1. Introduction + Alginate/Gypsum
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
what is the proper workflow in fixed pros?
diagnosis + tx planning
tooth prep
provisional crown fabrication
final impression / bite registration
form working + opposing casts
die trimming, mount casts, lab Rx
try in, insert final restoration, excess cement removal
homecare + regular recare
what are the 4 branches of prosthodontics?
fixed → tooth or implant supported
removable → tooth/implant/mucosa/combination
implant
maxillofacial prosthetics
what is the branch of Prosthodontics concerned with the replacement and/or restoration of teeth by artificial substitutes that cannot be removed by the patient?
fixed prosthodontics
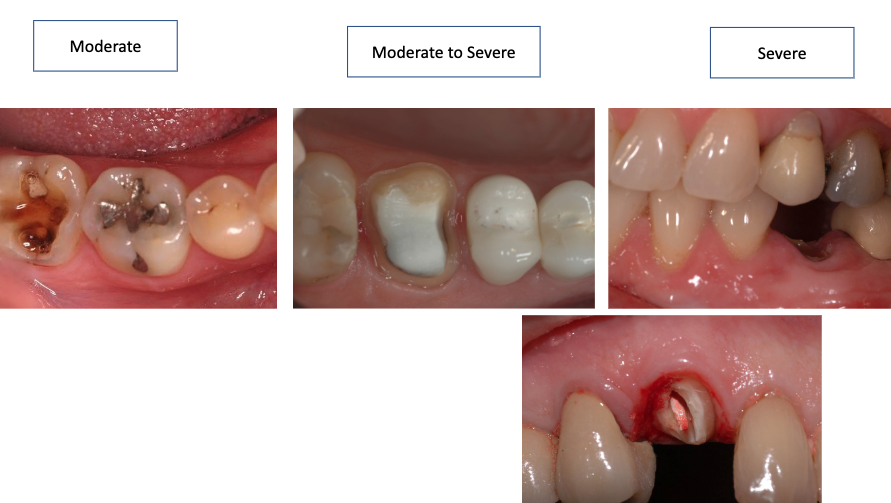
what are some indications of fixed pros?
loss of part of tooth structure
cracked tooth syndrome
missing tooth (1-3)
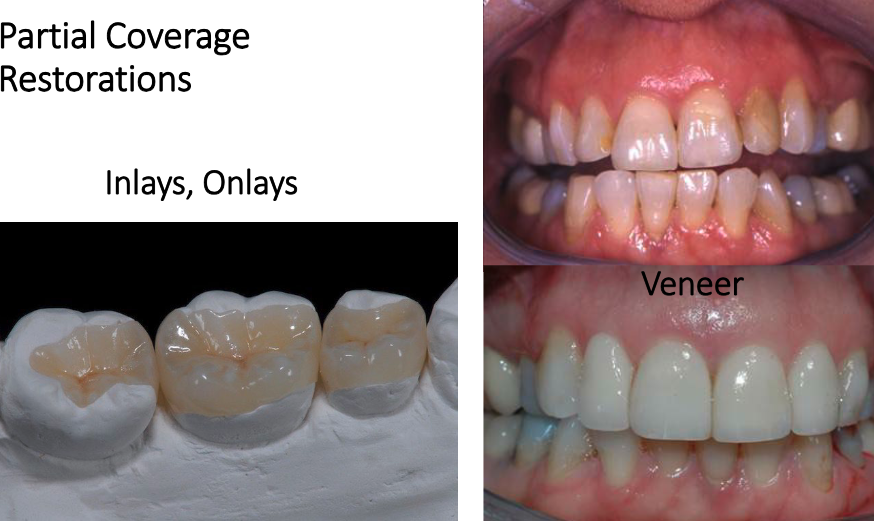
what are examples of partial coverage restorations?
inlays
onlays
veneers
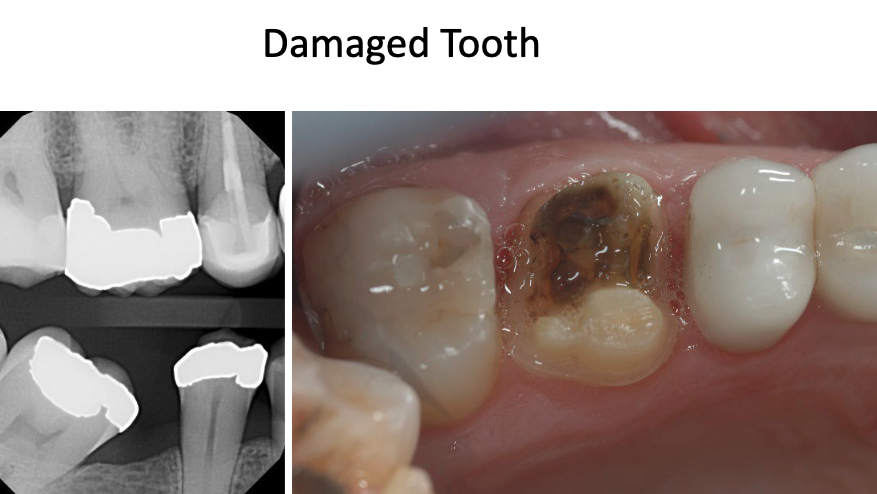
what restoration would we do on this MOD fractured tooth?
