Food Microbiology - Algae
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Algae
are aquatic, photosynthetic protists that can be found in both fresh and marine waters.
70%
percentage of oxygen that algae contributes to the Earth’s atmosphere
Unicellular or multicellular
Lack of complex structures and vascular tissues
Primarily found in aquatic environments
Difference of algae from plants
Alexandrium spp.
genus of bloom-forming marine dinoflagellates; found worldwide, typically sub-polar, temperate and tropical marine water.
Alexandrium spp. cysts
are known to be spherical or ellipsoidal with rounded ends along with minor distinctions depending on the species
Alexandirum spp. swimming cells
are roughly spherical with two flagella; either individual cells or in chains characterized by its reddish-brown color
Saxitoxins
Alexandrium spp. produces this most potent type of paralytic shellfish toxins
Paralytic shellfish toxins
ingestion of this toxin causes nausea, vomiting, numbness and respiratory paralysis and death; cooking the shellfish does not eliminate the risk of this illness
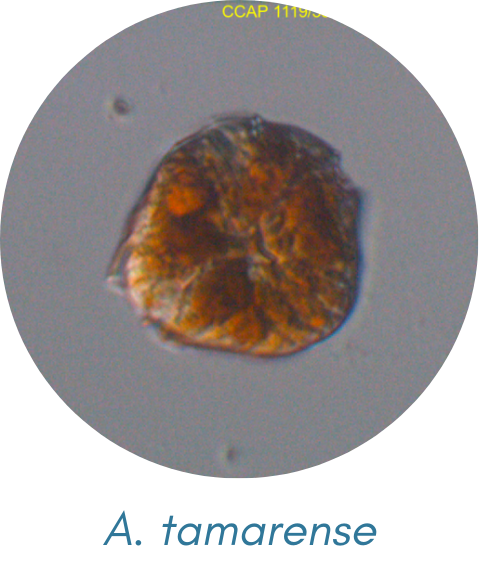

Alexandrium tamarense
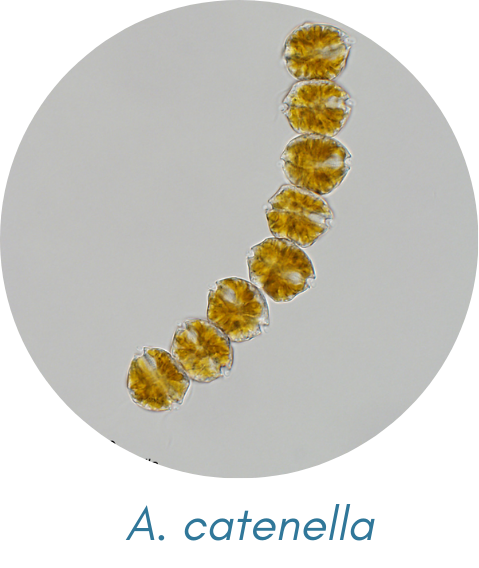

Alexandrium catanella
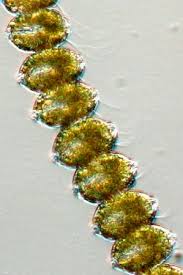
Alexandrium monilatum
Gambierdiscus toxicus
non-bloom forming dinoflagellates that are primarily found in warm, temperate environments and are observed to be epiphytes that grows along seaweeds and corals.
Gambierdiscus toxicus
Anteroposteriorly compressed ranging from 40-140 microns that contains yellow and or brown chloroplasts
Ciguatoxiuns
toxins produced by Gambierdiscus toxicus that are heat-stable neurotoxins that can cause ciguatera poisoning
Ciguatera poisoning
toxin produced by Gambierdiscus toxicus that affects the voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels
Maitotoxin
toxin produced by Gambierdiscus toxicus that are considered to be the most potent marine toxins; it affects the calcium channels of the cells
Gambierol
Polycyclic ether toxin that can contribute to ciguatera poisoning that affects the potassium channels
Ciguatera poisoning
most common non-bacterial seafood-borne illness worldwide;
Occurs through eating fish that consumed the algae ; toxins are heat stable
Ciguatera poisoning
a patient may feel these symptoms when experiencing this illness: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, pruritis, numbness, tingling sensations, low blood pressure, and paralysis
Karenia brevis
bloom-forming dinoflagellates that are known to cause red tides or HABs that are mostly found in shorelines; they do not have a specific season
Karena brevis
are known for their flattened clover leaf shape and lack of cellulose thecae layer, they are delicate and lyse easily
Brevetoxins (PbTXs)
are undetectable and preservation techniques are not applicable to remove risk of illness; they affect the polyether sodium channel neurotoxins.
Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning
symptoms of this illness includes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, paresthesia, paradoxical temperature sensations, and bradycardia
Pyrodinium bahamense
bloom-forming dinoflagellates that causes red tides; they are mainly found in warm, tropical and temperate waters; caused the first recorded red tide in the Philippines
1983; Samar and Leyte
The first red tide was recorded in this year and location
Pyrodinium bahamese
Polyhedral and irregularly spherical; Has a thecae layer; Either present as individual cells or in chains
Paralytic shellfish poisoning
illness caused by Pyrodinium bahamense due to their production og saxitoxins
Pyrodinium bahamense
Leading cause of PSP fatalities in various countries such as the Philippines and Mexico
Gymnodium catenatum
bloom-forming dinoflagellates that contributes to the occurence of red tides worldwide ; they have received much attention after causing a massive bloom which spanned across 200km of the shoreline of Mexico in April 1979
Gymnodinium catenatum
Cells are found to be spherical to squarish in shape; Often seen in long chains of 32 to 64 cells; Lacks a thecae layer
saxitoxins, ganyautoxins and hydrobenzoyl toxins
toxins of Gymnodium catenatum that are known as paralytic shellfish toxins
Dinophysis spp.
planktonic dinoflagellates that are the major origin of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning
Okadaic acids
lipid soluble toxins that causes diarrhetic shellfish poisoning this can be produced by Dinophysis spp.
0.2g
shellfish containing more than this amount of DSP toxins are considered unfit for consumption
Singapore and Philippines
muscles with DSP above human safety levels are confirmed in these countries
Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning
the symptoms of this illness includes gastrointestinal effects such as severe diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain
Pseudo-nitzschia spp.
are widely distributed pennate diatoms that have diverse temperature ranges, they can also occupy various habitats from open oceans to coastal waters.
Pseudo-nitzschia spp.
blooms are triggered by increased nutrients, high light levels adn warm seawater temperatures
US West Coast
occurence of toxigenic Pseudo-nitzschia spp. are greatest in this area
Vietnam, Korea, Japan, China and Russia
Areas where Pseudo-nitzschia spp. are recorded but with no poisoning recorded
Pseudo-nitzschia spp.
are green, phothosynthetic cells with bilaterl symmetry; frustules they create long chains that glide through the waters as a unit; have quiscent phase
frustules
Pseudo-nitzschia spp. have this silica walls called…
domoic acid
are potent neurotoxins that are produced by Pseudo-nitzschia spp. which accumulate in marine organisms such as shellfish, finfish and zooplankton ; this impacts nervous system of human and wildlife consumers
Amnesic shellfish poisoning
causes short term memory loss, gastrointestinal distress and neurological symptoms caused by the consumption of domoic acids produced by Pseudo-nitzschia spp.
Caulerpa spp.
belongs to a chlorophyta group, some spp. can be nontoxic and edible; they can growin rocks, sands, muds, and undergoes rapid proliferation
Caulerpa lentillifera and Caulerpa racemosa
are edible species of Caulerpa
Caulerpa toxifolia
are known to be killer alga
Caulerpa prolifera
is a toxic spp. of Caulerpa.
1984, Mediterranean
is the year Caulerpa taxifolia was first documented in this area as invasive.
Caulerpa spp.
Single cell thallus that is multinucleated; coenocytic morphology and consists of a creeping rhizome with rhizoids and photosynthetic branches.
Caulerpenyne
has shown antitumoral properties but is neurotoxic, affecting human cells like melanocytes, keratinocytes and fibroblasts at higher concentrations; it disrupts the calcium storage of cells that impacts DNA synthesis.
Caulerpicin
causes numbness and cold sensations in mouth fingers and toes
Caulerpa racemosa
are Caulerpa spp. that are able to produce Caulerpicin
Ciguatera poisoning
caused by consumption of Caulerpa-eating fish like Sarpa salpa (Mediterranean sea bream)
Acanthaphora specifera
is a species of red algae that is part of the Rodomelaceae family; they are widely distributed in Guam, Houtman, Abrolhos, and Hawaii
beta carotene, antheranxathin and carrageenan
Acanthophora specifera is a good source of this
2002 and 2003
years when Acathaphora specifera caused an outbreak in the Philippines that led to 33 deaths
Polycarvenoside A
a glycosidic toxin, it can cause infection via direct human consumption of contaminated seaweed or seafood contaminated with it.
Polycarvenoside
contains aglycone and polyene side chain that can cause epithelial damage and nutrient absorption impairment
Gracilaria verrucosa
belongs to Rhodophyta and Gracilariaceae family; it can grow in muddy/sandy bottoms, eulitoral and sublittoral zones, and forms large beds in calm coastal waters.
Asia, South America, Africa
Gracilaria verrucosa are cultivated in these continents
Gracilaria verrucosa
cylindricla thallys, and bushy branched appearance, elevated cystocarps with colors ranging from purplish brown to dark brown red.
Prostanoids
lipids contained by Gracilaria verrucosa that can cause nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, hypotension and bleeding that are rapid onset in humans
Ingestion
MOT of Gracilaria verrucosa
G. verrucosa and G. chorda
lead to deaths in Japan in years 1980, 1982, and 1993