Lec 2 (What are stem cells?)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are stem cells?
Undifferentiated cells
Capable of differentiating into a number of other cell types
Self-renewing properties; but many bone and nerve cells are NOT replaced!
What are the self-renewing properties of stem cells?
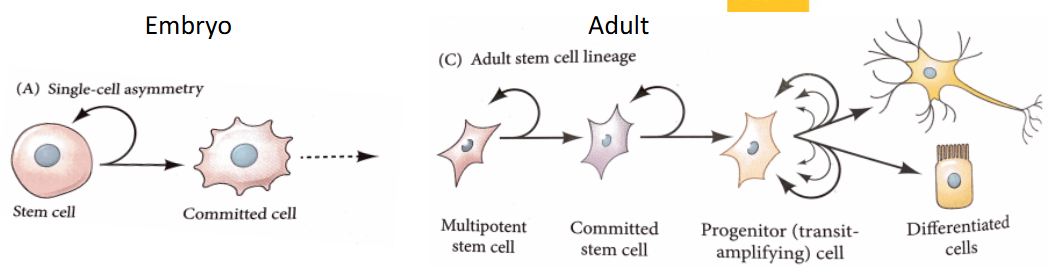
Mitosis through asymmetrical division
Daughter remains a stem cell (keeps replicating)
What type of cell is made from single-cell asymmetry of stem cells?
Committed cell
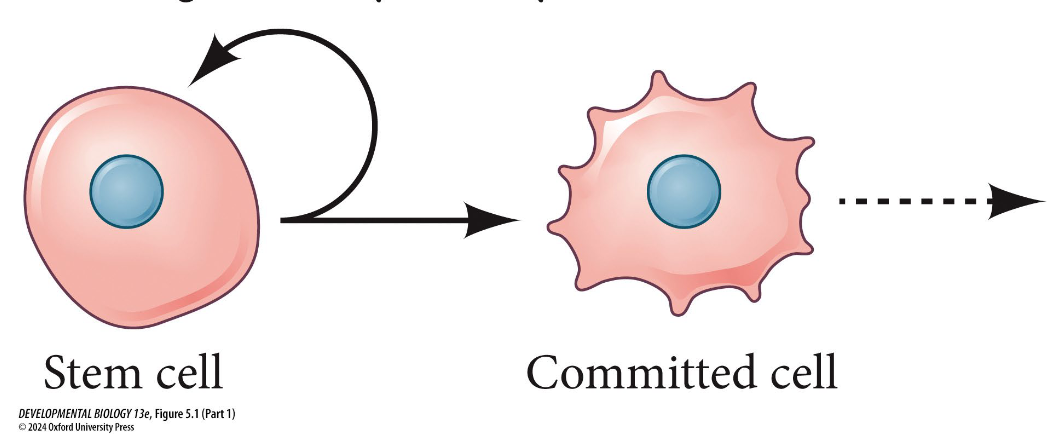
What are committed stem cells?
does not mean it is differentiated but it will be differentiating
What 2 cell types are made from single cell asymmetry?
another stem cell and a cell committed to differentiation
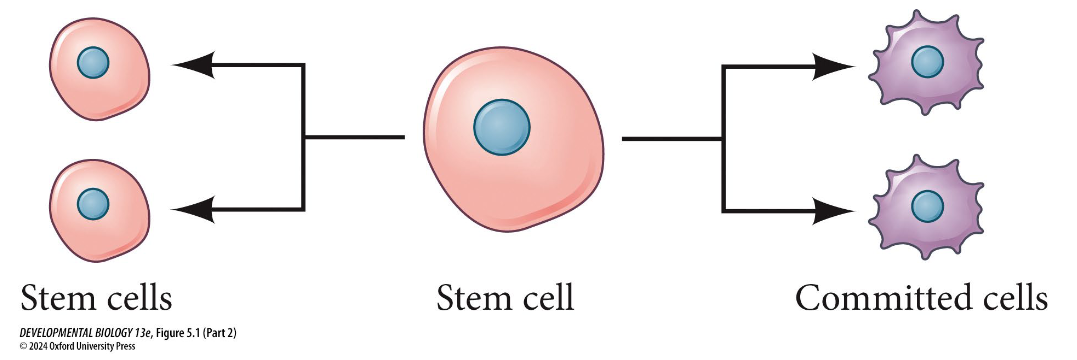
Symmetrical cell division results in either:
2 stem cells
2 committed cells
What are Totipotent stem cells?
able to give rise to all embryonic and adult lineages (Ex. Zygote)
Source: Zygote
What are Pluripotent stem cells?
able to give rise to all cell types in an adult (Ex. Embryonic stem cells)
Source: Blastocyst
What are Multipotent stem cells?
able to give rise to multiple cells within a lineage (Ex. Neuronal stem cells)
Source: Embryo or adult
What are Unipotent stem cells?
capable to give rise to single cell within lineage (Ex. Spermatozoa, epidermal stem cells)
Source: Adult
What type of stem cells line our intestine?
Unipotent
old cells shed into gut lumen to maintain gut health
Cells from basal layer are unipotent stem cells
What are blood forming stem cells called?
Hematopoietic
formed in human bone marrow
produce more HSCs
daughter cells capable to come a range of other cell types
What is BrdU?
thymidine analogue
actively dividing cells incorporate BrdU
What 4 features can be seen with in situ hybridization (ISH)?
spatial resolution of gene expression
temporal resolution of gene expression
genetic interactions of genes, gene relationships in specific diseases, genes as tissue markers
activity of specific alleles
What method can be used to visualize gene expression patterns in cells and tissues?
In situ hybridization (ISH)
What is ISH?
a technique that allows for precise localization of a specific segment of nucleic acid within a histologic section
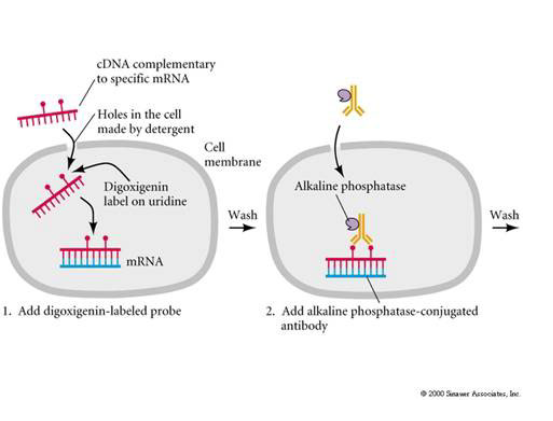
What is the 4 steps for ISH?
Probe: Synthesized RNA with antisense sequence of target - DIG
Target - mRNA
Antibody - detects DIG, is conjugated with AP
Colour reaction