Comprehensive Cardiac Physiology: Heart Anatomy, Valves, and Cardiac Cycle (1)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the three main functions of the cardiac system?
Transportation, Defense, and Regulation.
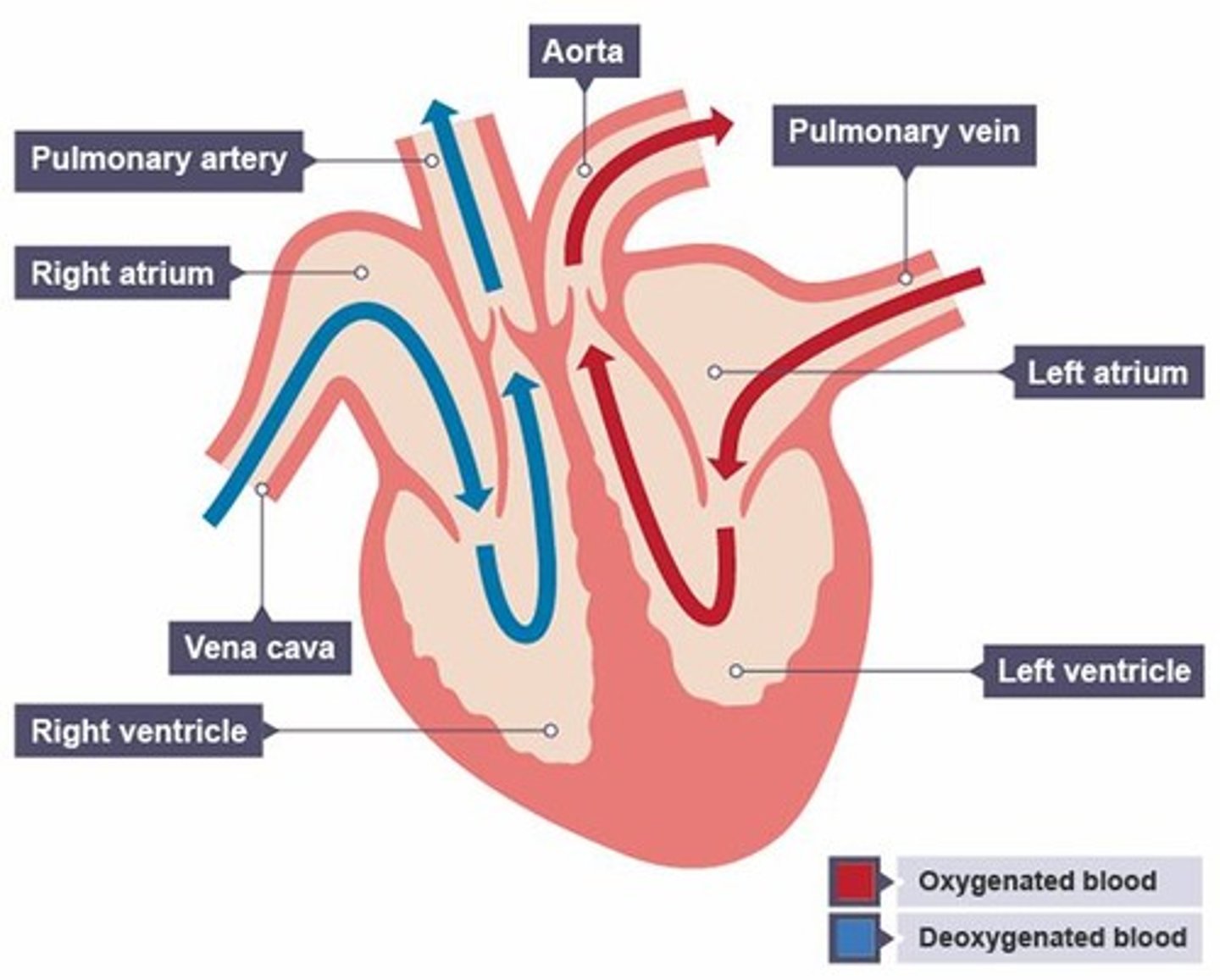
What does the cardiac system transport?
Oxygen, nutrients, waste, and hormones.
