Biology Ch. 11 Cell-Cell Interactions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
signal transduction
the conversion of a signal from one form to another
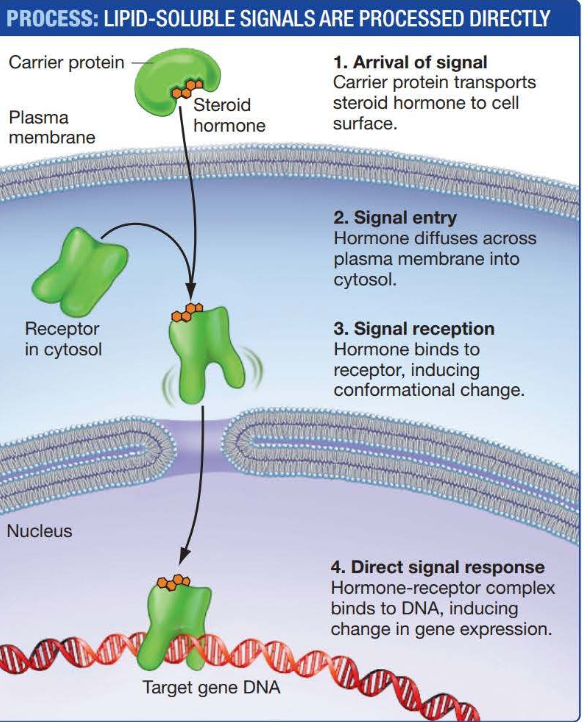
Some Cell-Cell Signaling Molecules Enter the Cell and Bind to Receptors in the Cytosol
because they are lipids, steroid hormoes can diffuse across cell membranse and bind to signal receptors located in the cytosol. the hormone-receptor complex may then be trasnported to the nucleus, where it changes the activity of genes
Signal Transduction Converts an Extracellular Signal to an Intracellular Signal
A lipid-insoluble signaling molecule will not pass through the membrane so the molecule activates a surface receptor that directs a process to generate intracellular signals.
Two major types of signal transduction
G-protein-coupled receptors initiate the production of intracellular second mesenger, which amplify and diversify the signal
Enzyme-linked receptors activate a series of proteins inside the cell, through the additiion of phosphate groups. The number and type of protein activated lead to the amplification and diversification of the signal
G proteins
when activated by a signal receptor, they trigger production of a second messenger
link the receipt of an extracellular signal to the prodcution of an intracellular signal
second messenger
a small, nonprotein signaling molecule or ion that elicits an intraceullular response to the first messenger
How do G-protein-coupled receptors work