single crown (full coverage)
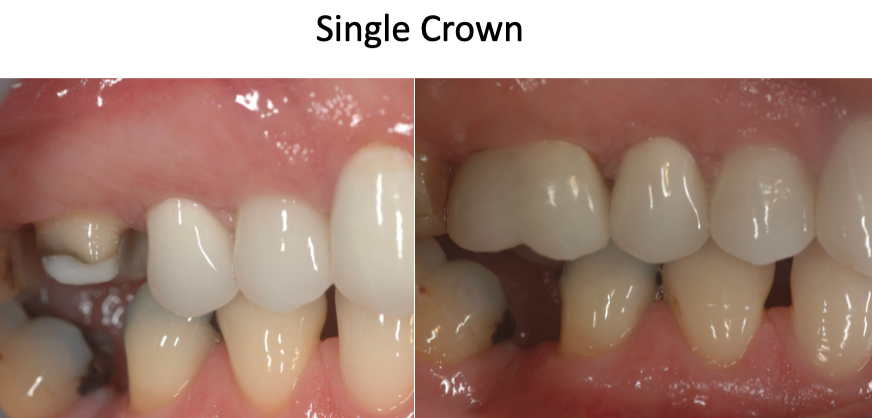
what are some examples of fixed dental prostheses (FDP)?
single crown
partial coverage (inlay, onlay, veneer)
resin bonded FPD
3-unit FPD
foundation restoration (post/core)
surveyed crown
what does retainer indicate?
on abutment tooth
what does pontic indicate?
replacement tooth
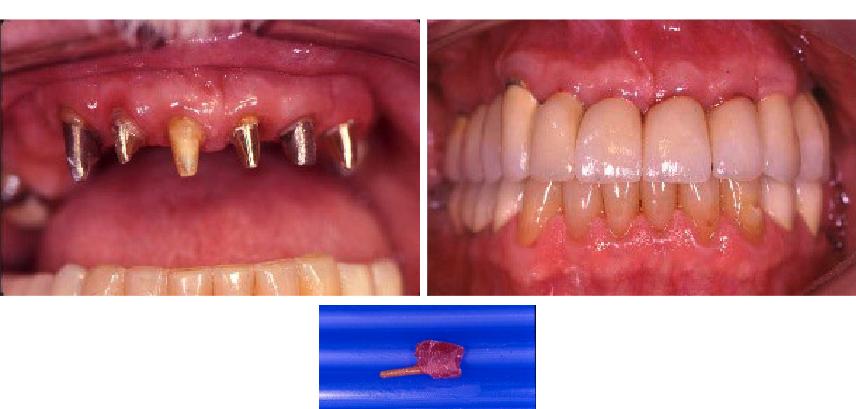
post/core (foundation restoration)
Incidence of complication for single restoration:
All ceramic crown %
Post/Core %
Conventional single crowns %
All ceramic crown 8%
Post/Core 10%
Conventional single crowns 11%
Incidence of complication for FPD:
Conventional FPD %
Resin Bonded FPD %
Conventional FPD 27%
Resin Bonded FPD 26%
what are the most common complications for all ceramic crowns?
Fracture 7%
Need for Endodontic Tx 3%
Loss of Retention 2%
what are the most common complications for post/core?
Post Loosening 5%
Root Fracture 3%
Caries 2 %
what are the most common complications for single crowns?
Need for Endodontic Tx 3% (IMPORTANT)
Porcelain Veneer Fracture 3%
Loss of Retention 2%
what are the most common complications for FPD?
Caries on abutment 18% (IMPORTANT)
Need for Endodontic Tx 11%
Loss of Retention 7%
what are the most common complications for resin bonded FPD?