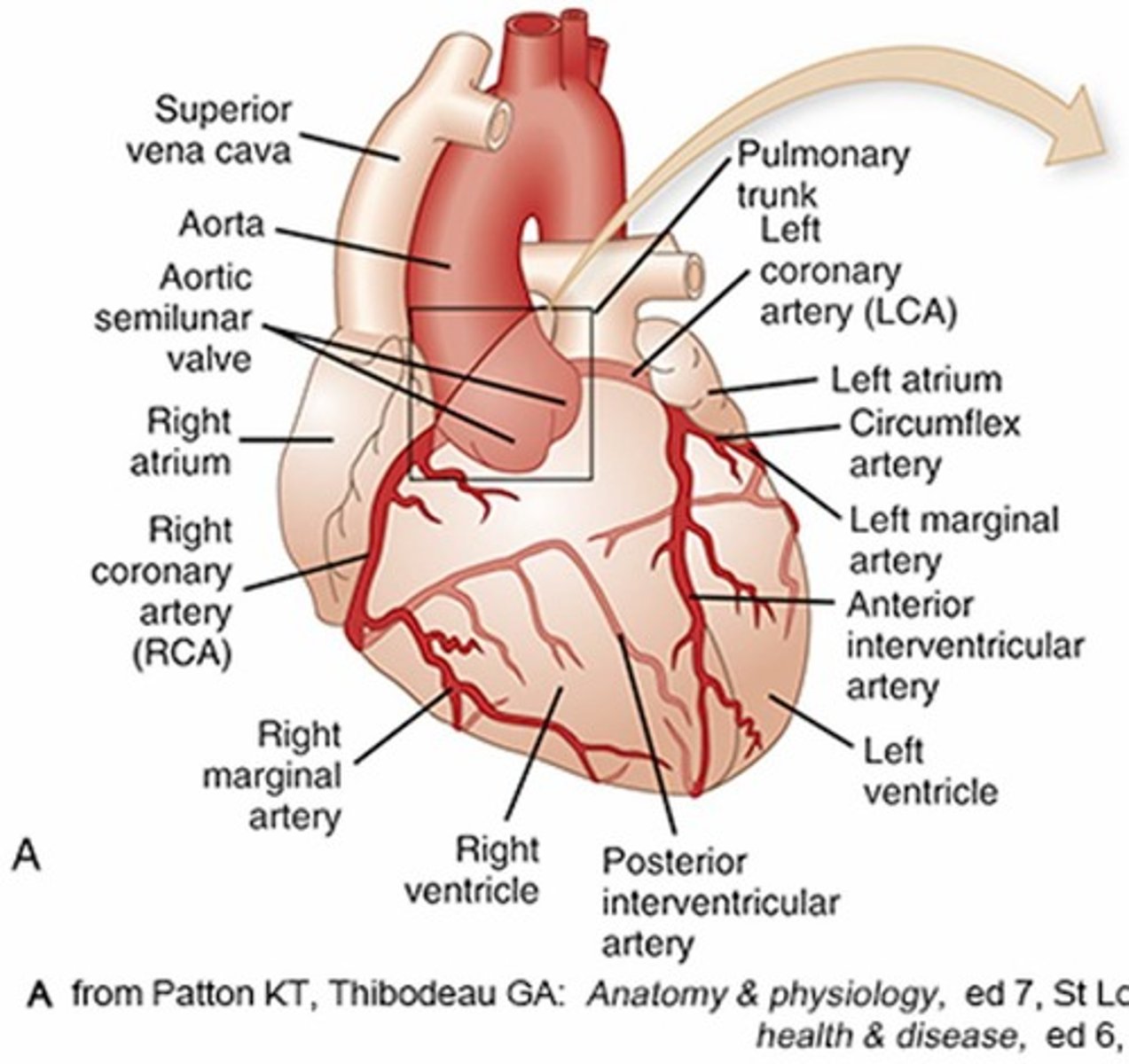
What is the role of white blood cells in the cardiac system?
They are part of the defense mechanism.
What does the cardiac system regulate?
Temperature, pH, and osmotic pressure.
What are the two vascular loops in the circulatory system?
Pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
What side of the heart is oxygenated?
The left side.
What side of the heart is not oxygenated?
The right side.
What are the upper and lower chambers of the heart called?
Upper chambers are atria; lower chambers are ventricles.
