Development/Classification of Bones & Joints
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is ossification?
The process by which bone form within the body
What is intramembranous ossification?
Occurs rapidly/takes place in bones that need protection (bone replaces membrane)
What is the ossification that forms flat bones of the calvaria(skull cap)?
intramembranous ossification
What is endochondral ossification?
When bone replaces cartilage and is much slower than intramembranous ossification.
What is the ossification that forms long bones and occurs in most parts of the skeleton?
endochondral ossification
The primary center of ossification in growing bones is called:
Diaphysis; which becomes the body in a fully developed bone.
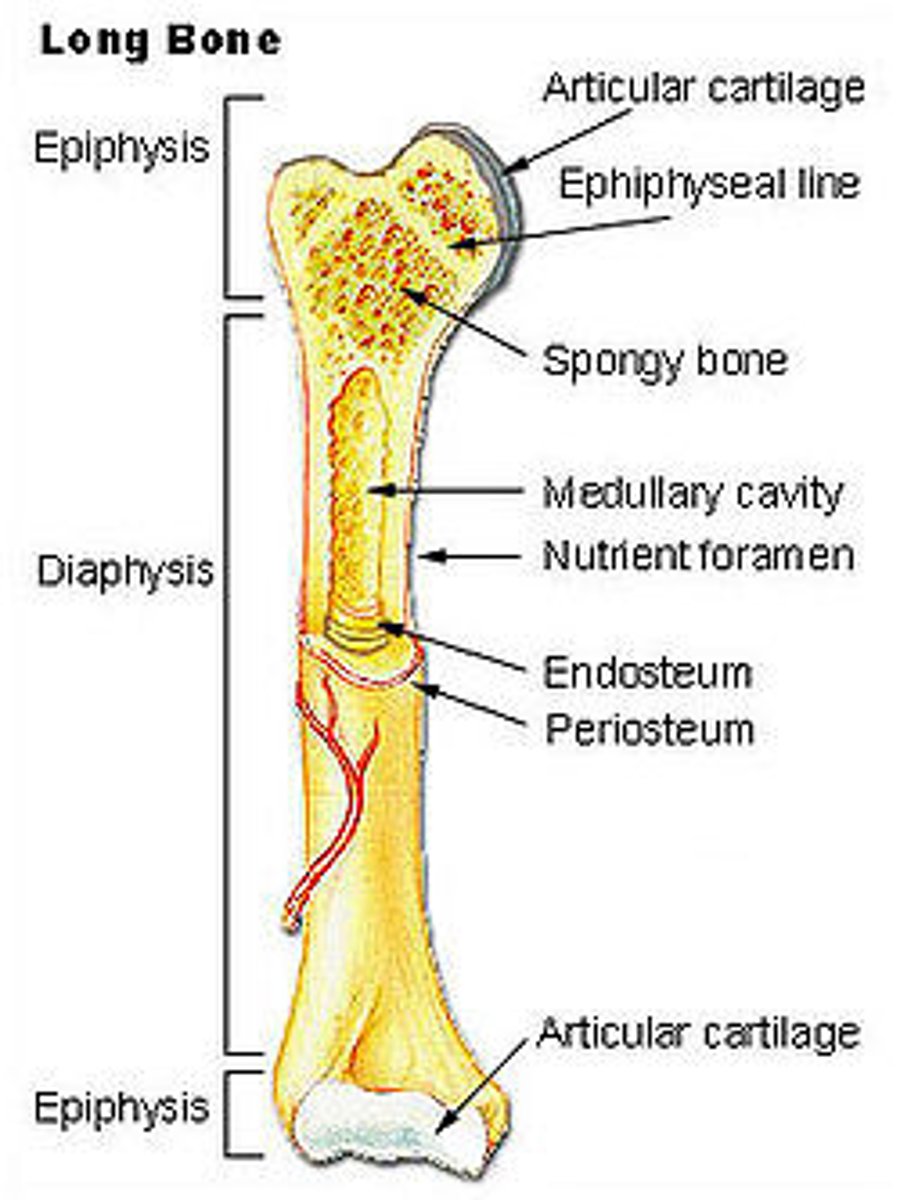
The secondary center of ossification that appears near ends of long bones is called:
Epiphysis
Which center of Endochondral ossification appears after birth?
Secondary center: epiphysis
Which center of Endochondral ossification appears before birth?
Primary center: diaphysis
When does epiphyseal fusion of long bones occur?
Age of puberty (20-25 years)
What cartilaginous plates are found between the metaphysis and each epiphysis until skeletal growth is complete?
Epiphyseal plates
How many bones do we have?
