MICR5842 L21: Principles of Infection and Immunity: mRNA Vaccines
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The information flow in cells begins with DNA, which can be replicated or transcribed to RNA, and then translated into proteins.
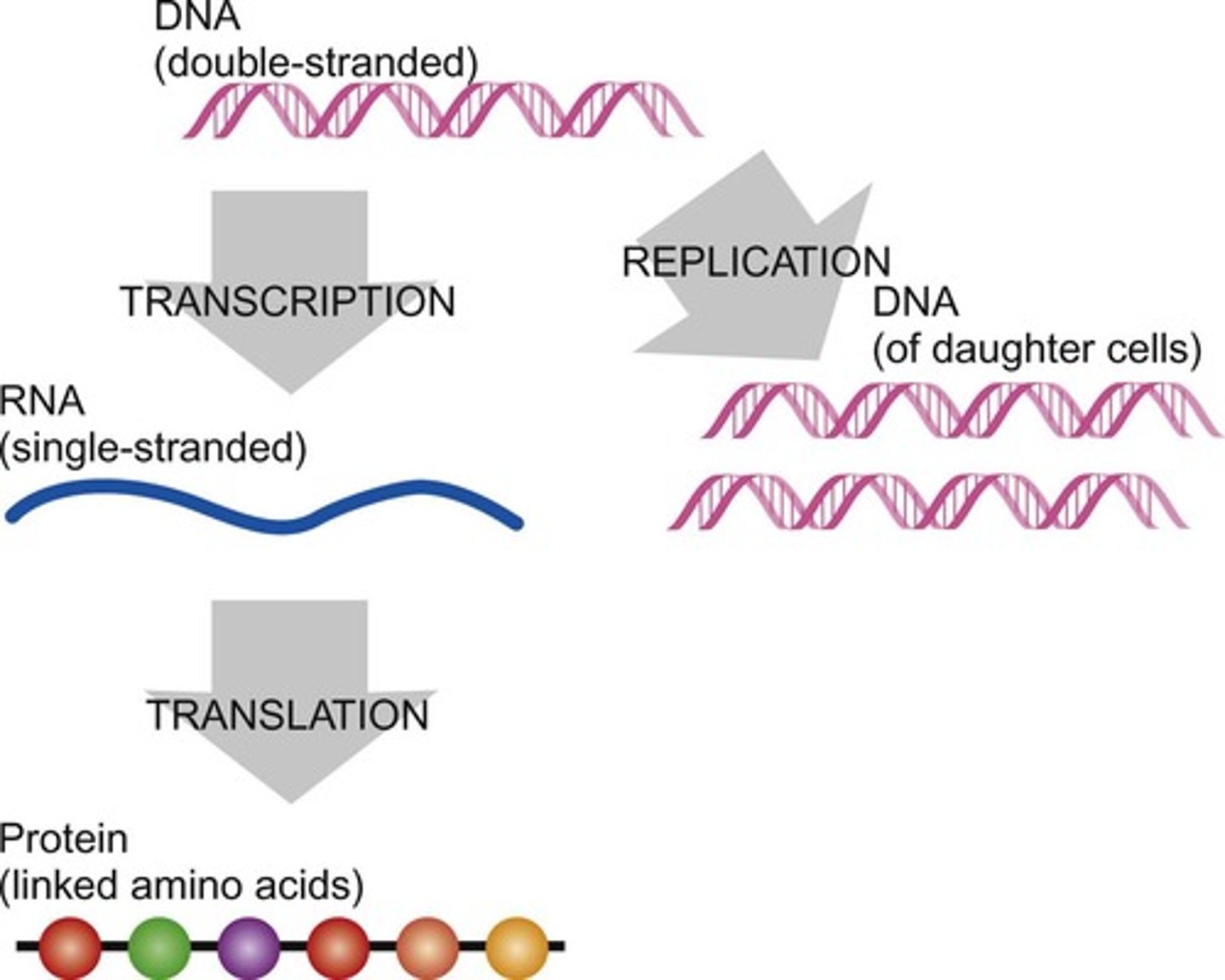
What is mRNA?
mRNA, or messenger RNA, is a temporary working copy of genes used during cell growth and metabolism, carrying information from the genome to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes read the mRNA message and recruit the proper tRNA to synthesize a new polypeptide chain.