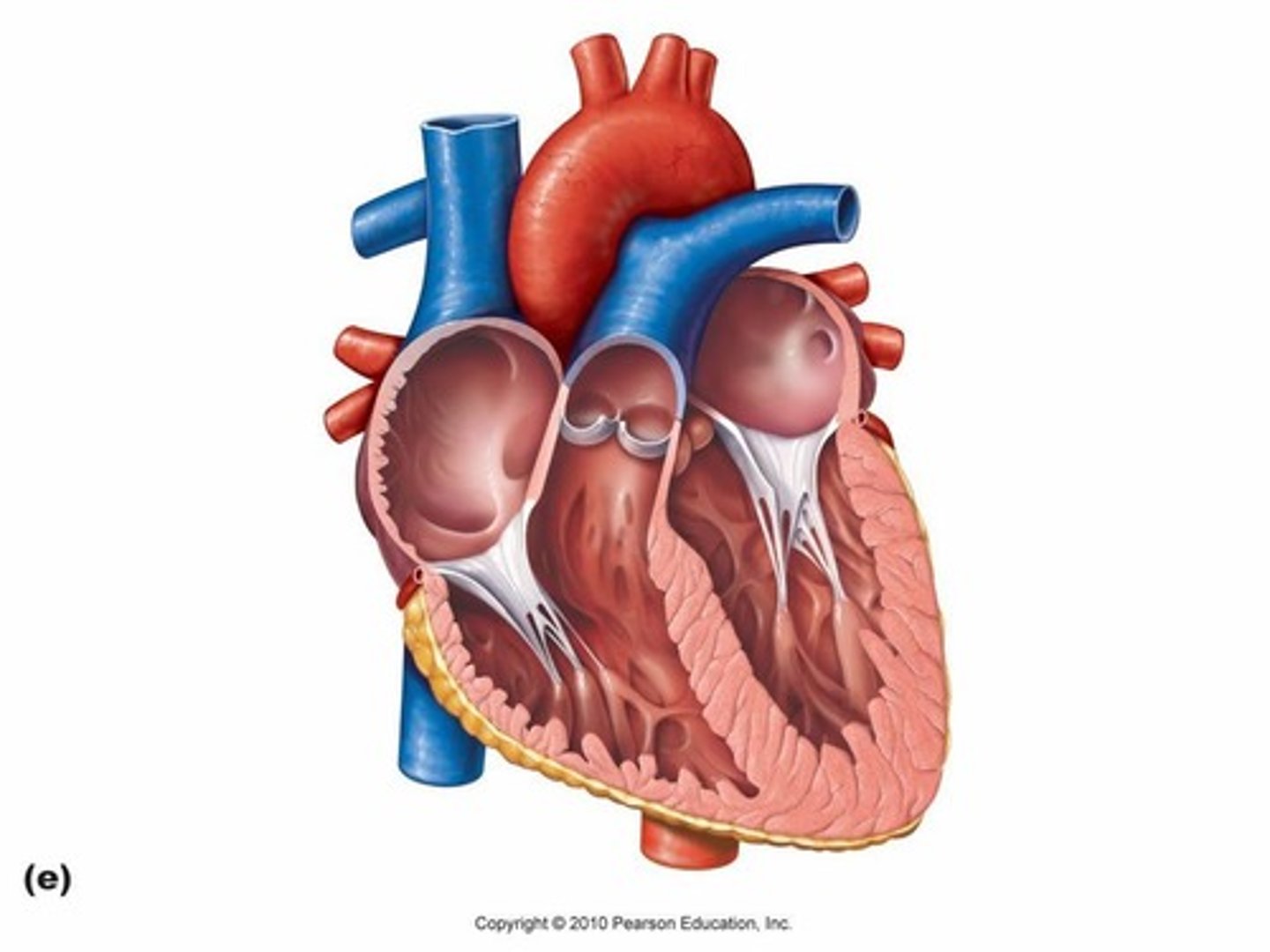
What are the atrioventricular valves?
Valves between the atria and ventricles that allow blood flow during ventricular emptying.
What are semilunar valves?
Valves between the ventricles and arteries that prevent backflow into the ventricles.
What is the aorta?
The large artery that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body.
What is the tricuspid valve?
The right atrioventricular valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle.
What is the mitral valve?
The left atrioventricular valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
What phases are involved in the cardiac cycle?
Atrial systole, ventricular systole (two phases), and ventricular diastole (two stages).
