Metabolism and Photosynthesis Flashcards
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the key concepts of photosynthesis, plant structure, and related functions from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
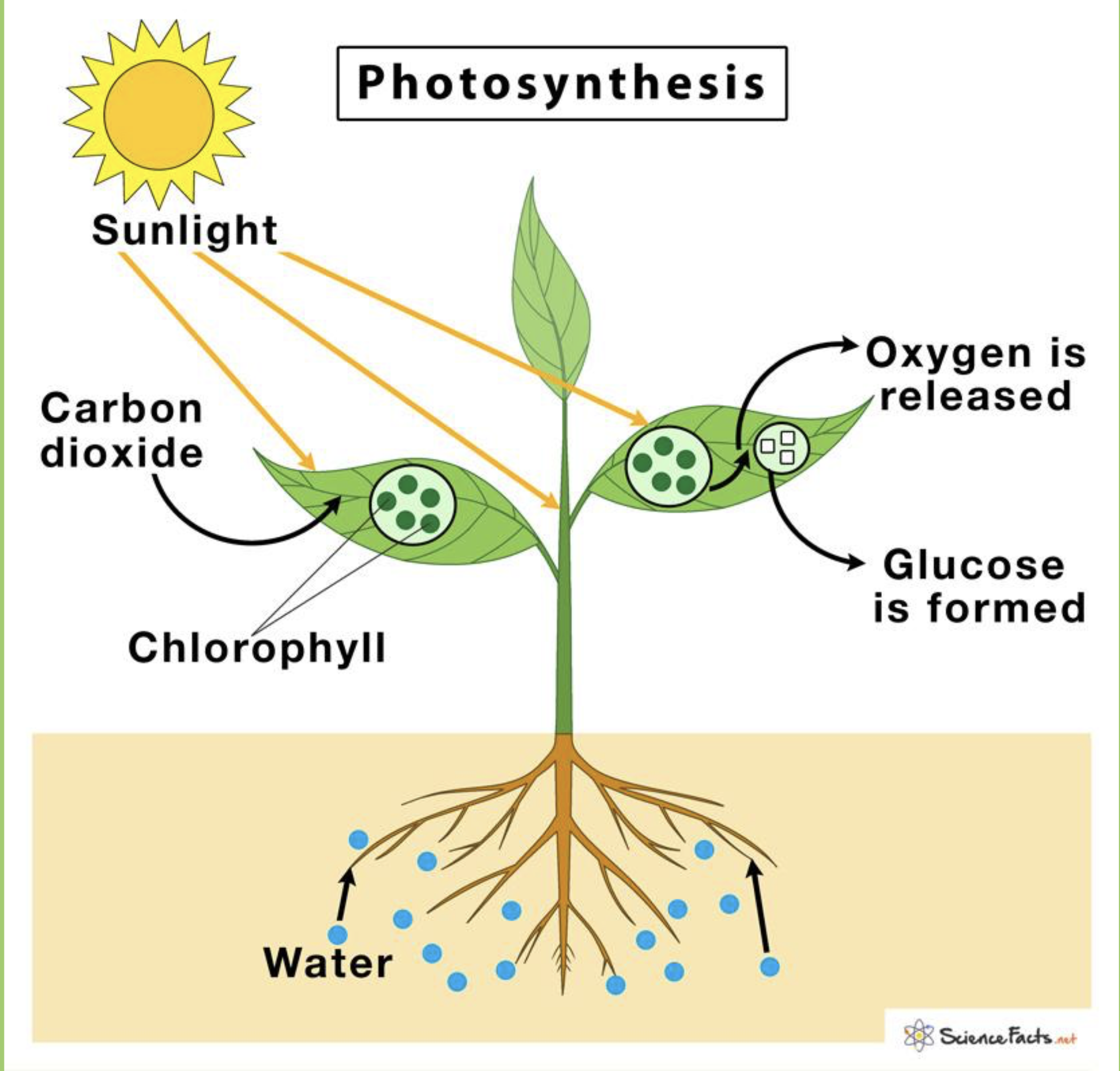
Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in plants that captures solar energy for photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts
organism that contains the chemical chlorophyll that captures solar energy
O2 and CO2 - Gas Exchange
The process by which oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants during photosynthesis and respiration.