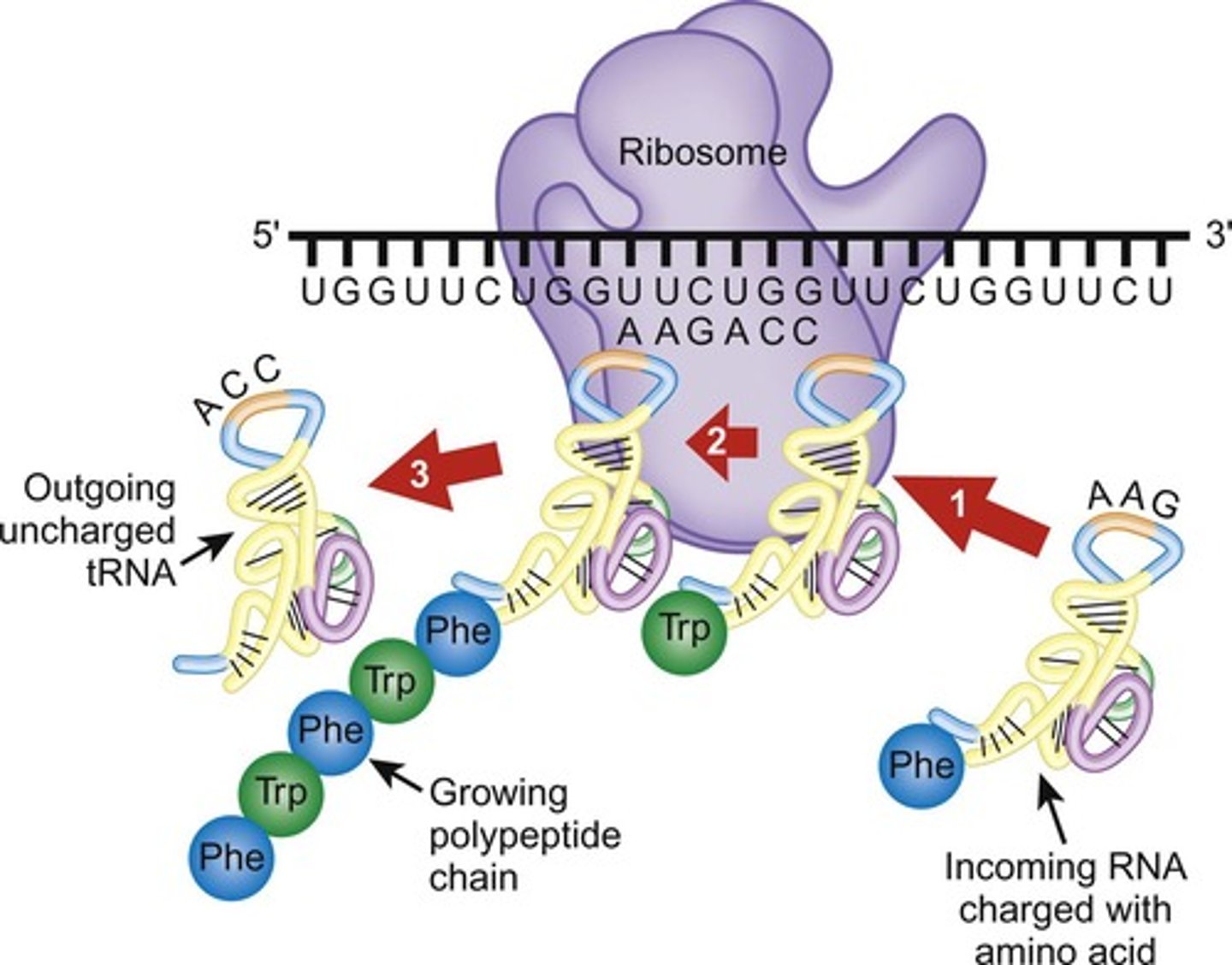
What are the major classes of RNA?
