Lecture 5: Nucleic Acids part 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Huntington’s disease
An autosomal dominant disease
Result of the huntingtin (HTT) gene, repeating a codon multiple times
(Codon is CAG, which codes from amino acid glutamine)
What results from many repetitions of the CAG codon
A mutated protein (mHTT), with a long polyglutamine component
How many repeats are almost guaranteed pathology (you get the disease)
Above 39 times
What causes the disease
Etiology of huntington’s disease
Almost entirely an inherited mutation, with very few cases of spontaneous Huntington’s
Average age of diagnosis
Approx 40 years old
Post-diagnosis, people usually live an additional 15-20 years, though quality of life declines from the time of diagnosis (cognitive/ motor issues)
Slide 6
Major symptoms of huntington’s
Dysregulated motor function
Cognitive dysfunction
Psychiatric disturbances
Dysregulated motor function
Movement disturbances: difficult to move, swallow, etc
Suffer from dystonia
Cognitive dysfunction
Patients exhibit memory memory dysfunction and executive dysfunction
Psychiatric disturbances
Preclinically (before major onset/ diagnosis): depression, mania, delusions
Irritability and agression at later stage
Sleep and other mood disorders
Visual motor symptoms of huntington
Chorea
Dystonia
Motor impersistence
Lack of fine motor movement
Gait disturbances
Chorea
Unpredictable and involuntary muscle movements
(Not being able to properly coordinate movement)
Dystonia
Unpredictable movements, but are repetitive and / or twisting motions
Combined together, these movements almost look rhytmic, like a combination of fidgeting and dancing
Motor impersistence
Can not maintain a voluntary action
(Patient asked to hold out their tongue, can not maintain it)
Lack of fine motor movement
Patient attempts to pinch with their index finger and thumb, but can’t do the fine control
