Mechanical Properties of Fluids
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Fluid
A substance that flows
thrust
total force exerted by a liquid on a surface
pressure
thrust acting normally per unit area
specific gravity/relative density
ratio of the density of the substance to the density of water at 4 degrees celcius
Hydrostatic Paradox
The pressure exerted by a column of liquid depends on its height and not on the shape of the vessel
atm pressure
1.013 X 10^5 Pa
absolute pressure
the total or actual pressure P at a point is called absolute pressure
guage pressure
the difference between the actual pressure at a point and the atmospheric pressure
Buoyancy
the upward force acting on a body immersed in a fluid is called the buoyant force. This phenomenon is called buoyancy.
center of buoyancy
the force of buoyance acts through the center of gravity of the displaced fluid which called the center center of buoyancy
Archemedes Principle
the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body and the upthrust acts through the center of gravity of the displaced fluid
Law of floatation
A body will float in a liquid if the weight of the liquid displaced by the immersed part of the body is equal to or greater than the weight of the body
fractional submerged volume of floating body
density of body/density of liquid
Viscosity
The frictional force that comes into play when a fluid is in motion and which opposes the relative motion between the different layers.
velocity gradient
the rate of change of velocity with distance in the direction of increasing distance
coefficient of viscosity(1 poise or 1dyne s cm^-2) (SI: poiseulle)
the tangential viscous force required to maintain a unit velocity gradient between its two parallel layers each of unit area
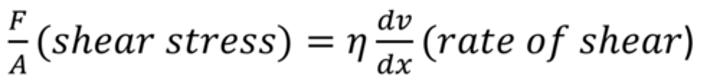
Stokes Law
When any object rises or falls through a fluid it will experience a viscous drag(F=6pi n rv)
terminal velocity
the maximum constant velocity acquired by a body while falling through a viscous medium is called a terminal velocity
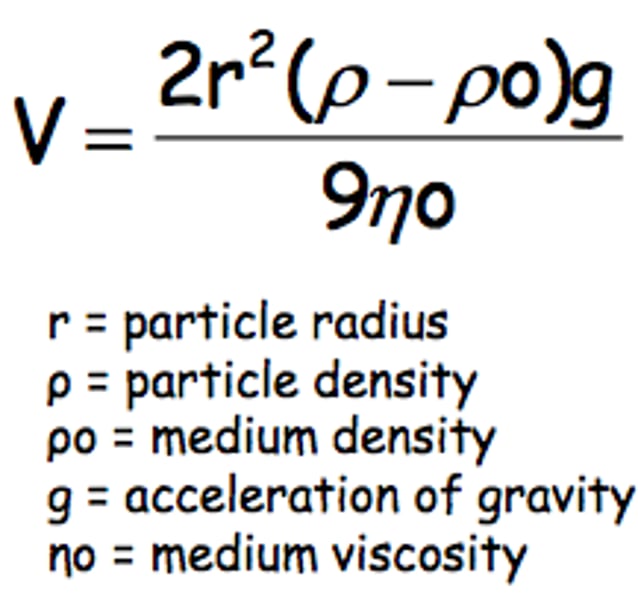
poiseulle's formula
formula
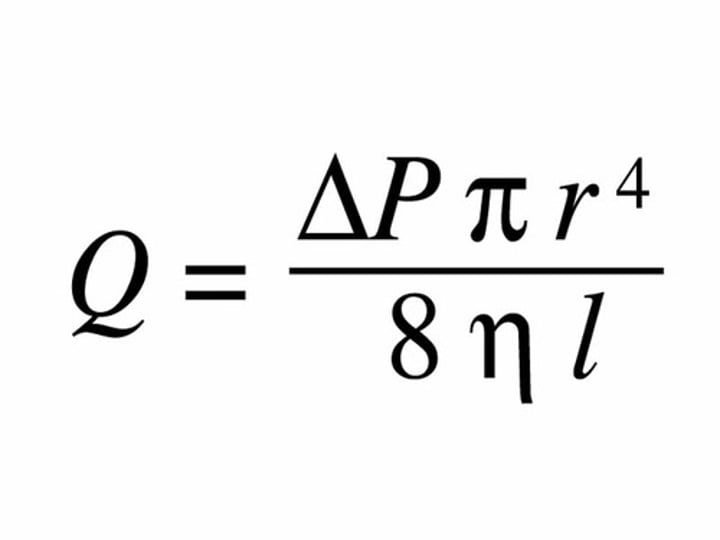
Streamline flow
When a fluid moves in such a way that each particle of the liquid passing a given point mores in the same path and with the same velocity as its predecessor.