In addition to mRNA, there are several classes of RNA that perform various roles, including non-coding RNA.
Why were mRNA-based therapies and vaccines initially avoided?
mRNA therapies were avoided due to instability, short half-life, and inefficiencies in delivery and antigen expression.
What advantages do mRNA-based therapies and vaccines offer?
mRNA therapies have transient activity, do not integrate into the human genome, are free of infectious pathogens, and can be rapidly designed and manufactured.
What is the significance of the 5′ cap and 3′ poly(A) tail in mRNA?
The 5′ cap and 3′ poly(A) tail are critical protective features that help stabilize mRNA and prevent degradation.
What challenges are associated with mRNA vaccines regarding immune response?
mRNA vaccines may require multiple booster injections to establish effective long-lasting immune protection.
What is the role of reverse transcriptase in molecular biology?
Reverse transcriptase allows for the flow of information from RNA back to DNA under certain circumstances.
What are some safety advantages of mRNA vaccines compared to DNA therapeutics?
mRNA vaccines do not integrate into the human genome, reducing potential risks associated with genetic alteration.
What is the impact of RNA-destroying enzymes on mRNA?
mRNA is highly sensitive to RNA-destroying enzymes, which can lead to its degradation in the extracellular environment.
What are the implications of mRNA's intrinsic thermal instability?
mRNA's thermal instability requires low-temperature storage to maintain its integrity.
What is the significance of the studies by Dolgin E. and Pardi N. regarding mRNA vaccines?
These studies provide insights into the history, advances, challenges, and opportunities of mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases.
How does mRNA contribute to the development of COVID-19 vaccines?
mRNA vaccines provide protection against severe illness, decrease hospitalization, and reduce mortality due to COVID-19.
What are the potential side effects of mRNA vaccines?
mRNA vaccines may lead to undesirable protein translation, unexpected side effects, or hypersensitivity reactions.
What is the role of translation in the context of mRNA?
Translation is the process by which ribosomes synthesize proteins using the genetic information carried by mRNA.
What are the challenges of in vivo delivery of mRNA?
Inefficient in vivo delivery is a significant challenge for the effective use of mRNA therapies and vaccines.
What does the term 'transient activity' refer to in mRNA therapies?
Transient activity refers to the temporary nature of mRNA's effects in the body, as it is naturally degraded over time.
What is the significance of the cell-free in vitro transcription technique for mRNA production?
This technique allows for rapid, scalable, and cost-effective manufacturing of mRNA with high yields.
What are the learning outcomes expected from the lecture on mRNA vaccines?
Students should be able to describe mRNA principles, key discoveries in mRNA biology, the use of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19, and future directions for mRNA therapies.
What is the role of the Australian Immunisation Handbook in relation to mRNA vaccines?
The Australian Immunisation Handbook provides guidelines and information regarding the use of vaccines, including mRNA vaccines.
What historical discoveries contributed to the development of mRNA vaccines?
Key discoveries in mRNA biology and its therapeutic applications laid the groundwork for the development of mRNA vaccines.
What was the significant conclusion made by researchers regarding ribosomal RNA and mRNA?
Stable ribosomal RNA does not include protein-encoding information; instead, mRNA is the transitory RNA molecule that translates the genetic code.
Who were the key researchers involved in the discovery of mRNA?
Boivin, Jeener, Al Hershey, Volkin, Astrachan, Brenner, Crick, Jacob, Monod, Meselson, Watson, Nirenberg, and Matthaei.
What role do ribosomes play in relation to mRNA?
Ribosomes create proteins based on the instructions provided by mRNA.
What was Sydney Brenner awarded the Nobel Prize for in 2002?
For discoveries concerning genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death.