Debonding 23% (IMPORTANT)
Tooth Discoloration 18%
Caries 7%
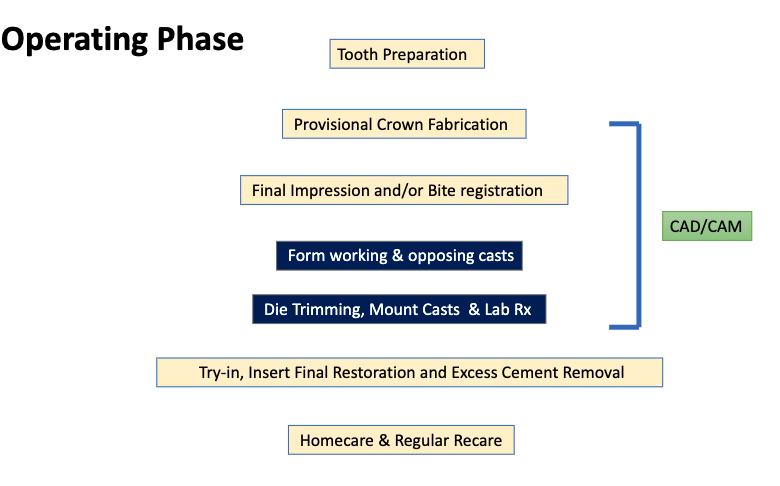
what is the proper workflow for single crown treatments?
diagnosis & treatment plan
actual treatment
prepatory phase
operating phase
post-operative, maintenance and recare
why are mounted diagnostic casts on an articulator important?
complement tool in addition to clinical exam
legal proof of pt’s current occlusion
can modify occlusal pre-treatment plan prior to establishing definitive Tx plan
can evaluate occlusion in centric and eccentric positions
determine inter arch distance, relationship between teeth and alvolar ridge, + make alterations w/o presence of pt
the analog/traditional model base of the preparatory phase will eventually be replaced by…?
CAD/CAM
what are the analog/traditional model base steps of the prepatory phase?
preliminary impressions to fabricate diagnostic casts
mount study casts on articulator for 3D analysis
diagnostic wax up on defective/missing tooth
clear template (for temp crown/bridge)
putty matrix (guide for tooth reduction)
what steps of the operating phase will eventually be replaced by CAD/CAM in the future?
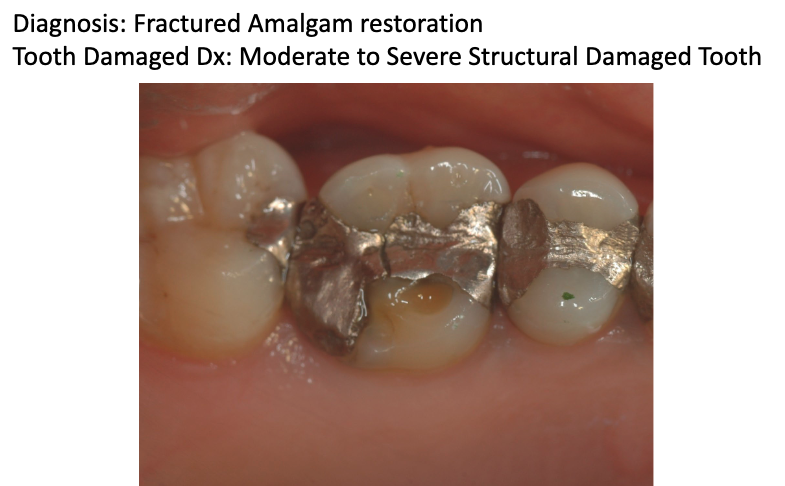
what treatment should be done for this tooth?
indirect restoration like crown
what proper infection control guidelines should be followed for any impressions taken in an operatory?
Rinse impression using cold running water to remove blood and debris
Rub impression using Cavi Wipe
Wrap it with Cavi-Wipe and place in plastic bag
what proper infection control guidelines should be followed for any impressions taken in a laboratory?
Place impression on a paper towel
Spray with Cavicide in 4th Fl Lab and leave it for 3 mins
Rinse impression using cold running water
Pour impression with Type III or IV/V dental stone
what is used to register and reproduce the form and relationship of teeth and oral tissues?
impression materials
what are the materials most commonly used to make impressions?
Hydrocolloids and synthetic elastomeric polymers
t/f: The impression will create a negative reproduction of the tissues, and by filling the impression with dental stone or other model material, a positive cast can be made
true
what anatomical landmarks must be picked up on a maxillary impression?
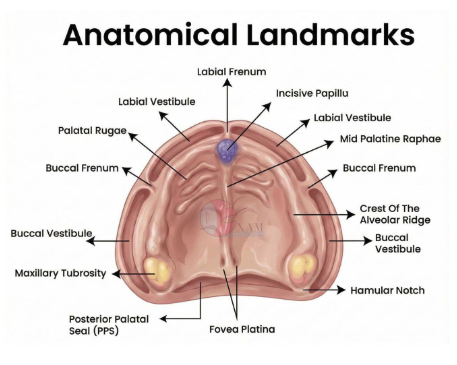
what anatomical landmarks must be picked up on a mandibular impression?
