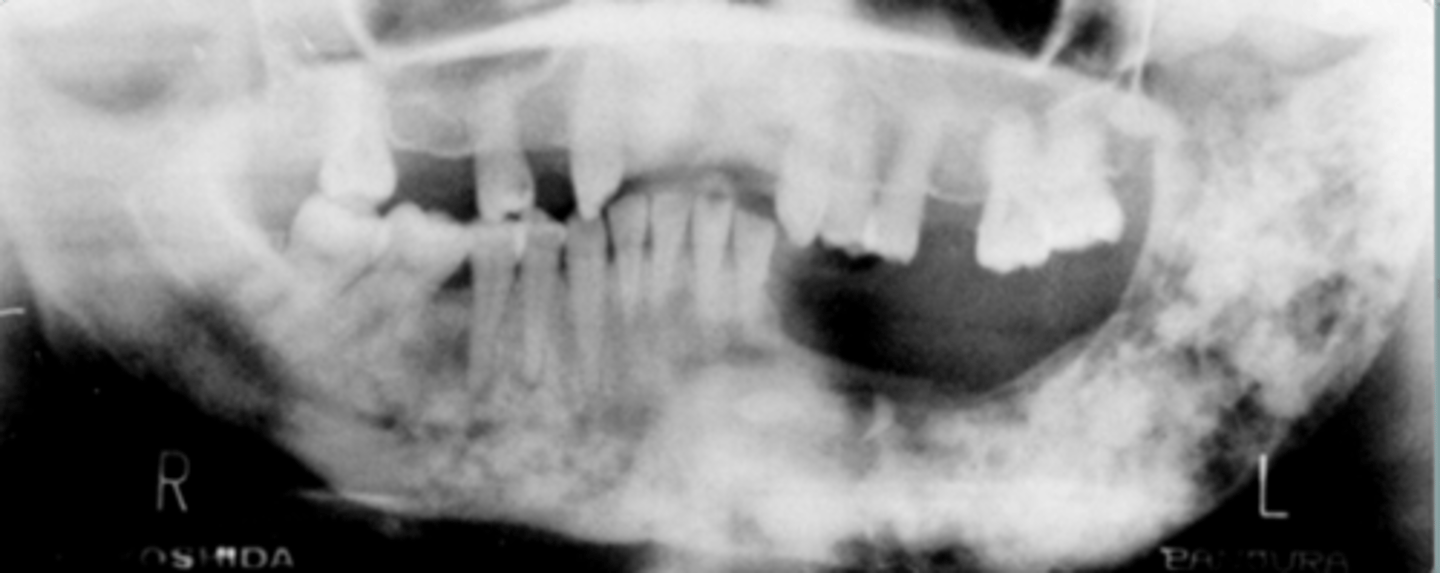
Diffuse Sclerosing Osteomyelitis
older age
proliferation reaction
sub-periosteal bone deposition
slight jaw enlargement
Radiographic Features of Diffuse Sclerosing Osteomyelitis
mixed
ill-defined
increased sclerotic bone
does not cross midline
shortening root
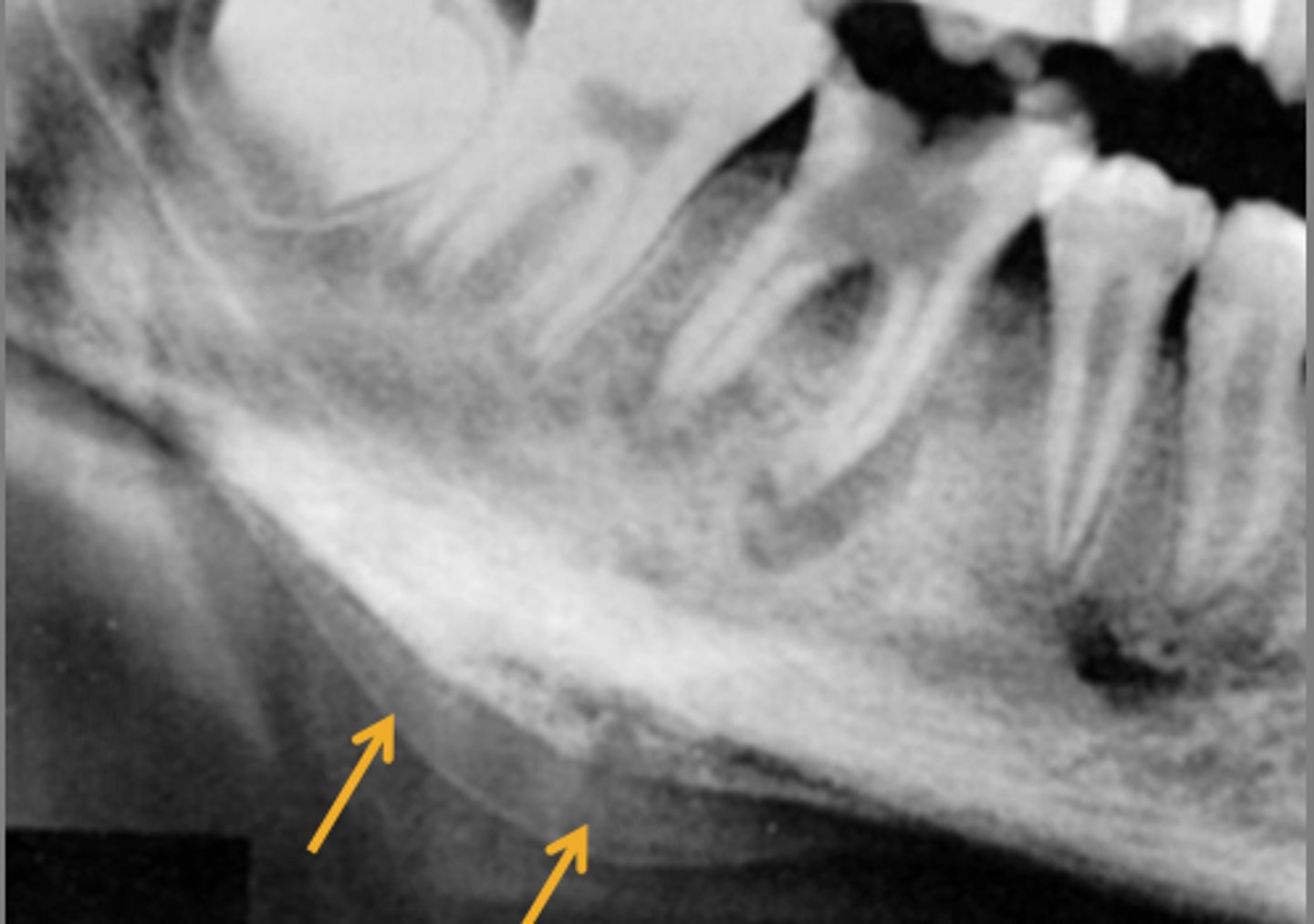