What did Sydney Brenner, François Jacob, and Matthew Meselson demonstrate?
They published their demonstration of the existence of messenger RNA.
What discovery allowed for the synthesis of long RNA transcripts from a DNA source?
The discovery of RNA polymerases from bacteriophages.
Which RNA polymerases are widely used for synthesizing large quantities of RNAs?
DNA-dependent phage T7, T3, and SP6 RNA polymerases.
What is required for the functional synthesis of mRNA in vitro?
In vitro transcription of the DNA template utilizing bacteriophage RNA polymerase, along with nucleoside triphosphates (NTPs), RNase inhibitor, pyrophosphatase, and buffer.
Why is encapsulation of mRNA in lipids important?
mRNA has a short half-life in vivo and is sensitive to RNA-destroying enzymes abundant in the extracellular environment.
What landmark experiment did Robert Malone conduct in 1987?
He mixed strands of messenger RNA with droplets of fat, using liposomes to deliver mRNA into human cells and frog embryos.
What did Robert Malone propose regarding mRNA as a drug?
He suggested that if cells could create proteins from delivered mRNA, it might be possible to treat RNA as a drug.
What did Malone, Felgner, and Verma demonstrate regarding mRNA delivery?
They demonstrated that exogenous mRNA coding for luciferase could be delivered into a cell line using liposomes, resulting in enzyme expression.