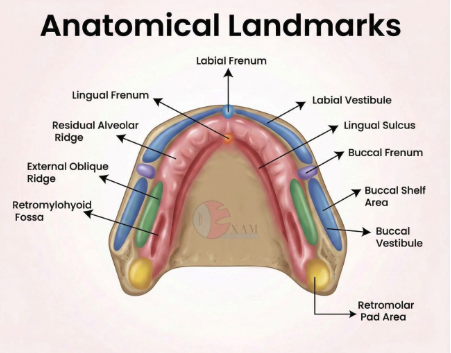
Casts of the mouth are used to evaluate the what important relationships/information?
relative alignment between maxillary and mandibular arches
occlusal relationship
fabrication of restoration and prostheses
The impression material is usually carried to the mouth by means of a _____
tray (plastic or metal; pre-fabricated or individual)
what are desireable qualities to look for when selecting an impression material?
Pleasant odor, taste, and color
Absence of toxic or irritant constituents Adequate shelf life
Economic
Easy to use
Good setting characteristics
Satisfactory consistency and texture
Readily wets oral tissues
Resistance to permanent distortion
Adequate strength
Dimensional stability over temperature and humidity normally found in clinical and laboratory setting
Compatibility with cast and die materials
Accuracy in clinical use
Readily disinfected without loss of accuracy
No release of gas during the setting of the impression or cast and die materials
what are the most widely used impression material in dentistry?
Alginates
Alginate impression products have acceptable elastic properties to form study casts for treatment planning, monitor changes, and fabricate fixed and removable prostheses
what are advantages of alginate hydrocolloids?
Inexpensive
Easy manipulation
Pleasant taste
Able to displace blood and body fluids
Hydrophilic
Easily poured
Can be used with stock trays
Accurate if handled properly
what are disadvantages of alginate hydrocolloids?
Low tear resistance
Must be poured immediately
Limited detail reproduction
Dimensionally unstable (syneresis vs imbibition)
Can only be used for single casts
Incompatible with epoxy resin die materials
t/f; alginate hydrocolloid impressions can be used for multiple casts
false (Can only be used for single casts)
alginate hydrocolloids are supplied as powders containing what substances? (mainly?)
Sodium or Potassium alginate (12 to 15%) → main
Calcium sulfate dehydrate (8 to 12%)
Sodium phosphate (2%)
Reinforcing filler (~70%)
Potassium sulfate or alkali zinc fluorides (~10%)
Coloring and flavoring agents
what 2 main reactions occur with alginate hydrocolloids?
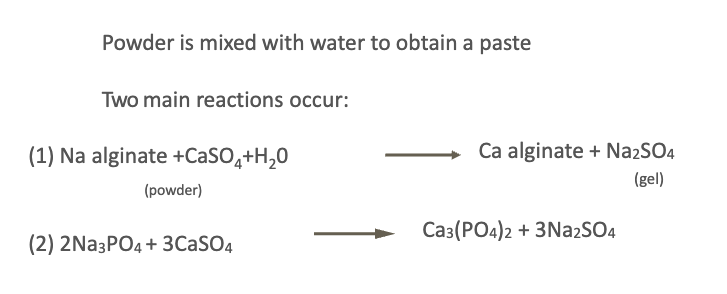
t/f: alginate hydrocolloids powder should be lightly shaken for aeration.
true
what is the correct water to powder ratio for alginate hydrocolloids?
1:1

should water or powder be added to the mixing bowl first?
always add water to mixing bowl first

how long is mixing time for regular setting alginate hydrocolloids? fast setting?
regular → 1 minute
fast set → 45 seconds
how long is setting time for alginate hydrocolloids?
3.5 minutes after mixxing
1. increase in strength
2. increase in tear strength
3.“better” consistency
4. decrease in working time
5. decrease in setting time
6. decreased flexibility
If we want the above characteristics, would we want a lower or higher W/P ratio?
lower
1. decrease in strength
2. decrease in tear strength
3. runny consistency
4. increase in working time
5. increase in setting time
6. increased flexibility
If we want the above characteristics, would we want a lower or higher W/P ratio?
higher
how does temperature of water affect working/setting times of alginate hydrocolloids?
Colder water will increase the working and setting times
Hot water will decrease working/setting times
*we should aim to use room temperature
t/f: Insufficient mixing results in a grainy mix and poor recording of details
true
Storage in either air (aka _____) or water (aka _______) results in significant dimensional change
syneresis; imbibition
If needed, impression can be stored in 100% humidity for how long prior to pouring?
30 minutes
Disinfection can be accomplished by immersion in …?
sodium hypochlorite or iodophors
what is loss of water due to dehydration that causes shrinkage?
syneresis
what is tendency to absorb water that results in swelling?
imbibition
what are some common mistakes that lead to inadequate working/setting time?
temperature of water is off (ideal should be 65-75 F)
incomplete spatulation
incorrect W/P ratio
improper storage of alginate powder (high humidity/open container)
what are some common mistakes that lead to distortion?
movement of tray during setting
premature removal
improper storage after removal
length of time between impresison making and pouring
delayed cast separation
what are some common mistakes that lead to tearing?
premature removal from the mouth
speed of impression removal
incorrect water-powder ratio
undercuts
not enough material
consistency of impression material is related to what 3 factors?
