ANT100 Exam 3 - Second Half
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Performance
an expression of self, identity, or culture
Why can performance be an effective method of delivering messages to audiences?
It focuses on visual ways of expressing a self, idea, or culture
Cultural Performance
how cultures and communities use performance to do things such as:
Expressing identity, entertain, pray for things (ritual), etc.
What is a ‘public self’ and how is it shaped by culture?
Our “public” selves are shaped by cultural expectations, norms, and values. (Our “ought” self)
What we should be, should look like, and how we should act based on expectations and norms
How can agency be reclaimed through performance?
performance can help one express their own identity and self, showing that they are an independent individual
Budhan Theater
created performances to raise awareness about discrimination and violence that lower classes face in India
How can performance be emergent/transformative?
Symbolic
Staged performances lets participants experience something intensively
Not only is expressive, but also creates something. Something new emerges with a meaning through the process of performance
Through doing or saying something, we come to experience it as reality
How can performance be used for social justice?
Think of Budhan theater. Performances to call out injustices or to raise awareness for issues
Social Justice
A communal effort dedicated to creating and sustaining a fair and equal society in which each person and all groups are valued and affirmed.
OR
The basic structure of society, or more exactly, the way in which the major social institutions distribute fundamental rights and duties and determine the division of advantages from social cooperation
Space Sexology
a new field that studies sex, intimacy, reproduction, and relationships in space
describe the technoscientific bias in how emotional needs and sexuality are treated (and ignored) by space science and space agencies and also who “belongs” in space
Space exploration is seen as a serious field of study, so sex and intimacy aren’t often considered. Space companies often ignore their astronauts physical/intimate needs because they want them to focus on whatever mission.
Regarding them deciding who “belongs” in space, typically white cis men are chosen to go into space. Not 100% sure how this relates how this relates to space intimacy, but anyways, it was very rare (little less uncommon recently) for women and poc to be chosen to go into space, showing discrimination towards race and biological sex in a space setting.
potential consequences of ignoring sex and intimacy’s place in space exploration/settlement
decrease in motivation/mood
frustration/changes in attitude
needs not being satisfied
how views on sex and intimacy in space reflect and perpetuate other forms of marginalization, exclusion and structural violence
sexual violence/assault against marginalized groups
people of color and women excluded more often
possible sexism, racism, homophobia in an enclosed location in space
Erotopolitics
politics regarding sexuality and intimacy
describe how erotopolitics impacts the space industry and even popular culture
raises awareness about sexuality and intimacy in space exploration and space media (books, movies, et
Identify the 6 types of nutrients
carbohydrates, proteins, fats/lipids, vitamins, minerals, and water
Two categories of nutrients
energy yielding and non-energy yielding
which nutrients are energy yielding?
carbohydrates
proteins
fats/lipids
which nutrients are non-energy yielding?
vitamins
minerals
water
direct evidence
reflects the actual physical/chemical ingestion/digestion of food
dental microwear analysis
biogeochemistry
indirect evidence
reflects a species level adaptation and not what an individual organism may have actually eaten
Skeletal Morphology
Tooth Morphology
Skeletal Morphology
the morphology of the craniofacial skeleton has been adapted to withstand stresses and strains associated with oral food processing
Tooth Morphology
Incisor size: proxy for amount of incisal preparation of food
Large incisors: larger, tougher fruits
Smaller front teeth: easier to prep, smaller leaves and berries
Element
a pure substance in which all its atoms have the same number of protons
Stable Isotope
isotopes that do not go under radioactive decay
Radioactive Isotope
Isotope that does go under radioactive (exponential) decay
Identify the isotopes of carbon and nitrogen that are used for reconstructing prehistoric diet
identifying C4 in plants such as maize
finding the trophic level of the diet, different food sources
the ultimate source of carbon in organic organisms the process that moves that carbon from the atmosphere to the biosphere
didn’t understand what was being asked totally so here is a diagram of a carbon cycle!