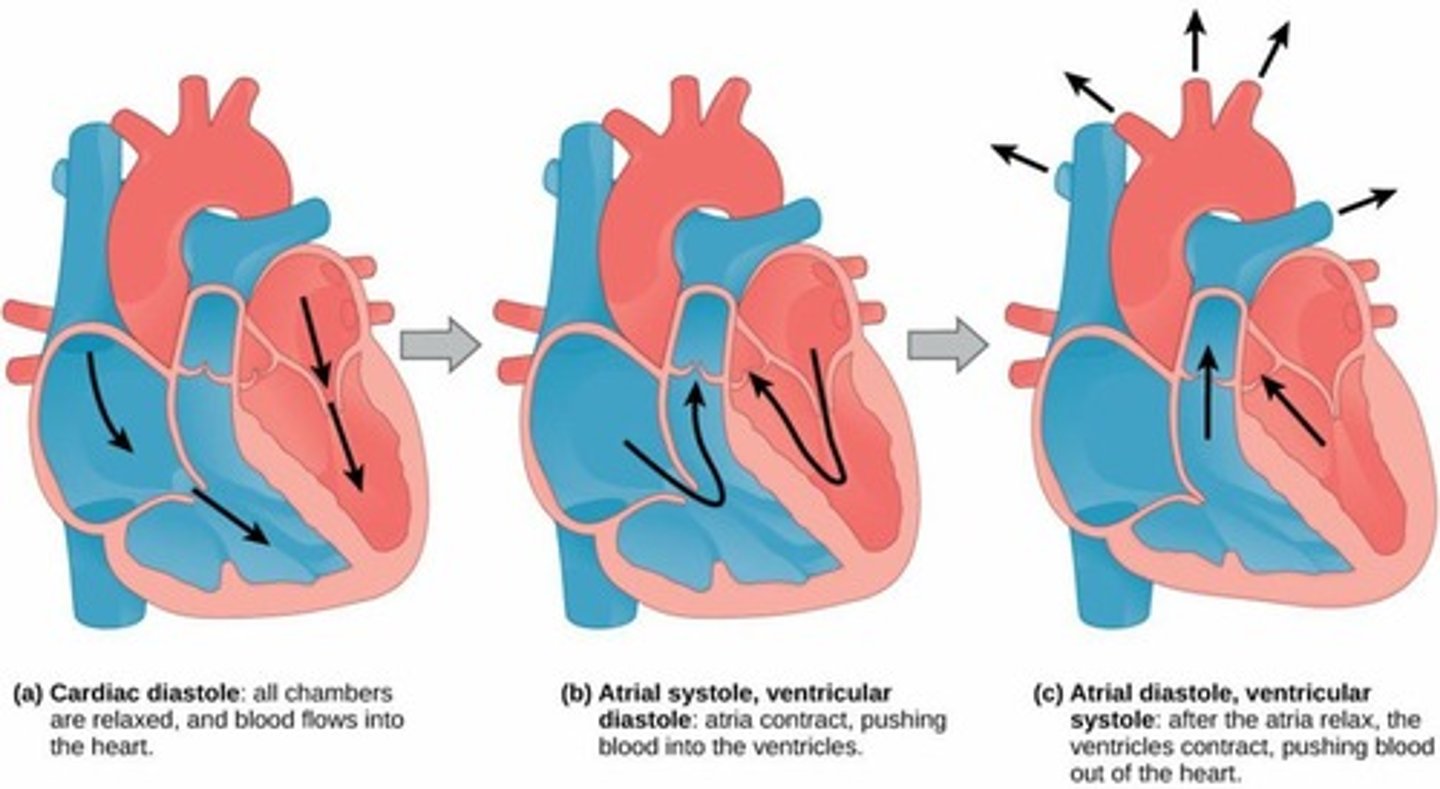
What is systole?
The contraction phase of the cardiac cycle.
What is diastole?
The relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle.
What is coronary circulation?
The blood supply to the heart muscle, providing oxygen and nutrients.
What are intercalated discs?
Structures that connect cardiac muscle fibers, forming a functional syncytium.
What is the pericardium?
A sac-like membrane that protects and surrounds the heart.
What are the functions of the pericardium?
Cushions the heart, holds it in place, prevents over-expansion, protects from infections, and provides lubrication.
How does the heart respond to changes in oxygen requirements?
Coronary blood flow is adjusted accordingly.
What is the significance of the heart being described as two pumps?
The left heart pumps to the systemic circuit, while the right heart pumps to the pulmonary circuit.