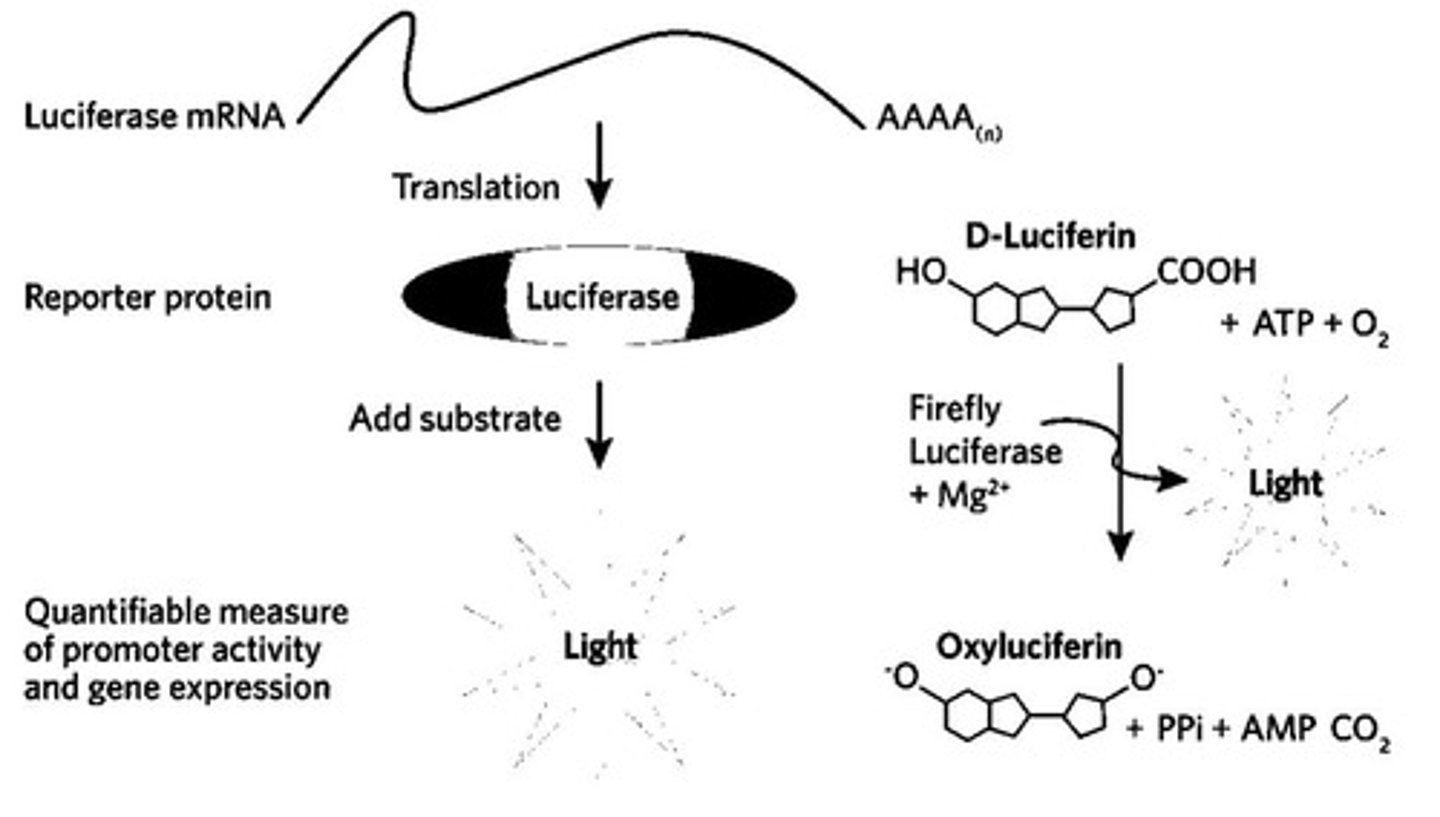
What was the significance of the 1990 experiment by Wolff and colleagues?
They demonstrated that intramuscular injection of 'naked' nucleic acids (DNA and mRNA) into mice induced protein expression in muscle cells.
What was the outcome of injecting RNA and DNA expression vectors into mouse skeletal muscle?
Protein expression was readily detected, and no special delivery system was required.
How long did luciferase activity persist after injection of the DNA luciferase expression vector?
Luciferase activity was present in the muscle for at least 2 months.
What are lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) used for?
Lipid nanoparticles are used for nucleic acid delivery.
What are the four main structural components of a prototypical lipid nanoparticle formulation?
A cationic or ionizable lipid, cholesterol, a helper lipid, and a PEGylated lipid.
What was the significance of the telegram from Jim Watson to Sydney Brenner in 1961?
Watson requested Brenner to delay publication of his article on mRNA until the Watson group's paper was ready.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in the synthesis of mRNA?
RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA from a DNA template during in vitro transcription.
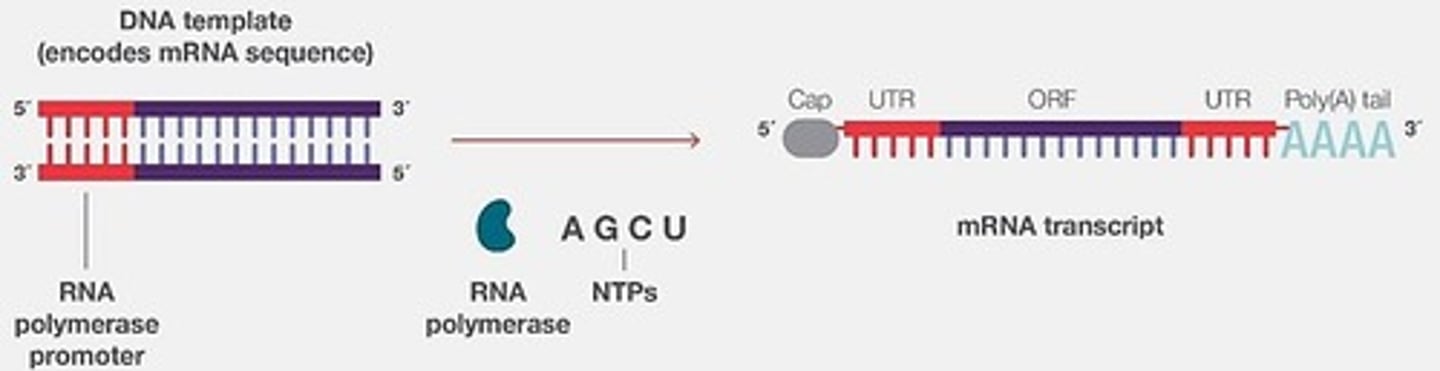
What was the main finding of the 1984 in vitro transcription experiment?