206 bones
What are the 4 classification of bones?
long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones
Which bone consists of a body and 2 ends/extremities? Commonly found in the appendicular skeleton
Long bones
The outer shell of most bones are composed of hard/dense bone tissue known as:
Compact bone/cortex (external layer)
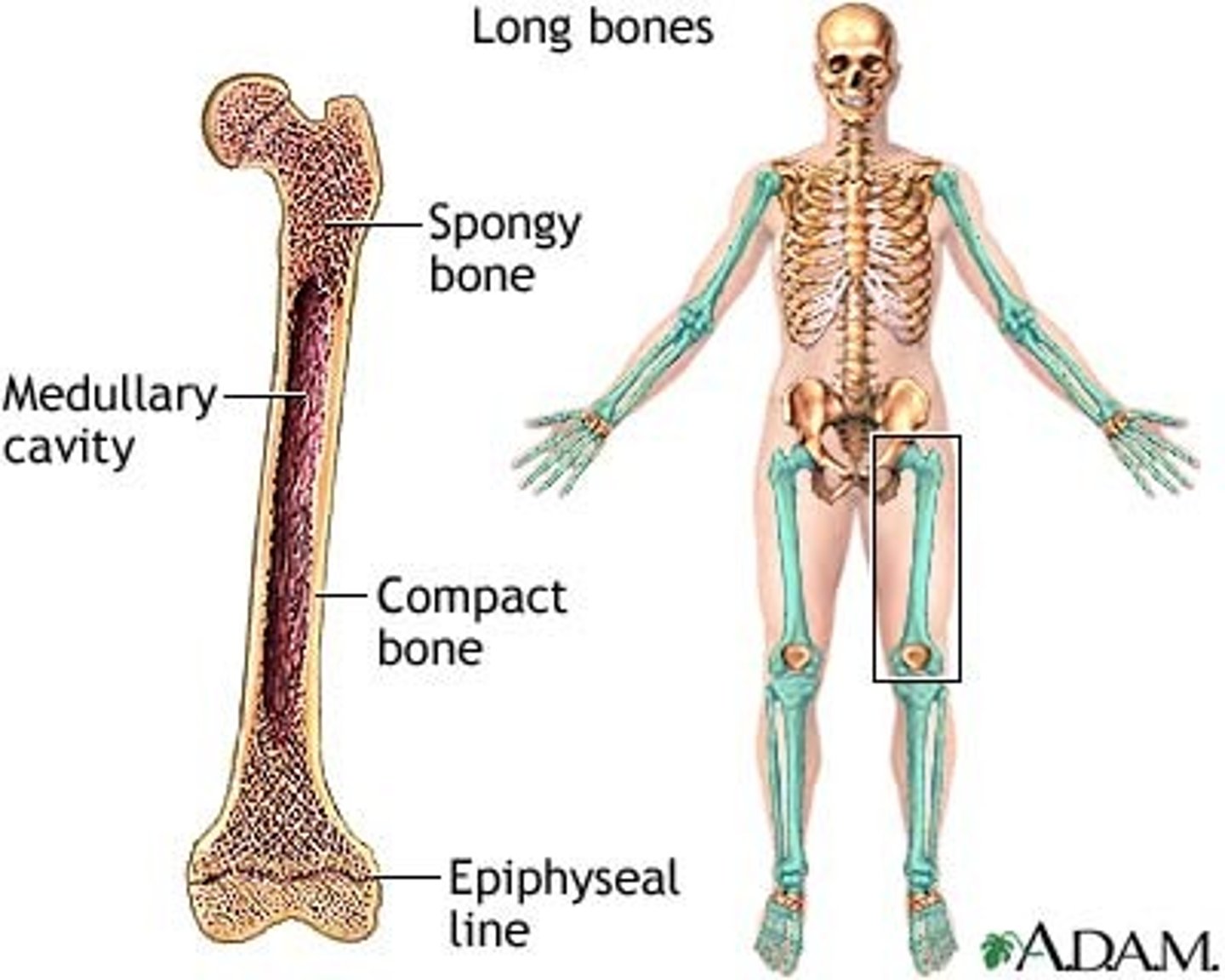
What is found inside the shell of compact bone (especially both ends of long bone) and contains red bone marrow (produces red blood cells)?
Spongy/cancellous bone
What is the hollow portion of bone that contains fatty yellow marrow?