W/P ratio
water temperature
spatulation
Porosity can be related to incorrect _____
spatulation
Gypsum products generally refer to the various forms of …?
calcium sulfate (hydrous and anhydrous)
gypsum products are manufactured by the calcination of …?
calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO 4 . 2H 2 0)
t/f: Gypsum products can also be obtained by calcining “synthetic” or “chemical” gypsum, a by-product of the manufacture of phosphoric acid
true
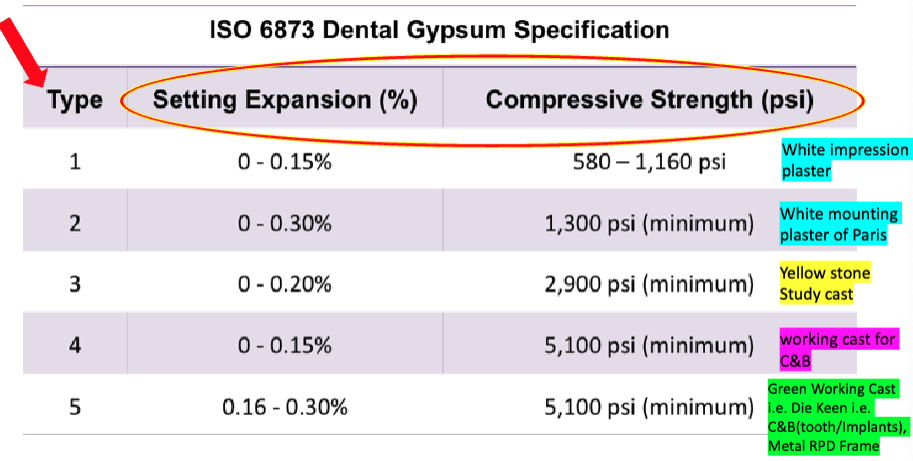
how does the ISO classify gypsum products? (what are the 5 types?)
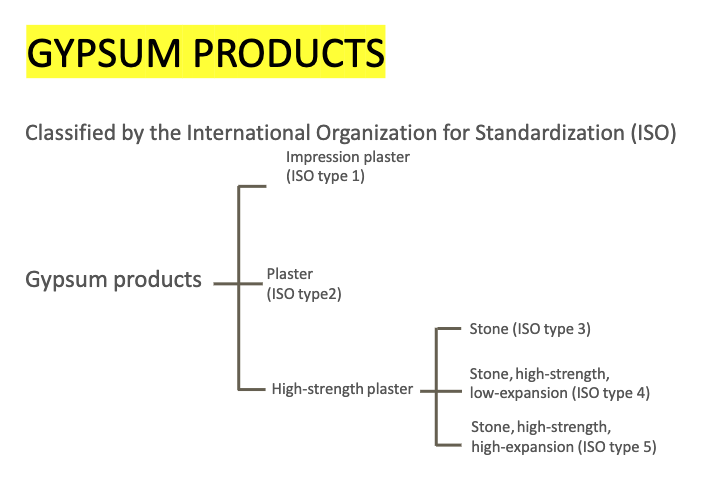
gypsum product: ISO type 1?
impression plaster
gypsum product: ISO type 2?
plaster
gypsum product: ISO type 3?
stone (high-strength plaster)
gypsum product: ISO type 4?
stone, high strength, low expansion (high-strength plaster)
gypsum product: ISO type 5?