It demonstrated the successful synthesis of functional synthetic mRNA using bacteriophage RNA polymerase.
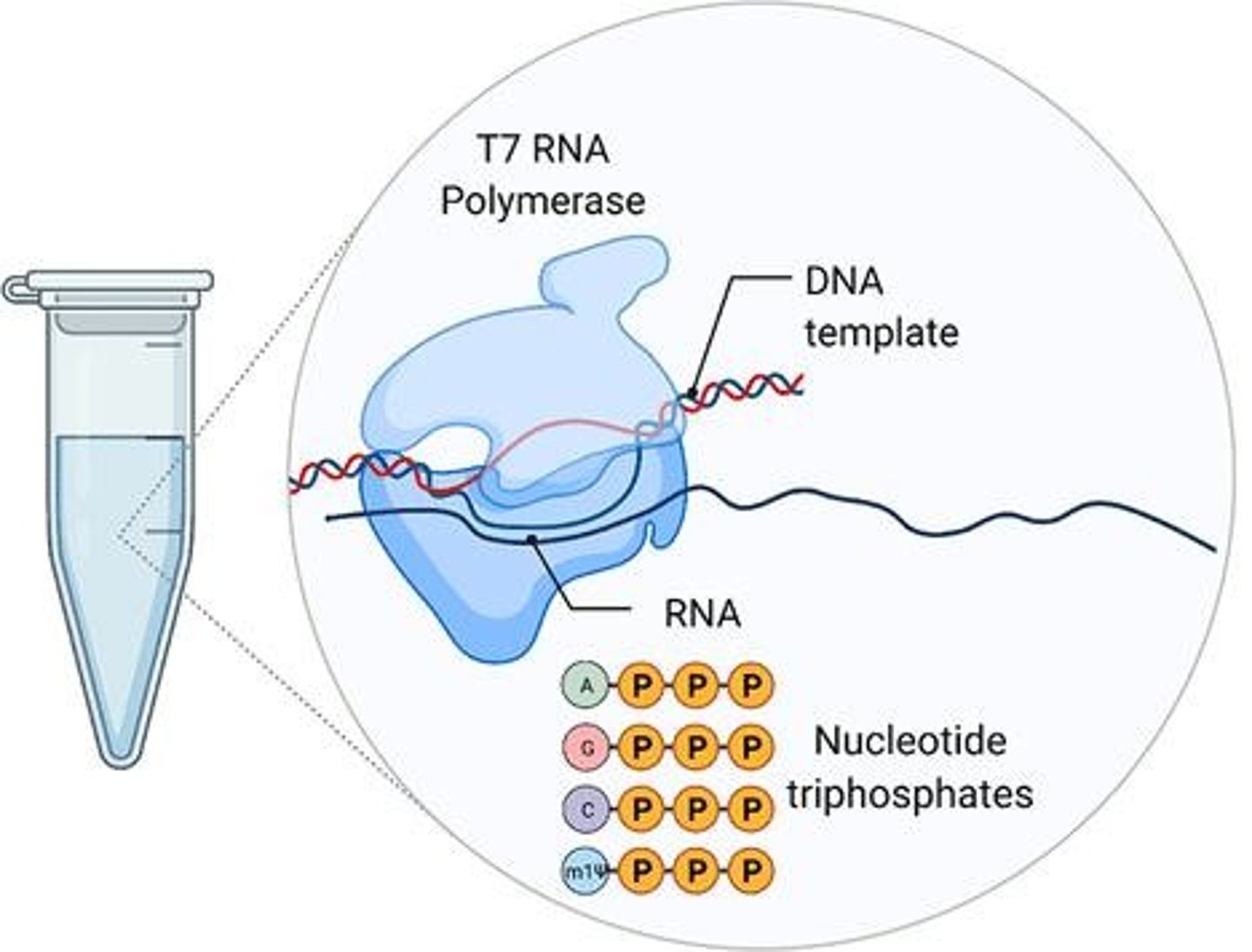
What does the term 'exogenous mRNA' refer to?
mRNA that is introduced into a cell from an external source.
