unit 9, waves and sound - physics 11
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
waves and sound
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
vibration
a cyclical (or repeated) motion back and forth or around an equilibrium (or rest) position
wave
the transfer of energy in the form of vibrations from one location to another
transverse wave
a wave in which the energy of the vibrations is transferred in a direction that is perpendicular to the direction in which each molecule vibrates
ex. water waves
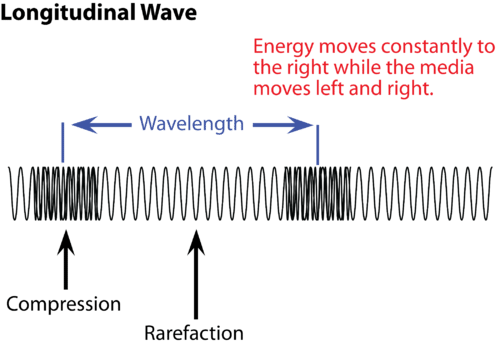
compressions
areas of high pressure in a longitudinal wave
rarefactions
areas of low pressure in a longitudinal wave
longitudinal wave
a wave in which the energy of the vibrations is transferred in a direction that is parallel to the direction in which each molecule vibrates
ex. sound waves
amplitude
max displacement from equilibrium
frequency
reciprocal of period
number of cycles completed each second
period
time required for each vibration to complete one full cycle
wavelength
distance between corresponding points on successive cycles of a wave
crest
max point of transverse wave
trough
min point of transverse wave
echolocation
the ability to determine the distance to an object by producing a sound and detecting the time required to hear its echo - can only be used to locate objects as long as, or longer than, wavelength of sound
interference
the process of generating a new wave when two or more waves meet
principle of superposition
at any point the amplitude of two interfering waves is the sum of the amplitudes of the individual waves
constructive interference
the process of forming a wave with a larger amplitude when two or more waves combine
standing wave (stationary wave)
interference pattern produced when incoming and reflected waves interfere with eachother
wave speed of a standing wave
0 because it is the difference between incoming and reflected waves
node
in a standing wave, the location where the particles of the medium are at rest
antinode
in a standing wave, the location where the particles of the medium are moving with the greatest speed
amplitude of antinode
twice the amplitude of original wave
mechanical wave
a wave that travels through a medium
sound waves
mechanical waves with frequencies that make them detectable through the ear
fundamental frequency (first harmonic)
the lowest frequency that can produce a standing wave in a given medium
when a source is moving away, observer at rest in a medium will detect
a lower frequency (+)
damping
a reduction in the amplitude of a wave as the result of energy absorption or destructive interference
resonance
the increase in amplitude when the original waves and reflected waves are in phase causing a buildup of energy in the medium
interference does not affect…
wave direction and amplitude
in order to form a standing wave pattern in a medium that is open at one end and closed at one end…
the length of the medium must be an odd multiple of a quarter wavelength
in order to form a standing wave patten in a medium that is fixed at both ends (or free at both ends)…
the length of the medium must be a multiple of a half wavelength
beats
fluctuations in the sound amplitude (ie superposition) when two sound waves are heard together. The interference alternates between constructive (loud) and destructive (quiet). This occurs when there is a small difference between the frequencies of the two sounds.
when a source is approaching, observer at rest in a medium will detect…
a higher frequency (-)