Lacrimal System IV : Disorders of the Orbit
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is the Aetiology for Orbital Disease ?
Inflammatory → TED
Infectious → Orbital cellulitis
Neoplastic → tumours
Trauma → orbital fracture
Malformation → skeletal abnormalities
Vascular →Carotid
What are the symptoms of Orbital Disease?
Eyelid swelling
Bulging eye(s) → retracted
Double vision → Extraocular muscles affected
Pain
Blurring → optic nerve compressed , blurring of central vision
changes in colour vision
What are the critical signs of orbital disease which require URGENT referral?
Globe dystopia
- Proptosis/exopathlmus → bulging eye
Hyperglobus → eye directed upwards
Hypoglobus → eye directed downwards
Restricted ocular motility
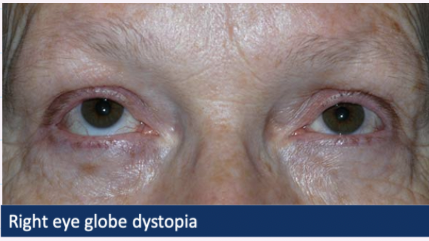
What are other signs of orbital disease?
Soft tissue involvement
Eyelid & periorbital oedema
Ptosis → droopy lid
Chemosis → swelling of conjunctiva
What are Fundus changes of orbital disease ?
Optic disc swelling/atrophy
Collaterals → new blood vessels around disc , don’t tend to leak
Choroidal folds → streaks
What is the Aetiology for Thyroid Eye disease?
systemic autoimmune disease/condition
→ increased or decreased thyroid production
ocular effects :
soft tissue around the eyes
muscles
What are early ocular symptoms of TED?
Non-specific FB sensation
Redness
Tearing
Photophobia
Eyelid puffiness
What are late ocular symptoms?
Persistent lid swelling
Chemosis → swelling of conjunctive
Prominent eyes → bulging, proptosis (cant close eyelids properly)
Double vision → thickened eyelid muscles
Loss of vision (optic nerve/corneal involvement)
What are the signs of TED?
Eyelid retraction
- Eyelid lag on downgaze
- Lagopthalmos
Uni or bilateral ptosis
- 50% of patients
- Choroidal folds
Variable ocular motility restriction
- 40% of patients
- due to EOM fibrosis
Other signs of TED?
Higher IOP in up gaze → restriction of muscles
conjunctival lid hyperaemia /oedema
superior limbic keratoconjucntivits
optic nerve swelling /pallor → paleness
RAPD + defective colour vision
What is the management of TED?
Referral to GP or ophthalmologist
Steroids
Radiotherapy
Surgical decompression
What is the Aetiology for Preseptal + Orbital Cellulitits?
Bacterial INFECTION (Staphylococcus, Haemophilus)
Periorbital or orbital tissue
most commonly <10 years old
severity varies from minor to life threatening
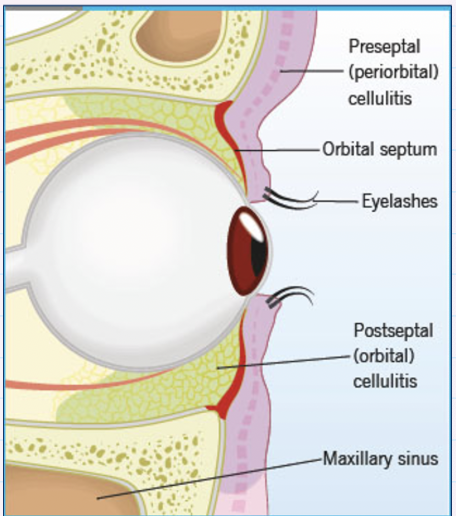
what is preseptal cellulitis caused by ?
Tissues lying anterior to orbital septum
high risk of extension into orbit in young children
What is orbital cellulitis caused by ?
Tissues lying posterior to orbital septum (within orbit)
Severe sight + life-threatening emergency
what does Preseptal cellulitis look like ?
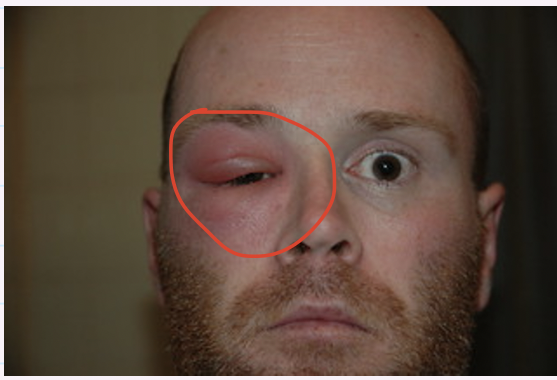
What does Orbital cellulitis look like?

What is the optometric management for orbital cellulitis?