What was the primary focus of Sydney Brenner's research?
Genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death.
Who laid the groundwork for lipid-based drug delivery systems?
Pieter Cullis, Professor at the University of British Columbia.
What are lipid nanoparticles (LPNs)?
Spherical vesicles made of ionizable lipids.
How do lipids in LPNs behave at different pH levels?
They are positively charged at low pH (enabling RNA complexation) and neutral at physiological pH (reducing potential toxic effects).
What components are included in lipid nanoparticles to enhance their function?
A helper lipid for cell binding, cholesterol to fill gaps, and polyethylene glycol (PEG) to reduce opsonization by serum proteins.
How are lipid nanoparticles taken up by cells?
They are taken up via endocytosis and sequestered in the endosome.
What happens to lipid nanoparticles after they are taken up by cells?
They fuse with the endosomal membrane, releasing mRNA into the cytosol.
What is the role of pseudouridine-modified mRNA?
It helps synthetic mRNA slip past the cell's innate immune defenses.
What happens to unmodified mRNA when it enters a cell?
It can be recognized by cell receptors, leading to inflammation and rapid degradation.
What key discovery did Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman make?
Altering part of the mRNA code helps synthetic mRNA to evade the cell's innate immune defenses.
What is the significance of chemically modified nucleotides in mRNA?
They enhance stability, transfection capability, and decrease immunogenicity.
What was the motivation for the Nobel Prize awarded to Karikó and Weissman in 2023?
For their discoveries concerning nucleoside base modifications that enabled the development of effective mRNA vaccines against COVID-19.
What are the canonical nucleobases found in RNA?
Adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U).
What are some mRNA-based gene editing tools developed between 2008 and 2013?
Zinc-finger nucleases, transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN), and CRISPR-Cas9.
What modifications are used to optimize mRNA production?
N1-methylpseudouridine, 5′ capping, and codon optimization.
What structural components are found in in vitro transcribed mRNA?
A 5' cap, a 5'-untranslated region (UTR), a 3'-UTR, an open reading frame (ORF), and a 3'-poly(A) tail.
What immune responses are activated by mRNA vaccines?
Cellular and humoral immunity.
What are the three phases of mRNA vaccine production?
Upstream mRNA manufacturing, downstream mRNA purification, and formulation of mRNA lipid nanoparticles.
What is the lifecycle of SARS-related coronaviruses like SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2?
It begins with the binding of the envelope Spike protein to its receptor, followed by the release of the RNA genome into the cytosol for translation into proteins.
What is the role of ribosomes in the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle?
They translate the RNA genome into proteins and produce copies of its genetic material.
What is the main function of lipid nanoparticles in mRNA delivery?
To encapsulate and deliver mRNA into cells effectively.
What is the significance of the 5' cap and poly(A) tail in mRNA?
They are crucial for mRNA stability and translation efficiency.
What occurs during virion assembly in SARS-CoV-2?
Subsequent RNA genomes are incorporated into newly synthesized virions, which are secreted from the plasma membrane.
What are the categories of SARS-CoV-2 variants?
Variants of interest, concern, or of high consequence based on mutations affecting transmissibility, disease severity, neutralisation by antibodies, effectiveness of treatments or vaccines, and diagnostic detection failures.
What is significant about the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2?
It is the most mutated variant so far, containing more than 60 mutations in its genome, including 37 mutations in the spike protein.
How were mRNA COVID-19 vaccines developed so quickly?
Through seminal research in mRNA technology, priority and collaboration, funding, large-scale manufacturing, and volunteers for clinical trials.
What type of vaccine is BNT162b2 (Comirnaty) by Pfizer/BioNTech?