Mendullary cavity
A dense fibrous membrane that covers bone except at articulating surfaces (hyaline layer) is called:
Periosteum
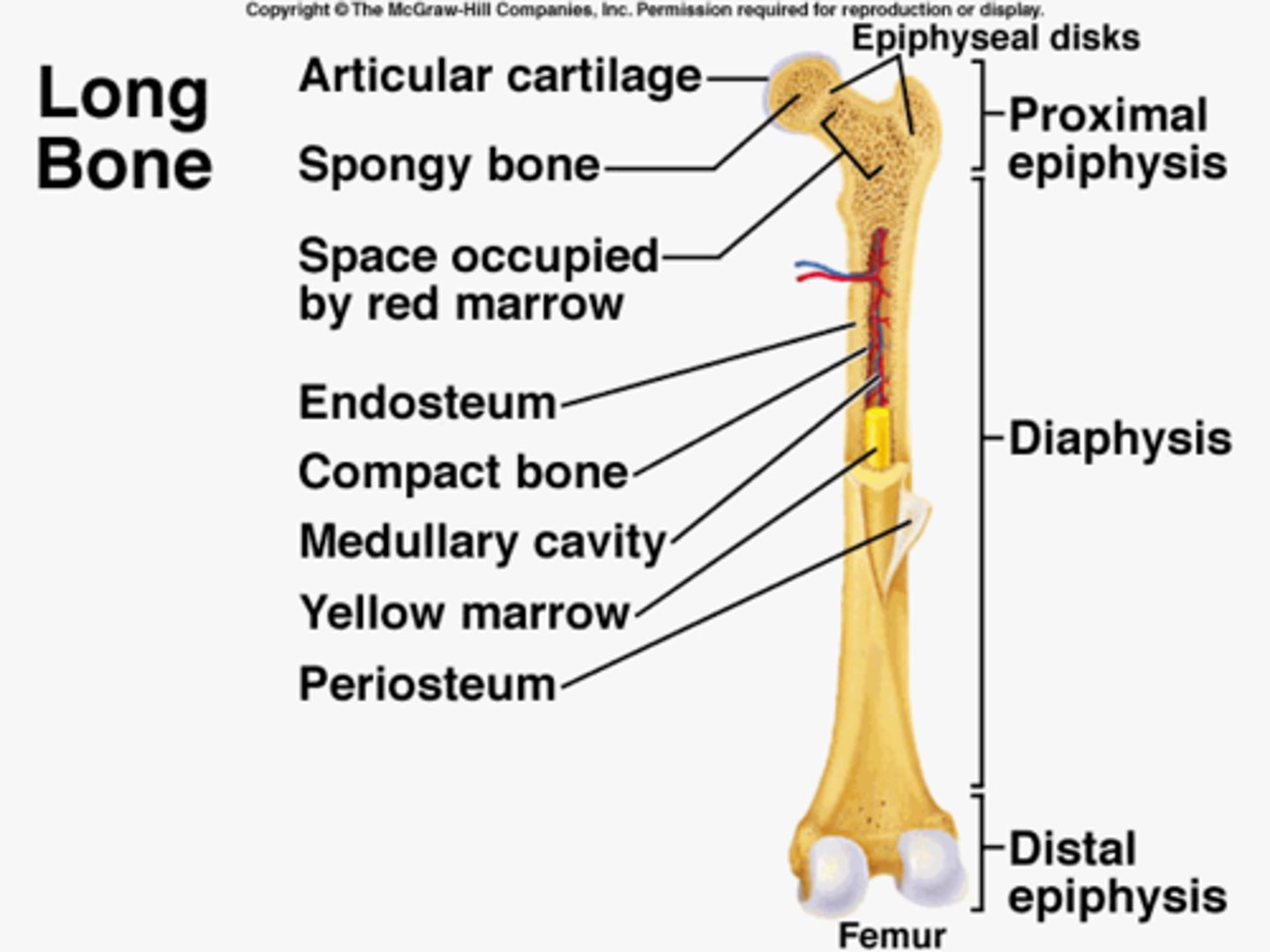
What is essential for bone growth, repair, and nutrients in a long bone?
Periosteum
What is the common type of cartilage/connecting tissue that appears clear/glossy and covers the ends of a long bone (articular cartilage)?
Hyaline cartilage
What bones are roughly cuboidal and found in only wrist/ankles?