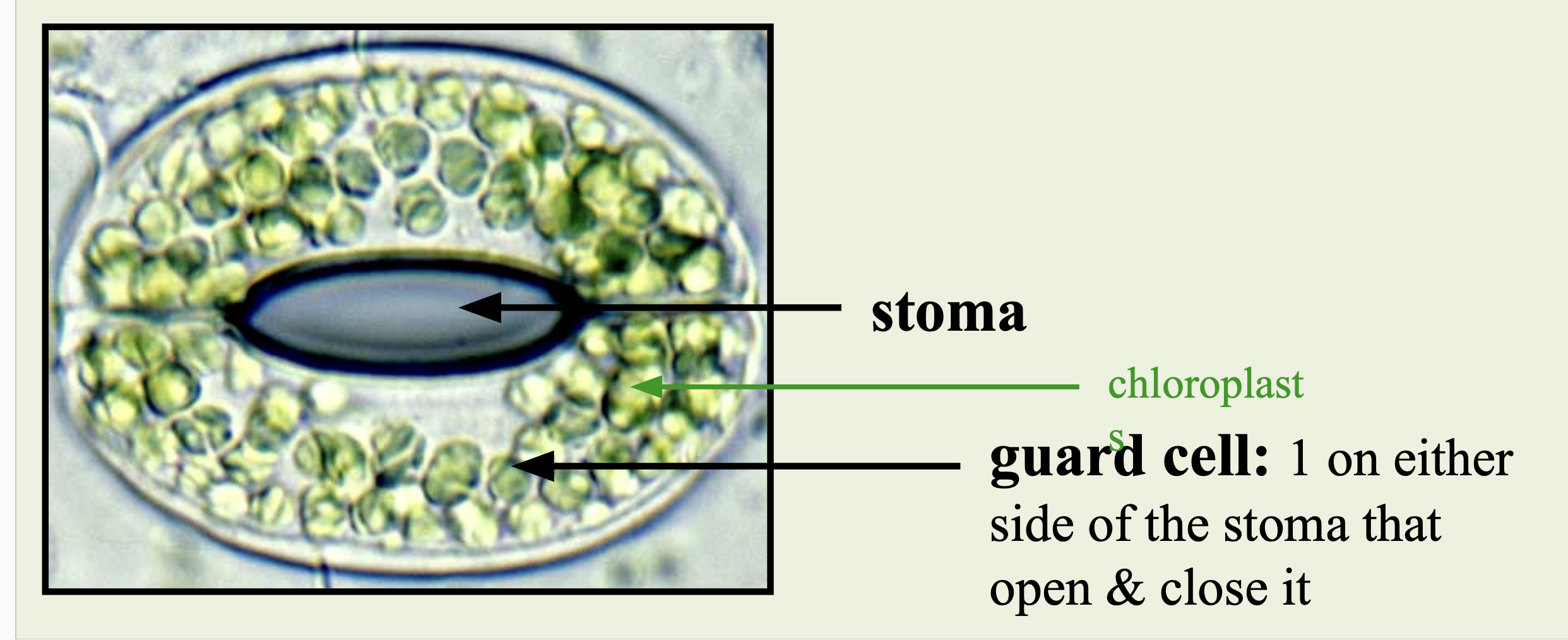
Stomata
Openings in the leaf that allow gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen to be exchanged.
Guard Cells
Specialized cells that control the opening and closing of stomata.
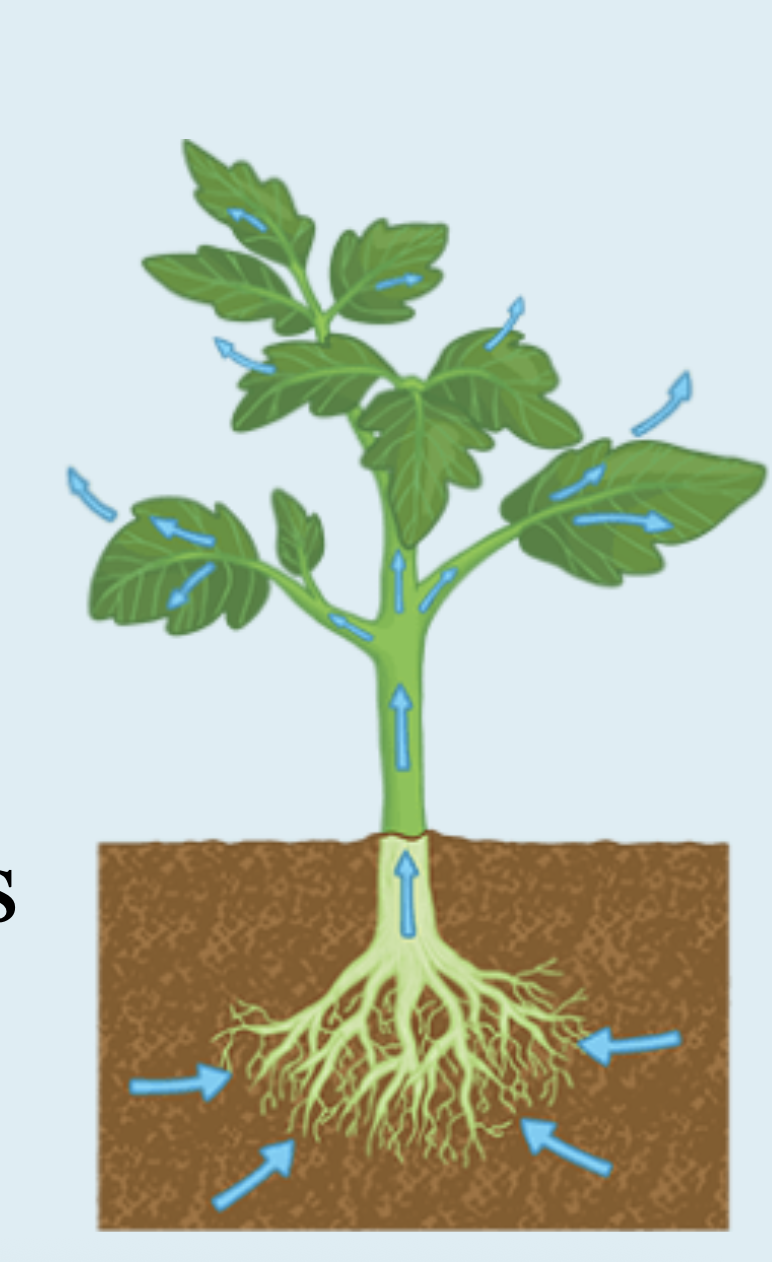
Transpiration
The loss of water through the leaf due to evaporation.
