A&P 1: Module 3 exam
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Explain why a patient with liver disease would have intolerance to fatty foods.
The liver produces bile which breaks down fats. If it is not producing bile (or less bile), fats will not be broken down effectively.
Explain in detail how stomach contents enter small intestine
The pyloric sphincter valve, located at the base of the stomach, relaxes causing a small quantity of chyme to pass through the opening into the first part of the small intestine. This initiates a reflex that causes the muscles of the sphincter to contract and close the opening temporarily. Then the sphincter relaxes again and allows more chyme to enter.
A patient experiencing vitamin toxicity. What type of vitamin would be causing this toxicity?
A. Water soluble vitamin
B. Fat soluble vitamin
C. All of the above
B. Fat soluble vitamin, they are stored within the body's fat stores making it harder for the body to rid itself of them.
Explain each digestive system functions are carried out by the small intestine
Digestion and Absorption
Chemical digestion continues as enzymes from the pancreatic juices break down starches and proteins, and begin digestion of fat.
Mechanical digestion continues as bile breaks down fat into smaller pieces
Absorption begins as digested food molecules, water and fat are absorbed into the bloodstream.
Name and explain four main functions performed by the digestive system
1. Ingestion: when food enters the mouth
2. Digestion: food breakdown occurs when food is moved, mixed and exposed to enzymes along the gastrointestinal tract. Divided into two parts, mechanical and chemical.
A. Mechanical occurs when food is broken down in small pieces using the teeth to chew food.
B. Chemical is the breakdown of food by enzymes
3. Absorption: the process of loving digested food into the bloodstream
4. Defecation: the excretion of indigestible food from the anus
What is the purpose of hormone Ghrelin?
A. Increase hunger, decrease satiety
B. Increase hunger, increase satiety
C. Decrease hunger, increase satiety
D. Decrease hunger, decrease satiety
A. Increase hunger, decrease satiety
Which of the following statements is false?
A. The ileocecal valve controls the entrance of chyme into to the large intestine.
B. Taste buds are located on the surface of the mouth and the wall of the pharynx.
C. The liver, pancreas, and tongue are considered accessory organs to the digestive system.
D. The stomach is located along the right side of the abdomen below the diaphragm.
D. The stomach is located along the right side of the abdomen below the diaphragm.
(It is located along the left side of the abdomen below the diaphragm)
True/false: lipids can be divided into two categories: complete or incomplete
False- proteins can be divided into those two categories
True/false: Anabolism combines smaller molecules to make larger molecules
True
True/False: The nasopharynx is the most superior region of the pharynx.
True
True/false: the pharynx has three types of skeletal muscle: circumferential, longitudinal and oblique
False - it only has two, does not include an oblique layer
True/false: the digestive work of salivary amylase is an example of mechanical digestion
False - chemical digestion
Which of the following statements is true concerning glycolysis?
A. Pyruvic acid are broken down into glucose.
B. Five ATP molecules are formed.
C. Glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules.
D. Glucose is broken down into two ADP molecules.
C. Glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules.
Which of the following statements is false concerning the second stage of glucose breakdown?
A. This second stage is also known as the TCA cycle.
B. Pyruvic acid is converted to carbon dioxide.
C. Additional ATP is formed.
D. This is also known as the electron transport system.
D. This is also known as the electron transport system (false)
Which of the following statements is false concerning the Electron Transport System?
A. Anaerobic respiration is more efficient than aerobic respiration.
B. Approximately a total of 34 ATP are formed.
C. Protons are pumped out of the inner mitochondrial membrane.
D. The proton motive force forms ATP molecules.
A. Anaerobic respiration is more efficient than aerobic respiration.
Pancreas
A. Storage site for bile
B. Attached to the soft palate
C. Secretes juices which digest all types of foods
D. Stores glycogen and produces urea
E. Forms food into a bolus
C. Secretes juices which digest all types of food
Stomach
A. Hangs from the cecum
B. Connects mouth to esophagus
C. Attaches to the greater omentum
D. Contains the hepatic flexure
C. Attaches to the greater omentum
Submucosal (layer of tissue):
A. Made of two layers of muscle
B. Innermost layer
C. Secretes mucous
D. Contains blood and lymph vessels
E. Begins in the mouth
D. Contains blood and lymph vessels
Dentin
A. Upper portion of gums
B. Outermost layer
C. Bone-like substance
D. Hard connective tissue
E.Contains longitudinal muscle
C. Bone like substance
Common bile duct
A. Contains secretions from the pancreas
B. Joins with the pancreatic duct
C. Enters the jejunum
D. Contains secretions from the salivary glands
E. Contains lymph vessels and nerves
B. Joins with the pancreatic duct
True/false: the esophagus is considered a primary organ of the GI tract
True
True/false: the tongue is considered a accessory organ of the GI tract
True
True/false: chemical digestion in the mouth is carried out by way of salivary amylase
True
Describe the clinical condition that results when the organ pictured above (specified by the pointer) is not able to function properly.