An mRNA-based vaccine targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen.
What type of vaccine is mRNA-1273 (Moderna COVID-19 Vaccine)?
An mRNA-based vaccine targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen.
What is the vaccine type of AZD1222 (Covishield and Vaxzevria) by Oxford/AstraZeneca?
A recombinant adenovirus vaccine using the ChAdOx1 vector.
What is the efficacy of RNA vaccines encoding the spike protein?
They have a 95% efficacy.
What is the efficacy range of vaccines using a viral vector, such as a non-replicating adenovirus?
62-90% efficacy.
What type of vaccine is Ad26.COV2.S (COVID-19 Vaccine Janssen) by Johnson & Johnson?
A recombinant adenovirus vaccine using the rAd5 vector.
What type of vaccine is Ad5-nCoV (Convidicea) by CanSino Biologics?
A recombinant protein vaccine/VPL.
What is the type of the SARS-CoV-2 rS (NVX-CoV2373) vaccine by Novavax?
A recombinant protein vaccine/VPL.
What type of vaccine is CoronaVac by Sinovac?
An inactivated vaccine.
What type of vaccine is BBIBP-CorV by Sinopharm?
An inactivated vaccine.
What type of vaccine is BBV152 (Covaxin) by Bharat Biotec?
An inactivated vaccine.
What is the effective date for the provisional registration of NUVAXOVID (NVX-CoV2373) in Australia?
26 July 2022.
What is the type of vaccine for SPIKEVAX (elasomeran) by Moderna?
An mRNA vaccine.
What type of vaccine is VAXZEVRIA (previously COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca)?
A viral vector vaccine using a chimpanzee adenovirus.
What is the vaccine type for COMIRNATY (tozinameran) by Pfizer Australia?
An mRNA vaccine.
What is the significance of the spike protein in COVID-19 vaccines?
It is the target for mRNA vaccines and is crucial for eliciting an immune response.
What are the two main types of vaccines mentioned in the notes?
mRNA vaccines and recombinant adenovirus vaccines.
What is the role of volunteers in the rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines?
They participated in clinical trials to test vaccine safety and efficacy.
What is the age range for individuals receiving the booster dose of Comirnaty COVID-19 vaccine?
Individuals aged 12-15 years old.
What are the two types of Comirnaty COVID-19 vaccines mentioned?
Comirnaty Original/Omicron BA.1 and Comirnaty Original/Omicron BA.4-5.
What type of vaccines are COMIRNATY and SPIKEVAX?
They are mRNA vaccines.
What is the composition of the mRNA vaccines mentioned?
Lipid nanoparticle-formulated, 5 nucleoside-modified RNA (modRNA) encoding for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
What is the purpose of bivalent vaccines?
To protect against both the original strain and Omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5.
What does COMIRNATY® Omicron XBB.1.5 encode?
The viral spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 (Omicron XBB.1.5).
What is the dosage of the COMIRNATY® Omicron XBB.1.5 vaccine?
Each 0.3 mL dose contains 30 µg mRNA encoding the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.5 spike glycoprotein.
What are some components of the COMIRNATY® vaccine?
ALC-0315, ALC-0159, DSPC, cholesterol, trometamol, trometamol hydrochloride, sucrose, and water for injections.
What is myocarditis?
An inflammatory disease of the heart muscle that can be caused by infectious and non-infectious conditions.
What is the relationship between COVID-19 vaccines and myocarditis?
There is a link, particularly in males under 40 years of age, mostly after the second dose.
What is the reported incidence of myocarditis after receiving Comirnaty and Spikevax vaccines?
Myocarditis was reported in around 1-2 in every 100,000 for Comirnaty and around 2 in every 100,000 for Spikevax.
How does the risk of myocarditis from COVID-19 infection compare to vaccination?
Myocarditis risk is higher after COVID-19 infection compared to vaccination.
What should be considered when evaluating the risk of myocarditis from COVID-19 vaccines?
The benefits of vaccination in protecting against severe COVID-19.