S1.1: The Particle Nature Of Matter
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Polyatomic ions
ions that are made of more than one atom
State symbols
solid (s), liquid (l), gas (g), and aqueous (aq)
Mole
the SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined in a fixed ratio and thus can be separated via physical methods and also retains individual identities of the element/compounds that makes it
Pure substance
A sample of matter, either a single element or a single compound, that has definite chemical and physical properties
Elements
A molecule composed of one kind of atom; cannot be broken into simpler units by chemical reactions.
Compounds
two or more elements chemically combined in fixed ratios
Heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that is not uniform in composition; components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture with visible phase barrier
Homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture with uniform composition
Atoms
Smallest unit of matter, with a nucleus consisting of protons and neutrons and electrons orbiting the nucleus
Molecules
Groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Ions
Atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to loss or gain of one or more electron
Avogardo's constant
6.02 x 10^23 particles
Significant Figure Rules
1. non-zeros are always significant; 2. zeros between two other sig figs are significant; 3. all final zeros after the decimal point are significant; 4. zeros used solely for spacing the decimal point are not significant unless a decimal point is present
Filtration
Removes an insoluble solid from a liquid/ solution
Mixture is poured through a filter paper held in a funnel.
Residue remains in the filter paper and does not pass through
Filtrate is able to pass through the pores of the paper and collected in the beaker
Solvation
Separates a heterogenous mixture of two solids based on differences in solubility.
one of the substances is soluble in a solvent, but the other solid is insoluble.
the solvent molecules (often water) surround the soluble molecules and dissolve the solid into a solution.
insoluble solid separated by filtration.
soluble substance separated from the solution by evaporation.
Evaporation
Separates a mixture which has a solute dissolved in a solvent
Heat solution in evaporation dish
Solvent evaporates leaving the solute behind
Distillation
Separates liquids based on their volatility
Place water ethanol mixture in round
bottom flask
Heat mixture ethanol evaporates first (lower boiling point)
ethanol rises up the distillation column and
passes through the condenser
ethanol cools and condense back to a liquid
to be collected in a flask
Chromatography
Separates a mixture of solutes in a solvent
Dissolve solute mixture in a solvent (mobile phase)
Place drops of solution on chromatography paper (stationary phase)
Place chromatography paper so that bottom is suspended in solvent
Solvent moves up through stationary phase
Different solutes move through the stationary phase at different rates depending
on their solubility and affinity for the stationary phase
Recrystallisation
Removes impurities that are mixed in with a solid
impure mixture dissolved in a hot solvent to
make a saturated solution
solution is cooled causing the solubility of the dissolved solids to decrease
The desired product forms crystals leaving
The impurities in the solution which is then filtered to obtain the pure product.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Matter is made up of small particles
All particles have kinetic energy
Kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature of the substance
Collisions between particles are elastic ∴ no loss in kinetic energy
Equation for density
Density = Mass / Volume
where:
Density is measured in units (kg/m³) or (g/cm³)
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, measured in units (kg) or (g)
Volume is the amount of space occupied by an object, measured in units (m³) or (cm³)
States of matter
solid, liquid, gas, plasma
Liquid vs aqueous
liquid is the melted physical state of a substance (as apposed to solid or gas)
aqueous means dissolved in water
Features of a solid
cannot be compressed
particles are very close together
strong forces of attraction
fixed shape
fixed volume.
cannot flow
Features of a liquid
cannot be compressed.
particles are quite close together
weaker forces of attraction
not fixed shape (shape of bottom of container)
fixed volume
can flow
particles move more freely
Features of a gas
can be compressed
particles are far apart
Weakest forces of attraction
not a fixed shape
not a fixed volume (same shape as the container)
volume depends on the temperature and the pressure
Changes in states of matter
Condensation, Evaporation, Sublimation, Melting, Freezing
Evaporation vs boiling
Evaporation occurs at the surface of the liquid and can occur at any temperatures, turning liquid into gas. Boiling occurs at a specific temperature, a change of state form liquid to gas throughout the liquid (so bubbles formed within the liquid)
Exothermic reaction
a chemical reaction in which heat is released to the surroundings
Endothermic reaction
A reaction that absorbs energy
Endothermic vs. Exothermic
Endo: Heat absorbed H>0
Exo: Heat released H
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of motion of the particles of a substance.
