Clinical Anatomy
0.0(0)Studied by 14 people
Card Sorting
1/125
Last updated 6:11 PM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1
New cards
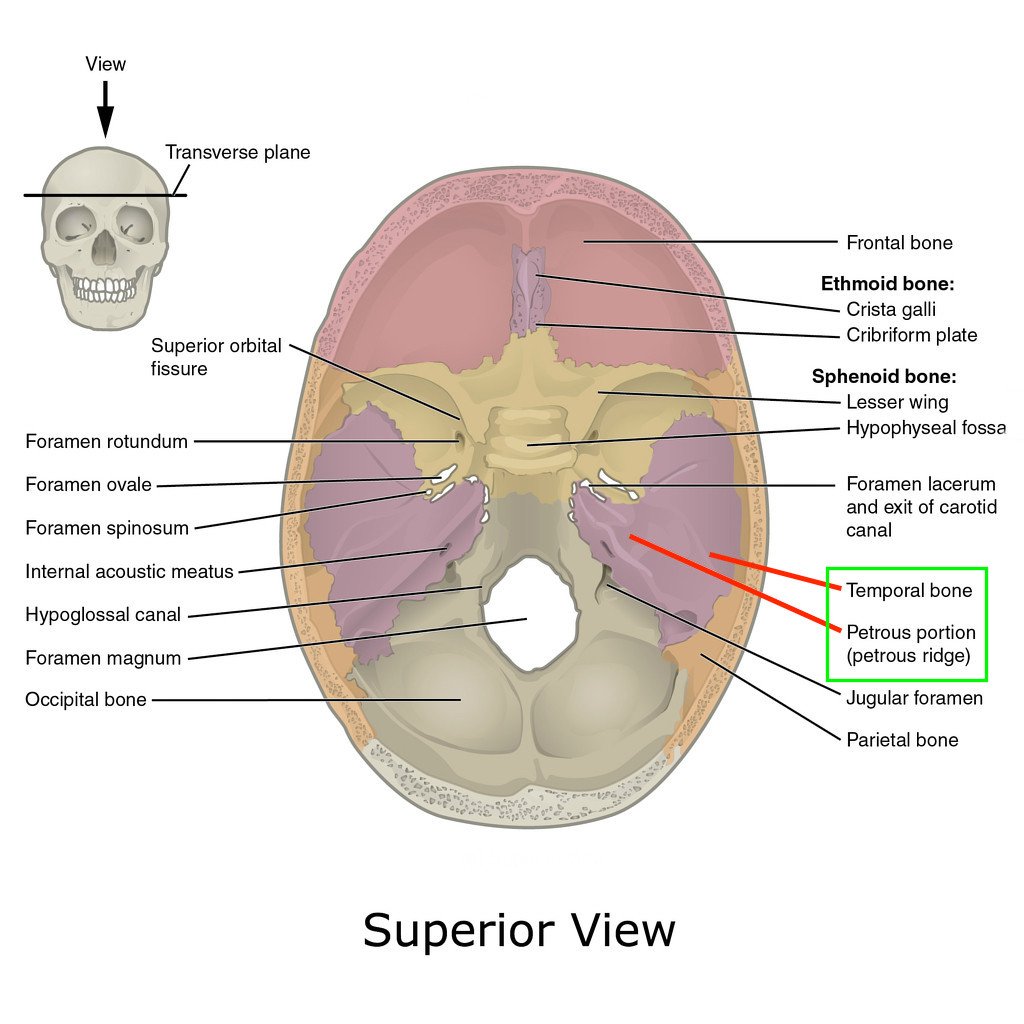
Petrous ridge
separates the MCF from the PCF
2
New cards
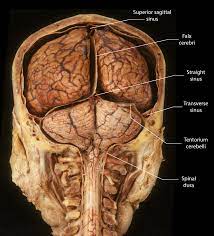
Tentorium
dural reflection that separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum and brainstem
3
New cards
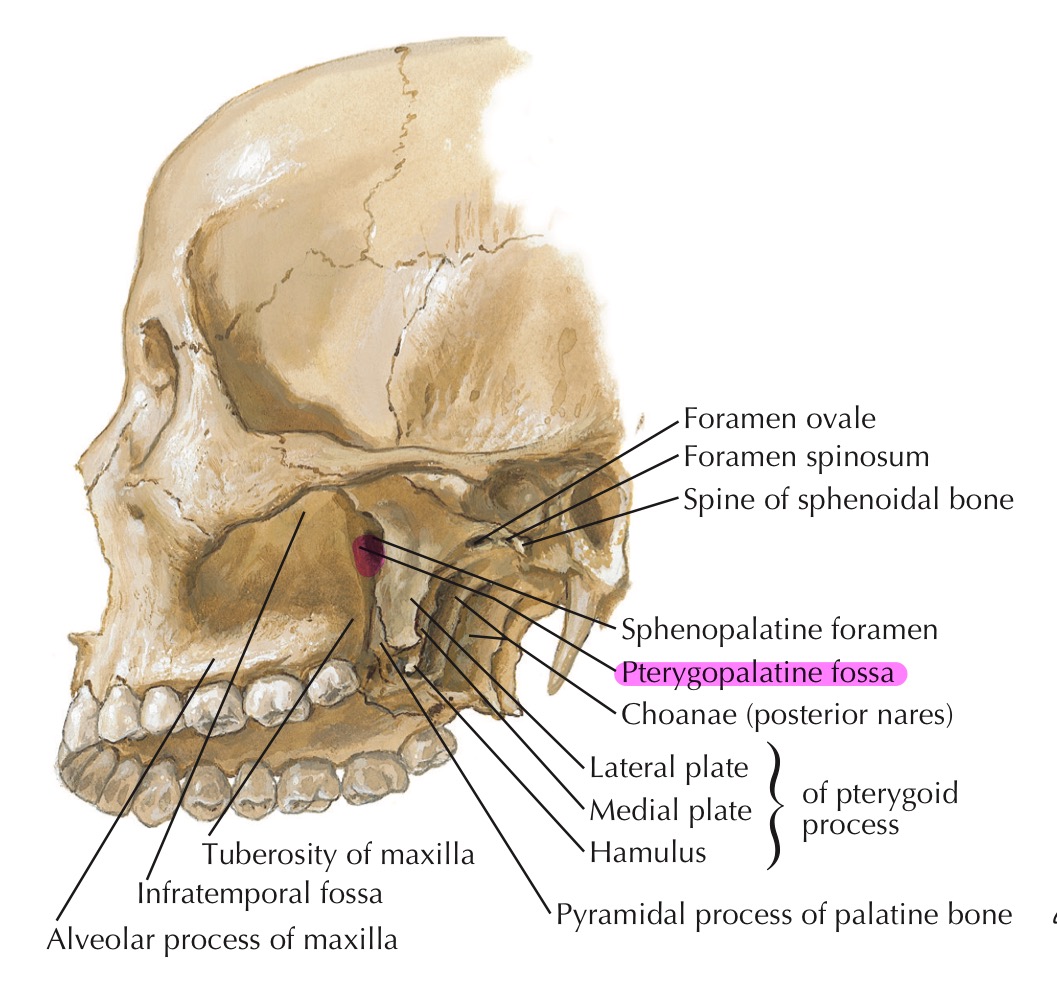
Where is the Pterygopalatine Fossa?
zygomatic arch, on the backside of the maxillary bone
4
New cards
What does the PPF hold?
Maxillary Nerve, Vidian nerve, Pterygopalatine ganglion, Maxillary artery
5
New cards
What is the infratemporal fossa?
space behind the masseter muscle and zygomatic arch
6
New cards
What fills most of the Infratemporal fossa?
temporalis muscle
7
New cards
What is found inside of the Infratemporal fossa?
Branches of the Maxillary artery, pterygoid venous plexus, nerves
8
New cards
What nerves are found in the infratemporal fossa?
Mandibular, inf. alveolar, lingual, buccal, chorda tympani, otic ganglion
9
New cards
CN V is AKA....?
Trigeminal nerve
10
New cards
Where does CN V leave the brainstem from?
pons
11
New cards
What leaves the pons and fuses to create the trigeminal ganglion?
large sensory branch and small motor branch
12
New cards
The trigeminal ganglion is AKA...?
Gasserian ganglion
13
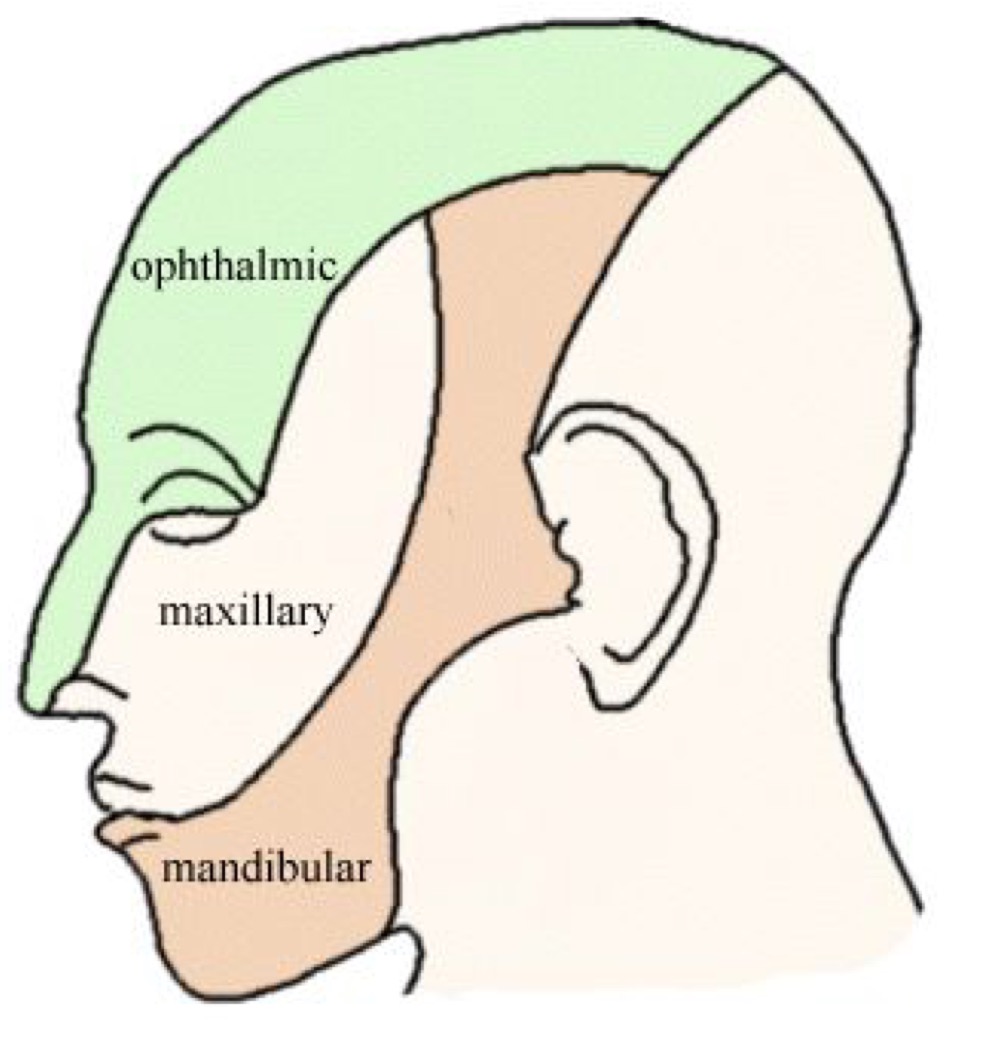
New cards
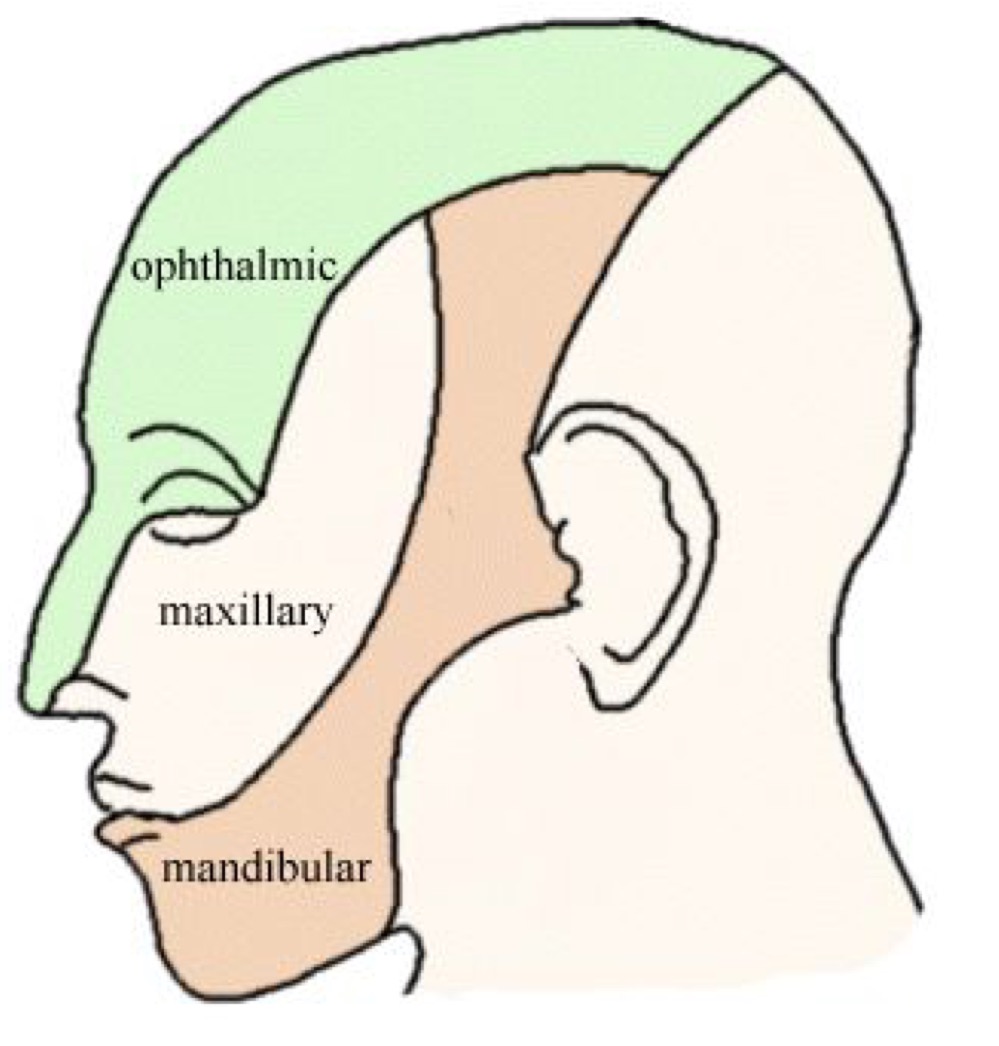
What are the 3 divisions of the gasserian ganglion?