stone, high strengthm, high expansion (high strength plaster)
ISO type 1
setting expansion:
compressive strength:
name:
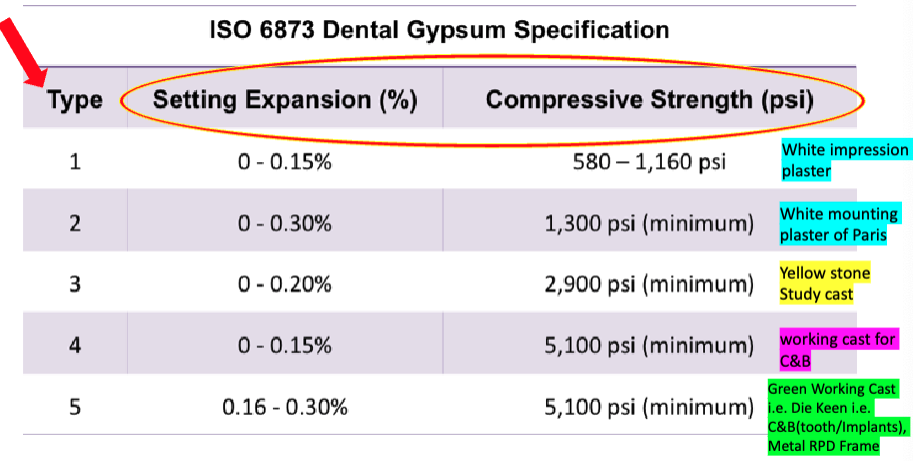
ISO type 2
setting expansion:
compressive strength:
name:
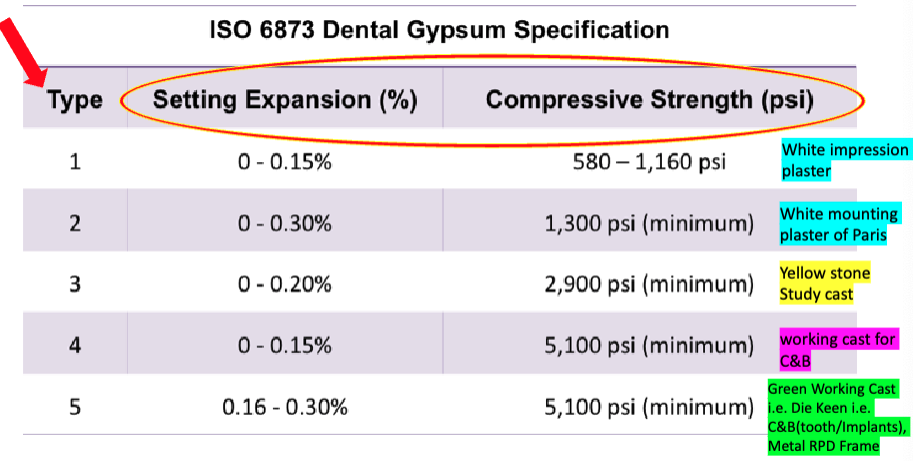
ISO type 3
setting expansion:
compressive strength:
name:
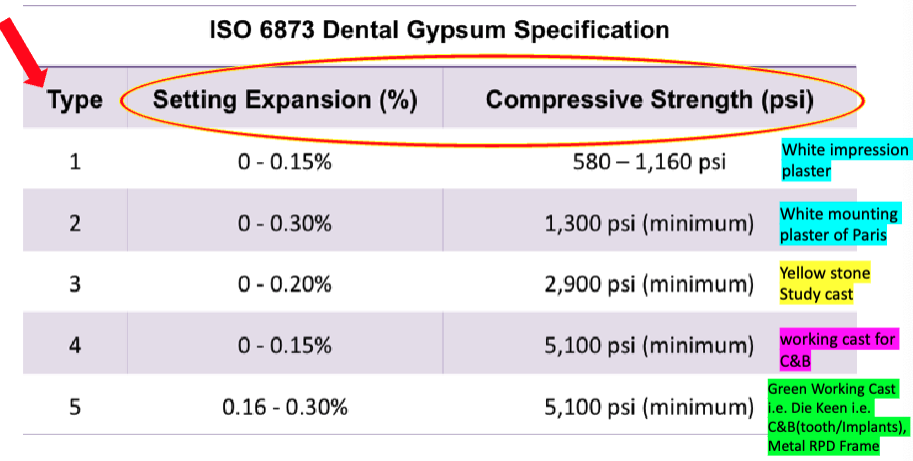
ISO type 4