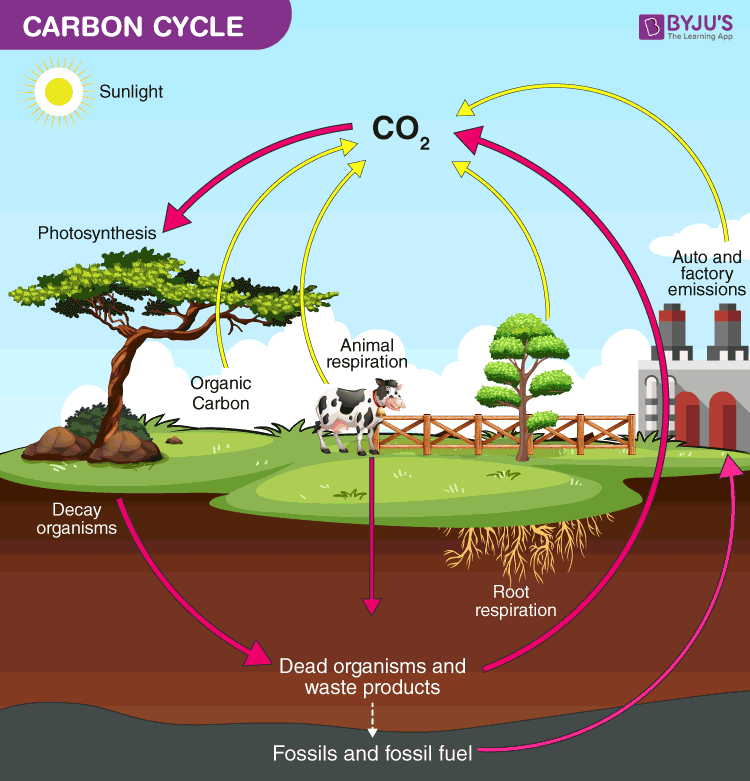
Photosynthesis
the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy.
During photosynthesis in green plants, light energy is captured and used to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds.
Identify the two elements and their isotopes that used in dietary reconstruction
Carbon and Nitrogen
What do the carbon and nitrogen isotopes tell us about diet?
Carbon: plants and stuff regarding food (fruits, vegetables, leaves, etc.)
Nitrogen: can tell us about trophic levels or inclusion of marine resources
Trophic Level
the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain.
what plants use Hatch-Slack Photosynthesis pathway
plants that use this pathway are known as C4 plants, e.g., tropical grasses like maize
what plants use Calvin photosynthesis pathway
plants that use this pathway are known as C3 plants, e.g., temperate plants
what plants use CAM photosynthesis pathway
succulents
Megadontic
Abnormally large teeth
2 factors that influence the microwear features and what type of conclusions we can make about diet based on this type of data
occlusal mechanics
pits form in teeth from hard foods (nuts, seeds)
scratches form from tough foods (leaves, meat)
abrasives
biogenic abrasives (aka endogenous grit; phytoliths/opals)
pedogenic abrasives (aka exogenous grit, aka dirt; quarzitic particles)
Differentiate between biogenic and pedogenic abrasives
Biogenic abrasives are formed through biological processes, such as the breakdown of organic matter, and contribute to soil structure and nutrient cycling.
Pedogenic abrasives, on the other hand, are formed through geological processes, including weathering and erosion, and play a crucial role in soil formation and development
Identify and define the 5 questions that forensic anthropologists try to answer
What: establishing the forensic context
Where: where are they most commonly involved/the location
When: the time
Who: creation of the biological profile
How: how it happened
Medicolegal
relating to both medicine and law
Taphonomy
the study of the transition of remains, parts, or products of organisms, from the biosphere to the lithosphere
Forensic Anthropology
the application of the science of physical anthropology to the legal process
how do forensic anthropologists create a biological profile and what is included in one
Sex estimation
Metric Variation
Bla bla variation
Sexual Dimorphism
Age estimation
Developmental
Good for juvenile material
Degenerative
Adult material
Broader categories
Define and differentiate between the 2 main methods that forensic anthropologists use to estimate sex from skeletal remains
Metric variation
based on size differences between females and males
Morphological variation
based on developmental differences between females and males
Sexual Dimorphism
morphological differences between males and females of the same species
Define and differentiate between the 2 main methods that forensic anthropologists use to estimate age from skeletal remains
Developmental
Based on processes of skeletal and dental growth/development/maturation
good for juvinile material
greater accuracy
Degenerative
Based on random processes associated with aging
adult material
not as accurate/increasing error
broader categories
Difference between cause and matter of death
Cause: mechanisms of death. Disease or injury responsible for initiating the sequence of events that culminated in death
physiological deaths - systemic/cellular
Toxicological deaths - exogenous agent
Morphological deaths - physical change
Matter: fashion in which the cause of death comes into being
5 different types of matter (regarding death)
Natural
Accidental
Suicide
Homicide
Undetermined
differentiate between accidental trauma and violence related trauma
Accidental trauma is injuries/death that happened without any intent
Violence related trauma has intent behind it whether its self-intent or the aggressors intent
antemortem
happened/occured before death
perimortem
happened/occured around the time of death
postmortem
happened/occured after death