v1 - ophthalmic
v2 - maxillary
v3 - mandibular
v2 - maxillary
v3 - mandibular
14
New cards
Which divisions of CN V are purely sensory? Which are mixed?
v1 and v2 - purely sensory
v3 - mixed
v3 - mixed
15
New cards
Which part of CN V passes through the PPF?
v2
16
New cards
What does the v1 sensory field include?
cornea, superior palpebral conjunctiva, bulbar conjunctiva
17
New cards
What CN is the submandibular gland innervated by?
CN VII
18
New cards
What gland is located under the tongue?
Sublingual
19
New cards
What is the parotid gland?
makes saliva and brings it to the upper part of the mouth
20
New cards
Where does the parotid gland enter?
above and lateral to 2nd molar
21
New cards
What innervates the platysma?
CN VII
22
New cards
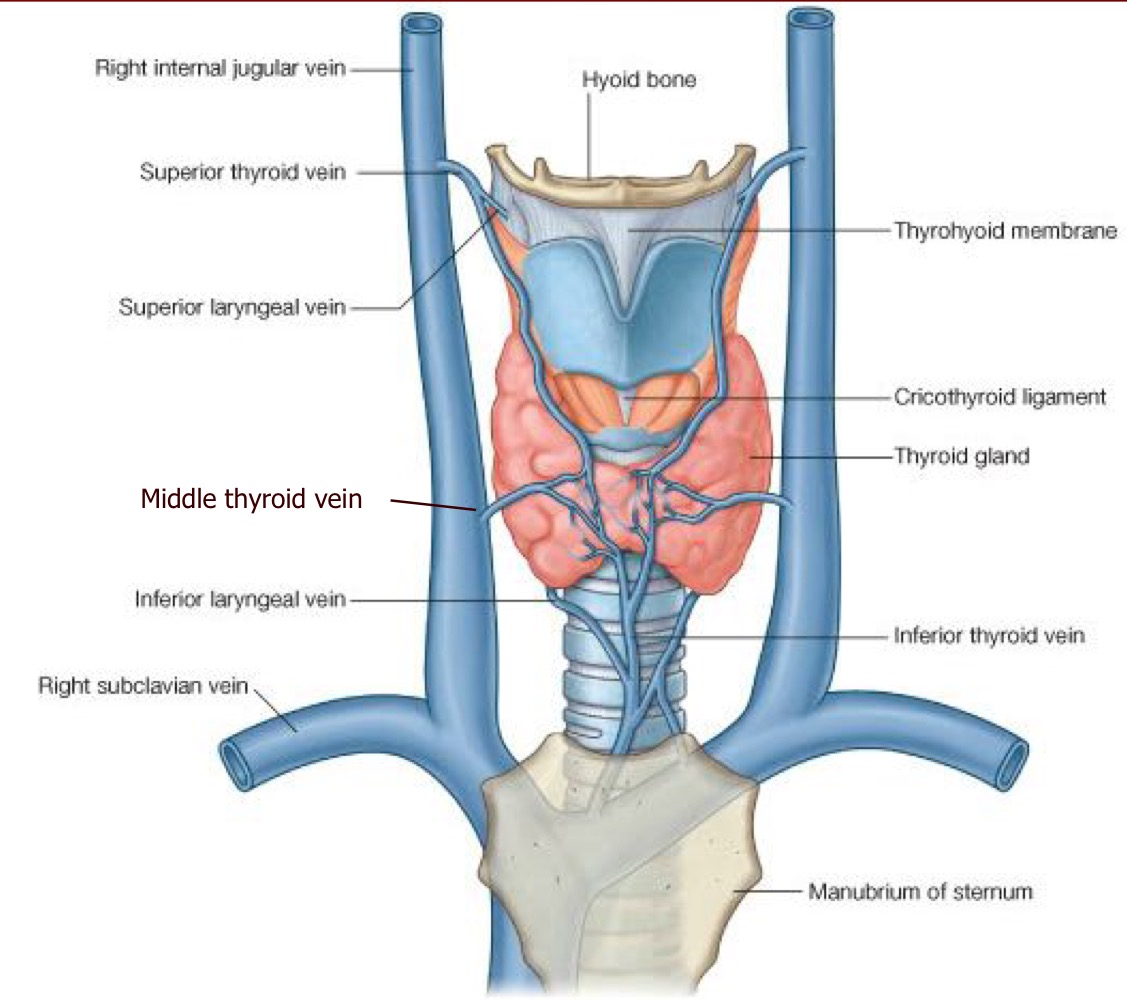
Where is the thyroid?
bridges the midling, covers the 2-3rd tracheal ring
23
New cards
What type of gland is the thyroid?
endocrine
24
New cards
What is the purpose of the thyroid gland?
it regulates calcium
25
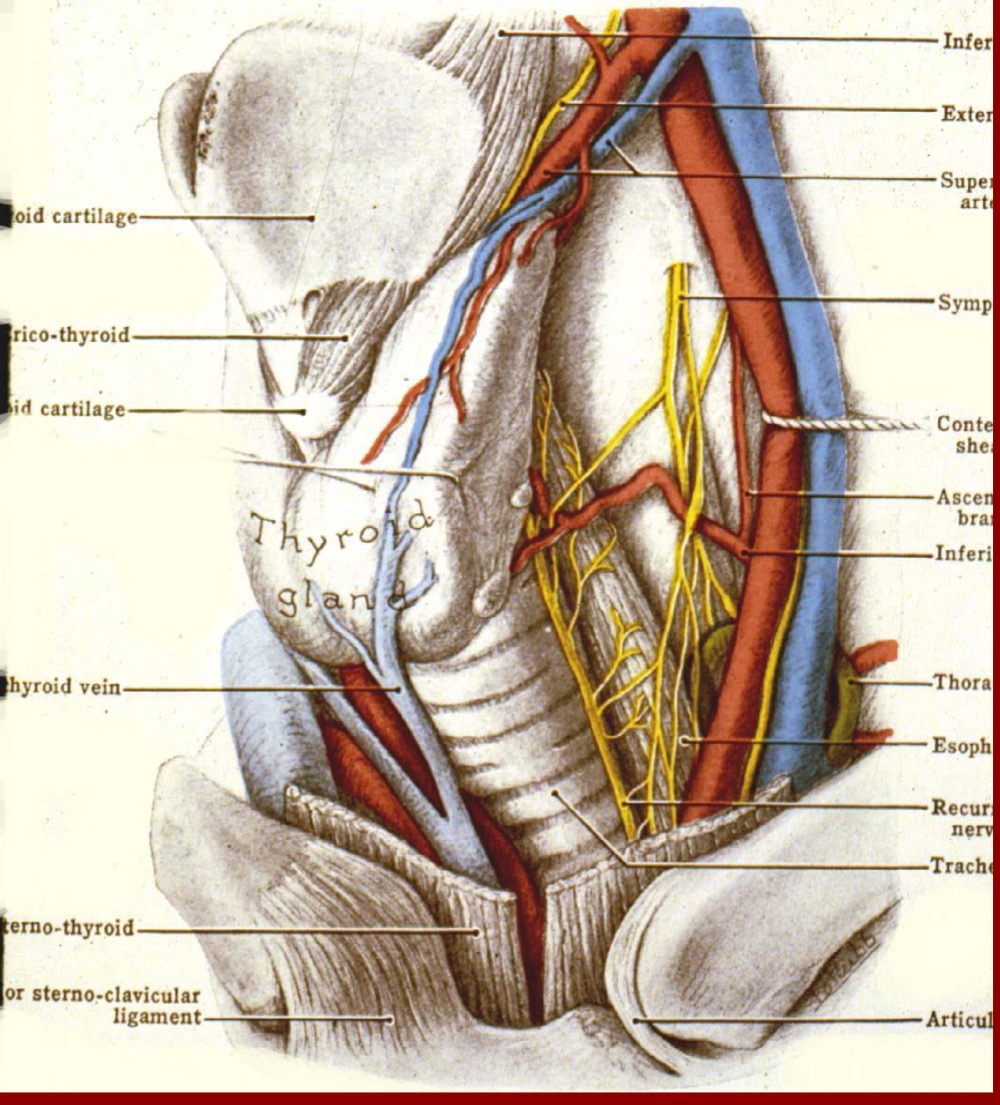
New cards
What arteries serve the thyroid?
1. external carotid
2. thyrocervical trunk
2. thyrocervical trunk
26
New cards
What veins serve the thyroid?
1. internal jugular
2. inferior thyroid vein
3. brachiocephalic
2. inferior thyroid vein
3. brachiocephalic
27
New cards
How many parathyroid glands do we usually have?
4
28
New cards
What glands were recently discovered?
Tubarial glands
29
New cards
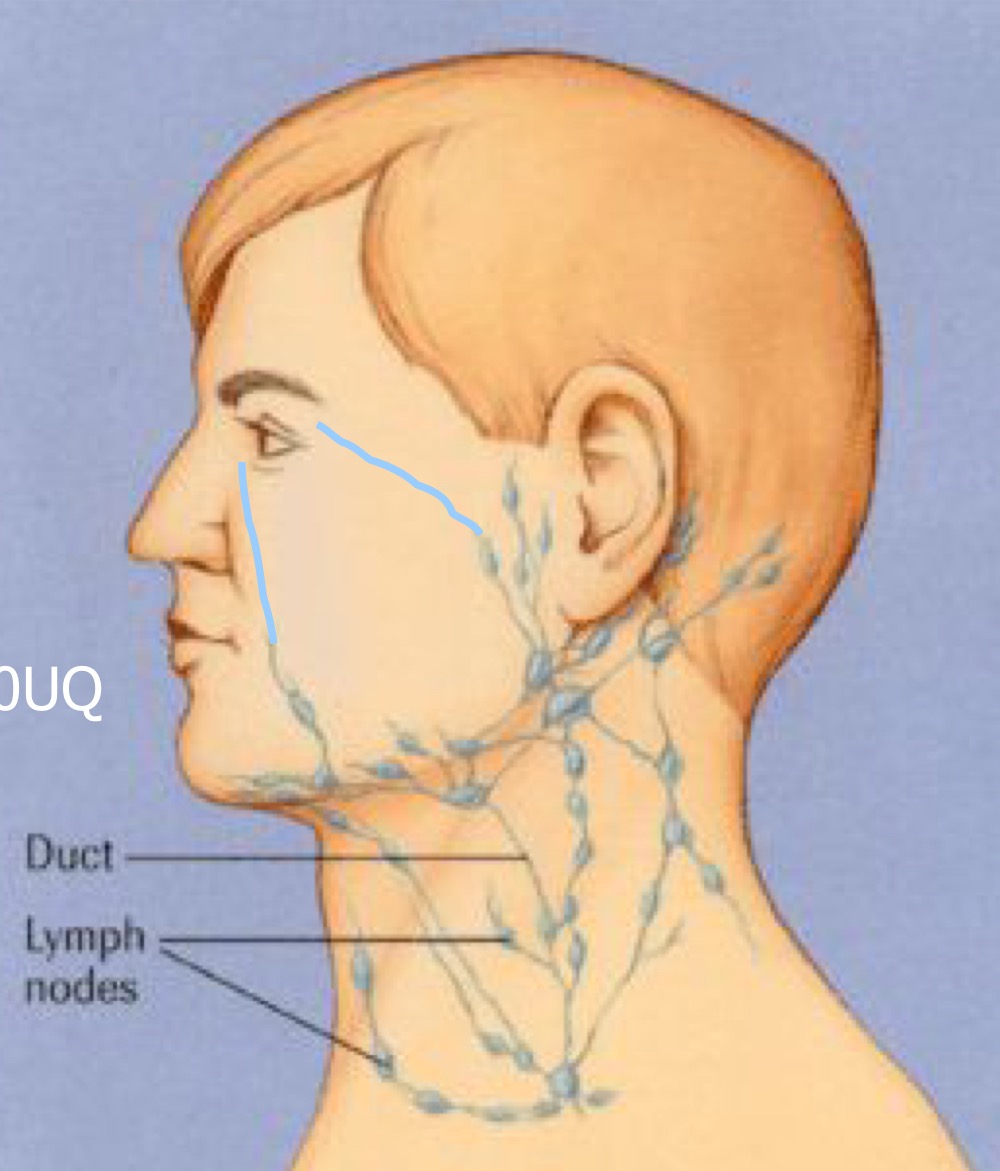
Which lymph node does the medial portion of the lid and conjunctiva drain too?
