ap human GEOGRAPHY 💜
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
cloropleth map
uses color shadings
isoline map
uses lines
cartogram
size of countries or regions is according to data
mercator
accurate direction
peters
land mass size accuracy
robinson
most used
small scale analysis
lots of land
large scale analysis
little land, detail
remote sensing
collection through satellite
possibilism
cultures respond to environment differently
functional region
centered around an activity
etm stage 3
cancer and heart disease
etm stage 4
alzheimer’s and dementia
etm stage 5
disease resistance
neolocalism
reembracing culture of a place
pidgin language
simplified mix of two language
isoglosses
variation in usage or pronunciation
dialect
regional variation of a language
acculturation
adopting new culture while retaining original
nation
cultural group of people
state
political group
devolution
regions given increased autonomy by central unit
antecedent boundary
physical landscape
subsequent boundary
based on cultural landscape and changes over time
superimposed boundary
outside influence draws boundary
consequent boundary
takes culture into account
defined boundary
established by a legal document
demarcated boundary
physical objects on landscape
definitional dispute
argue over how to interested docs or map used to define boundary (often antecedent)
locational dispute
where a boundary should be
operational or functional
who control or how boundary functions
territorial zone
12 miles for commercial vessels, no commercial may be challenged
contiguous zone
24 miles to enforce laws customs and immigration
EEZ
200 miles to extract resources
high seas
open to any behind EEZ
cracking
breaking majority to minority
packing
bring minority to majority
stacking
diluting minority pop with majority
hijacking
electoral candidates of same party run against
kidnapping
moving rep to area with support to area without support
irredentism
unite people with common culture spread across states
intensive agriculture
multiple energy inputs for higher yields
extensive agriculture
fewer inputs leasing to lower yield
pastoral nomadism
relying on animals for survival
shifting cultivation
grow crop until soil is infertile and move to another field
mixed crop and livestock
crops grown for animals
milk shed
distance dairy can travel
transhumanance
high elevations in summer to low elevations in winter
double cropping
harvesting same crop on same field multiple times a year
inter or multi cropping
two or more crops on same field
economy of scale
increasing efficiency to decrease costs with increases profit
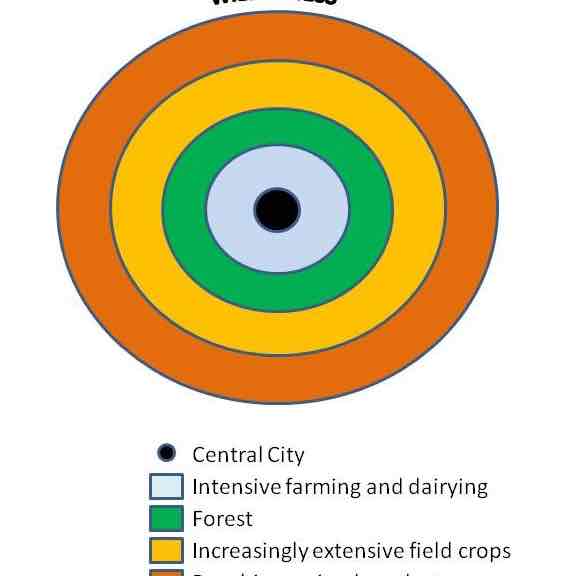
von thunen model
1- horticulture (dairy and gardening)
2- forest (wood)
3- grains (wheat and corn)
4- livestock
close to market - land is more expensive
subsidies
financial support to farmers
borcherts model
divided transportation by time period
streetcar suburbs
communities along rail lines
edge city
economic activity in periphery of city
megacity
10 million people
metacity
20 million people
megalopolis
chain of connected cities
nodal cities
cities with power on smaller scale
rank size rule
1/n size
primate city
twice size of second largest city
gravity model
larger places attract more people
central place theory
people go to places for goods and services
threshold
size required to support a service
range
furtherest people travel for a thing
CBD
commercial heart of city
concentric model
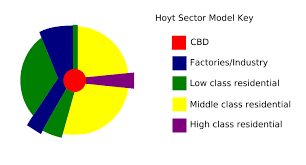
hoyt sector
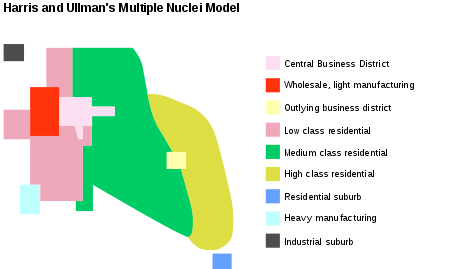
multiple nuclei model
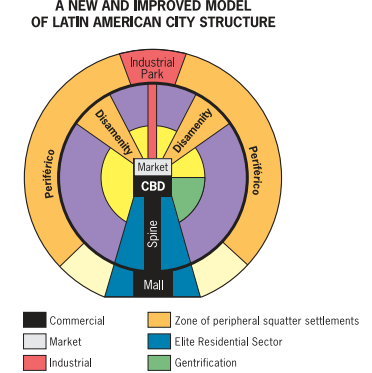
griffin ford model
periférico- impoverished areas
disamenity zones- crime areas (favelas and barrios)
african cities
traditional CBD with formal economy
colonial CBD
periphery with informal and squatter settlements
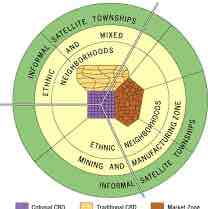
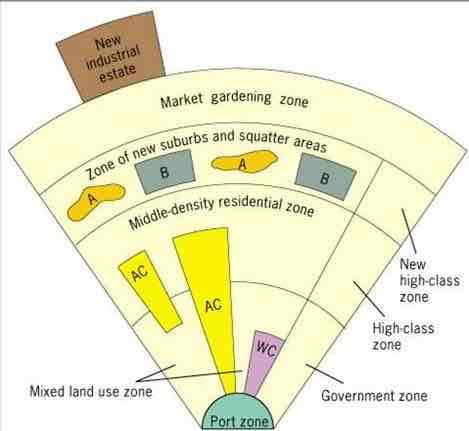
mcgee model
southeast asian cities
former colonial ports
smart growth policy
establish walkable cities with a strong community
green belts
undeveloped land to limit growth
redlining
banks refusing loans to minorities
inclusionary zoning
incentives for business owners to sit property aside for low income renters
urban redevelopment
removing landscape and rebuilding
tertiary sector
info and services for people
quaternary sector
manage and process into and data
quinary sector
create info and make high level decisions
least cost theory
explains where people locate factories
agglomeration
grouping businesses together to minimize costs
PPP
compares cost of goods in different countries
GNI/GNP
money produced by citizens
GDP
money produced on country’s soil
GINI
measures wealth inequality
NGOs
provide microcredit to help women start business
rostow stages
development of countries in a linear way
IMF
aid countries needed financial assistance
technopole
info based and high tech manufacturing jobs (growth pole)
spin and spread effects lead to positive economy outside pole
backwash (brain drain)