guard cells are open, water is “sucked” upwards like a straw
guard cells must balance gas exchange with potential loss of water
Cuticle
A waxy protective layer on plant surfaces that helps prevent water loss and keeps unwanted substance out.
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants.
Vacuole
A large, central space in plant cells that stores water and helps maintain turgor pressure.
Cell wall
plants lack a skeletal system and need to be upright towards the sun for photosynthesis
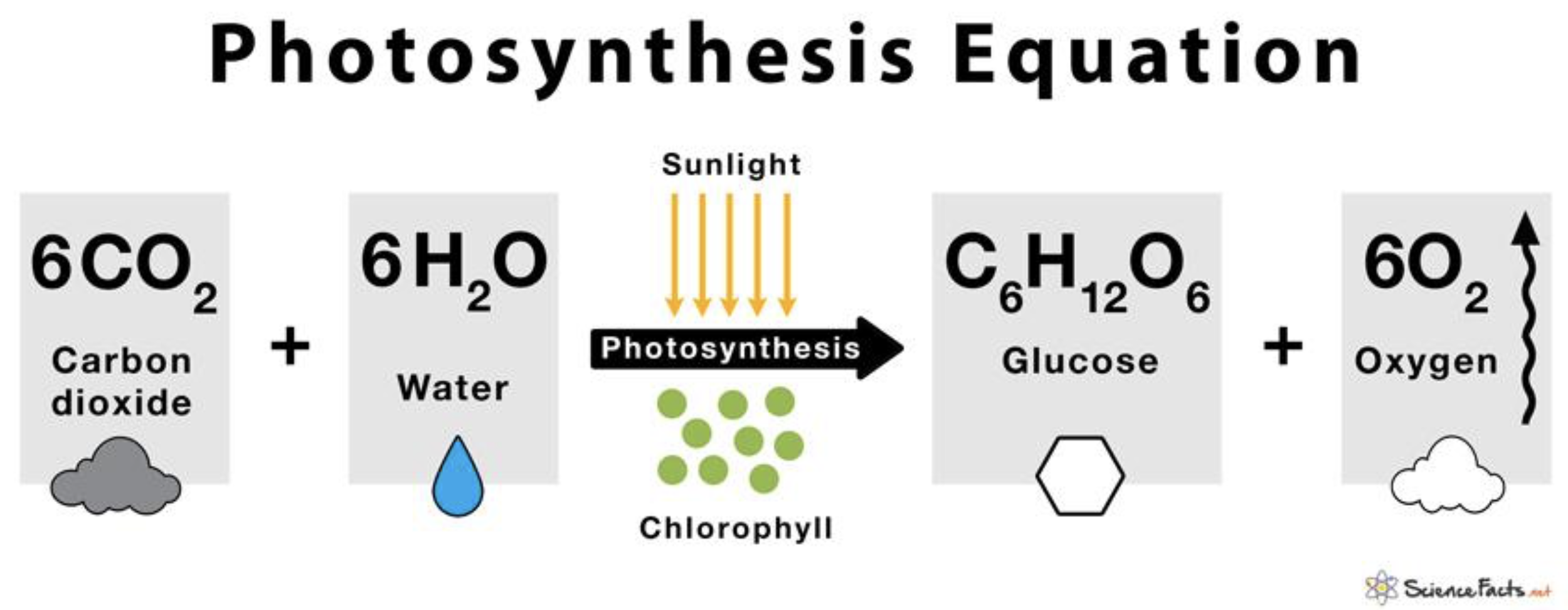
Photosynthesis Equation
The process by which plants convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy in the form of glucose, with oxygen as a byproduct. The general equation is 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
Root function
Roots anchor the plant, absorb water and nutrients, and store energy.
Transport Tissues
Specialised tissues in plants, including xylem and phloem, that facilitate the movement of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
Xylem
Vascular tissue that transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves.
Phloem
Vascular tissue that transports sugars produced in the leaves to other parts of the plant.