Short bones
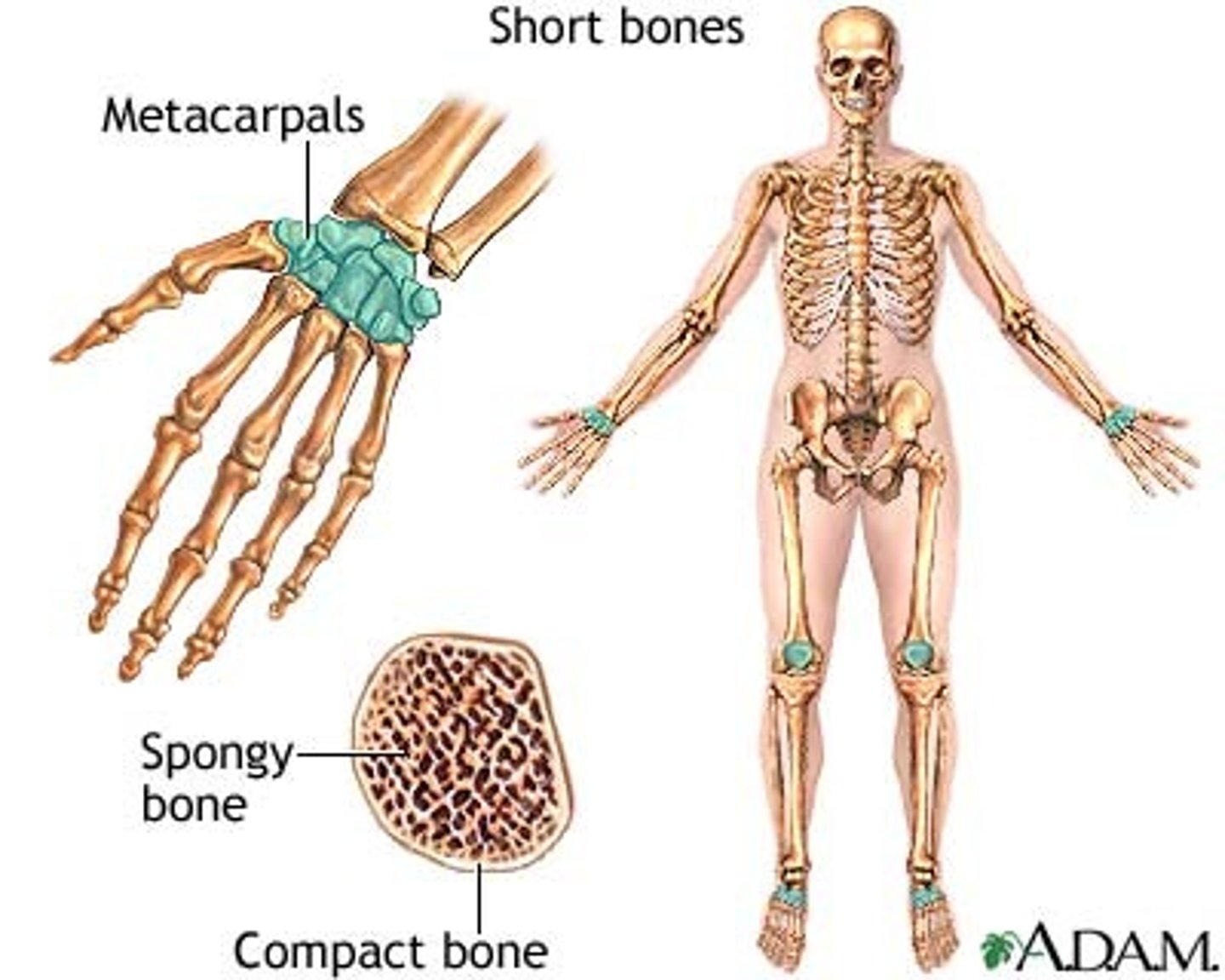
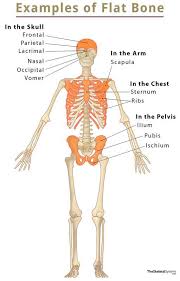
What bone provides protection for interior contents?
Flat bones
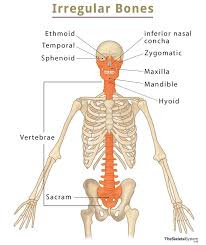
What bones have peculiar(odd) shapes?
Irregular bones
What are the 3 FUNCTIONAL classification of joints?
- synarthroses (nonmovable)
- amphiarthroses (limited movement)
- diarthroses (freely movable)
What are the 3 STRUCTURAL classification joints?
- Fibrous (little to no movement)
- Cartilaginous (limited/slightly moveable)
- Synovial (freely movable)
Roots around teeth, skull sutures, and distal tibiofibular joint
are all examples of what structural classification joint?
Fibrous
Epiphyses, vertebrae/intervertebral disk spaces, symphysis pubis, and the sternum are all examples of what structural classification joint?
Cartilaginous
What structural classification joint is found in upper/lower limbs, and contain synovial fluid?
Examples include: First carpometacarpal of thumb, proximal radioulnar joint (near elbow), interphalangeal joints, and hip joints.
Synovial
What are the 3 type of fibrous joints?
- Sultures (immovable)
- Gomphoses (limited movement)
- Syndesmoses (slightly movable)