setting expansion:
compressive strength:
name:
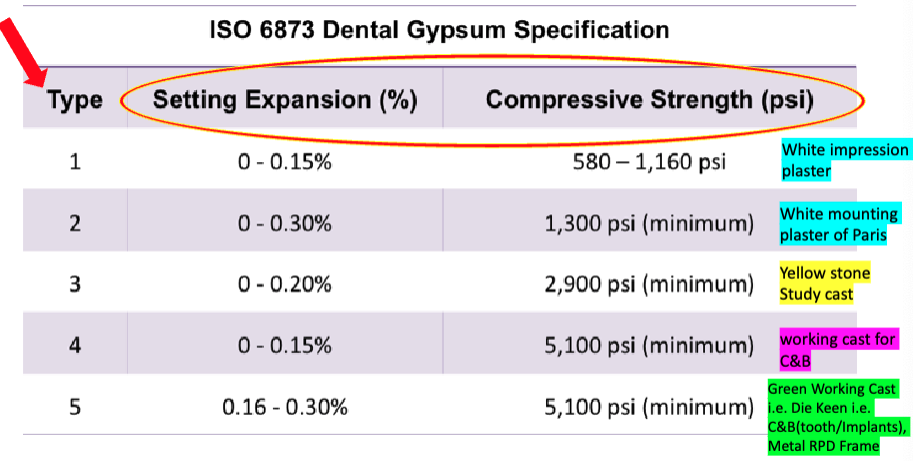
ISO type 5
setting expansion:
compressive strength:
name:
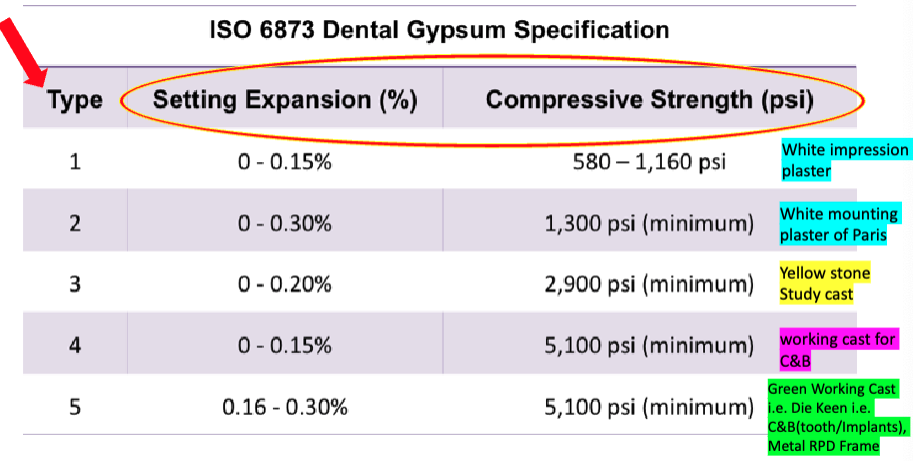
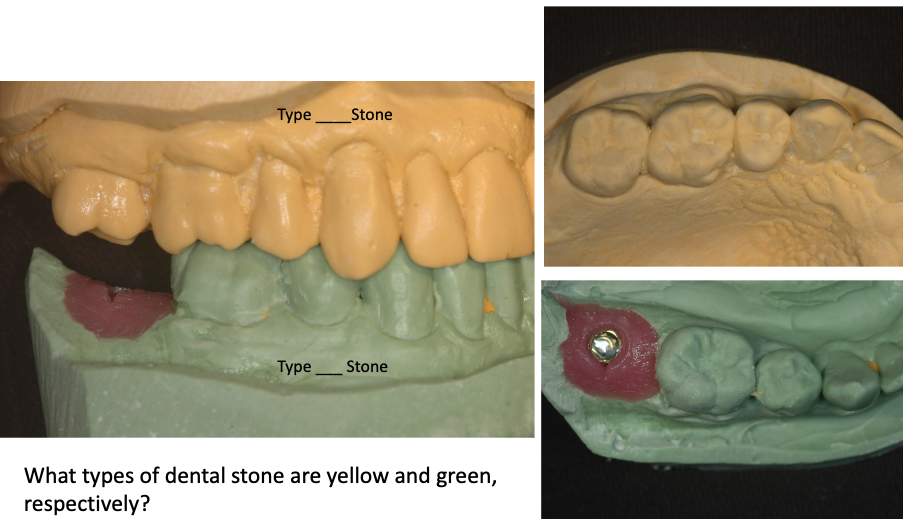
yellow = type 3 (yellow stone, study cast)
green = type 5
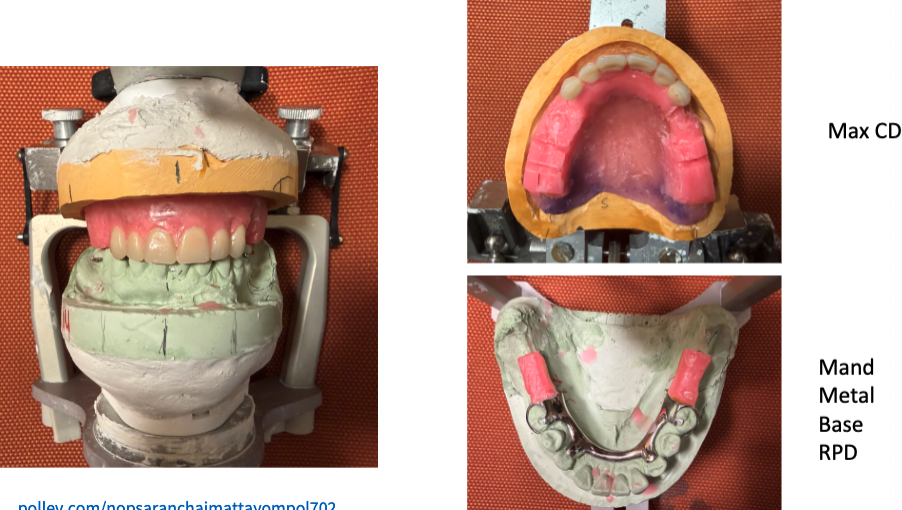

did the student use the proper type of dental stones?