Same day EMERGENCY referral
compare the predisposing factors + symptoms of preseptal + orbital cellulitis
Both PF:
fever, infection, ocular infection, trauma
Both Symptoms :
Lid swelling , redness + tenderness
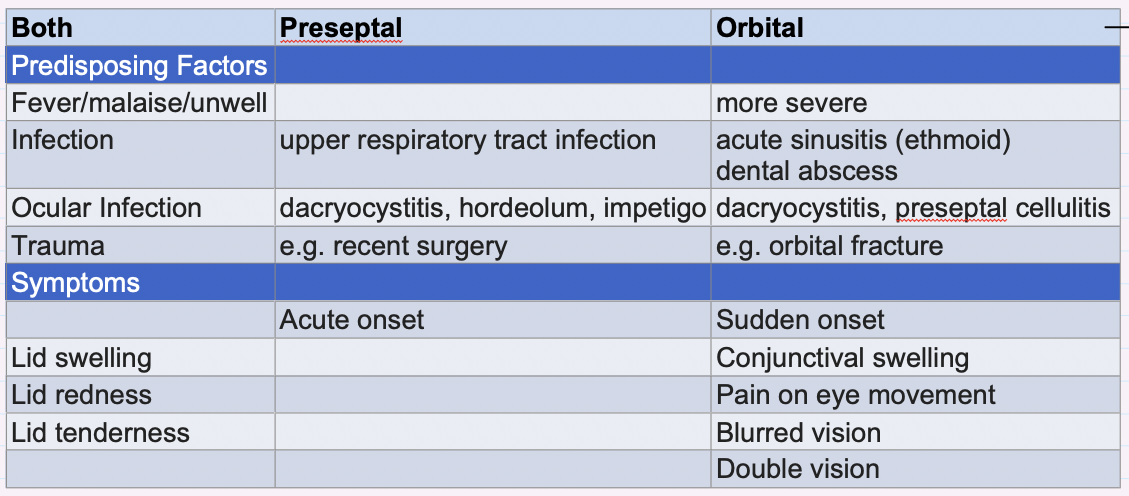
Preseptal and orbital cellulitis signs difference?
Preseptal cellulitis :
Proptosis absent
Ocular motility, VA, colour vision + RAPD = normal
Orbital cellulitis:
Proptosis present
Ocular motility → painful + restricted
VA→ reduced in severe cases
Colour vision → reduced in severe cases
RAPD → present in severe cases
What is Preseptal and Orbital cellulitis management?
Optometrist :
Emergency SAME DAY referral
Not up to us to decide which is which
What is the secondary care of preseptal + orbital cellulitis?
Systemic antibiotics
Hospital admission
Blood tests
CT scan
Co-management ENT
What is a Dermoid/epidermoid cyst?
Choristoma (mass of normal tissue in an abnormal location)
Thin walled, cystic lesion
May contain sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles
formed at birth but may not present until adulthood
What are the 2 types of dermoid cyst?
> Superficial
painless slow growing nodule
often around the eyelid/brow
> Deep
Presents in adolescence or adulthood
Increasingly protruding eye , acute inflammation
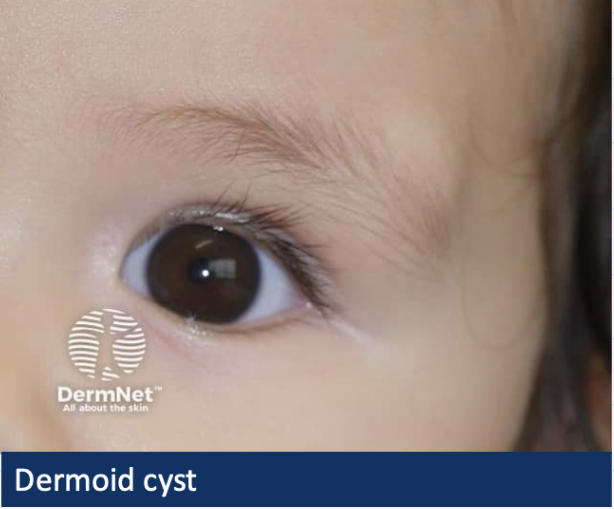
What is the Management for dermoid cysts?
refer routinely for removal → slow growing + can rupture
What is a Blow out fracture?
Blunt-trauma → fight, squash ball injuries → wear goggles
Fracture an orbital wall
- Typically orbital floor or medial wall
Tissue or muscle trapped
What are the symptoms + signs of a blow out fracture?
Bruising, tenderness, periorbital swelling
Double vision → eye tethered so won’t look up
Loss of sensation in cheek → infraorbital nerve trapped
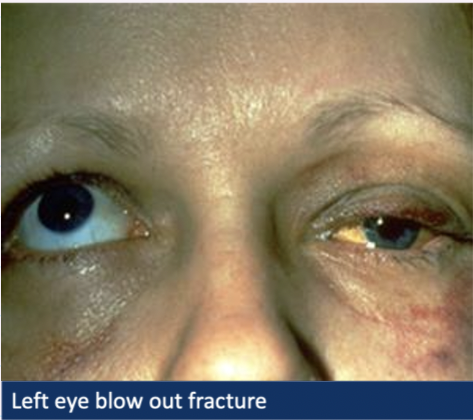
What is the management for a Blow out fracture?
SAME DAY referral → make it clear that you’ve seen double vision or abnormalities in ocular motility
What is Mucromycosis?
Rare aggressive fungal infection
often fatal
typically affects px with immunosuppression
inhaled spores → URTI which spreads to orbit + brain
gradual onset + periorbital swelling, diplopia
appear similar to orbital cellulitis
SAME DAYY REFERRAL