submandibular nodes
30
New cards
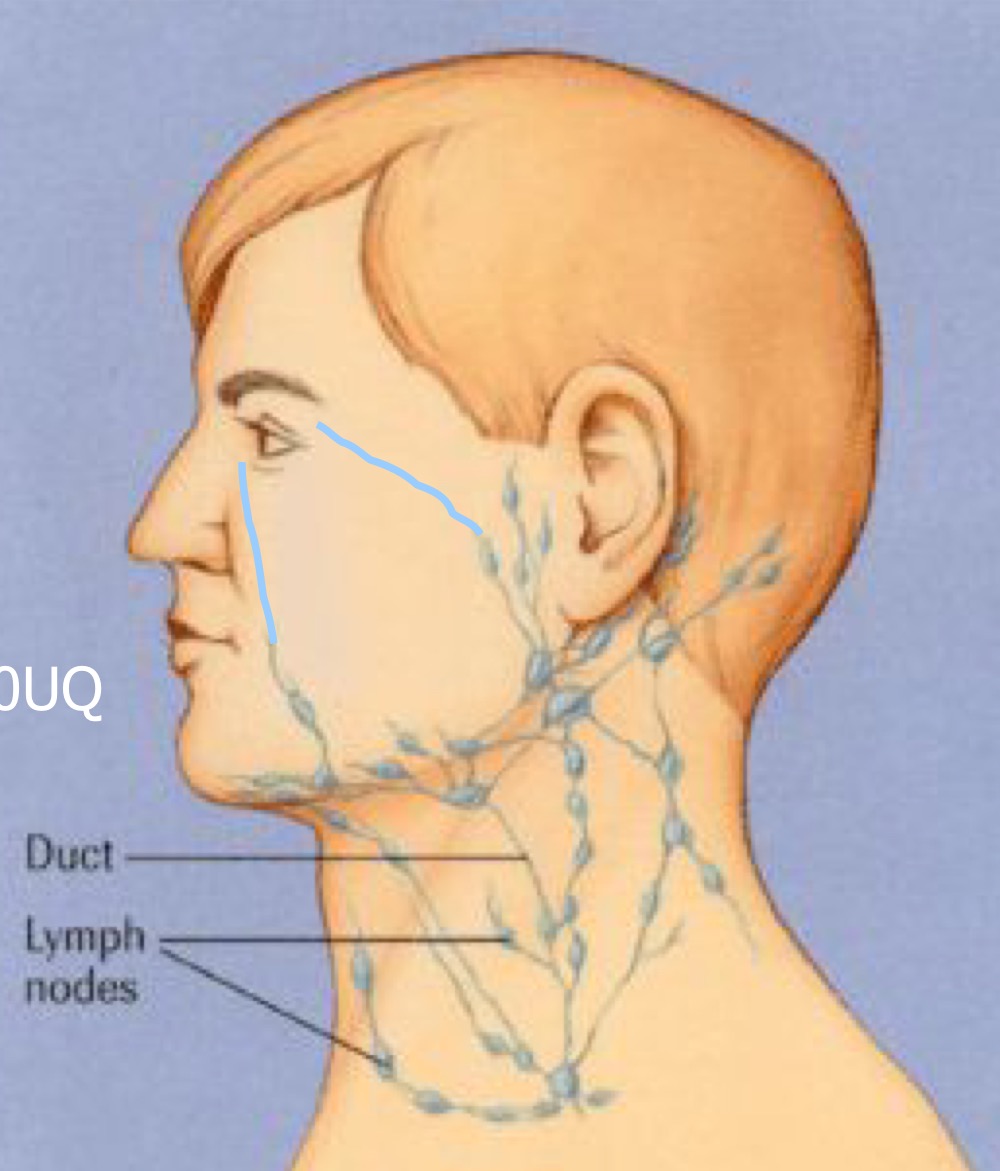
Which lymph node does the lateral portion of lids and conjunctiva drain into?
preauricular nodes AKA superficial parotic nodes
31
New cards
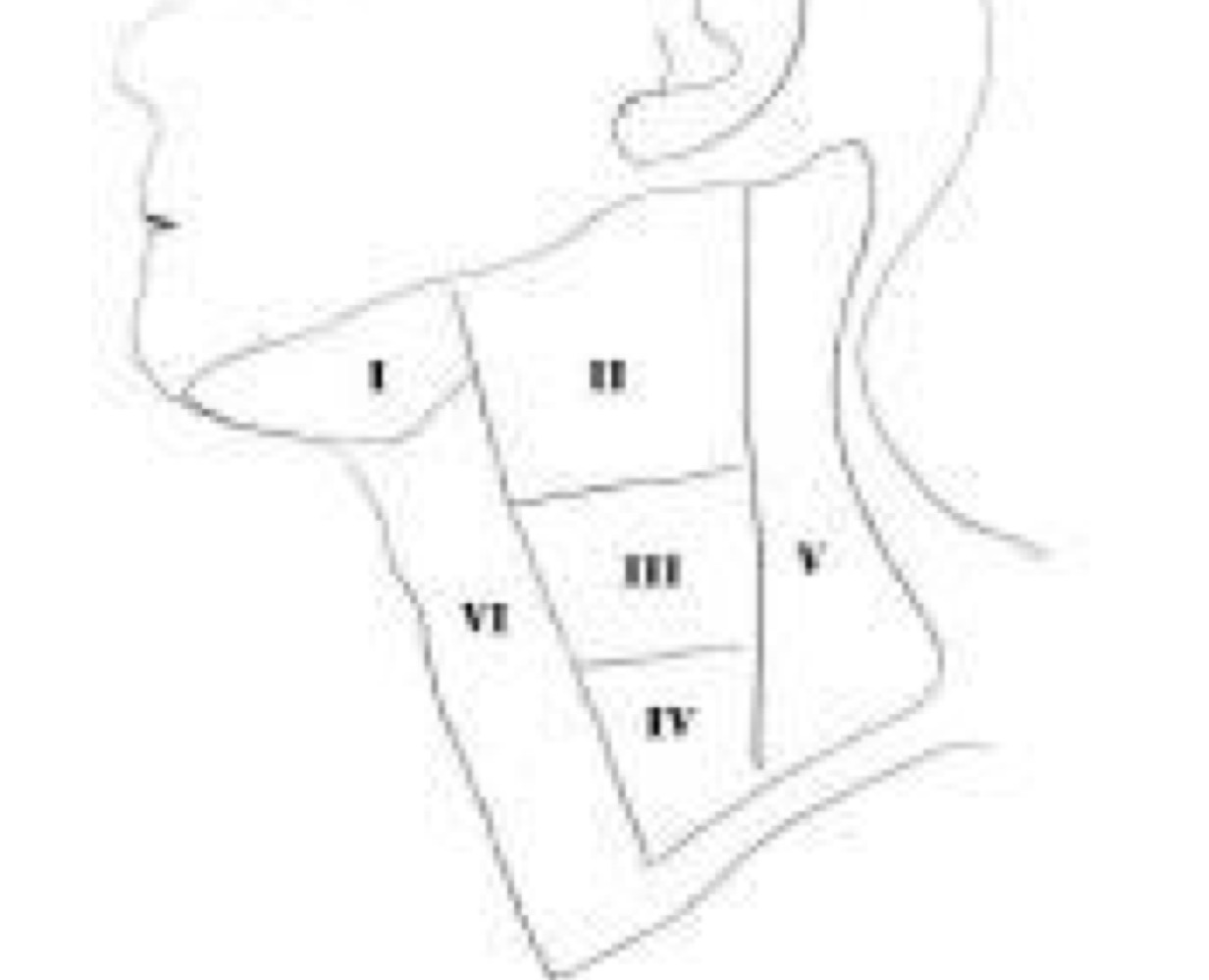
What are lymphatic basins?
How the lymph structures are divided in the neck
32
New cards
What are the lymphatic basins important?
drainage patterns exist, can tell where lesion/swollen lymph nodes are
33
New cards
Larynx principle functions
valve separating the air way for the system, voice production
34
New cards
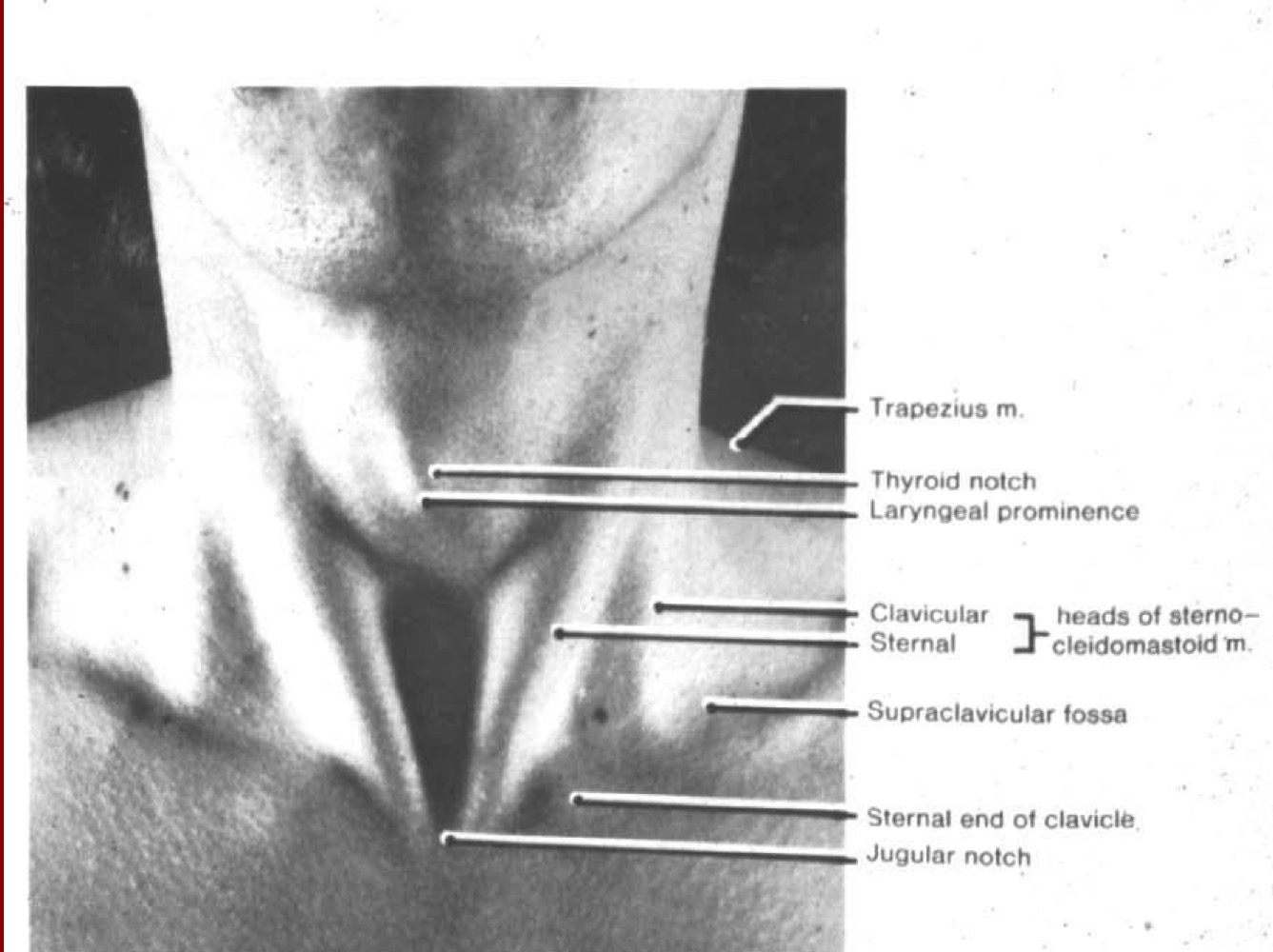
What are surface features of the larynx?
Laryngeal prominence, thyroid notch
35
New cards
What structures of the larynx rise while swallowing?
laryngeal prominence, thyroid notch
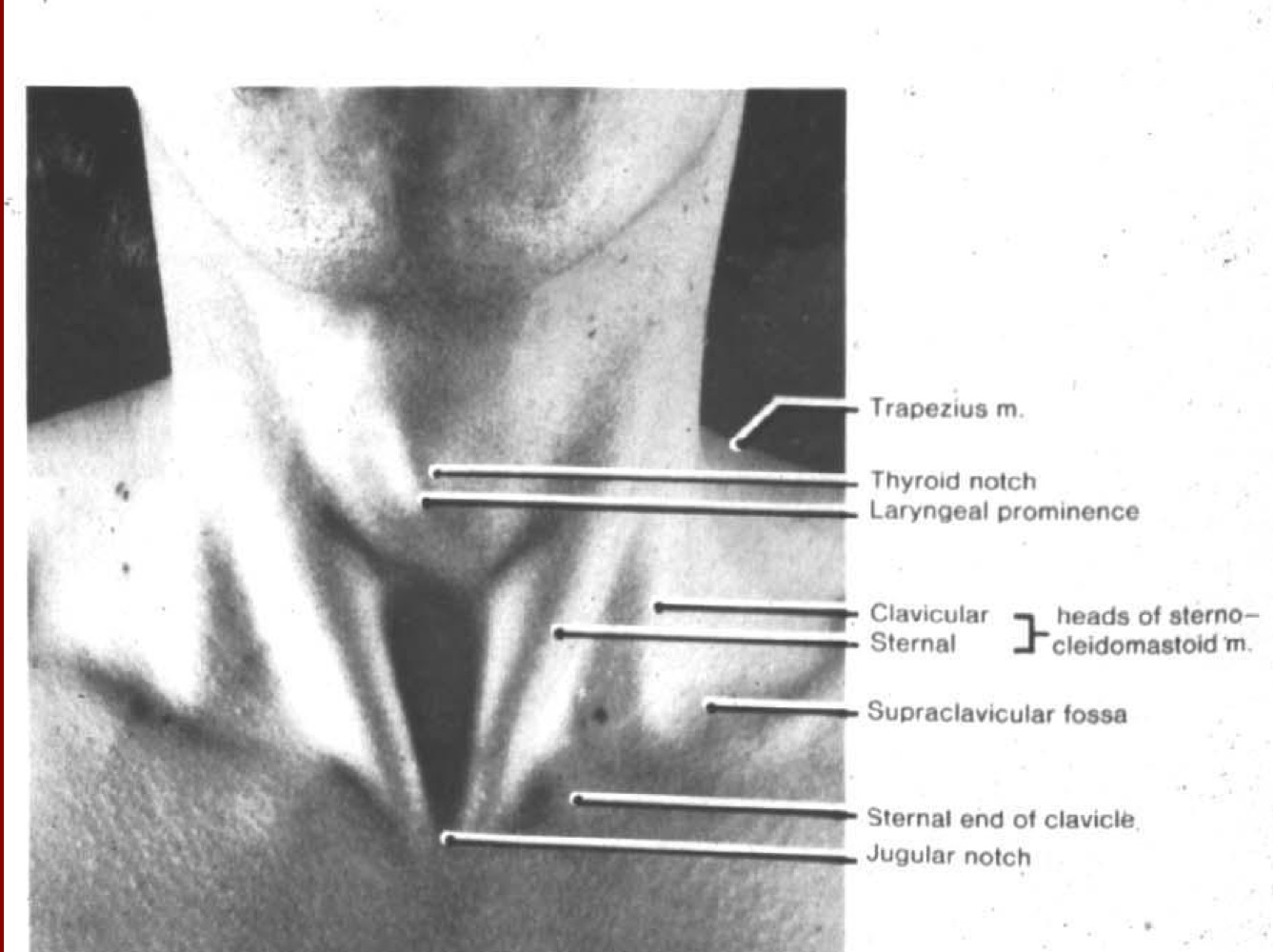
36
New cards
What are the 3 paired and 3 unpaired Laryngeal cartilages?
Arytenoid, Corniculate, Cuneiform
Thyroid (u), Cricoid (u), Epiglottis (u)
Thyroid (u), Cricoid (u), Epiglottis (u)
37
New cards
relative depth of voice is related to ___.
length of vocal cord
38
New cards
What CN are the muscles of the larynx innervated by?
(recurrent laryngeal branch of) CN X
39
New cards
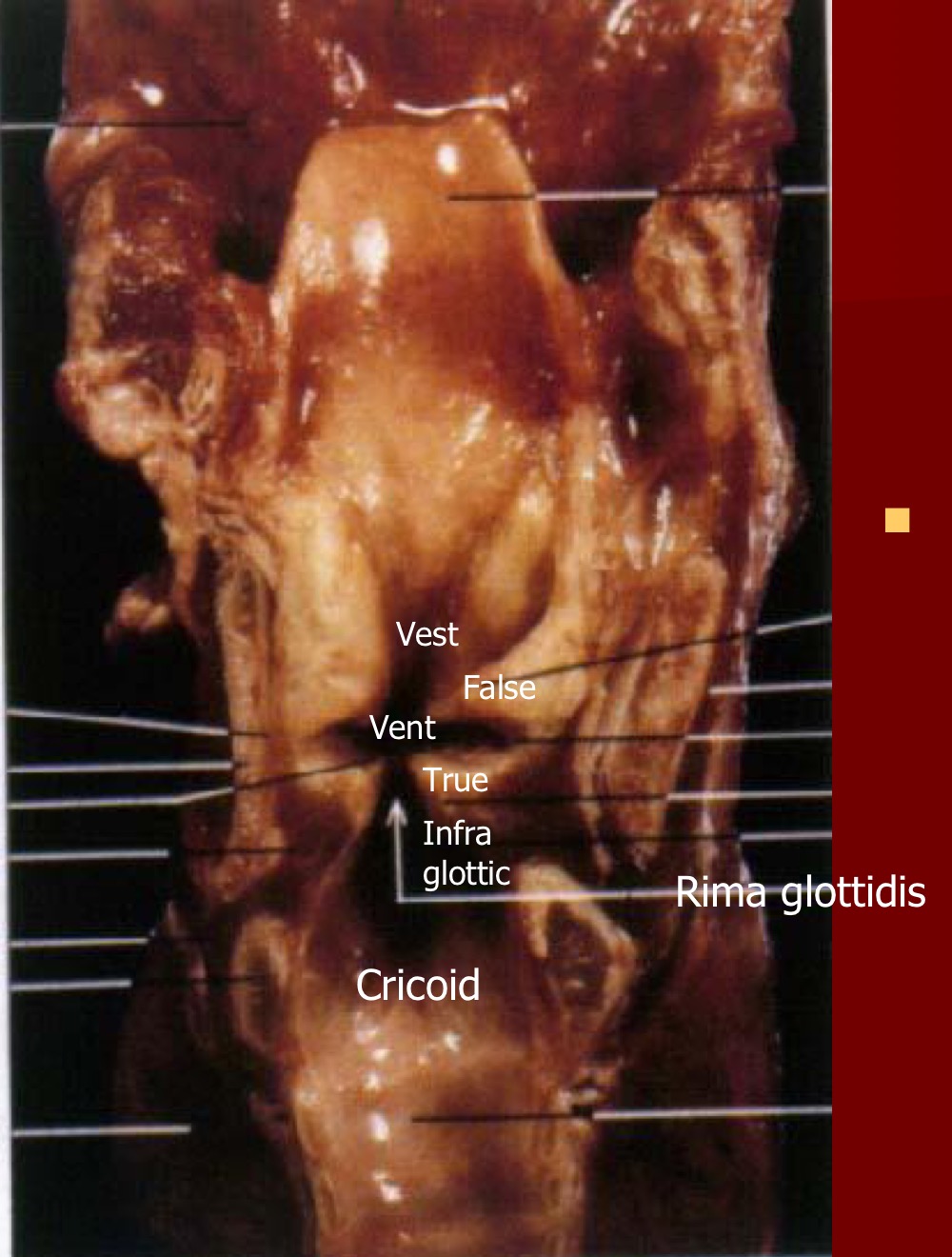
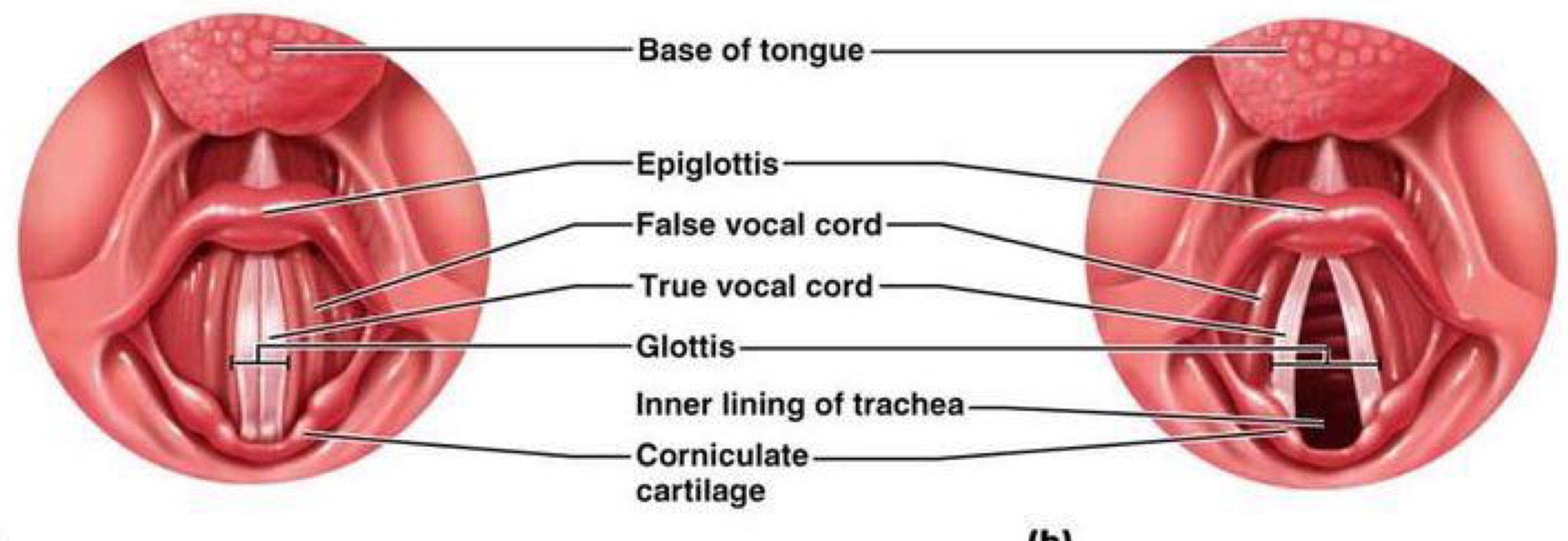
rima glottidis
aperture between vocal folds
40
New cards
glottis
collective term for vocal folds, rima and narrow part of larynx at level of folds
41
New cards
3 stages of deglutition
1. voluntary - bolus pushed from mouth -> oropharynx
2. involuntary - rapid, no chewing or breathing
3. voluntary - contraction of inferior constrictor of pharynx
2. involuntary - rapid, no chewing or breathing
3. voluntary - contraction of inferior constrictor of pharynx
42
New cards
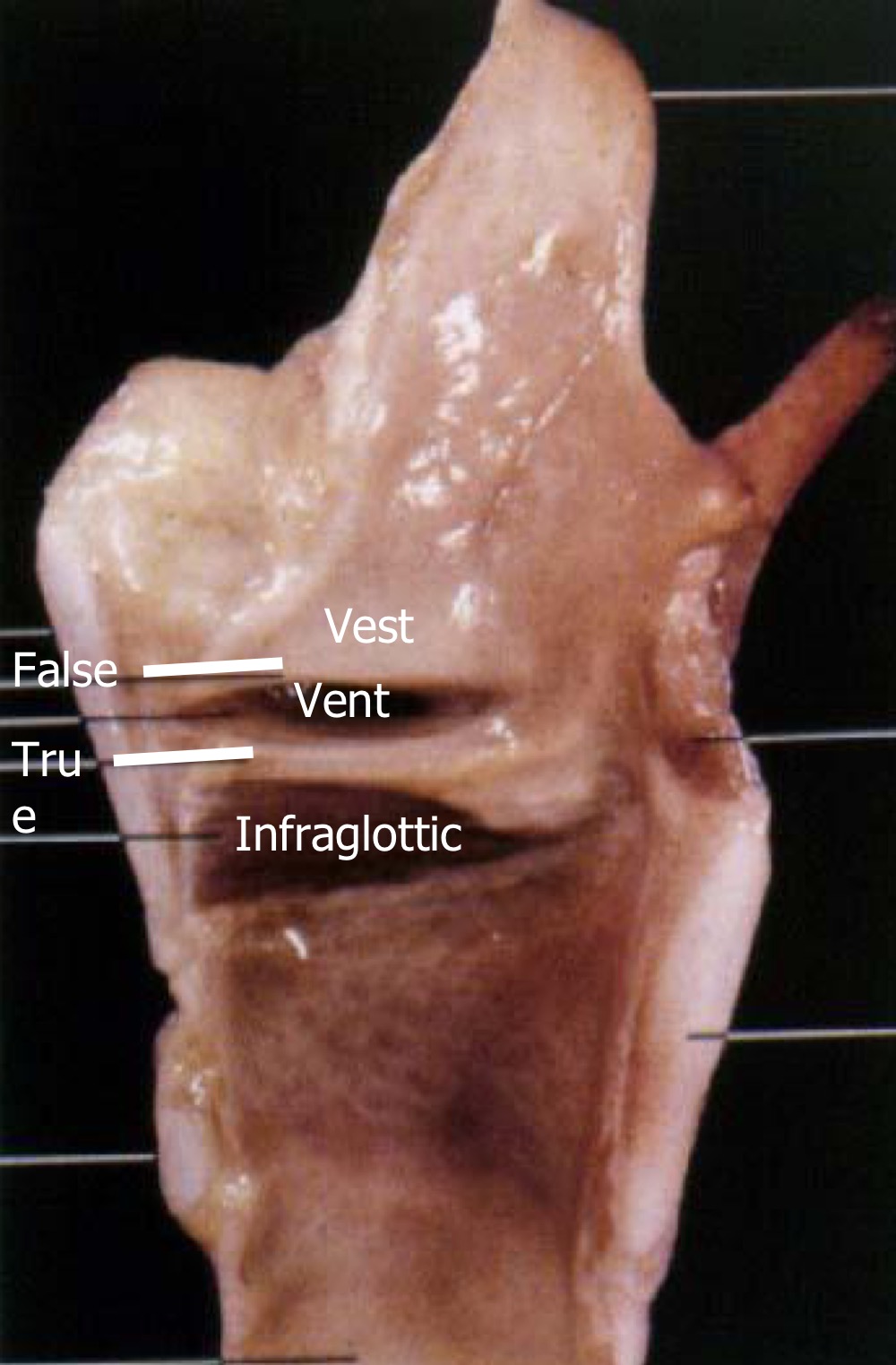
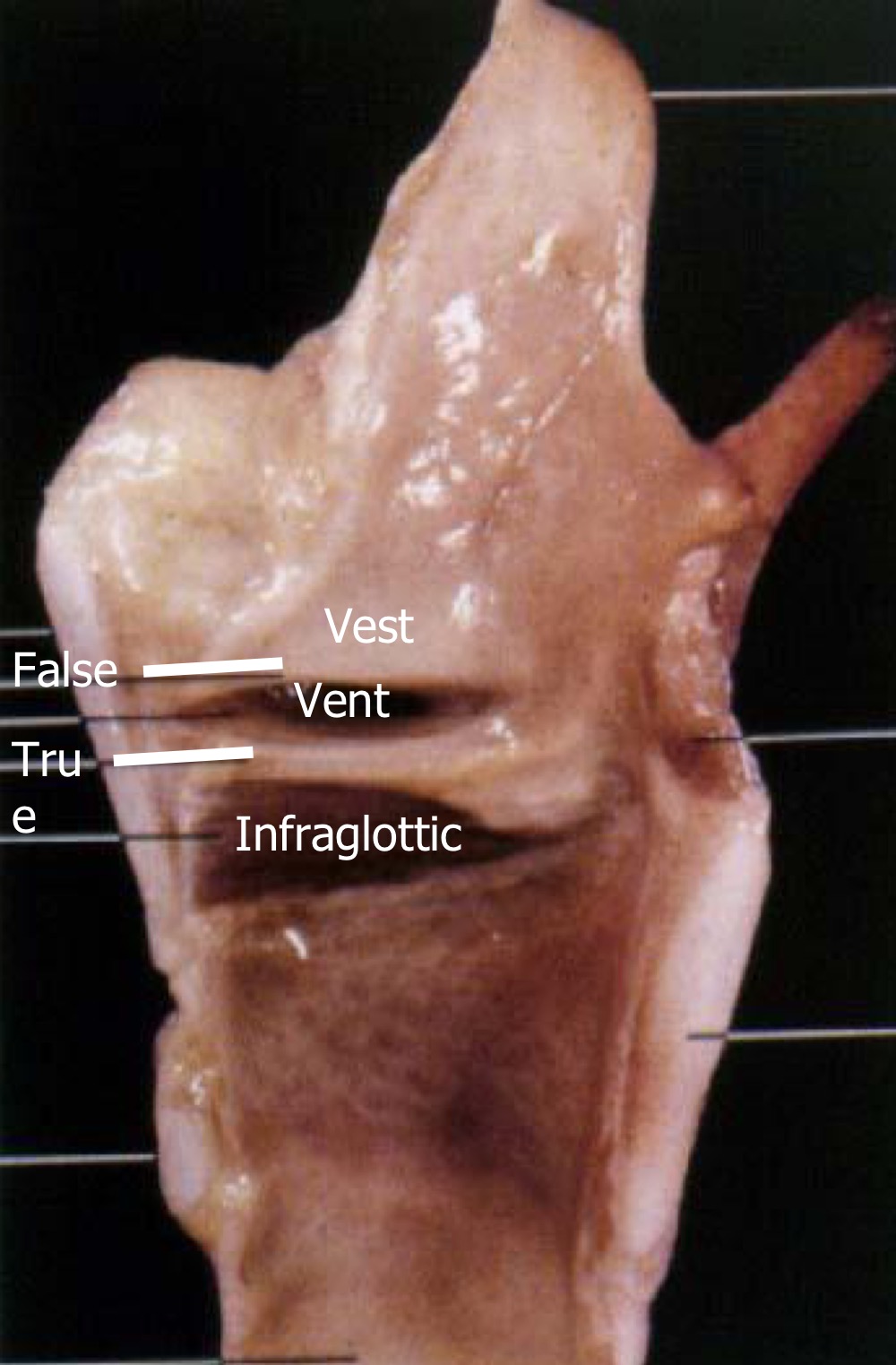
vestibule
above false vocal folds
43
New cards
vestibular folds
false vocal folds
44
New cards
ventricle of larynx
between the true and false vocal folds
45
New cards
infraglottic cavity
below true vocal folds
46
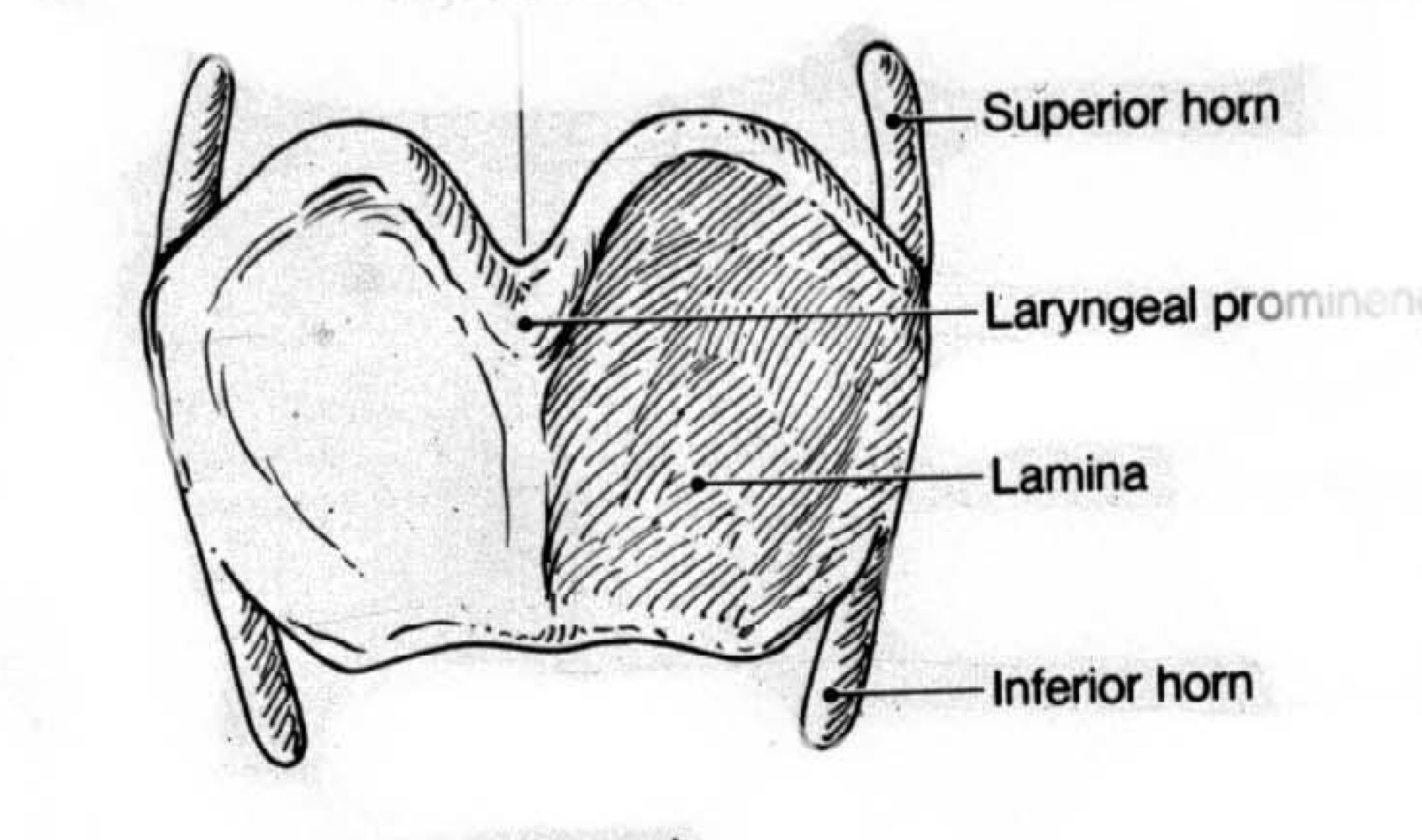
New cards
thyroid cartilage has ___ and___ horn
superior and inferior
47
New cards
when the lids close, what happens to the eyes?
they elevate (look upwards)
48
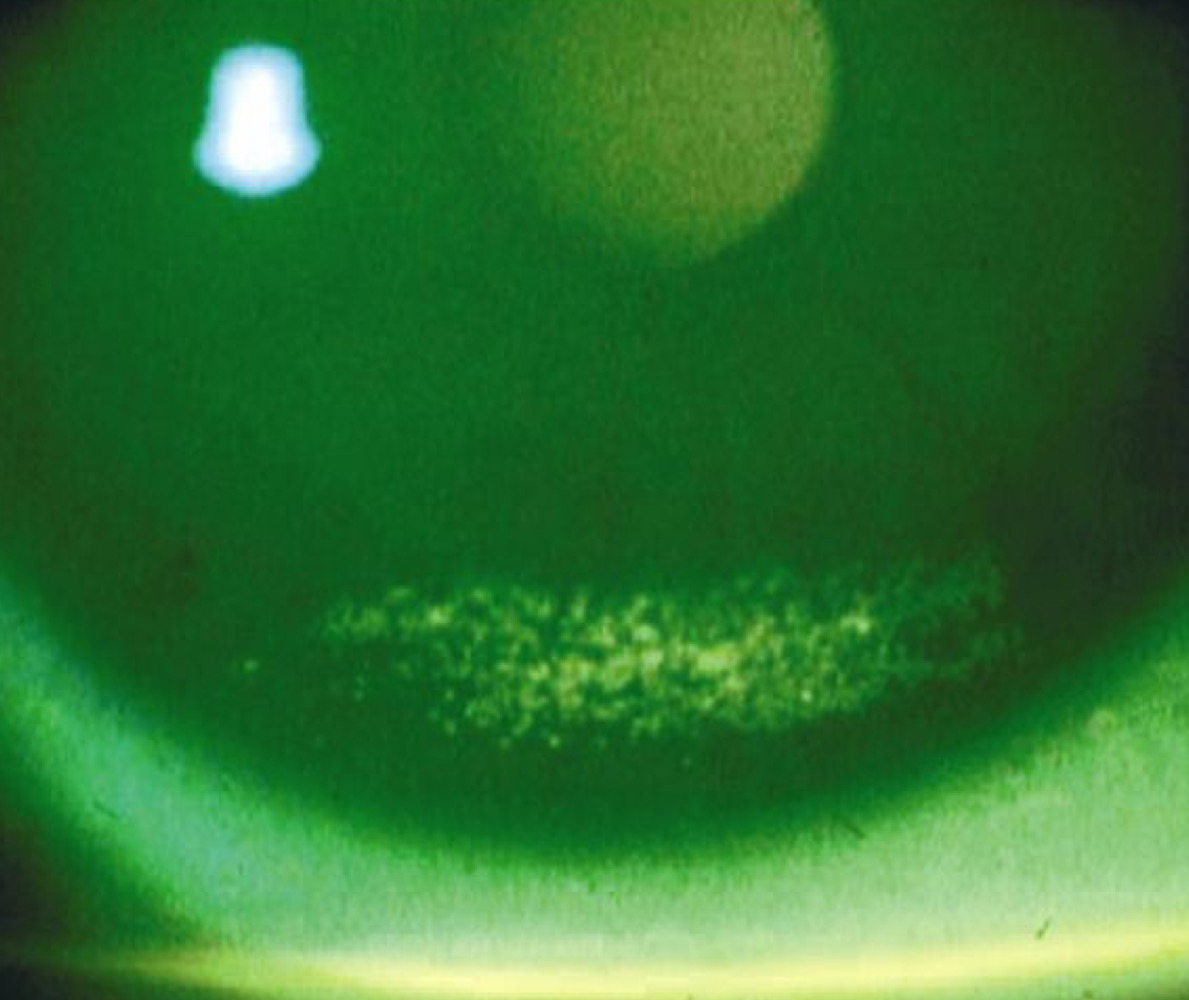
New cards
if the lids are not closed fully during sleep, which part of the cornea will be damaged?
inferior cornea
49
New cards
where is the tear meniscus located?
both top and bottom lids
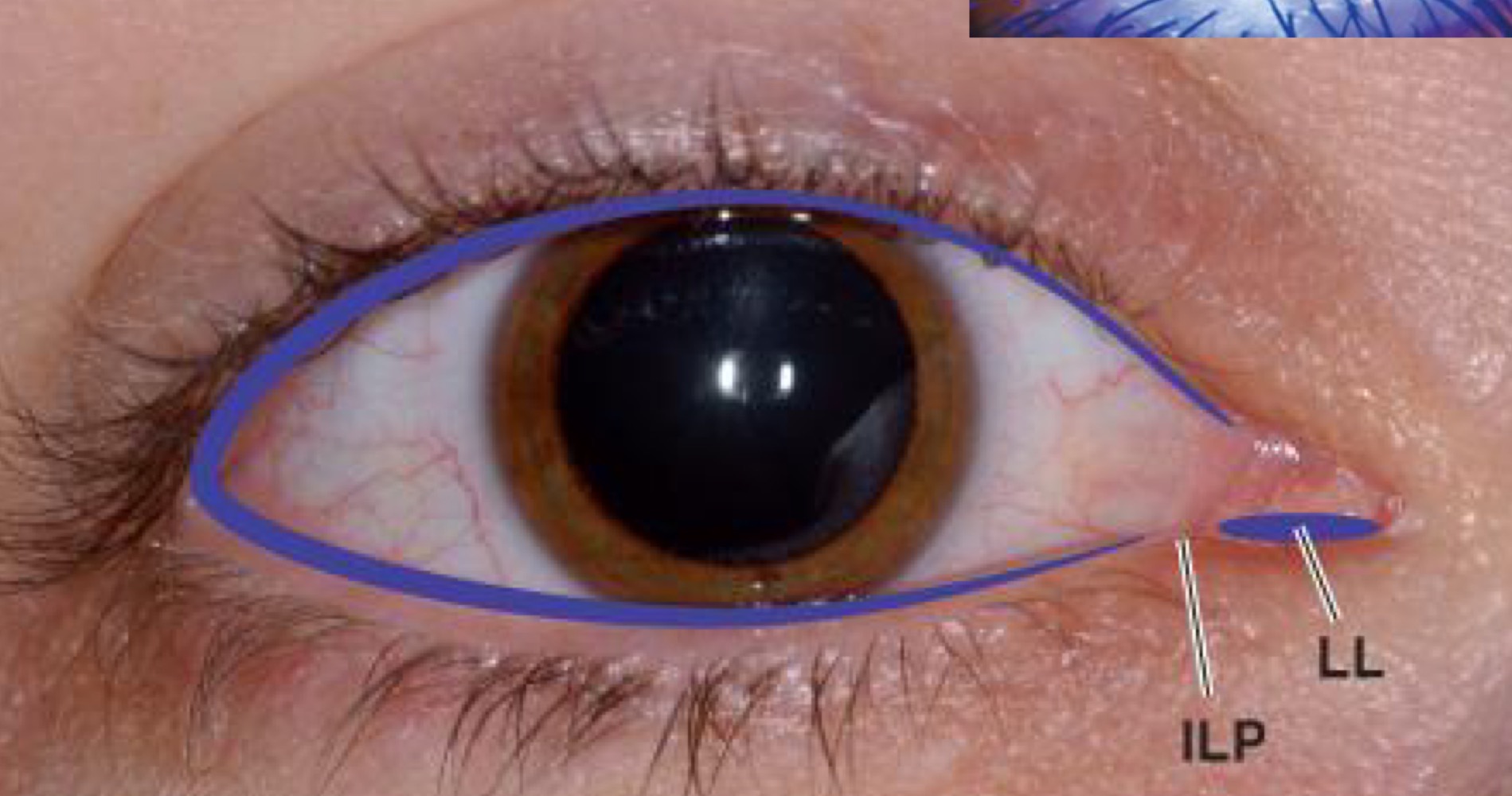
50
New cards
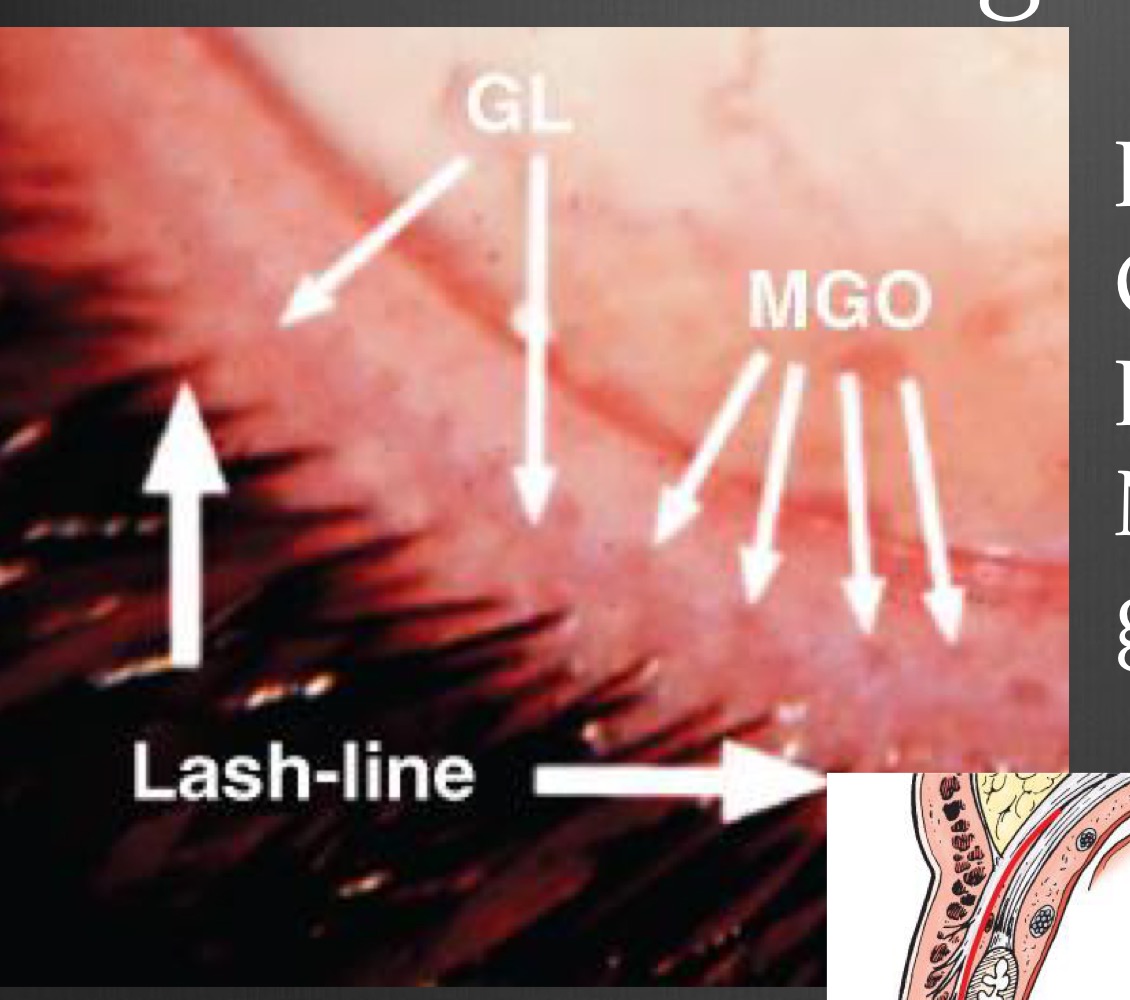
Landmarks of the lid
MGOs, Grey line, Lashes
51
New cards
Layers of skin on the lid
epidermis, dermis, NO hypodermis
52
New cards
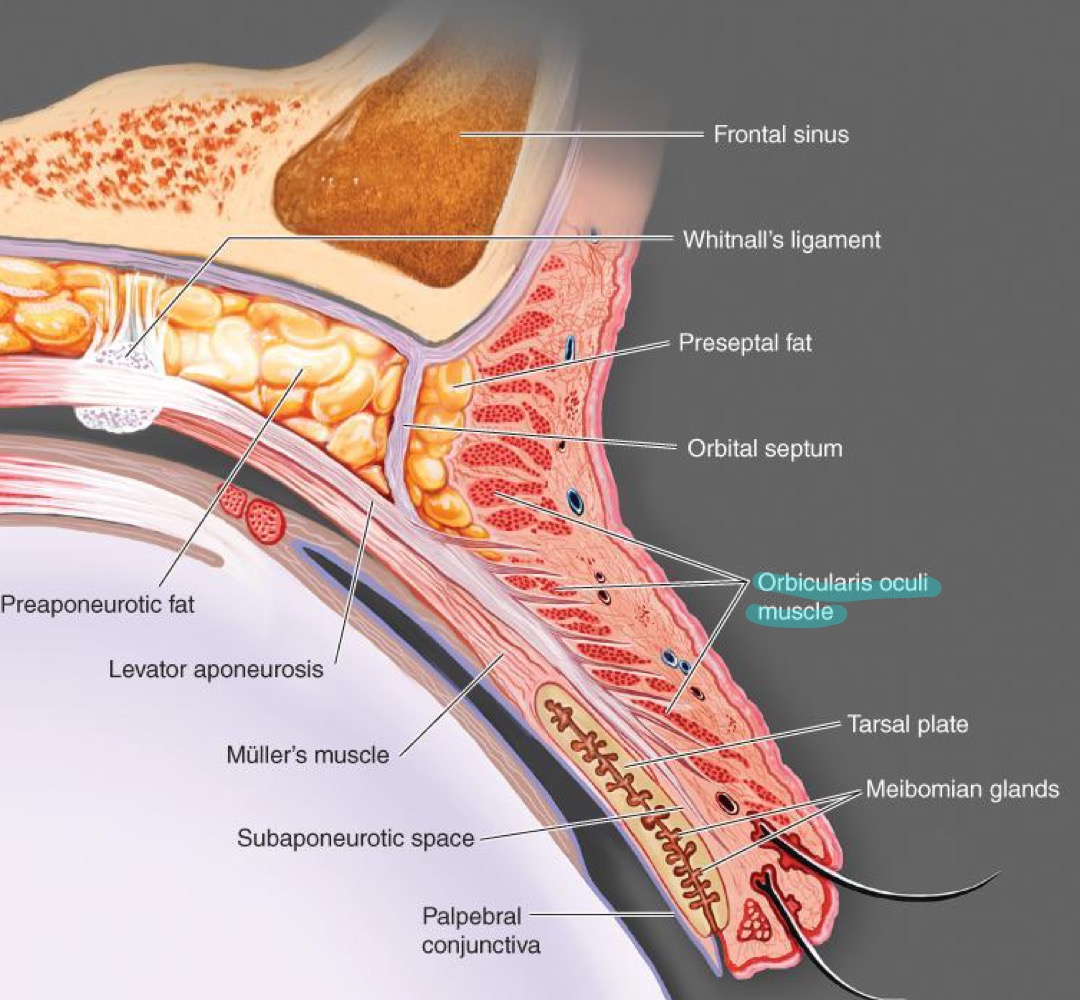
what muscles are found in the lid?
orbicularis oculi muscle, levator palpebral muscle, Mueller's muscle
53
New cards
what does the orbicularis oculi muscle do?
closes the lids
54
New cards
What does the levator palpebral muscle do? What type of muscle is it?
raises the lid, skeletal muscle
55
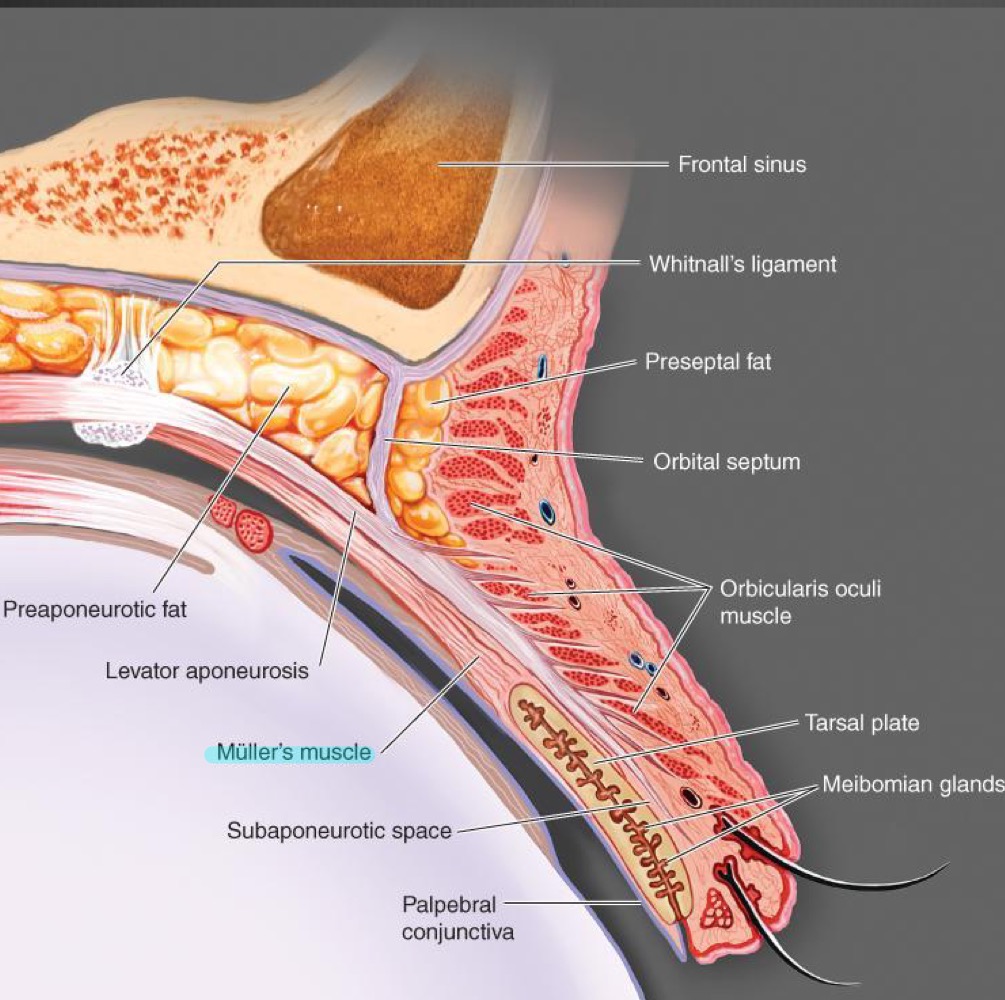
New cards
What does the Mueller's muscle do? What type of muscle is it?
it holds the lid once its been lifted, smooth muscle
56
New cards
What is the levator aponeurosis?
Orbital septum
57
New cards
What is the function of the levator aponeurosis?
barrier, travels around the whole eye
58
New cards
What is the tarsal plate?
reinforcement for the lid, where the Meibomian (tarsal) glands
59
New cards
In the lid we can find palpebral conjunctival ___ and ___.
stroma and epithelium
60
New cards
Layers that can be found in the lid epidermis and dermis
basal cell, prickle cell, granular, keratinized, rete pegs, lid skin
61
New cards
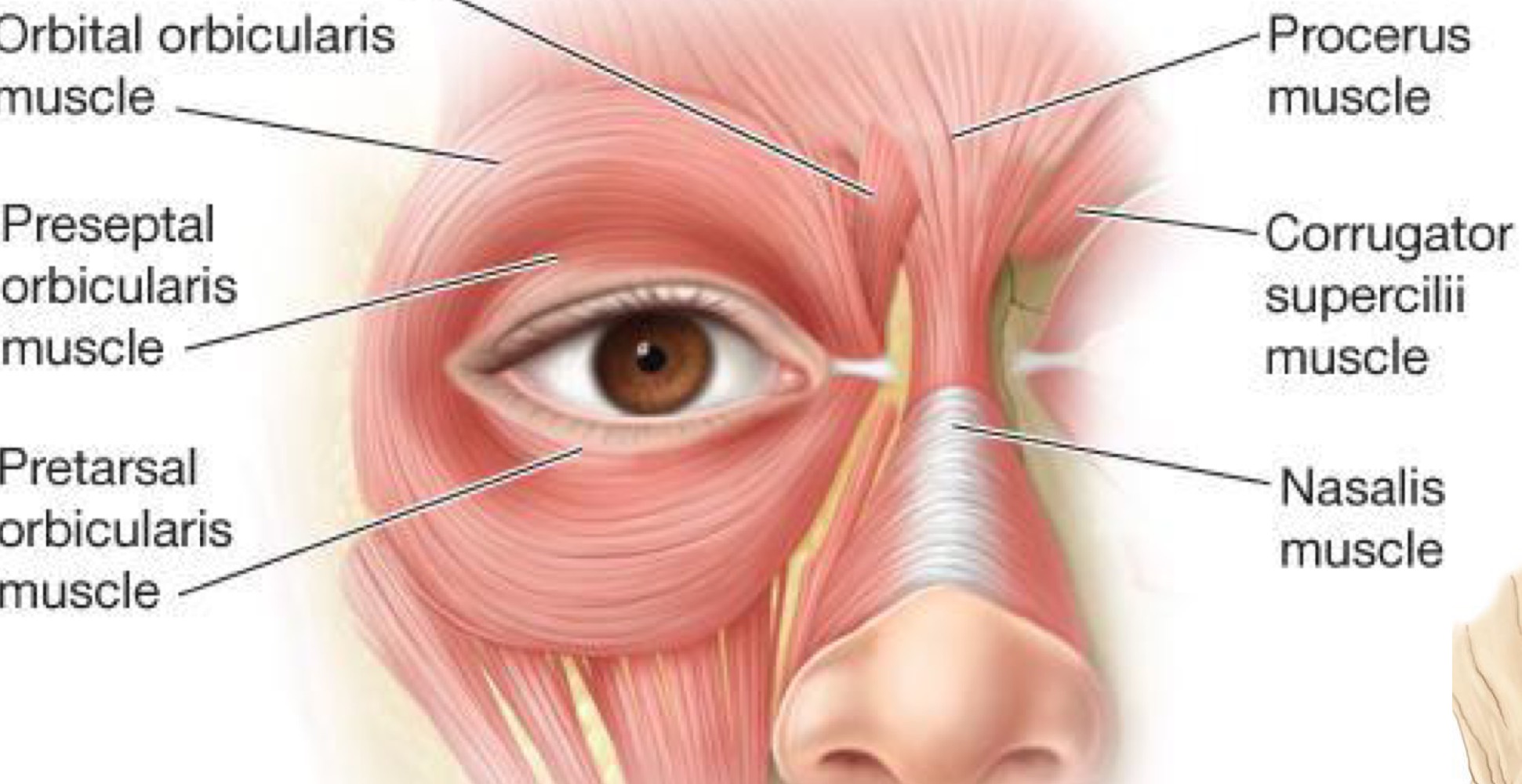
What are the subparts of the orbicularis oculi muscle?
orbital, preseptal, pertarsal, muscle of riolan, horner's muscle
62
New cards
orbital part of the OOM
portion that is over/outside the bone, outermost section
63
New cards
Preseptal part of OOM
below the orbital rim
64
New cards
Pretarsal part of the OOM
overlies the tarsal plate, getting closer to the lid margin
65
New cards
Muscle of Riolan part of OOM
rims the lid margins, upper and lower
66
New cards
Horner's muscle part of OOM
where the superior and inferior muscle of riolan fuse at the medial canthus and attach to the bone
67
New cards
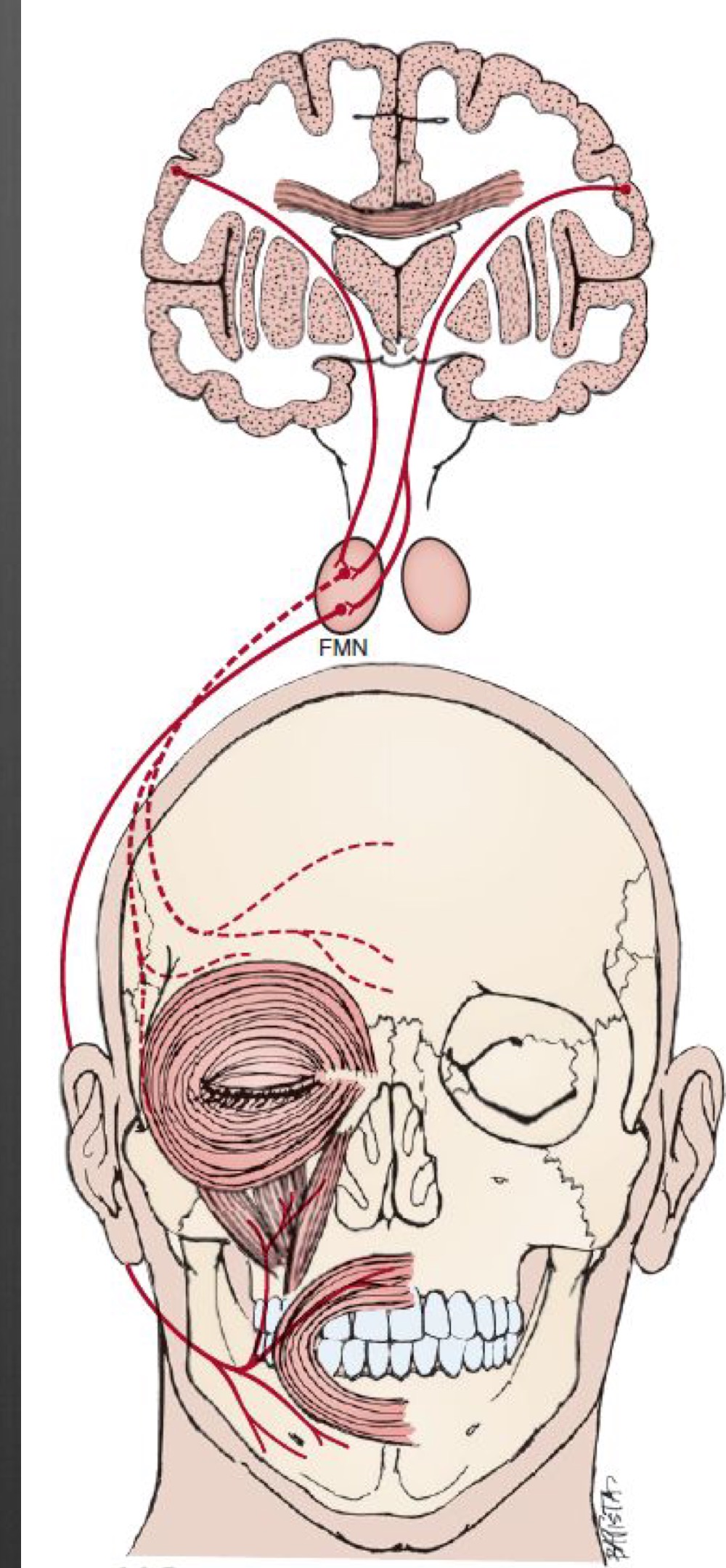
inputs to the portion of the motor nucleus of CN VII serving the temporal branch are ___
bilateral
68
New cards
If there is a lesion below the moto nucleus of CN VII, is bilateral cortical representation affected? How will the lid close?