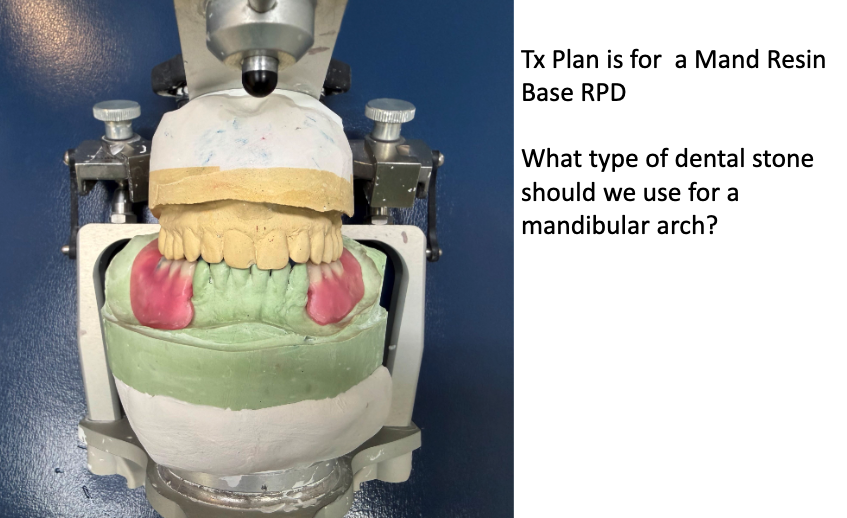
wrong stone was used. yellow stone shouldve been used to compensate for shrinkage of resin base
did the student use the proper type of dental stones?
no. yellow stone shouldve been used on mandibular (not sure about maxillary)
Type __ allows expansion to compensate for acrylic shrinkage
3
Type 4 or 5 provides limited expansion. Therefore, these stones are good for prostheses that require high precision such as …?
crown and bridge or Fixed Dental prostheses including dental implant restorations, and metal base RPD Framework
Both plaster and stone are products of …?
partial dehydration of gypsum
Traditional hemihydrate plaster is produced by what process?
dry calcination
Medium- and high- strength plasters (stones) are manufactured by ______(what process)___ to have a stronger set mass (sometimes refer to Alpha Hemihydrate)
wet calcination
describe the setting process of plaster/stone
hemihydrate + water mixed in proper proportions form thick slurry (2-phase suspension of hemihydrate particles in saturated aqueous solution)
setting reaction is reverse of first stage of dehydration (exothermic)
______ is defined as a saturated calcium sulfate solution made by placing stone debris in a container of water.
Slurry water
When using slurry water instead of regular tap water, it will…?
- decrease setting time or shorten setting time
- decrease compressive strength (not good)
- increase dimensional change (not good)
what are the 4 stages of plaster setting designated as?
fluid
plastic
friable
carvable
plaster/stone
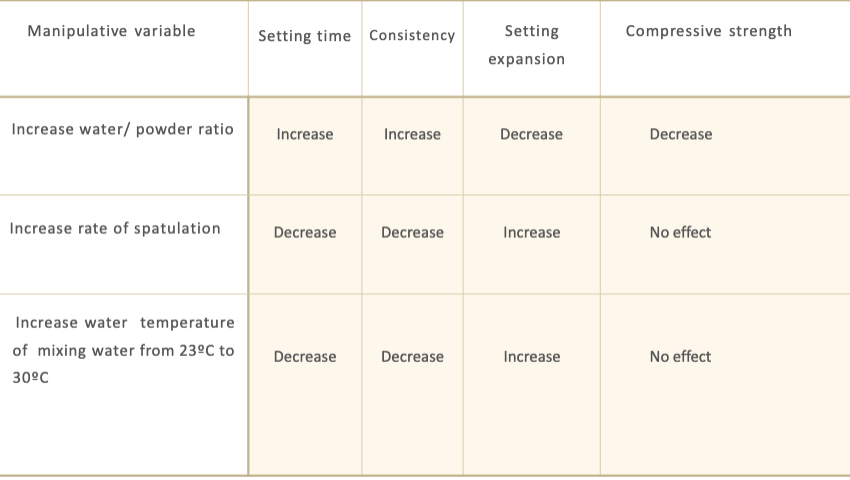
what variables affect the setting of gypsum products?
W/P ratio
temperature of water
spatulation (speed/time)
hand mixing vs vacuum mixing
air moisture contamination
Reduce gypsum Setting expansion can be controlled with the use of additives in the powder like…?
K2SO4 or Sodium Citate
Strength is ______ proportional to the water/powder ratio
However, using a low water/powder ratio for maximum strength also increases setting expansion
inversely
Removal of uncombined water from cast gypsum by low-temperature drying approximately ______- the strength
doubles
t/f: Long-term immersion in water is contraindicated; if needed, use a saturated solution of calcium sulfate
true