Gait disturbances
Typically slower, more variable lengths of stride, uncoordinated
What is the regular functioning Huntingtin gene theorized do
Role in proper neuronal functioning
(Mice that have this gene deleted do not survive - critical for neurodevelopment)
Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant mutation in a very specific section of the genome, found in one gene:
Huntingtin
Because of the specificity of the disease, we may be able to develop treatments by
Further refinement of CRISPR/ Cas9 technology
Two major types of nucleic acids
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
How are RNA and DNA molecules different (2)
The sugar that attaches to the phosphate backbone and the base
Difference in the pyrimidine base
Deoxyribose vs ribose
Lack of oxygen on deoxyribose
(Makes DNA more stable and better able to adhere to its complementary strand)
The difference in pyrimidine base of RNA and DNA
No thymine in RNA
No uracil in DNA
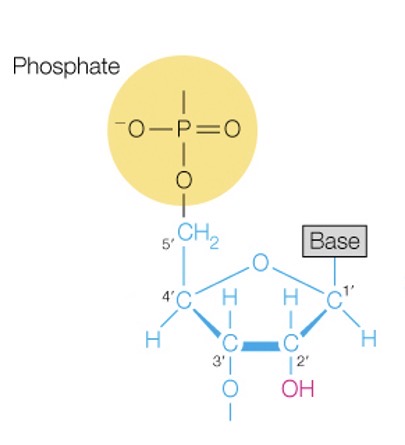
RNA unit
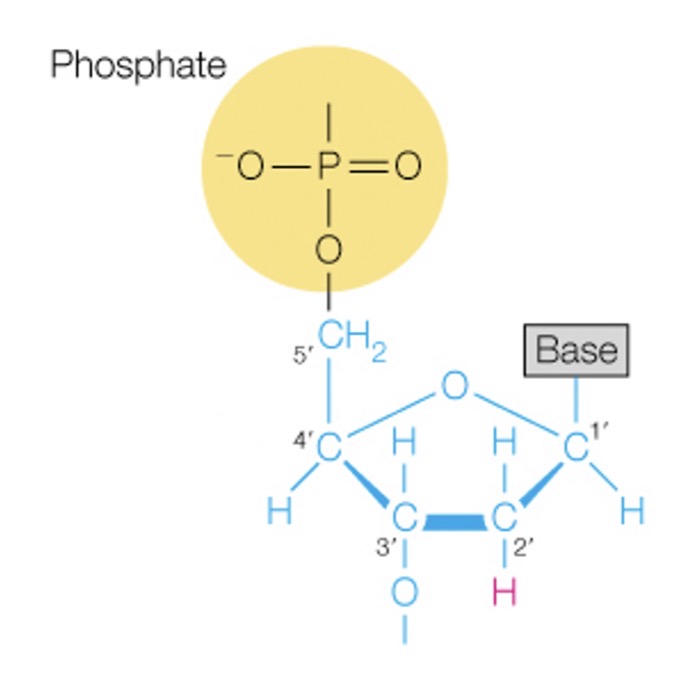
DNA unit
What kind of polymers are the nucleic acids
Heteropolymer (chain doesn’t repeat exactly, has different bases to create code)
Nucleobases
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, uracil
Purines
Two cyclic chains, slightly larger molecules
Adenine and Guanine
Adenine
Forms two hydrogen bonds with T or U
Guanine
Forms three hydrogen bonds with C
Pyrimidines
One cyclic chain
Cytosine and Thymine/ Uracil
Cytosine
Forms three hydrogen bonds with G
Thymine
Forms two hydrogen bonds with A
Uracil
Forms two hydrogen bonds with A
5- Methylcytosine
Plays a role in DNA transcription regulation/ epigenetics
Why do chains with a lot of Cs and Gs have higher melting points
More hydrogen bonds
Nucleoside
Base + sugar
Nucleotide
The whole package without bonding between phosphates (phosphodiester linkages)
Phosphate + base + sugar