Bilateral representation IS affected, lids WILL NOT close effectively
69
New cards
What type of tissue is the orbital septum? Where is it?
striated white tissue that runs all the way around the lids
70
New cards
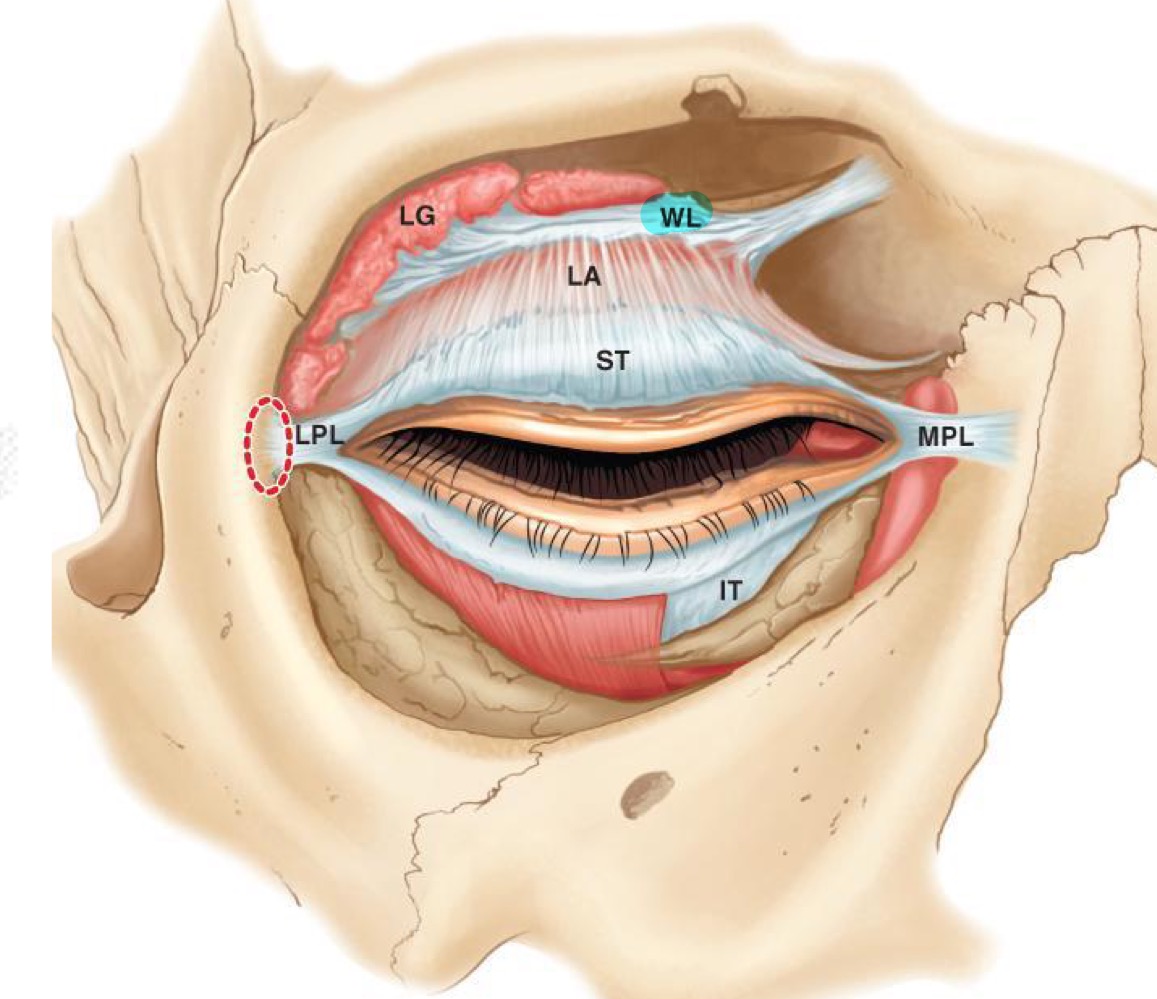
What is Whitnall's Ligament?
large CT band that connects to upper medial portion behind the orbital rim, and then runs right along the levator all the way across to lacrimal gland
71
New cards
What type of tissue is the tarsal plate
dense connective tissue
72
New cards
What are the glands of the lids
Sebaceous, accessory, moll-modified sweat, eccrine (merocrine), meibomian, glands of zeiss, glands of moll, goblet cells
73
New cards
What do the lateral palpebral arteries arise from?
lacrimal artery
74
New cards
What do the medial palpebral arteries arise from?
ophthalmic artery
75
New cards
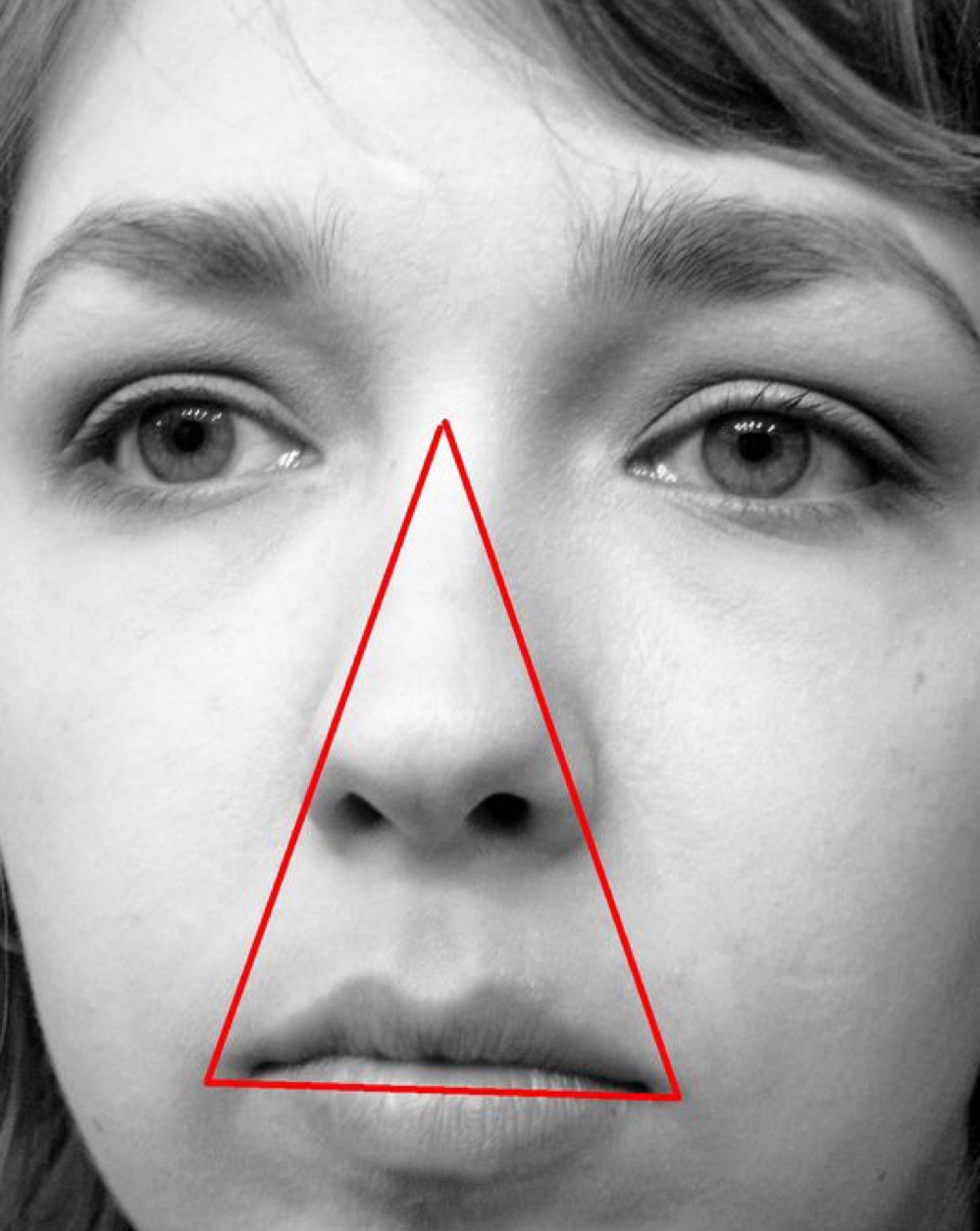
Why is this area considered a danger zone?
infections in this area can cause cavernous sinus thrombosis or brain abscess
76
New cards
where drainage of the face goes into the _____ _____.
cavernous sinus
77
New cards
what type of gland is the lacrimal gland?
exocrine
78
New cards
what is pathway of tears in the nasolacrimal system?
Lacrimal gland → Inferior puncta → Lacrimal sac → Nasolacrimal duct → Inferior concha/meatus
79
New cards
Blink cycle
1. lid is open
2. lacrimal sac is at atmospheric pressure and is filled with tears
3. initiate a blink
4. lacrimal sac is squeezed
5. tears are squirted out the bottom into inferior meatus
6. valve of Hasner closes after tears are deposited
7. lids come together
8. both puncta are immersed in lacrimal lake and draw in fluid to reinflate the sac (relieve negative pressure)
2. lacrimal sac is at atmospheric pressure and is filled with tears
3. initiate a blink
4. lacrimal sac is squeezed
5. tears are squirted out the bottom into inferior meatus
6. valve of Hasner closes after tears are deposited
7. lids come together
8. both puncta are immersed in lacrimal lake and draw in fluid to reinflate the sac (relieve negative pressure)
80
New cards
What animal does the human embryo represent?
fish
81
New cards
What is the branchial apparatus composed of?
branchial arches, branchial grooves, pharyngeal pouches
82
New cards
When do the branchial arches appear?
3rd week
83
New cards
How many branchial arches are there? Which are vestigial?
6 arches, 5th and 6th are vestigial
84
New cards
What are the first 2 branchial arches named?
1. Mandibular
2. Hyoid
2. Hyoid
85
New cards
What are the divisions of the 1st branchial arch?
(smaller) upper maxillary processes
(larger) lower mandibular processes
(larger) lower mandibular processes
86
New cards
What process is above the mandibular arch?
frontonasal process
87
New cards
What does each arch contain
aortic arch artery, cartilaginous bar, somemuscle, cranial nerve
88
New cards
what CN innervates the 1st arch?
CN V
89
New cards
what CN innervates the frontonasal process?
CN V1
90
New cards
what CN innervates the maxillary process of arch 1?
CN V2
91
New cards
What CN innervates the mandibular process of Arch 1?
CN V3
92
New cards
What CN innervates the 2nd branchial arch?
CN VII - muscles of arch 2 are muscles of facial expression
93
New cards
What CN innervates the 3rd branchial arch?
CN IX - glossopharyngeal, pharynx, esophagus
94
New cards
What CN innervates the 4th-6th arch?
CN X (recurrent laryngeal branches of CN X)
95
New cards
What is each arch lined with on the inside and outside? What do the linings cover?
1. inside - endoderm
outside - surface ectoderm
2. mesoderm and neural crest
outside - surface ectoderm
2. mesoderm and neural crest
96
New cards
What are the pinches inside and outside of the branchial groove called?
inside - pharyngeal pouch
outside - branchial groove
outside - branchial groove
97
New cards
What arches is branchial groove #1 between? Does it remain in adults?
Between Arch 1 and 2, remains in adults as external meatus
98
New cards
Do arches 3-6 remain in adults?
No, covered by fusion of arch 3 and 4-6 to produce a temporary cervical sinus
99
New cards
What does the temporary cervical sinus in embryos become in adults?
neck
100
New cards
What do all of the pharyngeal pouches become?
1st pouch - pharyngotympanic (eustachian) tube from middle ear cavity to back of oropharynx
2nd pouch - ducts of palatine tonsils
3rd pouch - lower parathyroids
4th pouch - upper parathyroids
5th-6th pouch - ultimobranchial bodies which give parafollicular cells of thyroid contributing to regulation of calcium
2nd pouch - ducts of palatine tonsils
3rd pouch - lower parathyroids
4th pouch - upper parathyroids
5th-6th pouch - ultimobranchial bodies which give parafollicular cells of thyroid contributing to regulation of calcium