Proliferative Periostitis /Garre's Osteomyelitis
younger patient
female
rare nonsuppurative type
mild infection below periosteum
inferior border of the mandible
hard bony swelling
Radiographic Features of Proliferative Periostitis
thin convex shell of bone
laminated/onion skin appearance
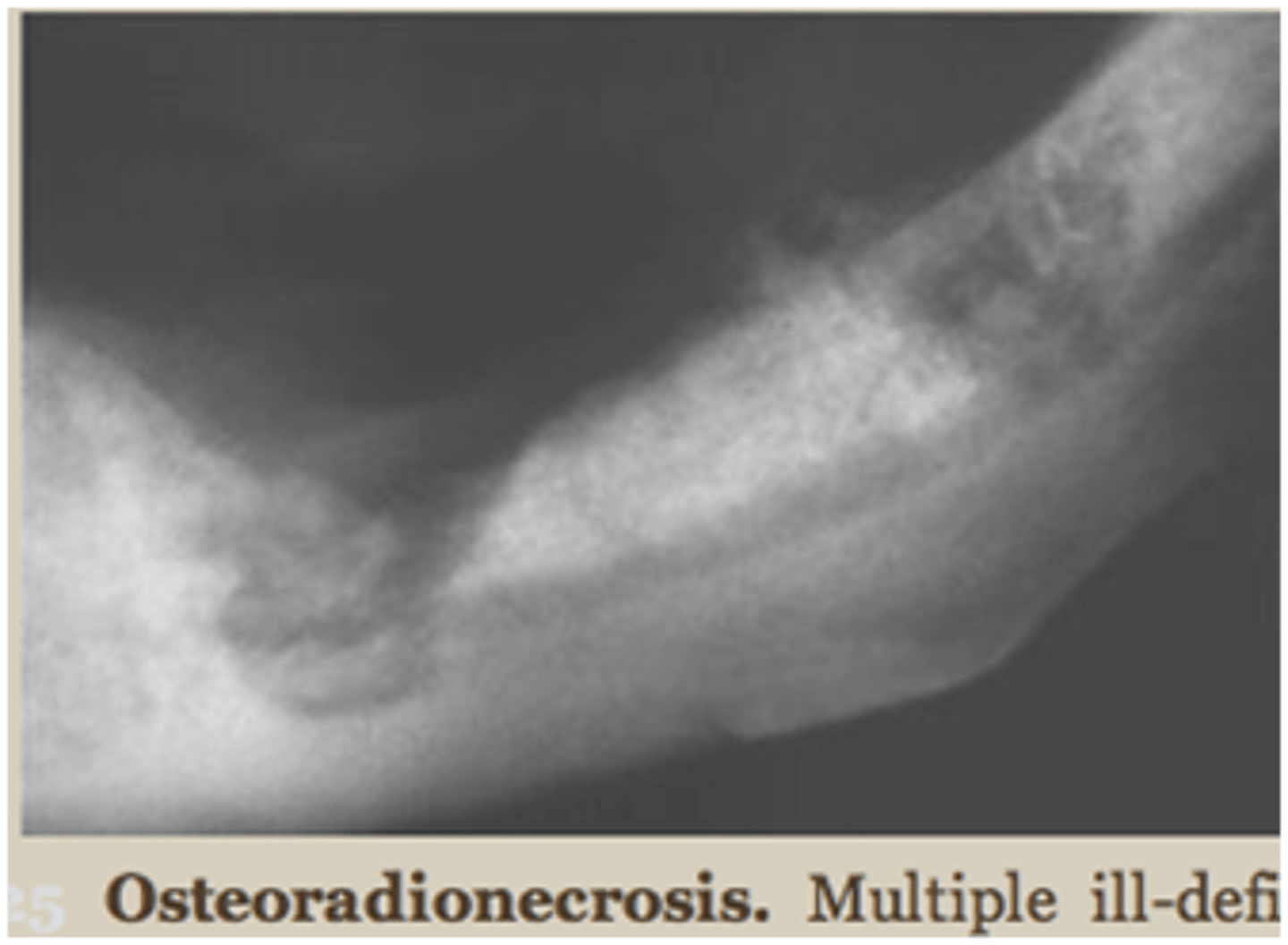
Osteoradionecrosis
mandible
men
history of radiation therapy
hypo vascularity
chronic hypoxia
clinical signs of inflammation
Radiographic Features of Osteoradionecrosis
similar to chronic osteomyelitis
more widespread
Pericoronitis
inflammation around the crown of a partially erupted tooth
Where is pericoronitis commonly found?
third molars
Radiographic features of pericoronitis
underlying osteitis
loss of cortical outline