When the gallbladder is unable to breakdown fat and cholesterol present in the body, gallstones will occur. Pain occurs when these stones block the duct passing from the gallbladder to the liver.
Label the following three types of raised bumps on the tongue.
Describe the purpose of type C.
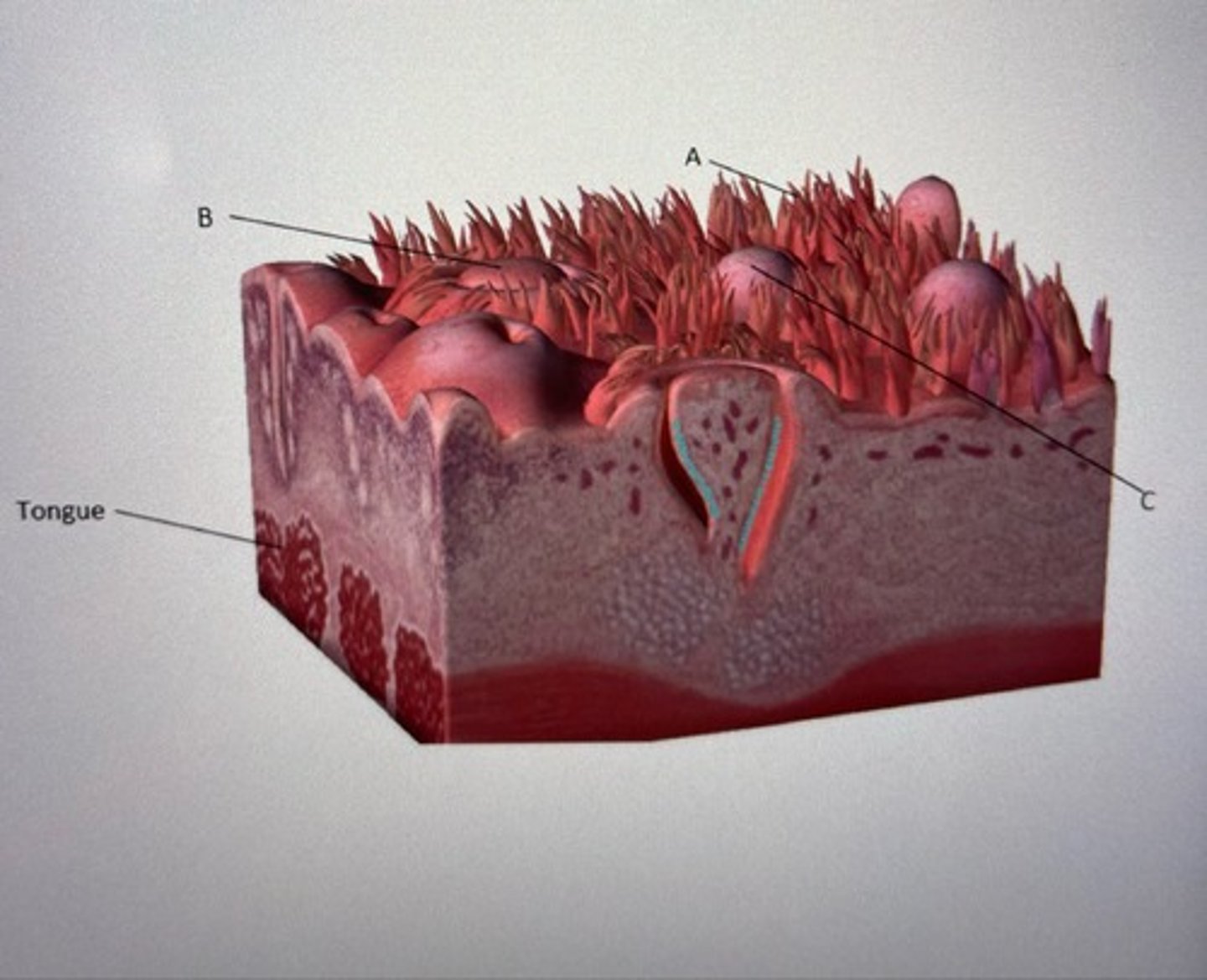
A: filiform papillae
B: circumvallate papillae
C: Fungiform papillae
Describe C: All three are raised bumps on the tongue that work together to grip and move food. Fungiform papillae contains taste buds.
Describe parietal cells and chief cells: name their location, secretions and purposes.
The parietal cells are located in the wall of the stomach body, they secrete hydrocholoric acid, The acidic pH kills bacteria infested with food. The secretion is important for the activation of pepsin.
The chief cells secrete pepsinogen in the stomach. Hydrochloric acid will convert the inactive pepsinogen into active enzyme pepsin, this will help breakdown proteins.
Pancreas
A. Lipase
B. Urea
C. Salivary amylase
A. Lipase
Liver
A. Lipase
B. Urea
C. Salivary amylase
B. Urea
Mouth
A. Lipase
B. Urea
C. Salivary amylase
C. Salivary amylase
Look carefully at the diagram below. Label the following 5 organs of the digestive system.
To receive credit for the intestines you must label the specific region.
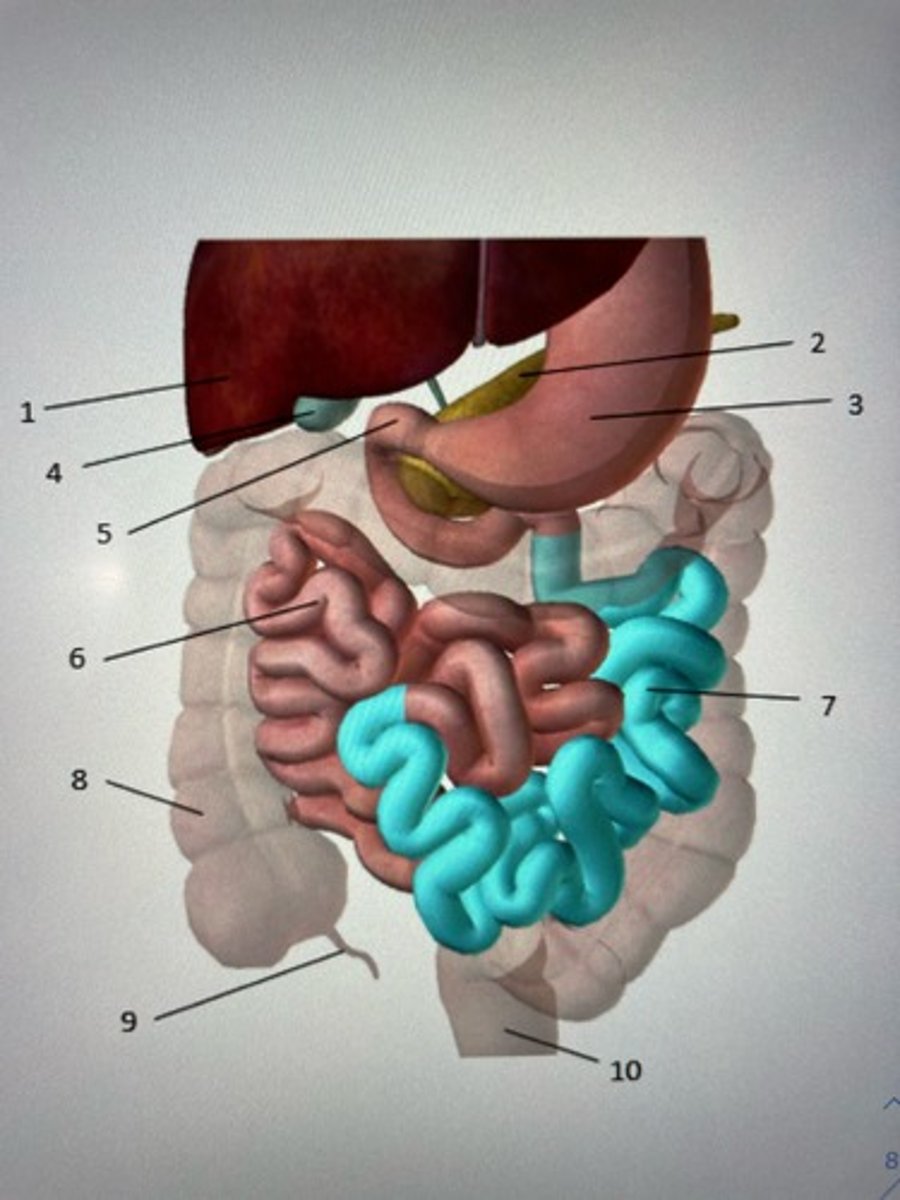
3.
4.
7.
9.
10.
3: Stomach
4: Gallbladder
7: Jejunum
9: Appendix
10: Rectum
Label the diagram below, including left or right. Describe tooth (A).
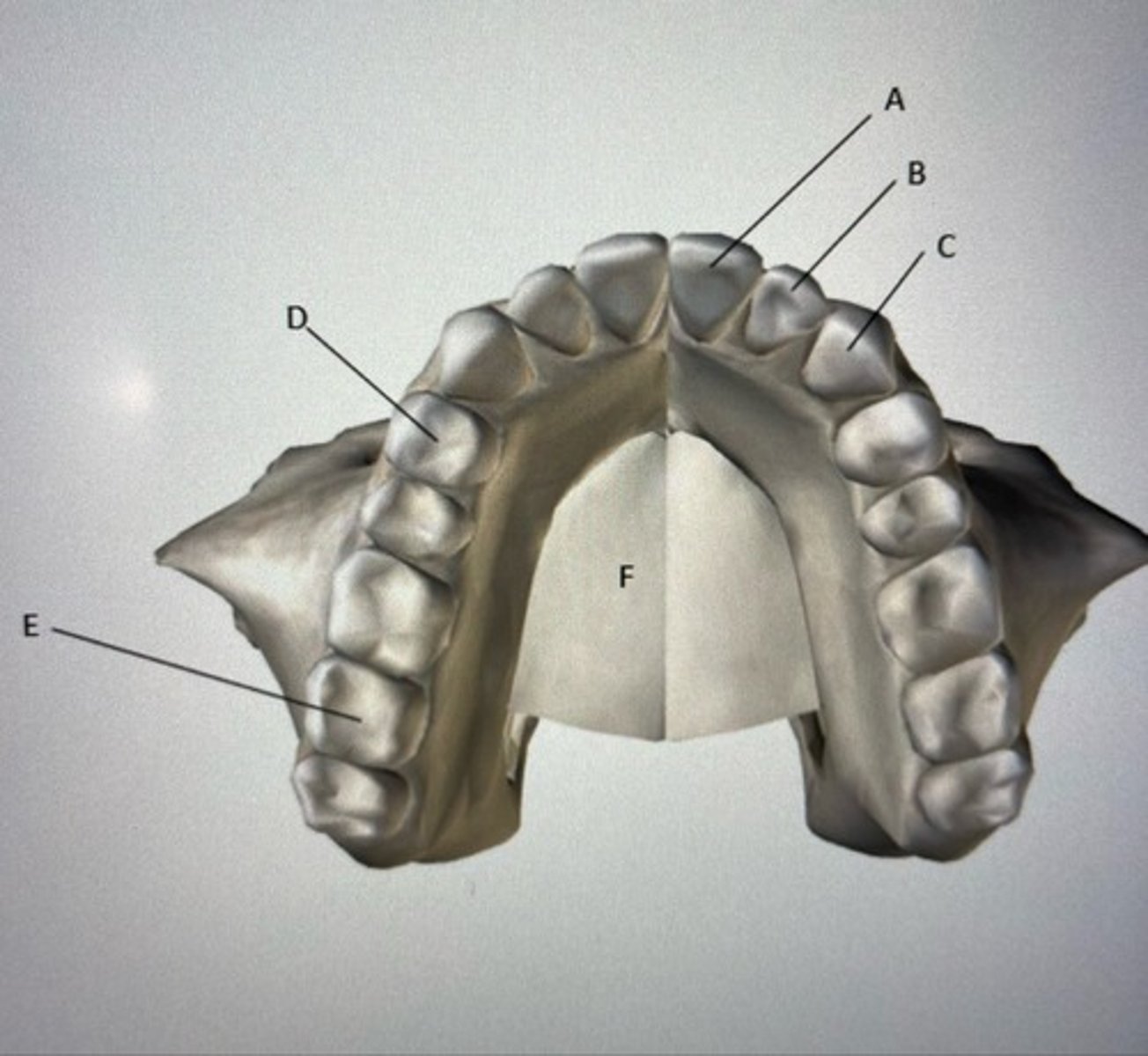
A: Left central incisor
C: Left canine
E: Right molar
F: Maxilla
Describe tooth type A: The central incisor is chisel shaped which is used for tearing.