Celsius scale
Based on the freezing and boiling points of water
Kelvin (K) scale
The temperature scale that assigns 0 K to the coldest temperature possible, absolute zero (-273 C), the temperature at which molecular motion stops. The size of the kelvin is identical to that of the Celsius degree.
Directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the particles in the substance.
Celcius to Kelvin
K=C+273
Directly proportional relationship
as one amount increases, another amount increases at the same rate. (when x doubles, y doubles)
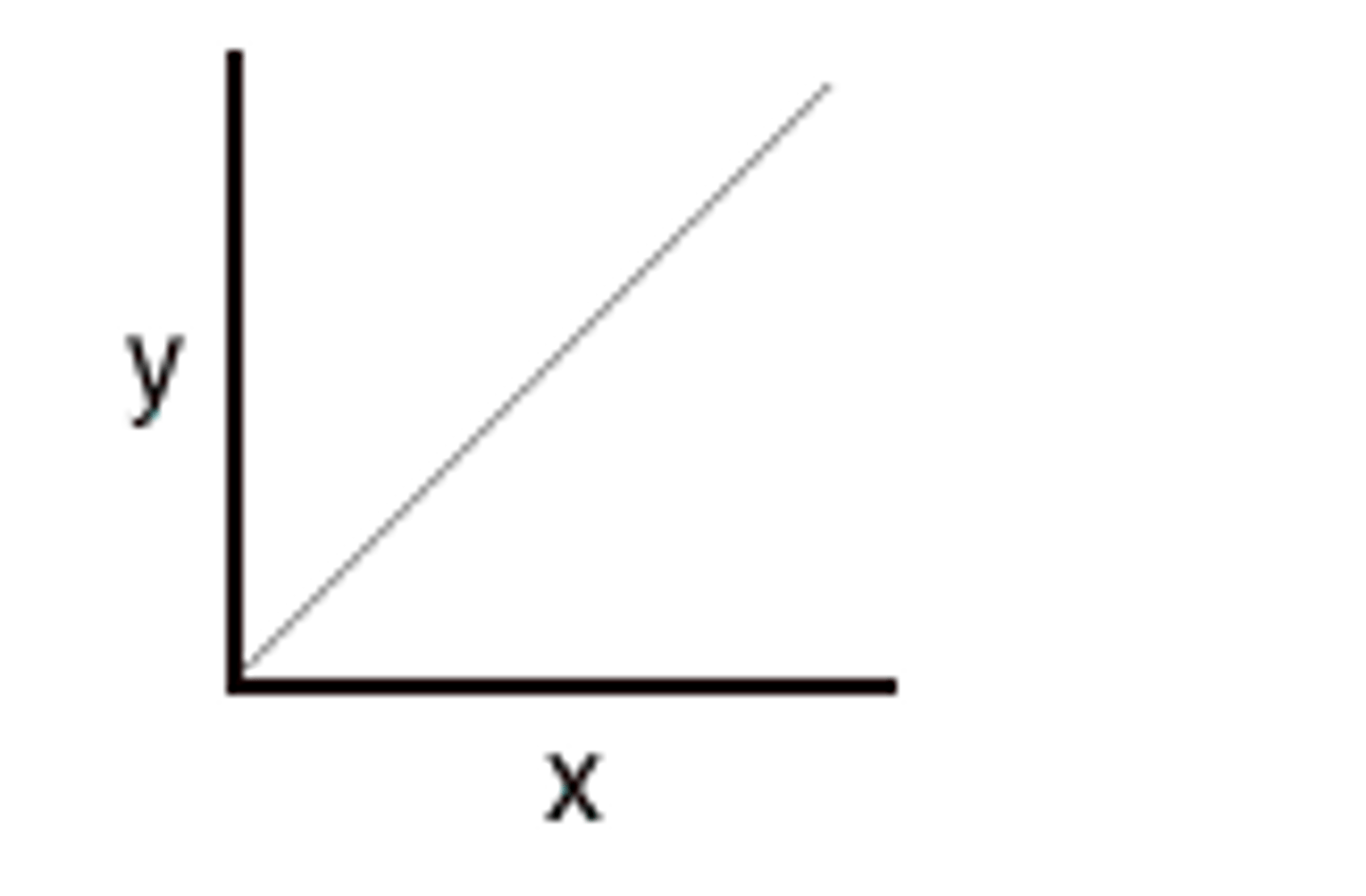
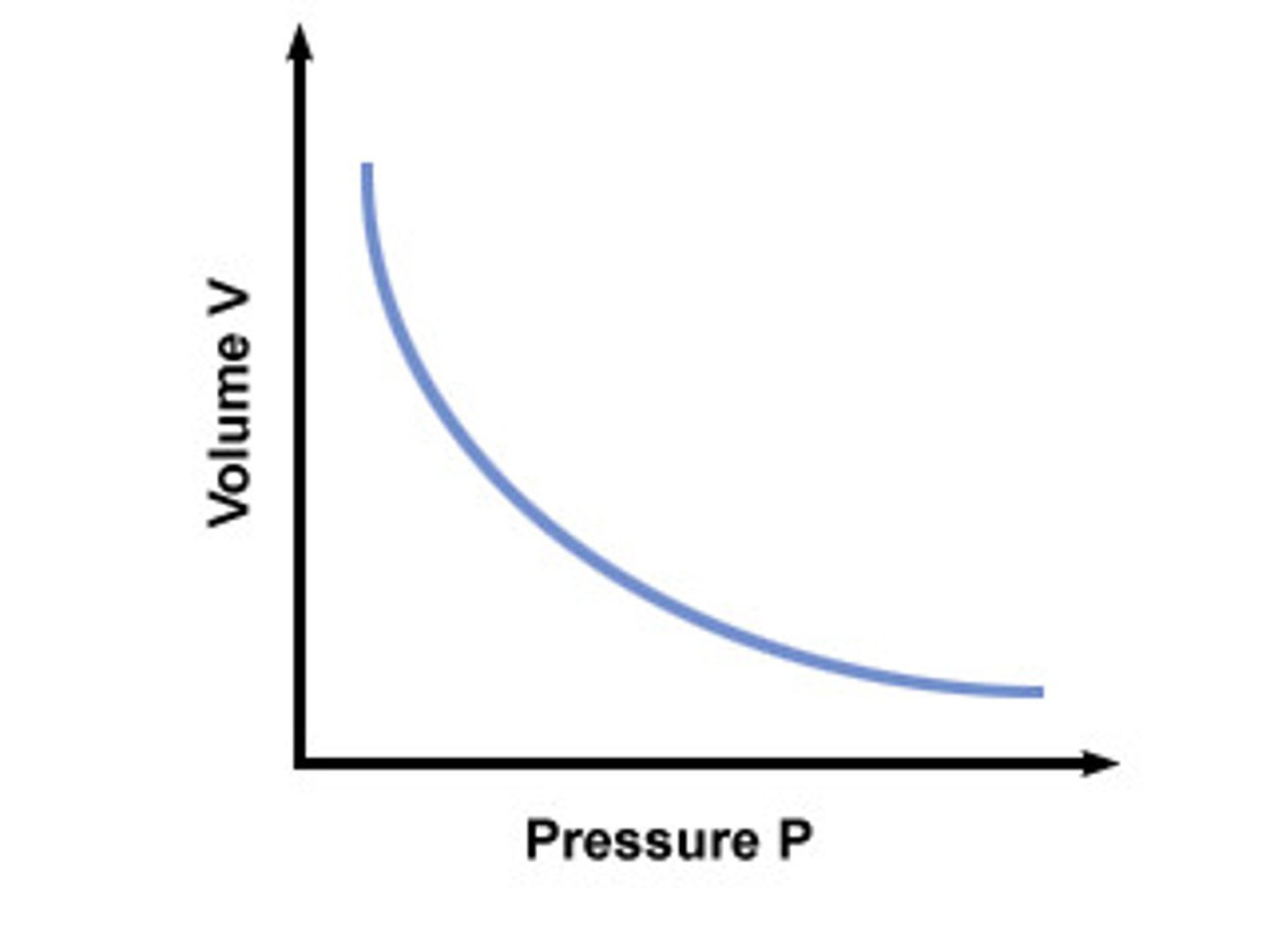
Inversely proportional relationship