Streamline
The path of the tangent at any point showing the direction of the flow of the liquid.
tube flow
a collection of streamlines
Turbulent flow
When the path and velocity of a liquid particle change haphazardly.
Laminar flow
a liquid that flows in the form of layers sliding past each other
Critical Velocity
the limiting value of velocity up to which the flow of liquid is laminar, above which the flow is turbulent
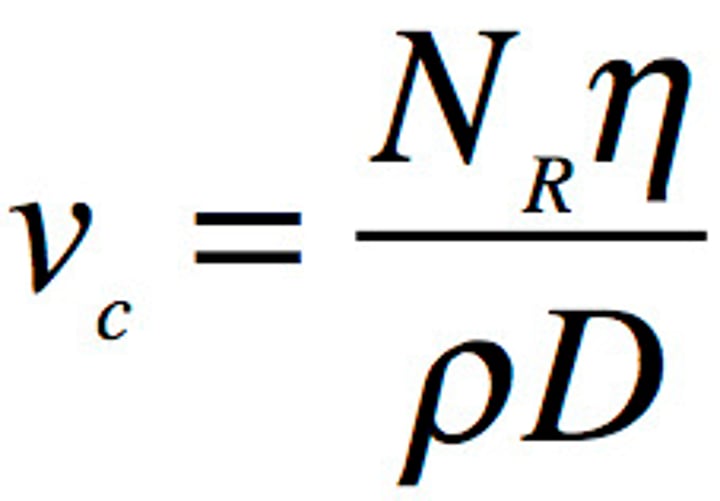
Reynold's number
R<2000 - flow is laminar, R>3000 flow is turbulent, 2000-3000 - unstable

ideal fluid
An ideal fluid is non-viscous, incompressible, and its flow is steady and irrotational.
equation of continuity
during streamline flow of an ideal fluid, the product of area of cross section and the normal fluid velocity remains constant
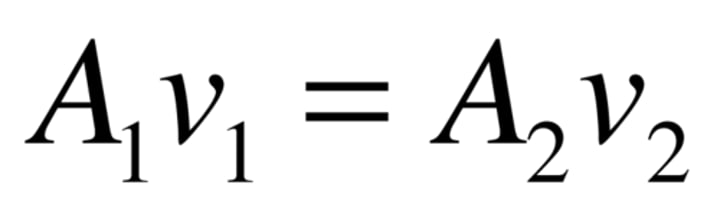
Bernoulli's Principle
Pressure energy(PV), kinetic energy and potential energy per unit volume of an ideal fluid remains constant along a streamline
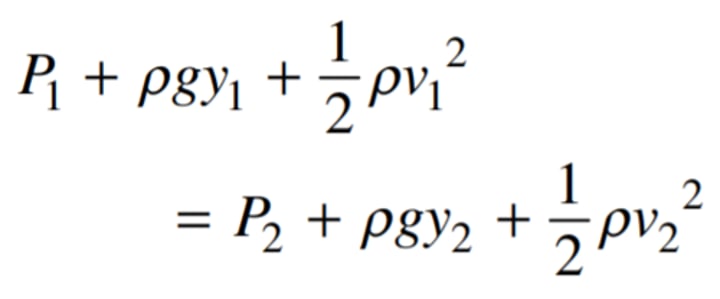
dynamic lift
the force that acts on a body by virtue of its motion through a fluid
cohesive force
force of attraction between identical molecules
adhesive force
force of attraction between molecules of different chemical identities
molecular range
maximum distance up to which a molecule can exert some force
Sphere of Influence
sphere drawn around a molecule of its molecular range
Surface tension
It is a property of which the free surface of a liquid at rest behaves like an elastic stretched membrane and tends to contract to occupy minimum surface area.
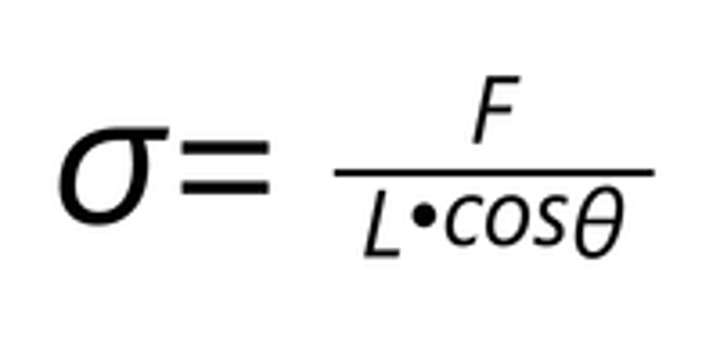
Surface energy
extra energy associated with the free surface(work done/increase in surface area)
capilarity
the phenomenon of rise of a liquid in a capillary tube in comparison to the surroundings.