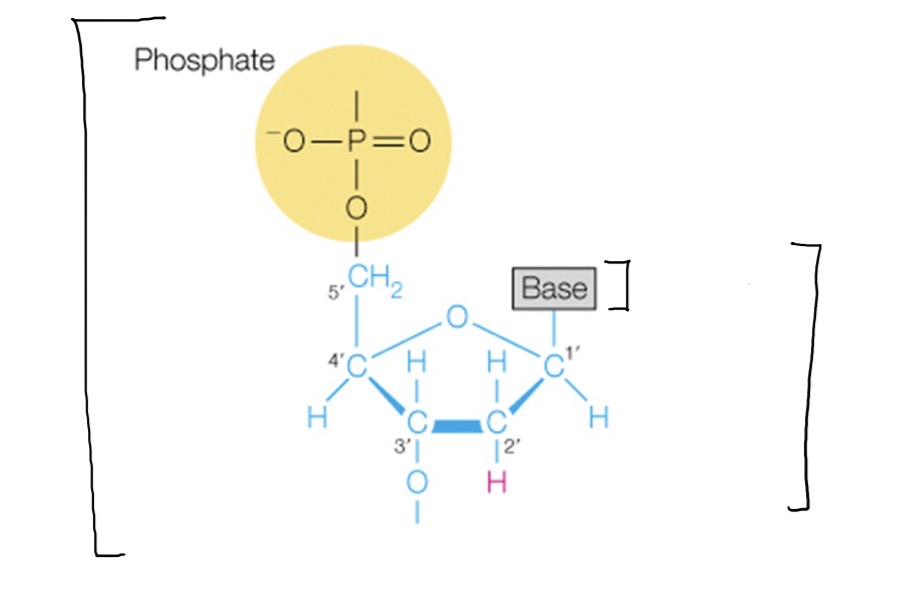
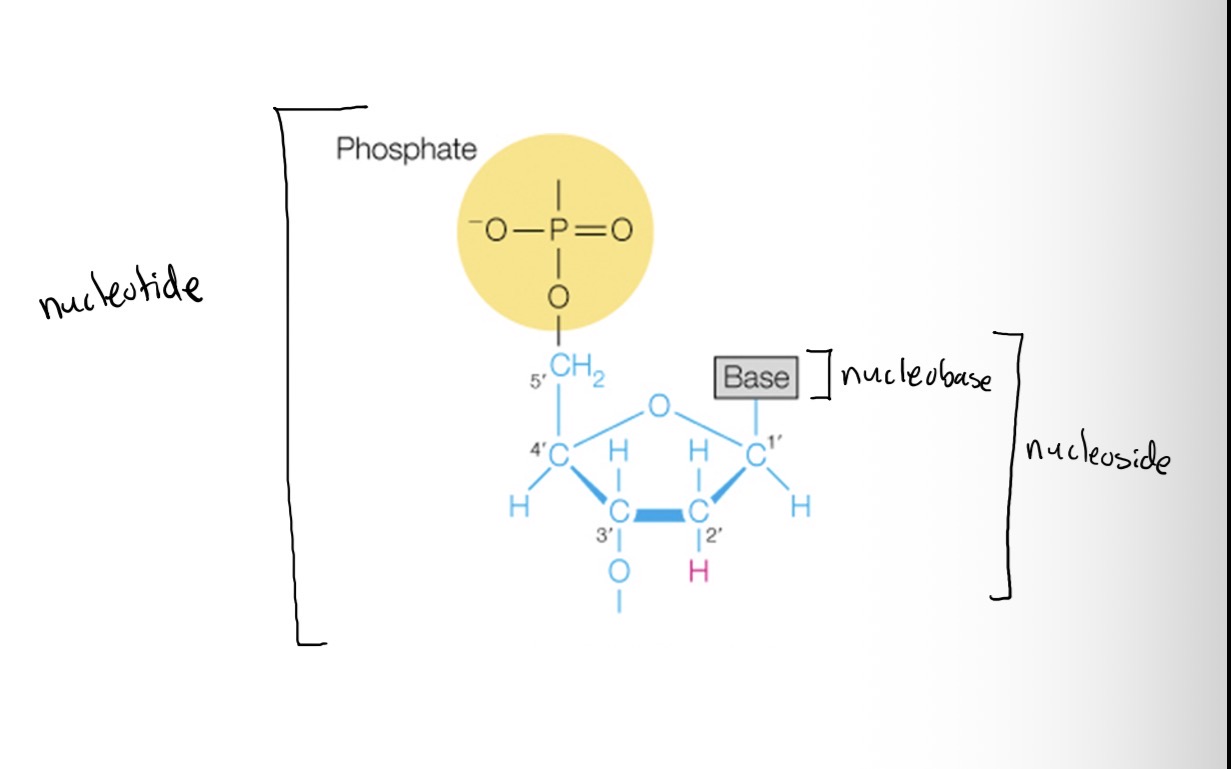
Two important structural components of nucleic acids
Polynucleotides have a sense of direction
Each of the nucleosides are different
Polynucleotides (DNA and RNA) have a sense of direction. How so?
One side of the chain is 5’ end
One side is 3’ end
This has profound effects on how the stand is “read” by transcription proteins. Generally read in a 5 to 3 direction
What is the 5’ end
The phosphate attach to the 5-carbon
How are each of the nucleosides different
They are heteromeric, consisting of many different bases
Studies on the chemical nature of the substance inducing transformation of pneumococcal types
Used, and destroyed, pathogenic bacteria (pneumococci) and harvested nucleic acids from these cells
Then, used a different strain of pneumococci, that were non-pathogenic
(Moved pieces of DNA)
Steps of experiment 1
Pathogenic (smooth) cell was killed via heat
Nucleic acids extracted and put into non pathogenic (rough) cell
Rough pneumoniae grew and transformed into smooth pneumoniae (pathogenic)
Protein / nucleic acids question
Are the proteins or nucleic acids the carriers of pathogens?
Independent functions of viral protein and nucleic acid in growth of bacteriophage
Radiolabelled two separate components of a bacteriophage with radioactive elements
◦The protein coat of the virus with radioactive sulfur (35 P)
◦The nucleic acid of the virus with radioactive phosphorus (32 P)
32 P was found in the daughter viruses (indicating nucleic acid is the carrier)
Secondary structure
Molecule has a defined structure in three dimensions
Each turn of the molecule rotates 36 degrees (each stack of nucleotide)
Complete circle in 10 base pairs
Symmetry in secondary structure
Distance between each of the first carbons in AT and GC pairings is exactly the same
Angle between each base pairing is exactly 36 degrees