a change in one quantity causes a change by the same factor, in the opposite direction, of another quantity. (when x doubles, y halves)
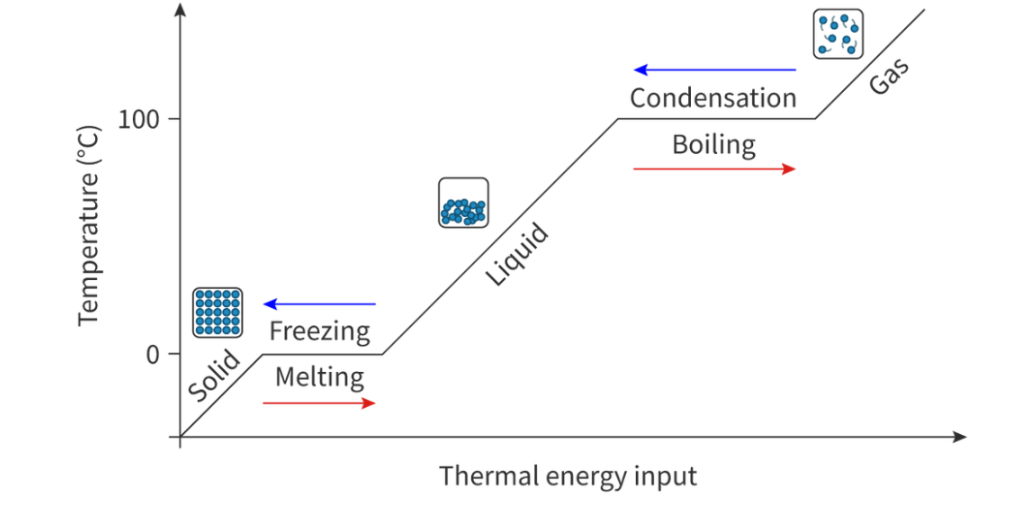
Heating and cooling curves
Sloped line: Heat is transformed into kinetic and potential energy. Average kinetic energy increases as temperature increases
Horizontal line: Energy input used to overcome intermolecular forces and change the state. Heat is therefore only transformed into potential energy. Average kinetic energy of the particles does not change and therefore the temperature remains constant
Assumptions of Ideal Gases
1. no interaction between gas molecules
2. collisions of gaseous molecules are perfectly elastic
3. gas particles move in continuous, rapid, random motion
4. no forces of attraction between gas particles
5. temperature of gases depend on average kinetic energy
pressure
the amount of force exerted per unit area of a surface
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up
kilopascals to pascals
x1000
Convert between the units of meters cubed, (m3) decimeters cubed (dm3), and centimeters cubed (dm3)
1 cubic metre (m^3)= 1000 cubic decimetre (dm3)
1 cubic metre(m^3)= 1,000,000 cubic centimetre (dm3)
Mole formula
moles = mass/molar mass
empirical formula
a formula with the lowest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound