A&P Ch 14 Intro to the brain and brain stem
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Rostral
-Toward the forehead
Caudal
-Toward the spinal cord
Brain weight
-About 1600g (3.5 lb) for men
-1450g for woman
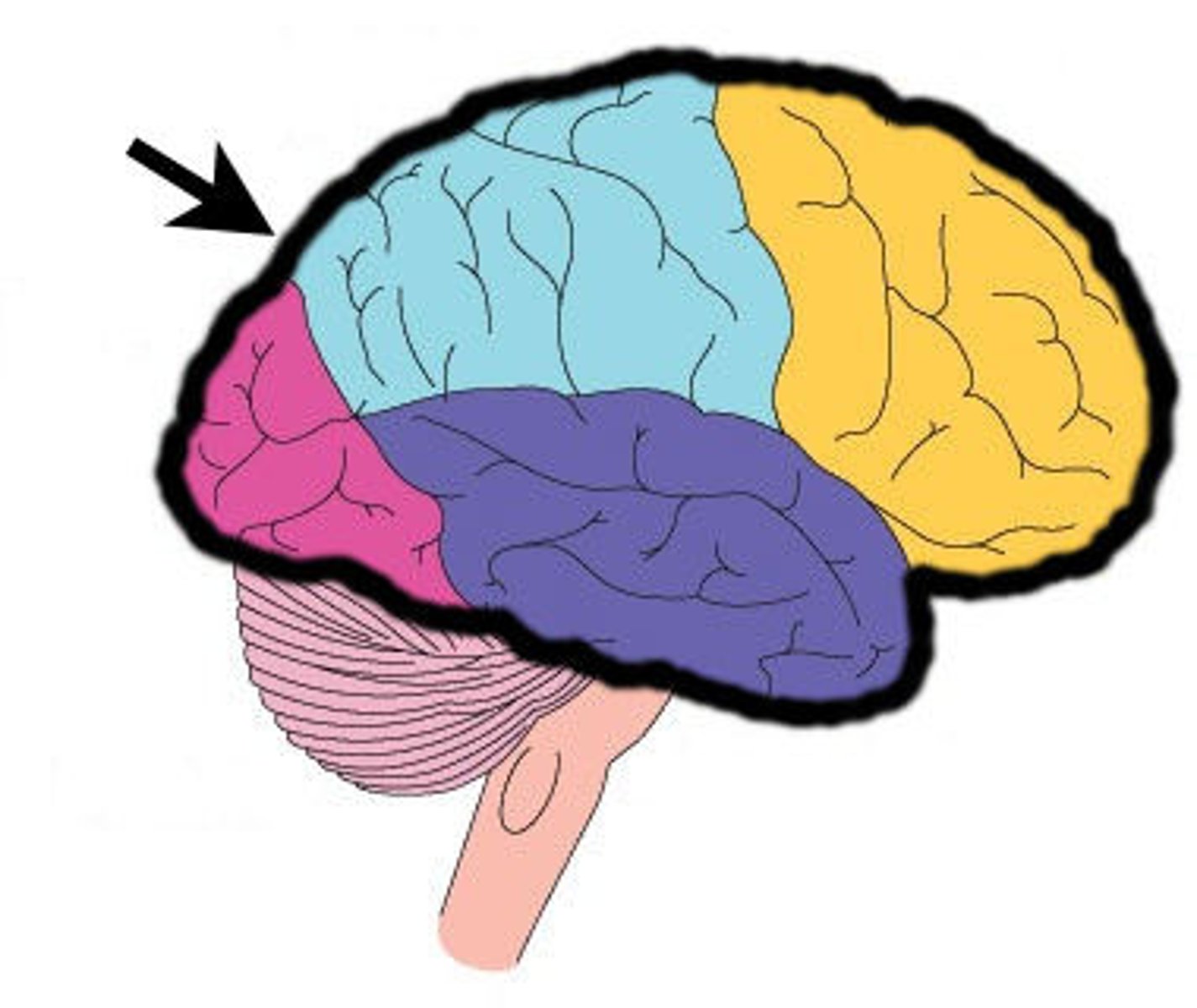
Cerebrum
-83% of brain volume
-Cerebral hemispheres
-Gyri and sulci
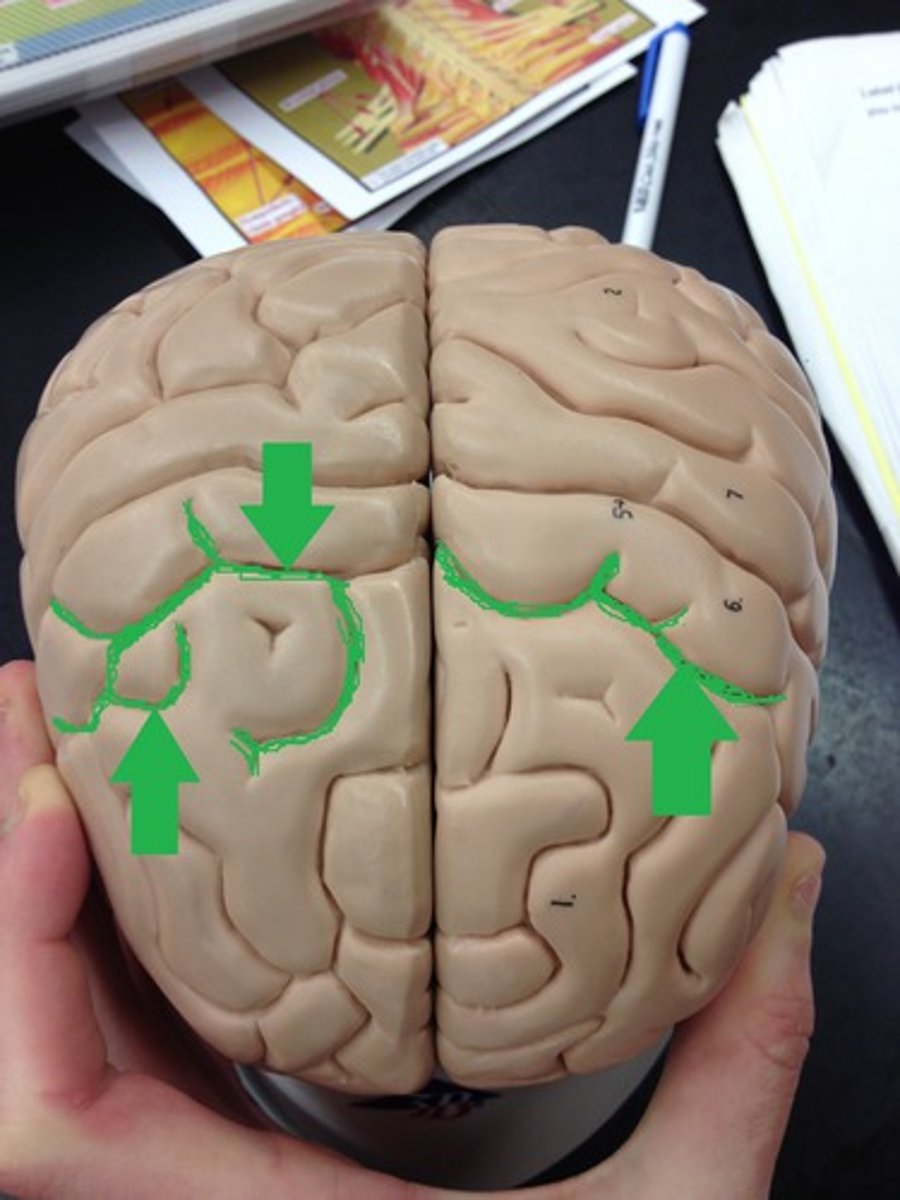
-Longitudinal fissure
-Corpus callosum
Longitudinal fissure
-Deep groove that separates cerebral hemispheres
Gyri
-Raised areas
Sulci
-Shallow grooves
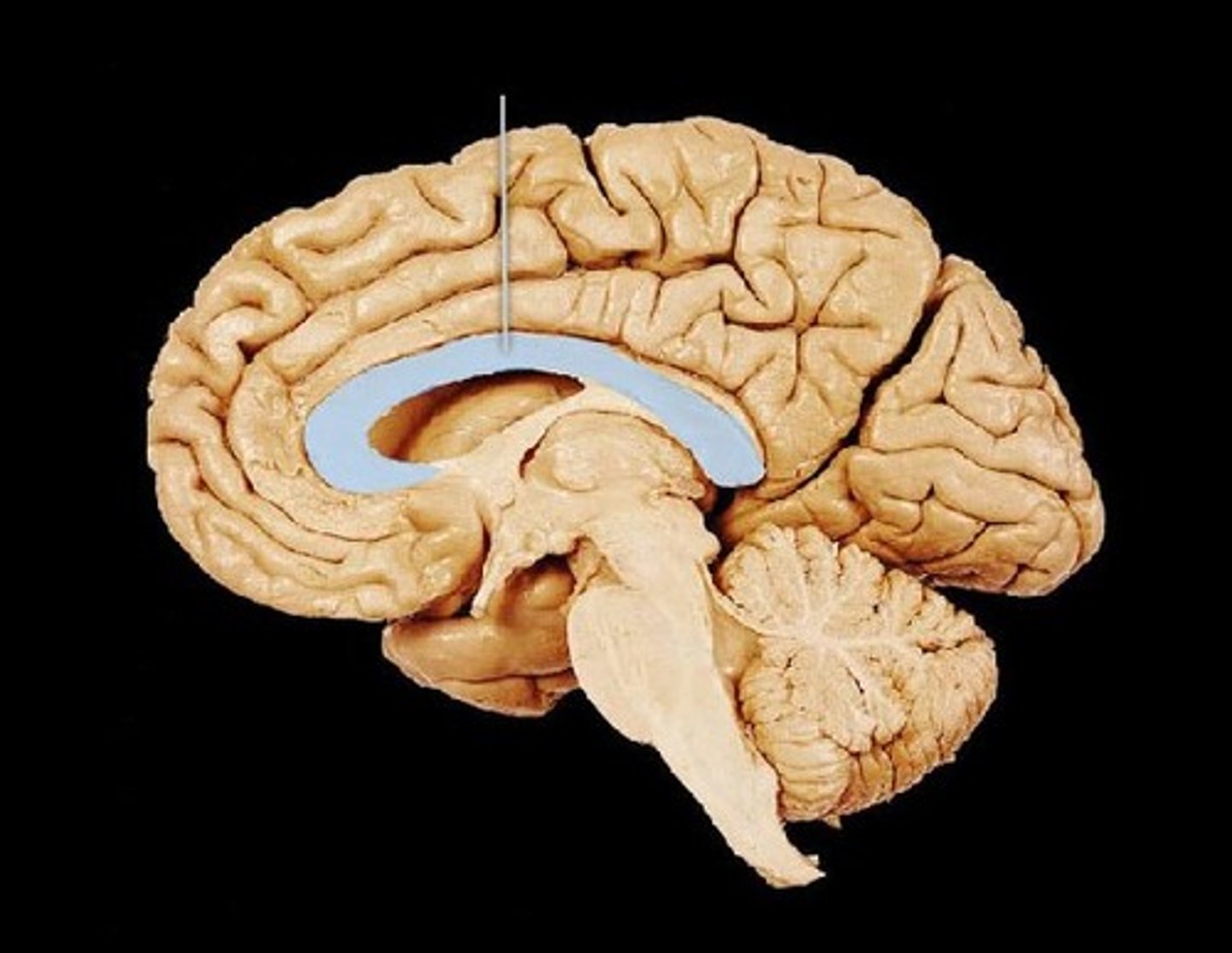
Corpus callosum
-Thick nerve bundle at bottom of longitudinal fissure that connects hemispheres
-White fibrous tract
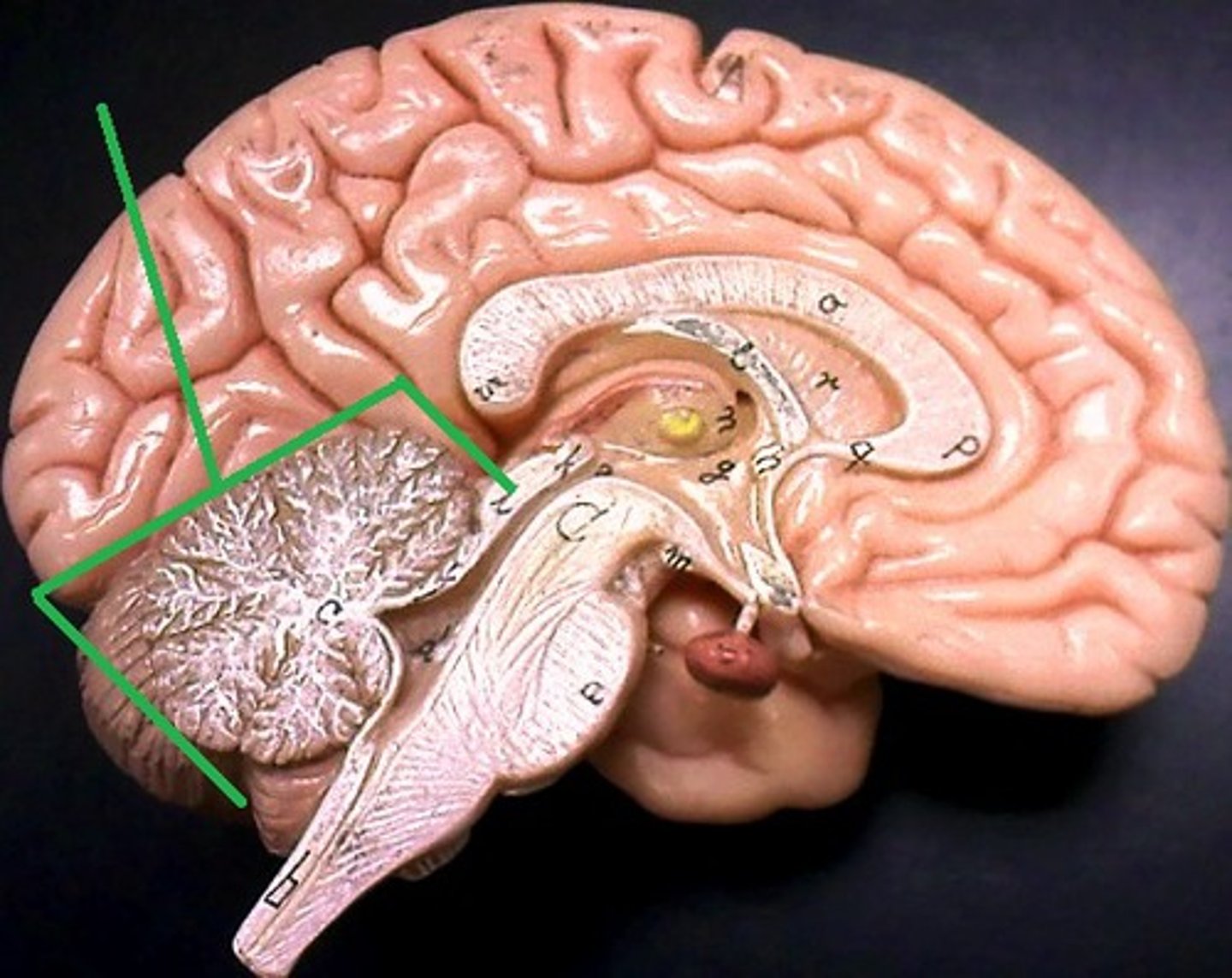
Cerebellum location
-Occupies posterior cranial fossa
-Separated from cerebrum by transverse cerebral fissure
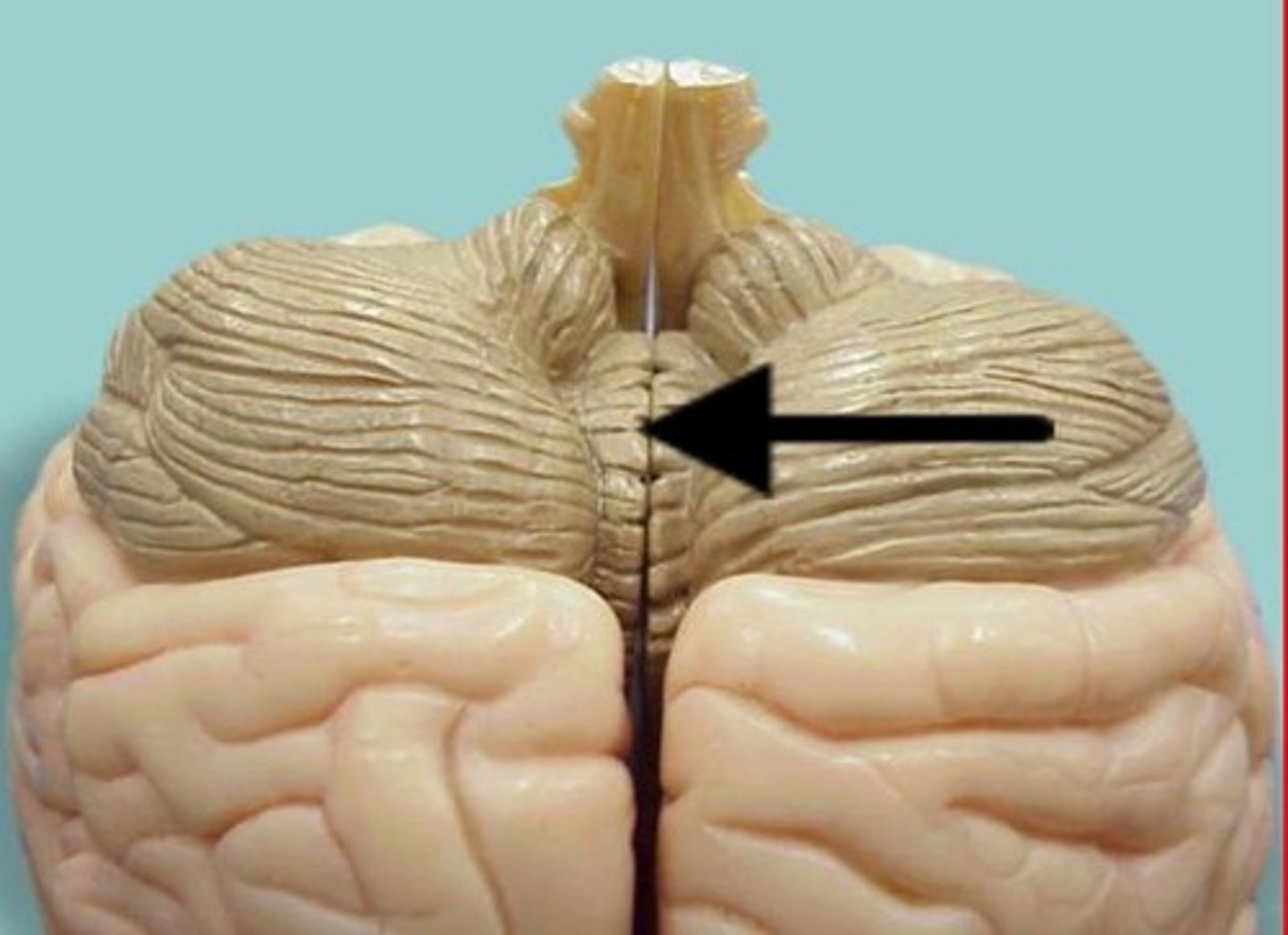
vermis
-Connects both halves of cerebellar hemispheres
Folia
-Cerebellum
-Superficial cortex of gray matter with folds
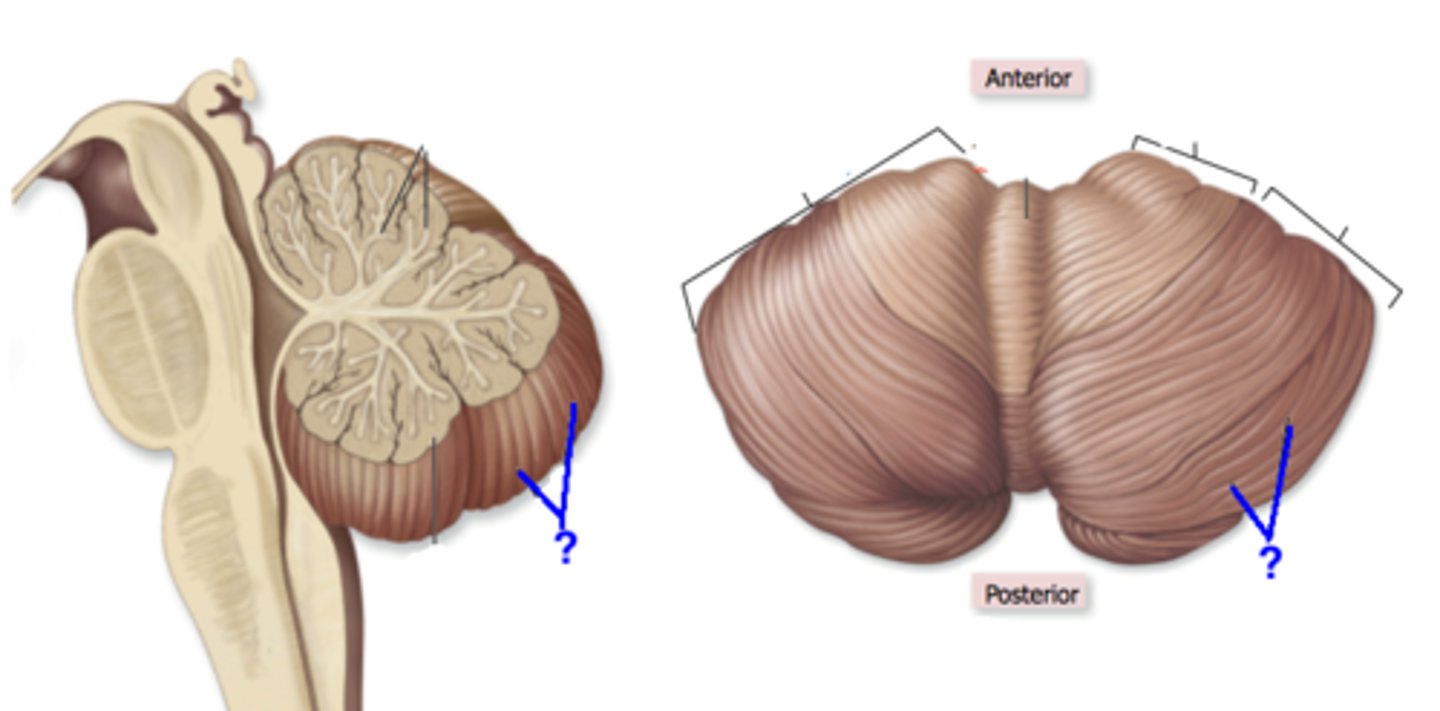
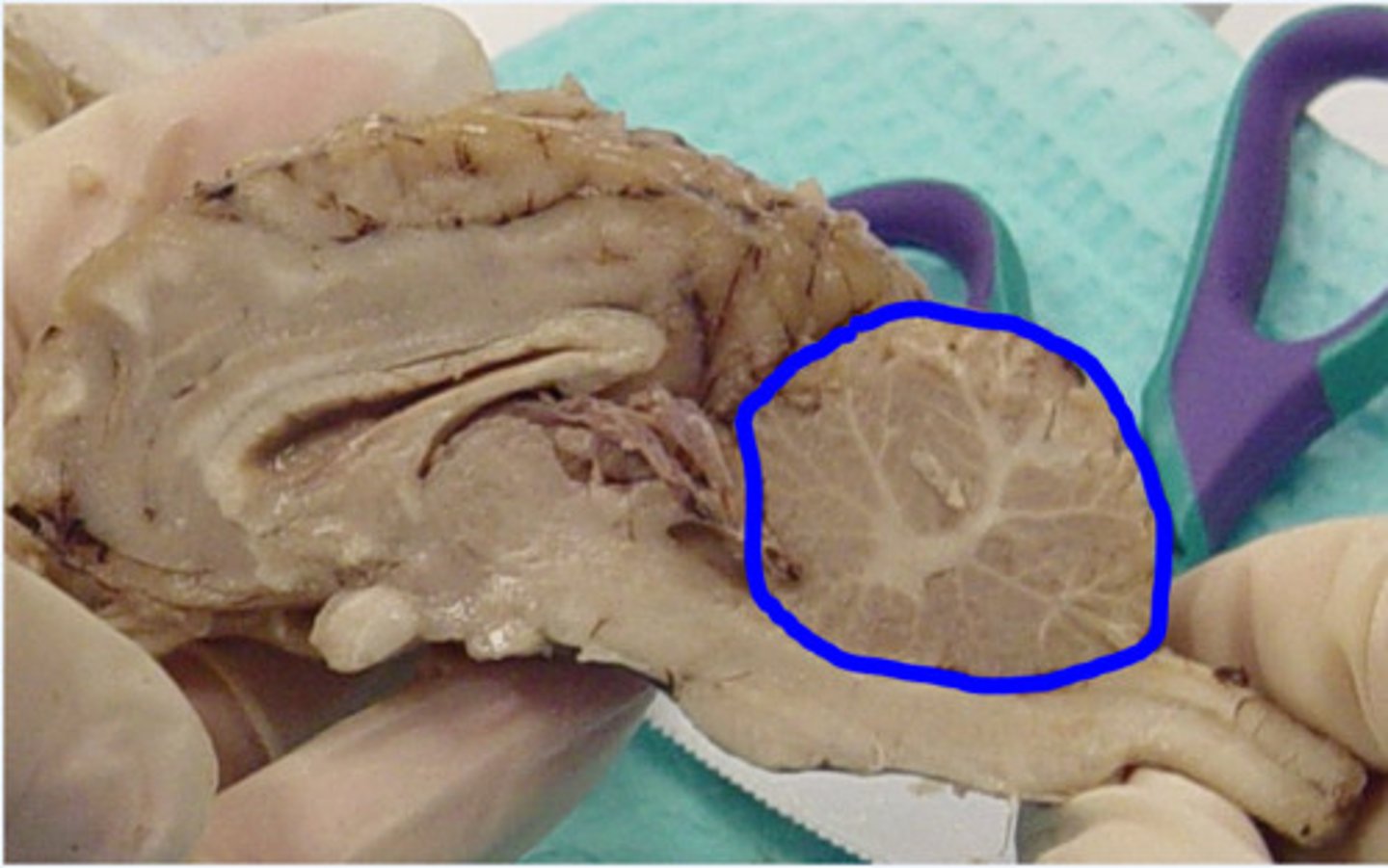
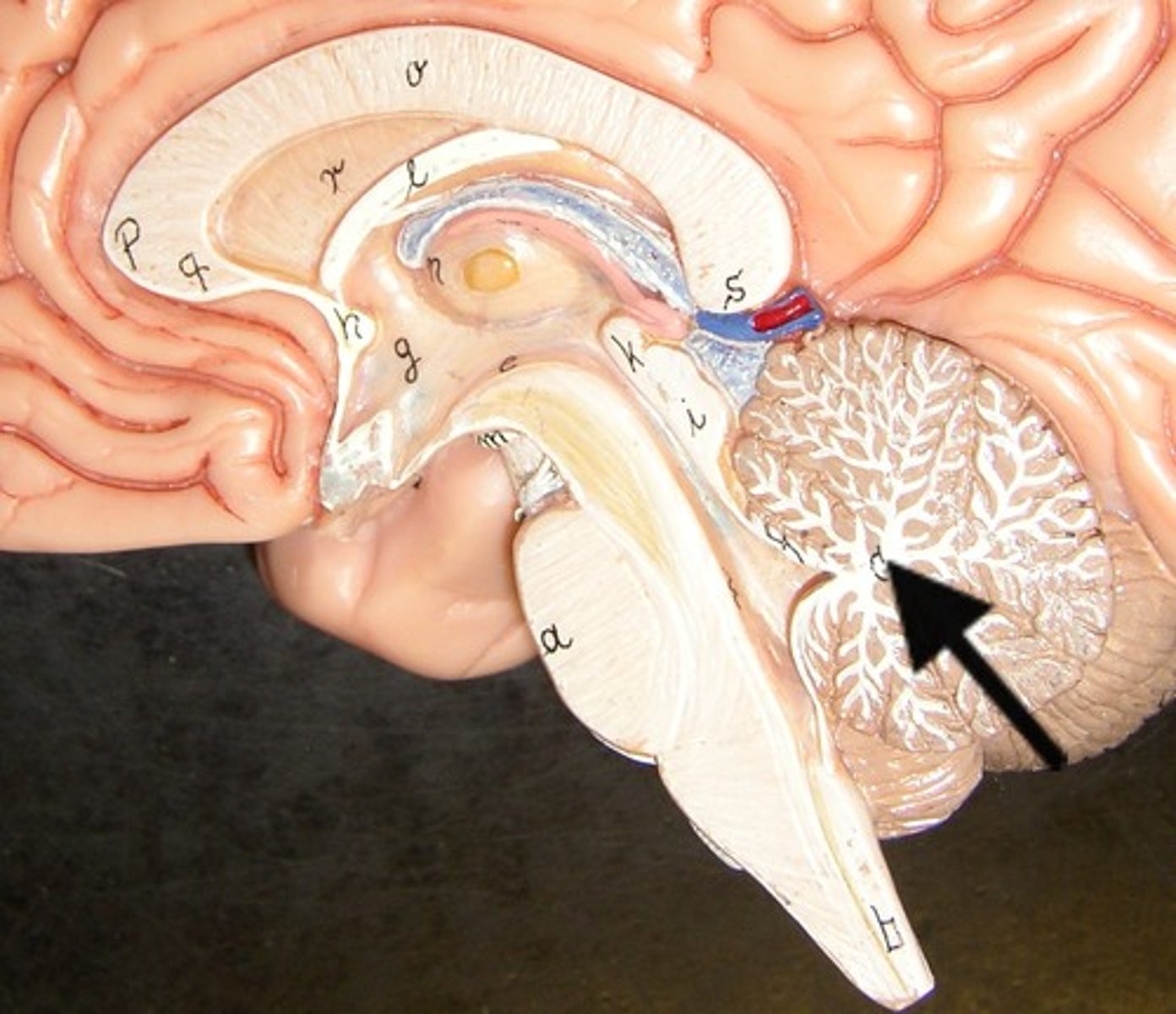
Arbor vitae
-Cerebellum
-"tree of life"
-branching white mater
Cerebellum
-contains over 50% of brain neurons ~ 100 billion
-Many small granule cells
-Large Purkinje cells have axons that synapse on deep nuclei
-~10% of brain volume
-Also has sulci, gyri, and fissures
-Small in many hyperactive children
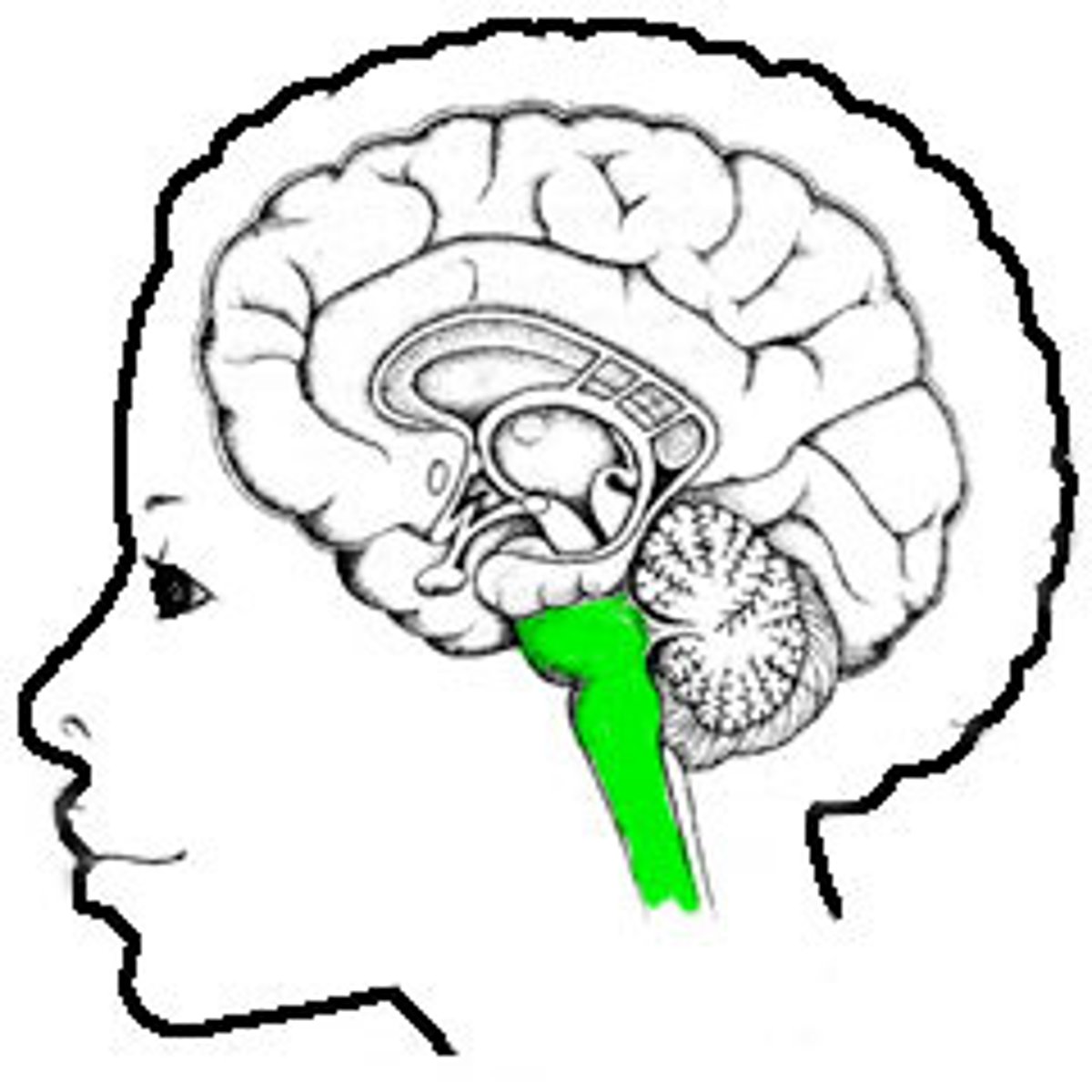
Brain stem location
-What remains of the brain if the cerebrum and cerebellum are removed
Brain stem
-Midbrain
-Pons
-Medulla oblongata
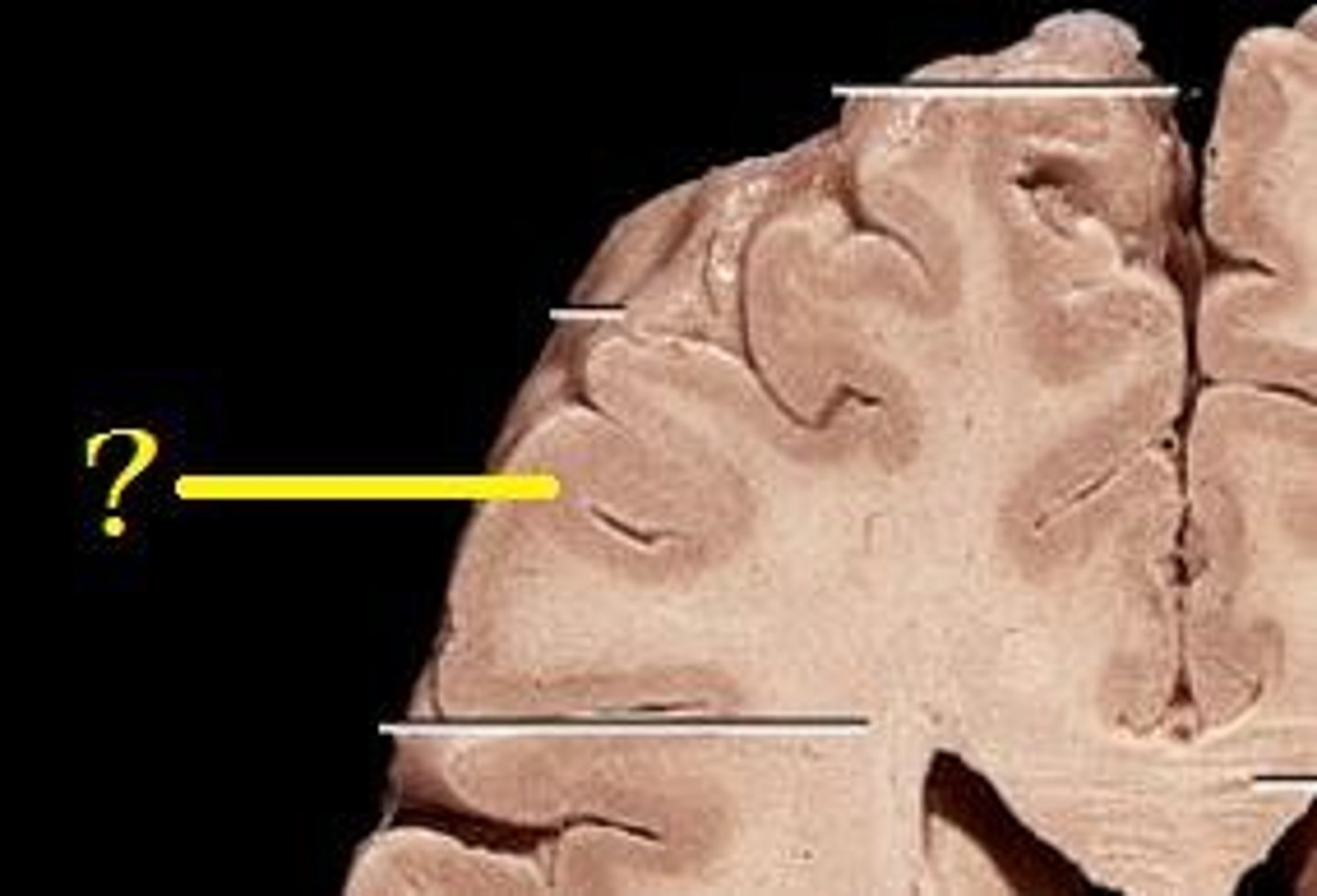
Gray matter
-The seat of neurosomas, dendrites, and synapse
-Dull color due to little myelin
-Surface of brain
-Forms nuclei deep within brain
White mater
-Bundles of axons
-Lies deep in brain
-Pearly white color from myelin
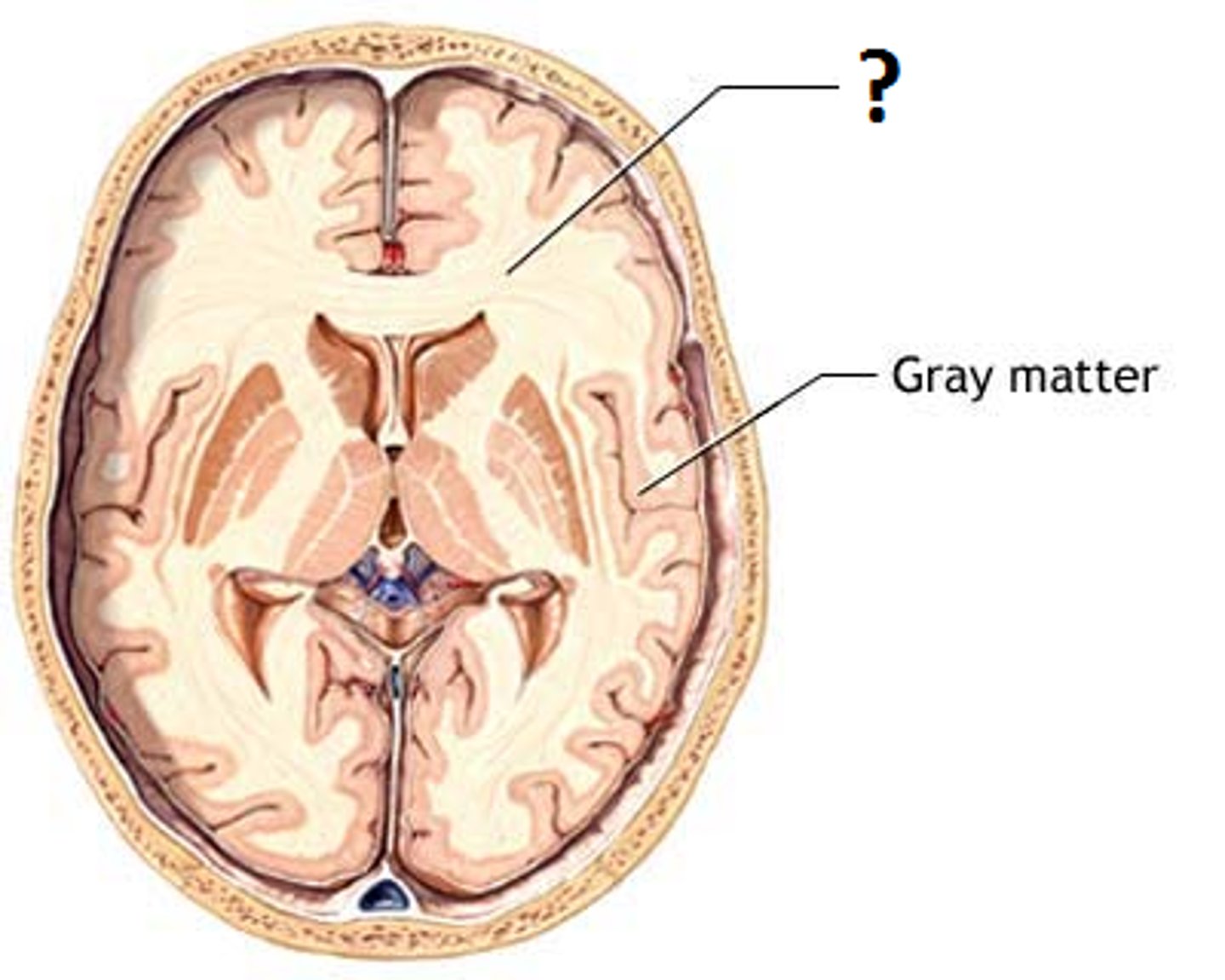
White mater function
-Composed of tracts, or bundles of axons, that connects one part of the brain to another, and the spinal cord
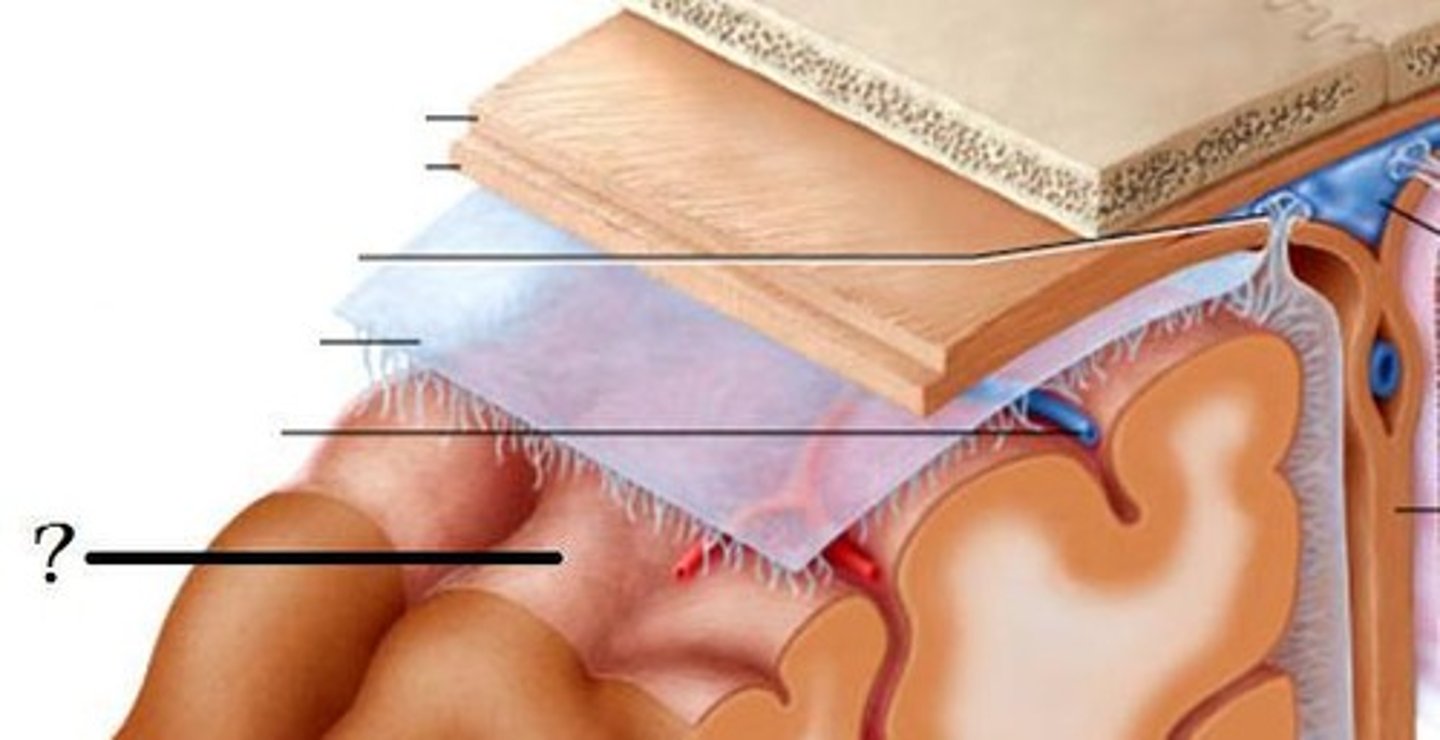
Meninges
-Three connective tissue membranes that envelope the CNS
-Protect the CNS and provide structural framework for its arteries and veins
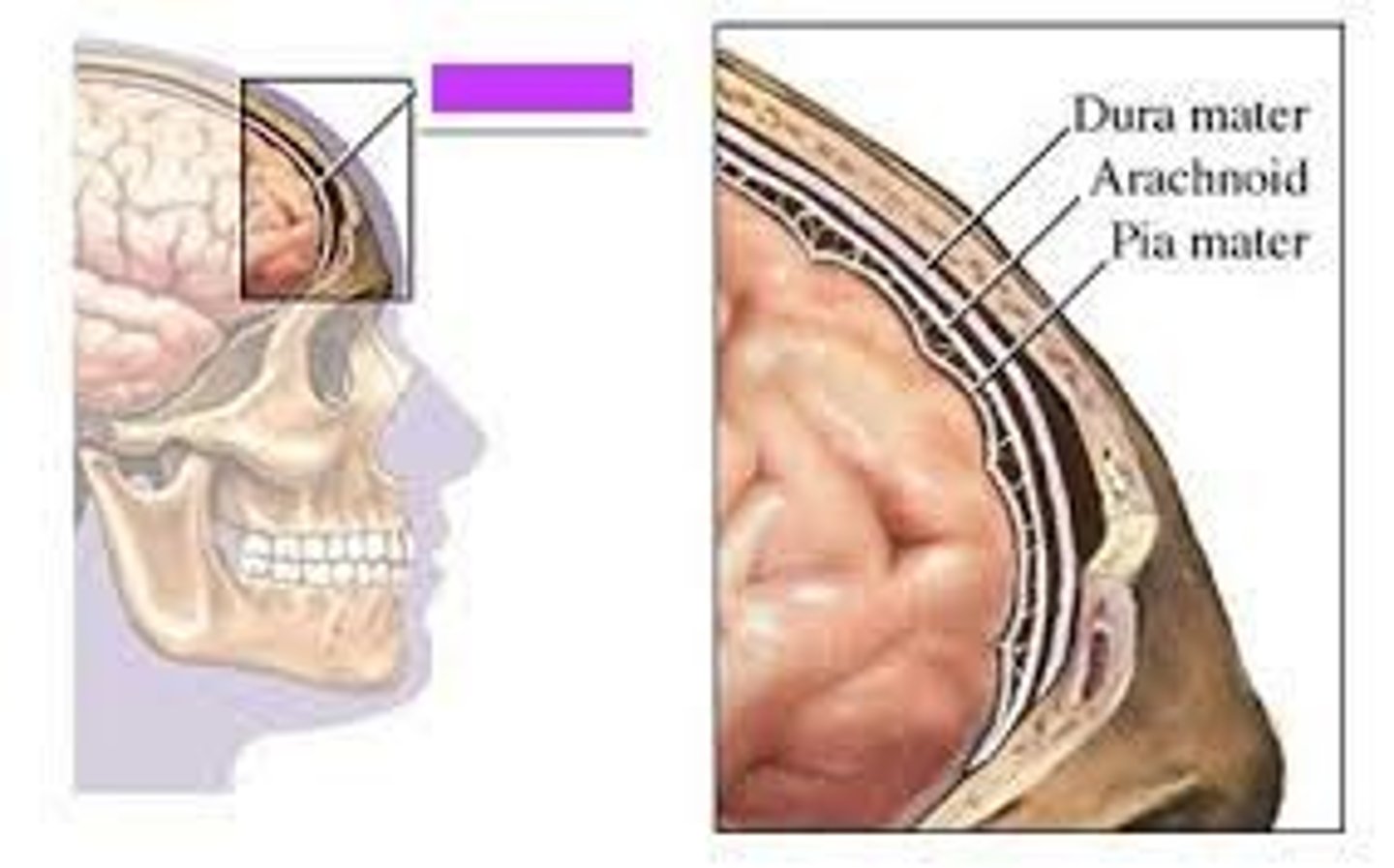
Meninges Location
-Lies between the nervous tissue and bone
Meningitis
-Inflammation of the meninges
-Serious disease of infancy and childhood
Meningitis causes
-Caused by bacterial or viral invasion of the CNS
-Especially between 3 months and two years of age
Cranial dura mater
-Outer periosteal
-Inner meningeal
-Folds inward to extend between parts of the brain
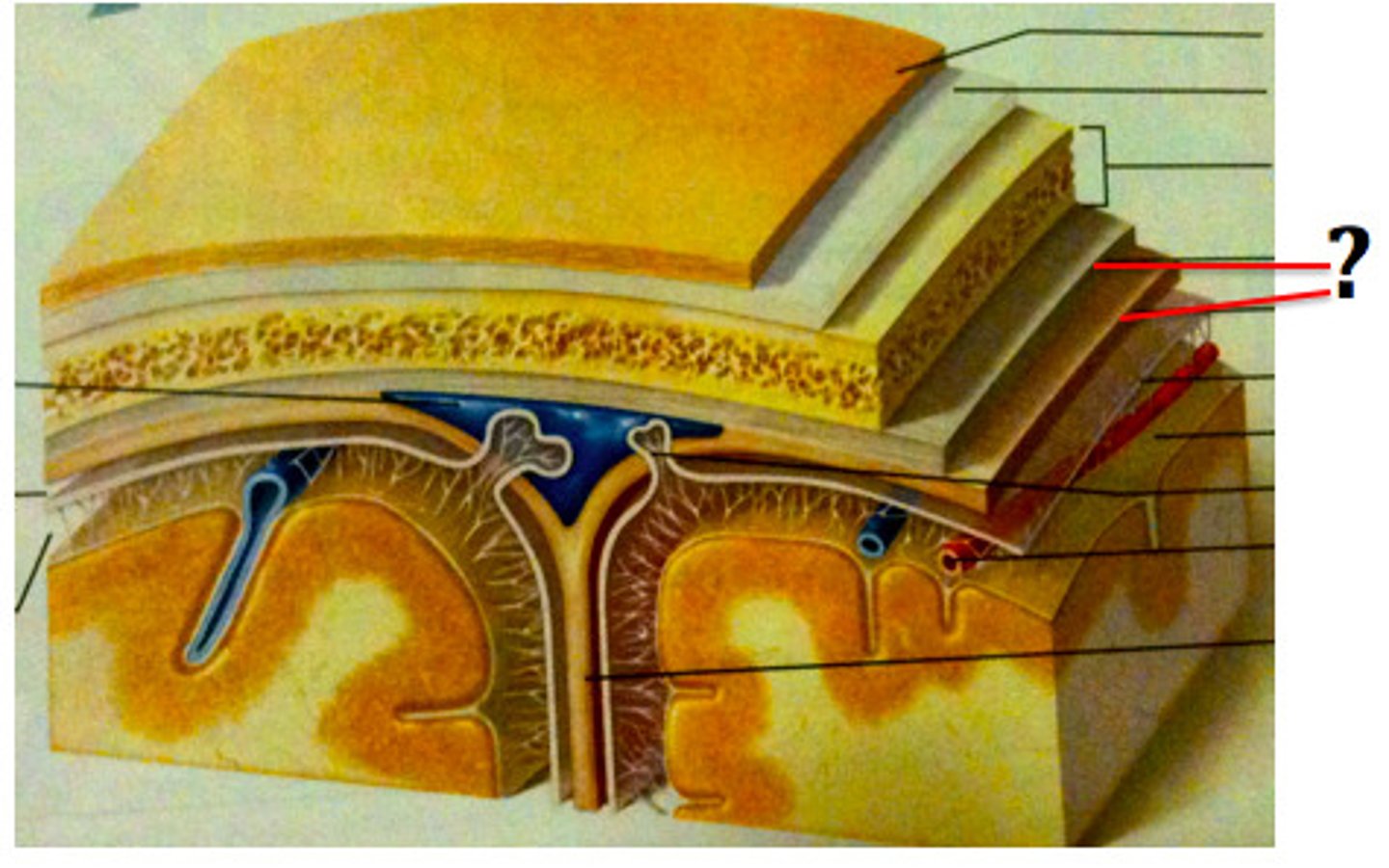
Cranial dura mater location
-Layers separated by dural sinuses
-Pressed closely against cranial bones
=No epidural space
=Only attached to bone around foramen magnum, stella turcica, crista galli, and sutures of the skull
Periosteal
-Equivalent to periosteum of cranial bones
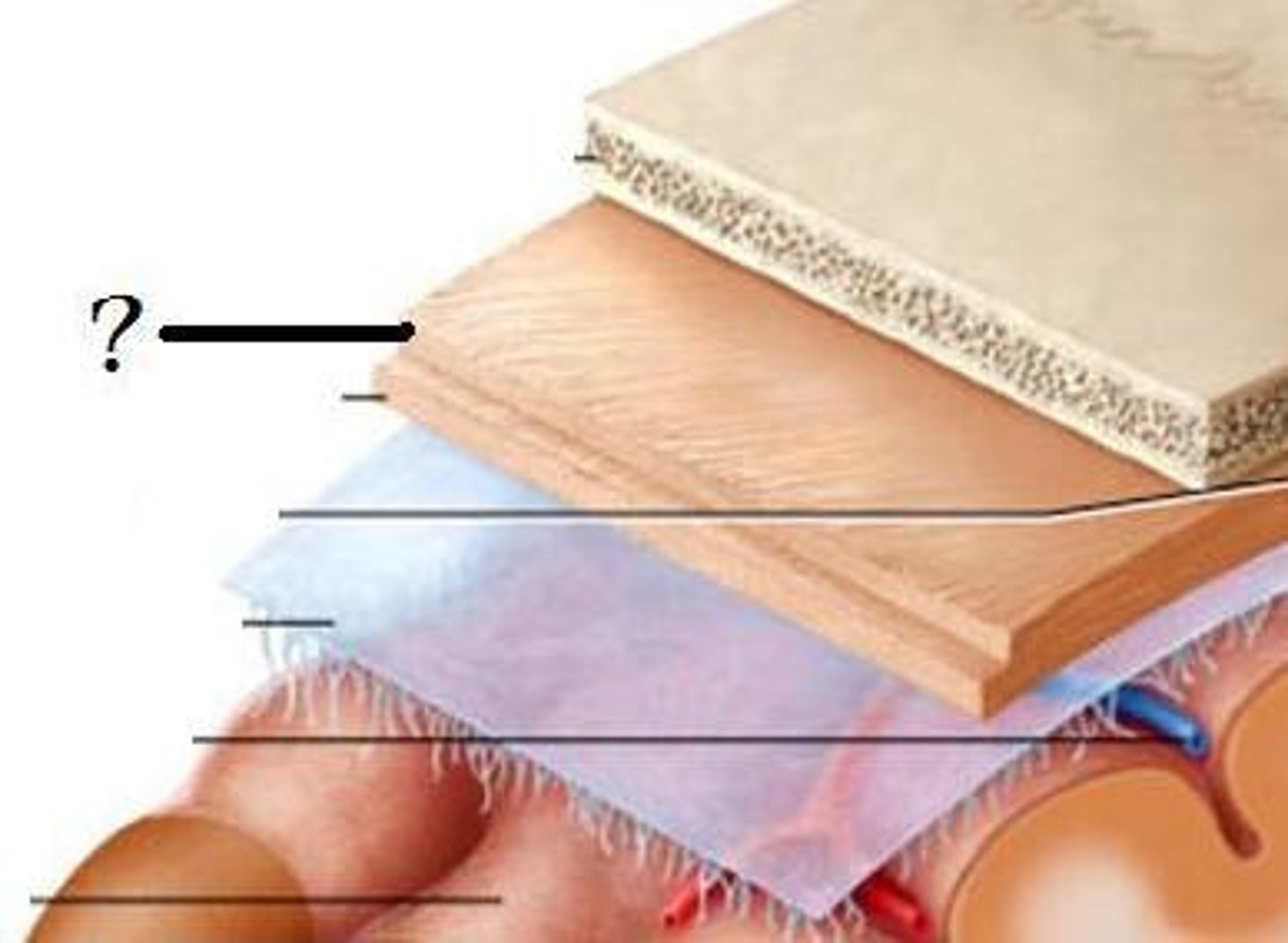
Meningeal
-Continuous into vertebral canal and forms dural sheath around spinal cord
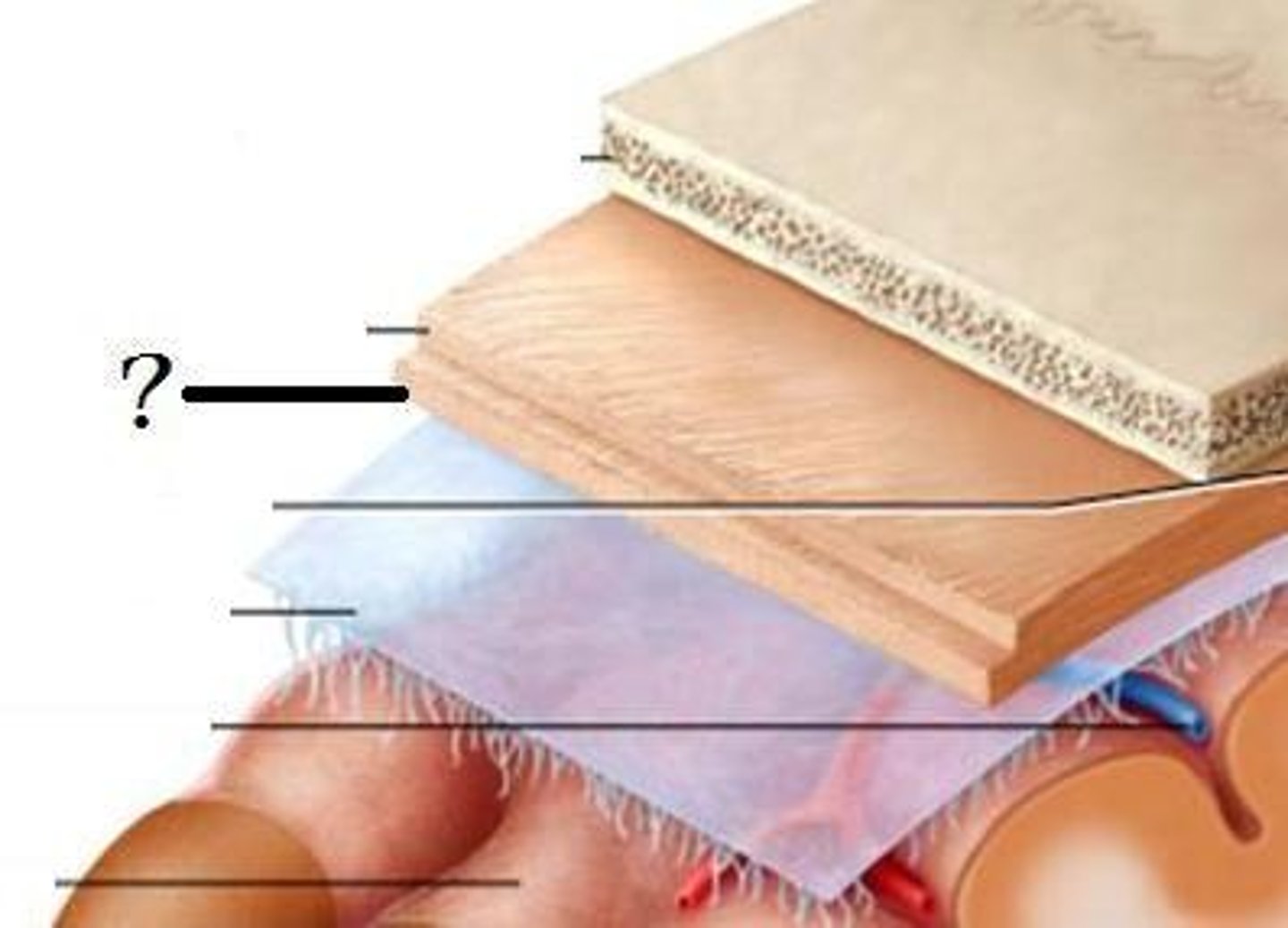
Dural sinuses
-Separates layers of cranial dura mater
-Collect blood circulating though brain
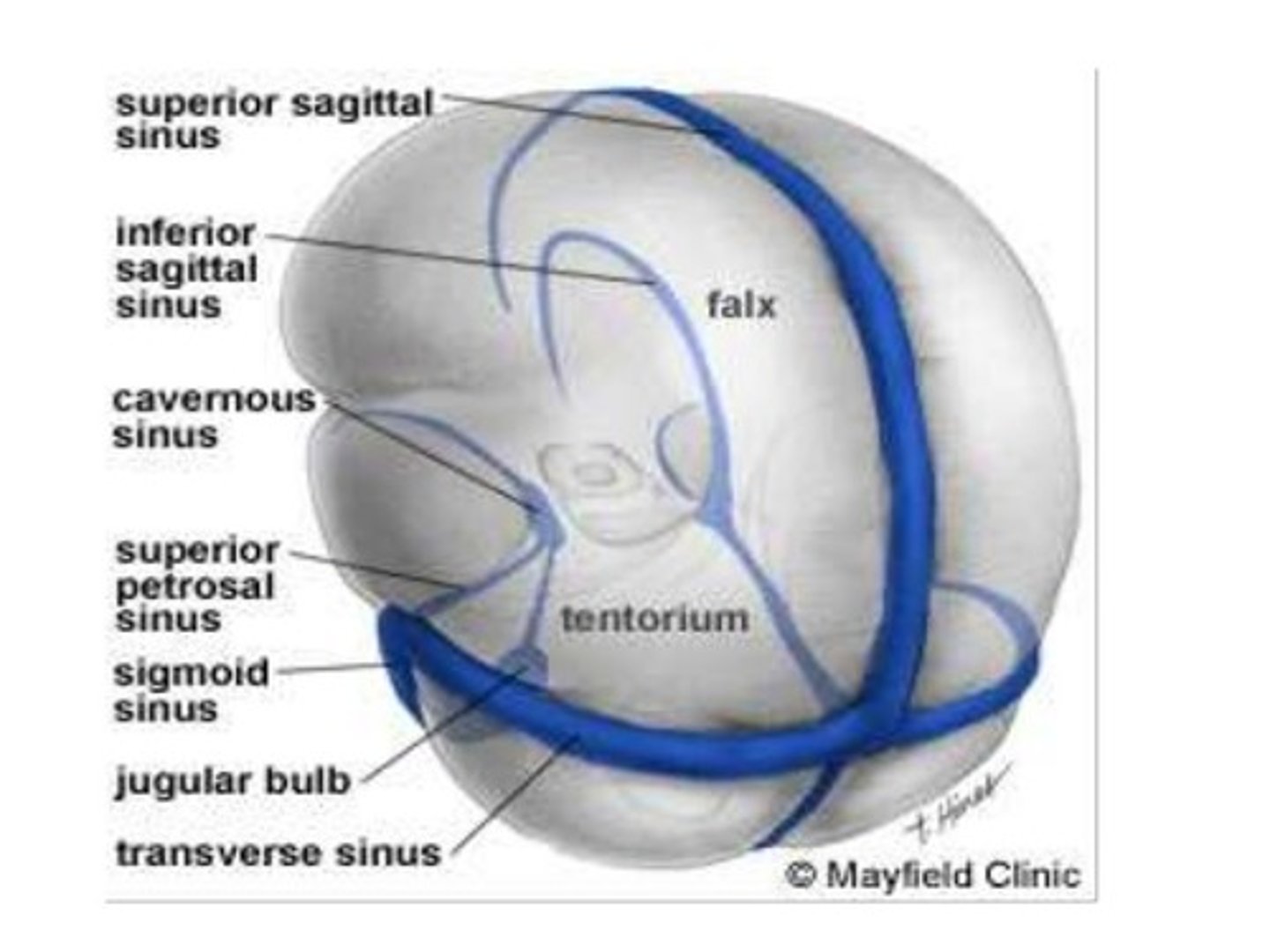
Arachnoid mater
-Transparent membrane over brain surface
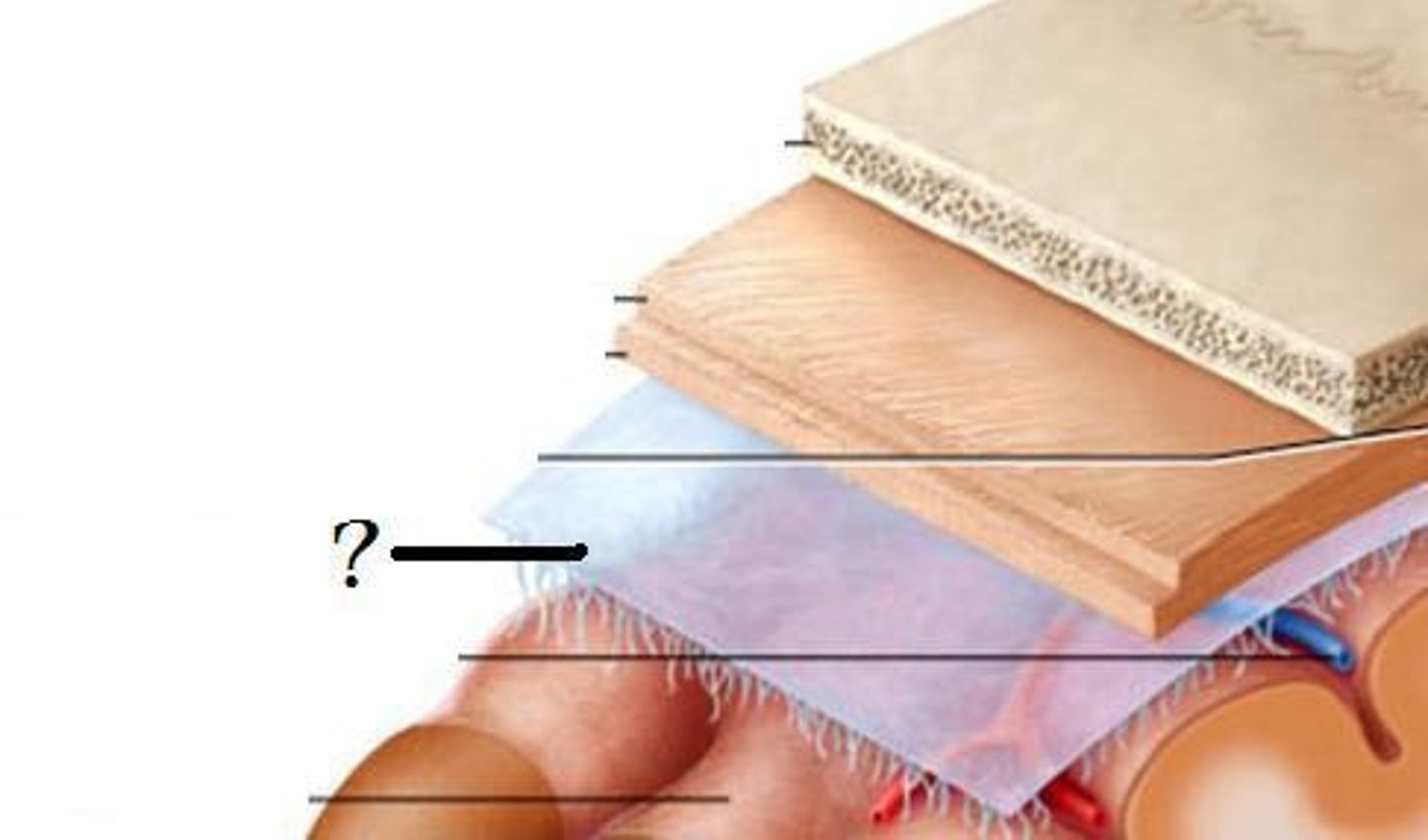
Subarachnoid space
-Separates arachnoid mater from pia mater below
-Contains CSF
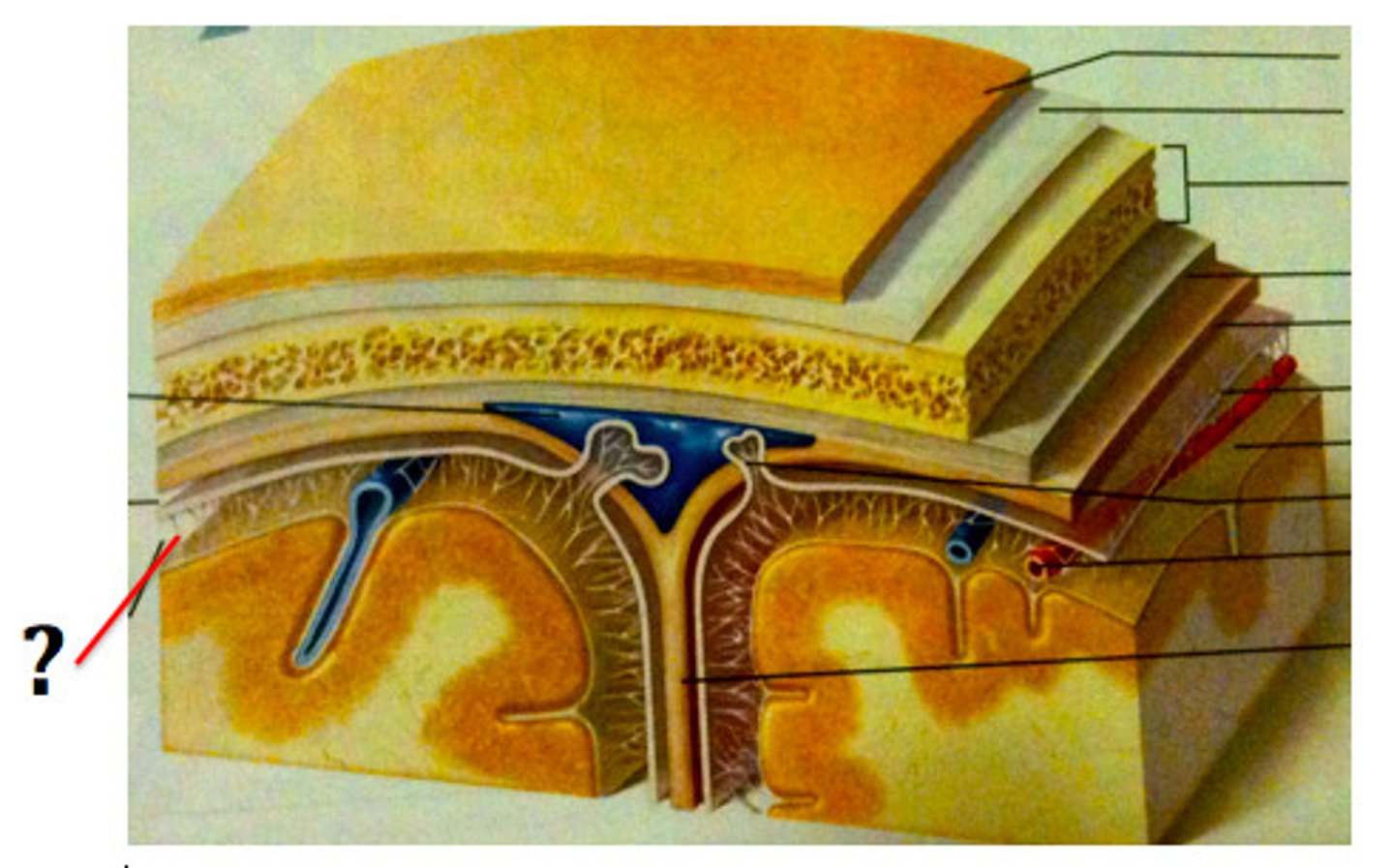
Subdural space
-Separates arachnoid from dura mater above in some spaces
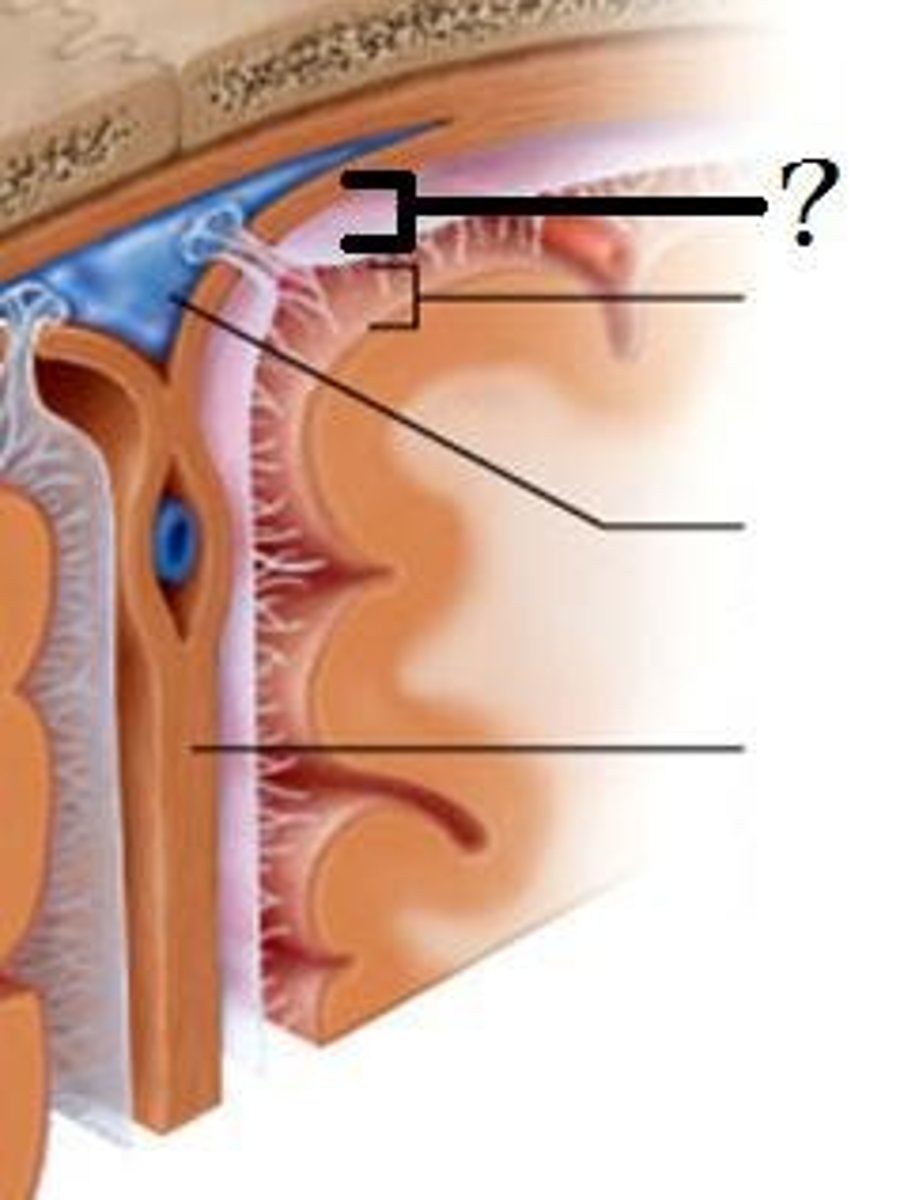
Pia mater
-Very thin membrane that follows contours of brain, even dipping into sulci
-Not usually visible without a microscope
Ventricles
-Internal chambers within the brain
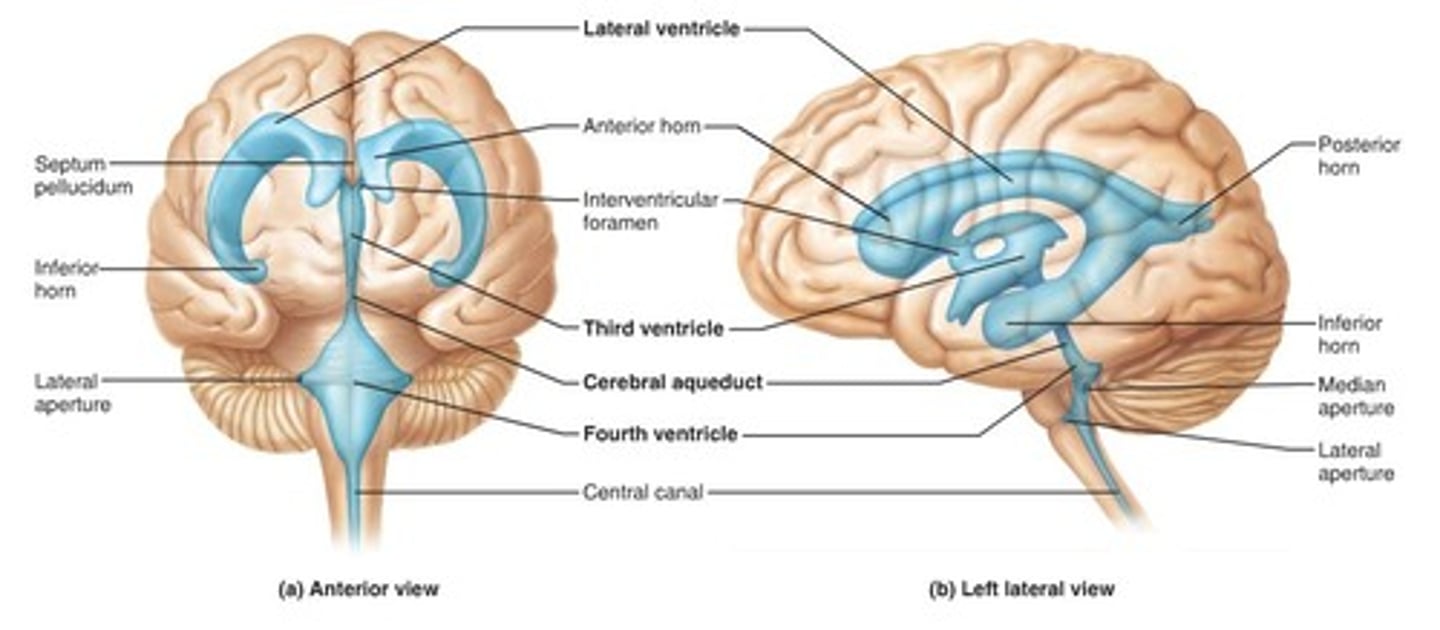
Lateral ventricles
-One in each cerebral hemispheres
-Interventricular foramen
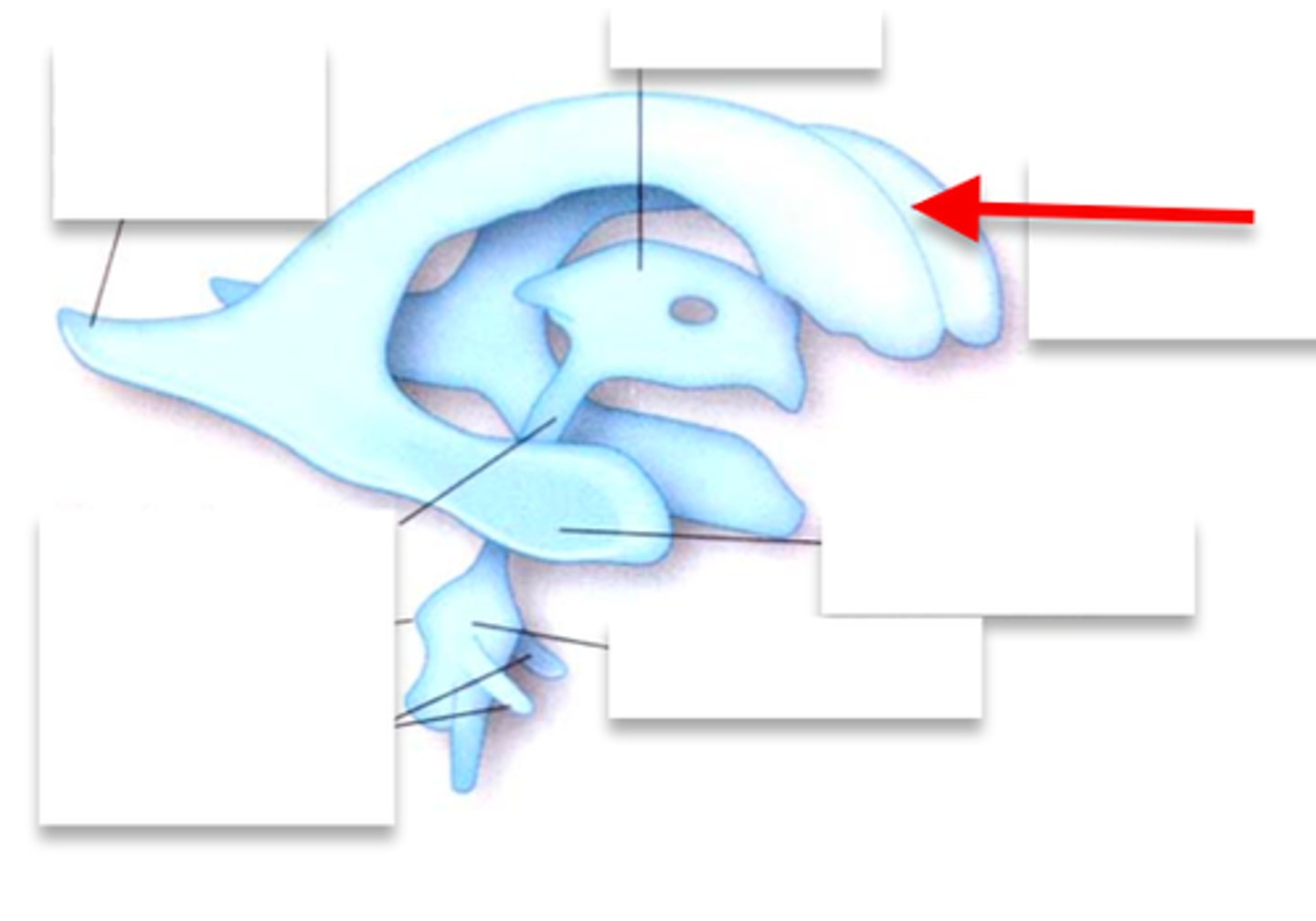
Interventricular foramen
-Tiny pore that connects to third ventricle
Third ventricle
-Narrow medial space beneath corpus callosum
-Connects to cerebral aqueduct
Cerebral aqueduct
-Runs through midbrain and connects to third and fourth ventricles
Fourth ventricle
-Small triangular chamber between pons and cerebellum
-Connects to central canal that runs through spinal cord
Choroid plexus
-Spongy mass of blood capillaries on the floor of each ventricle
Ependymal
-Type of neuroglia that lines ventricles and covers choroid plexus
-Produces CSF
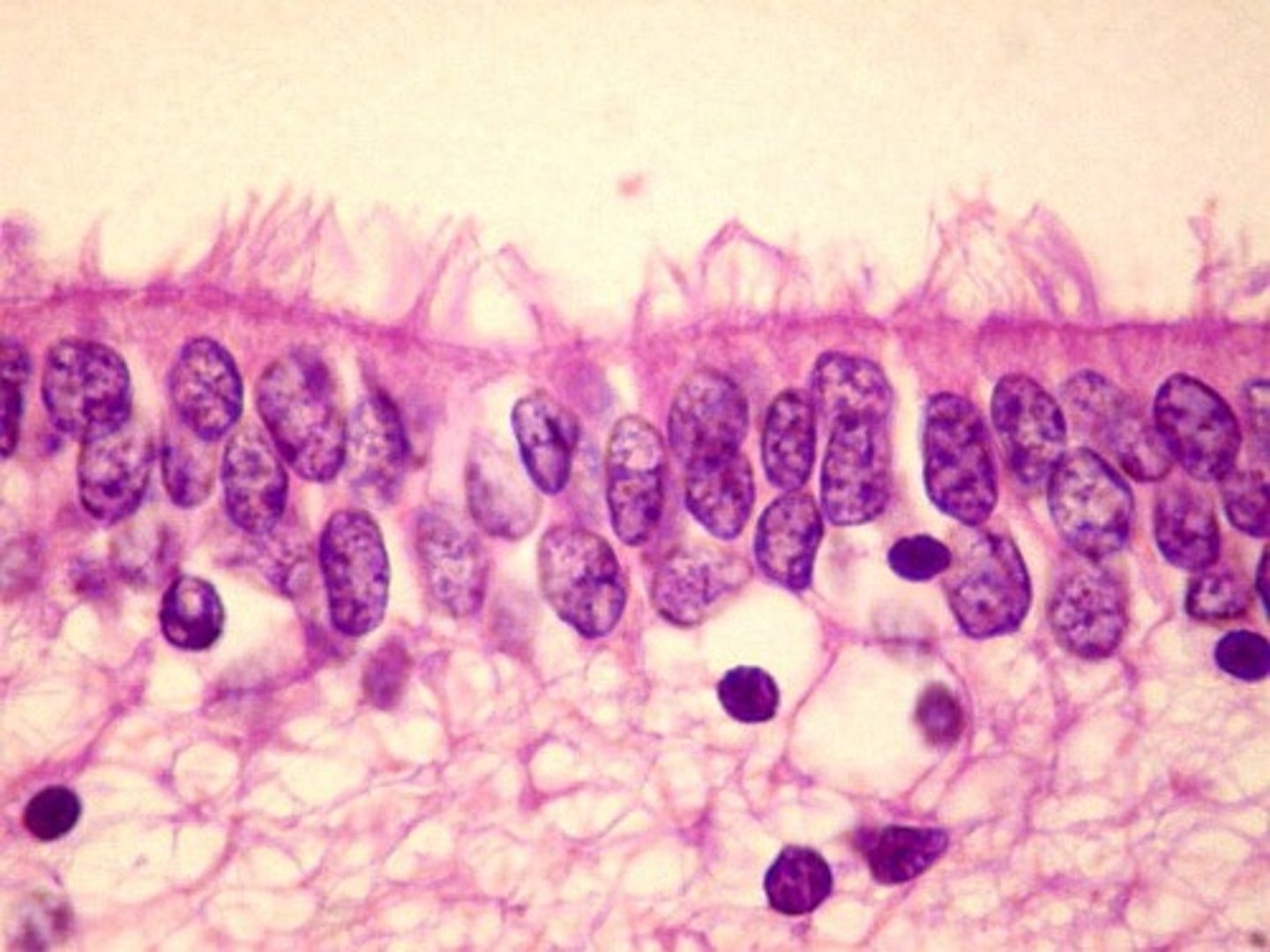
Cerebrospinal fluid
-CSF
-Clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of CNS
-Bathes its external surface
CSF production
-Brain produces and absorbs 500 mL/day
-100-160 present at one time
-produced 40% in subarachnoid space
-Produced evenly by ependymal cells lining ventricles and by the choroid plexuses
CSF creation
-Begins with filtration of blood plasma through capillaries of the brain
-More sodium and chloride then plasma
-Less potassium, glucose, and very little protein
Bouyancy
-Allows brain to attain considerable size without being impaired by its own weight
Without CSF
-If it rested heavily on floor of cranium, the pressure would kill the nervous tissue
Shock absorbtion
-Protects the brain from striking the cranium when the head is jolted
severe jolting
-cause shaken child syndrome and concussions
Chemical stability
-Flow of CSF rinses away metabolic wastes from the nervous tissue and homeostatically regulates its chemical environment
Blood flow to brain
-2% of bodies weight
-receives 15% of the blood
-750 mL /min
Neurons and blood flow
-High demand for ATP, and therefore, O2 and glucose
-Constant supply of blood is critical
10 second interruption
-may cause loss of consciousness
1-2 min interruption
-Can cause significant impairment of neural function
going 4 min
-Causes irreversible brain damage
Blood barrier system
-Regulates what substances can get from bloodstream into tissue fluid of the brain
-Though crucial it can contain harmful agents
Gaurded points of entry
-Blood capillaries throughout the brain tissue
-Capillaries of the choroid plexus
Blood CSF barrier
-Protects brain at the choroid plexus
-Forms tight junctions between ependymal cells
Blood barrier allows
-is highly permeable to water, glucose
-lipid-soluble substances such O2, CO2, alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, and anesthetics
Brain barrier system
-BBS
-Can be an obstacle for delivering medication such as antibiotics and cancer drugs
-Can be damaged by trauma and inflammation
Circumventricular organs
-CVO
-Places in the third and fourth ventricles where barrier is absent
Circumventricular organ functions
-Blood has direct access to the brain
-Enables brain to monitor and respond to fluctuations in blood glucose, pH, osmolarity, and other variables
Medulla oblongata location
-Begins at foramen magnum of skull
-Extends about 3 cm rostrally and ends at a groove just below pons
-Slightly wider than pons
Pyramids location
-Pair of ridges on anterior surface resembling side-by-side baseball bats
-Four pairs of cranial nerves begin or end in medulla (VIII (in part), XI, X, and XII)
-Separated by anterior median fissure
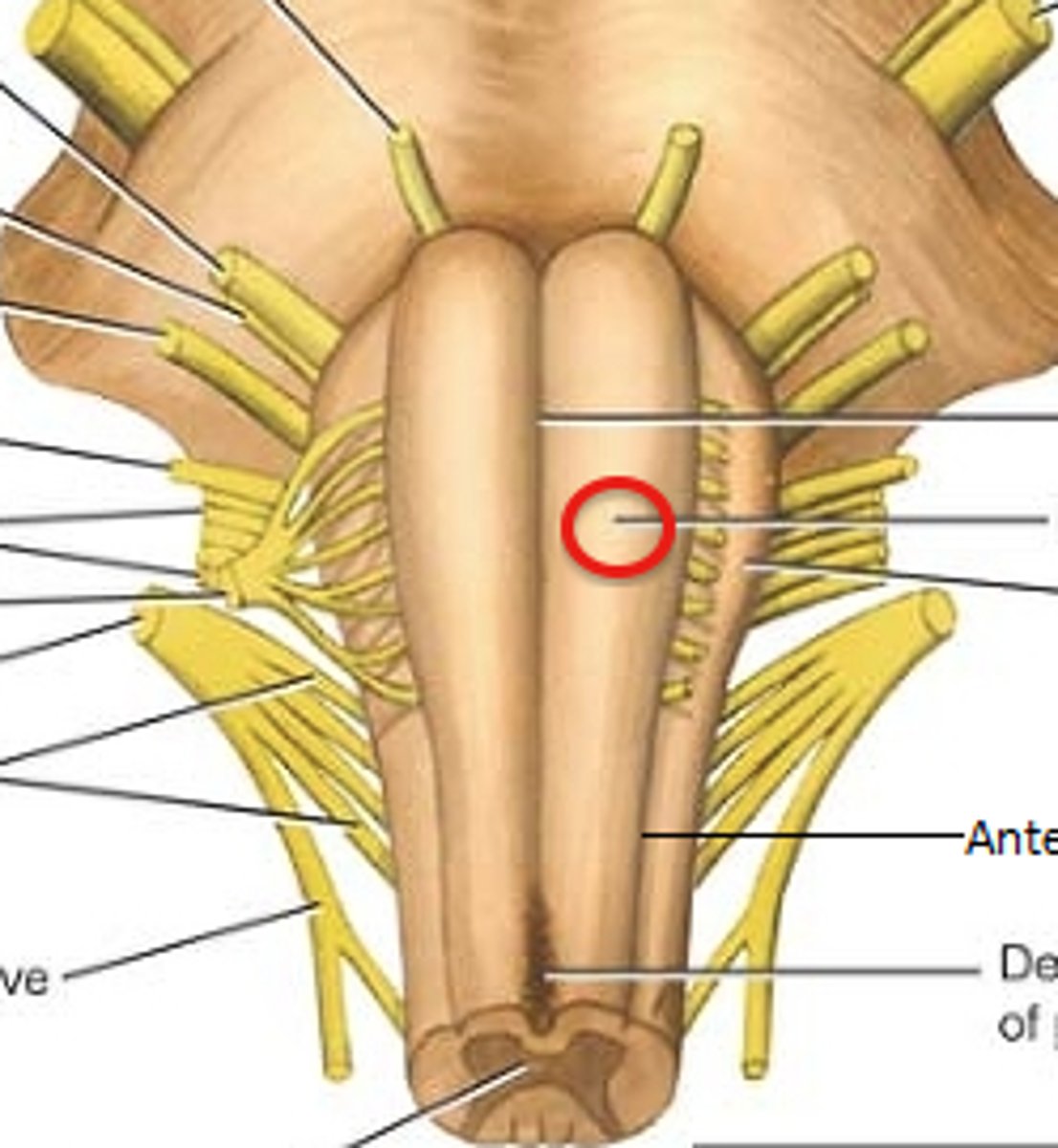
Medulla oblongata function
-Houses neurosomas of second-order sensory neurons
-All ascending and descending fibers connecting to brain and spinal cord pass through

Olives
-Prominent bulges lateral to each pyramid
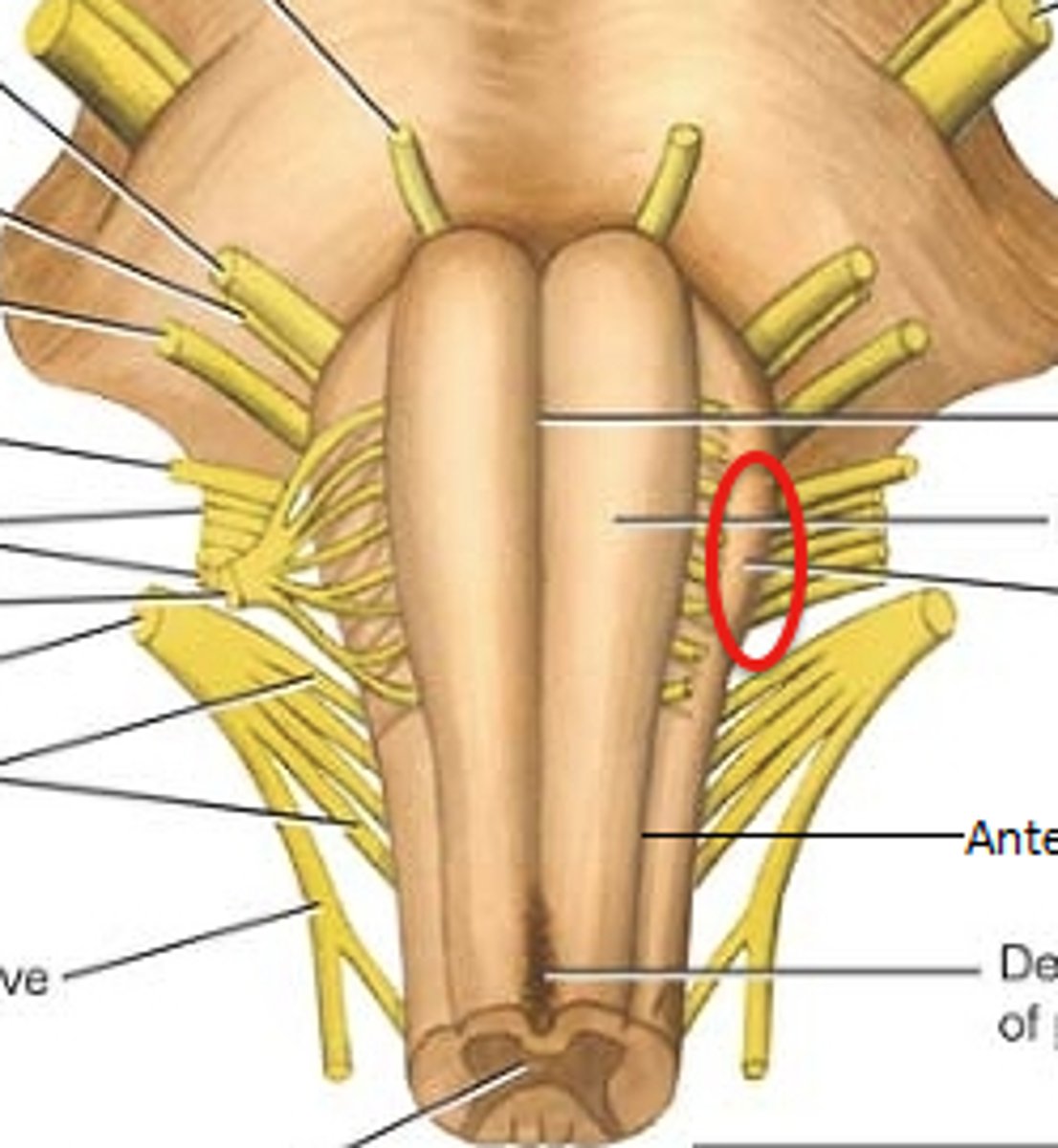
pyramids functions
-Carry motor signals to skeletal muscle

Inferior olivary nucleus
-Relay center for signals to cerebellum
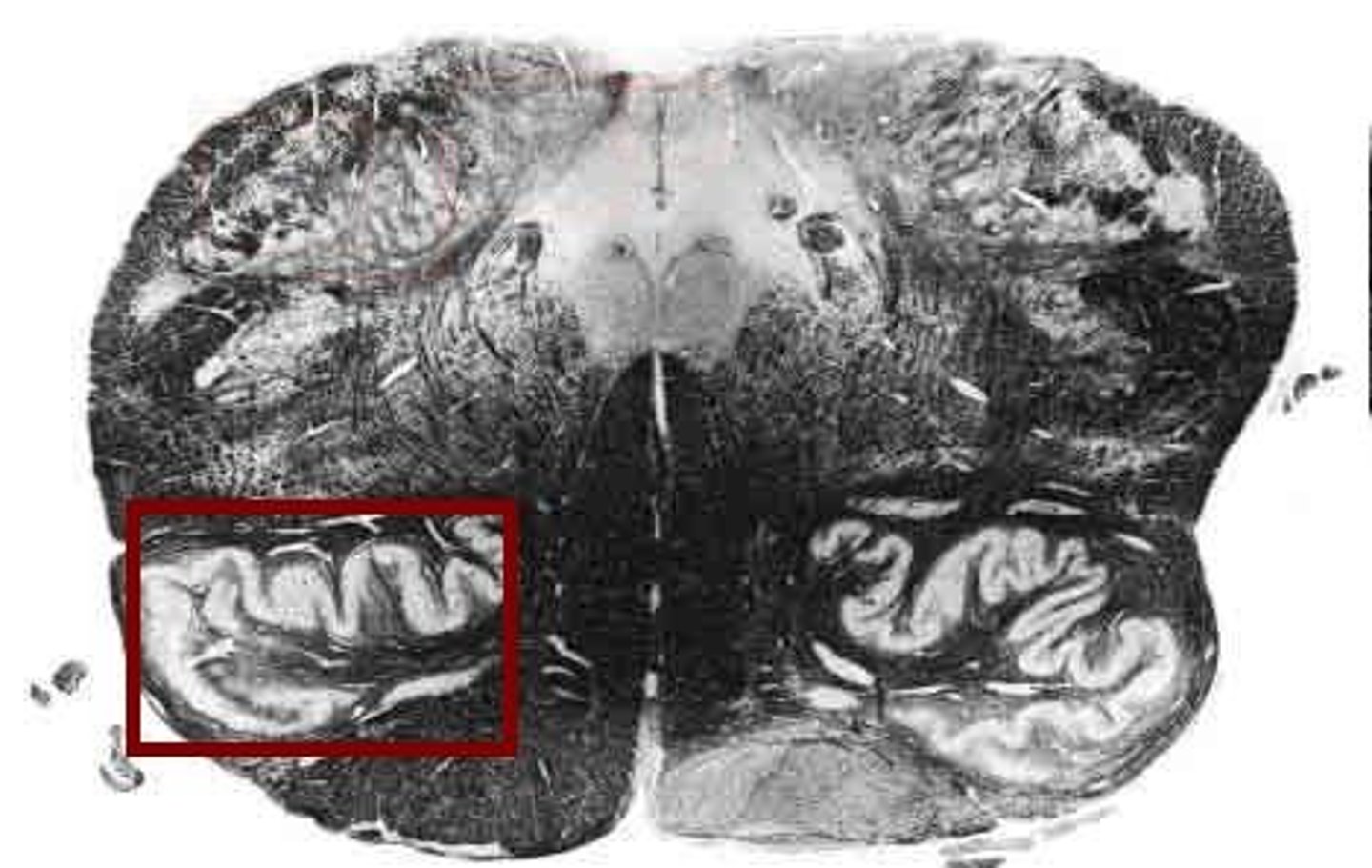
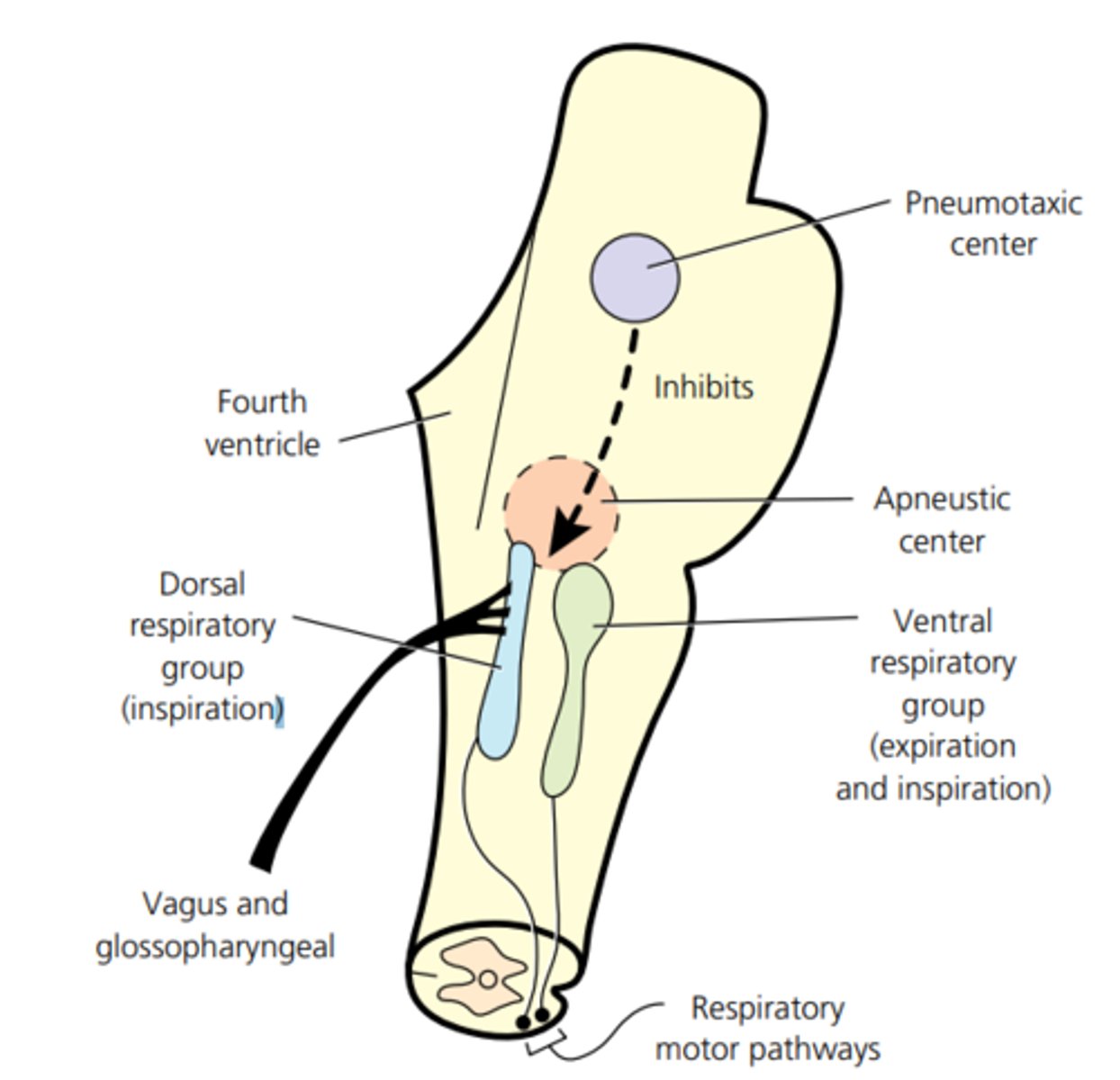
reticular formation
-Loose network of nuclei extending throughout the medulla, pons, and mid brain
-Contains cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory center
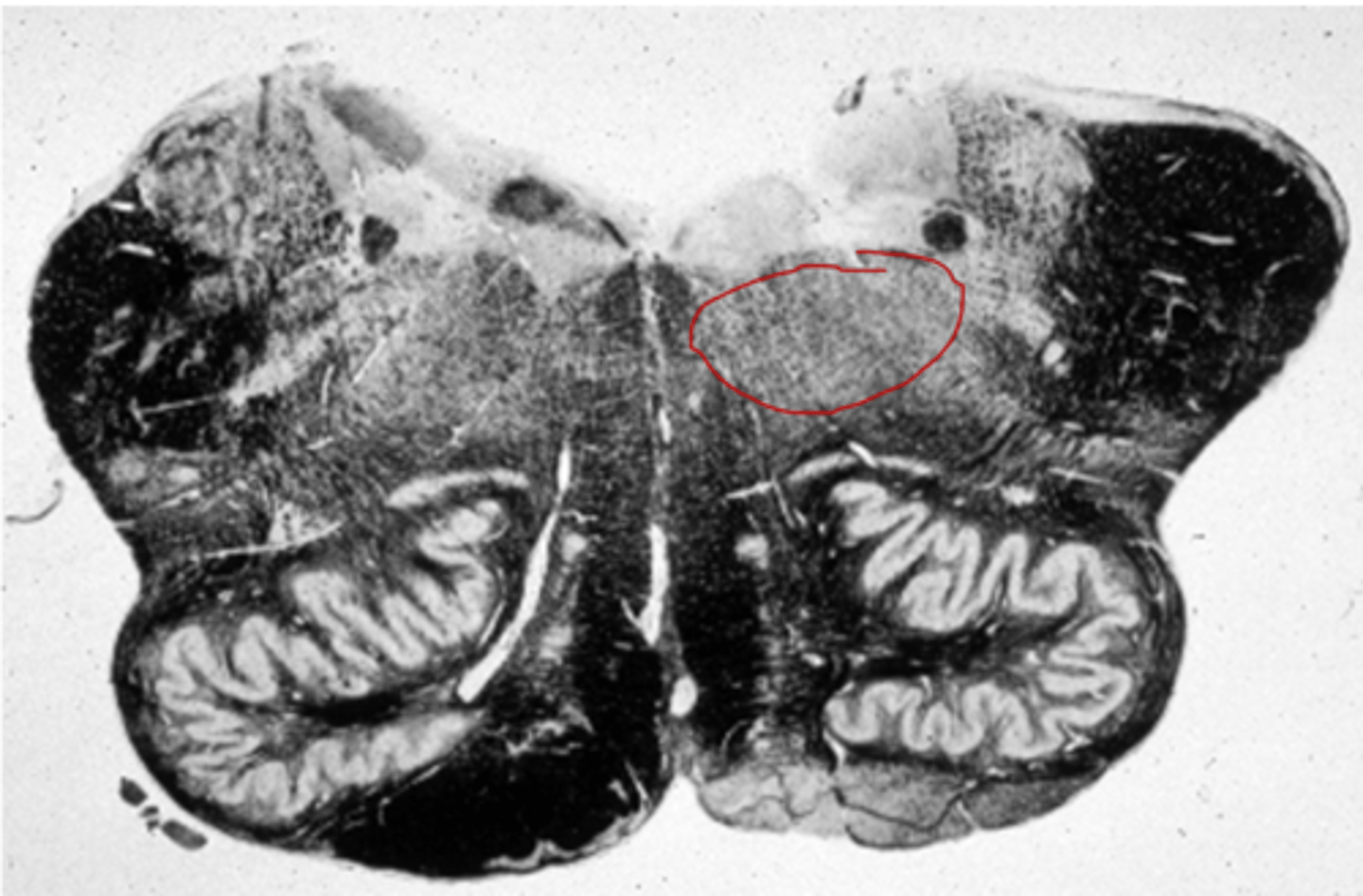
Pons location
-Anterior bulge in the brainstem, rostral to medulla
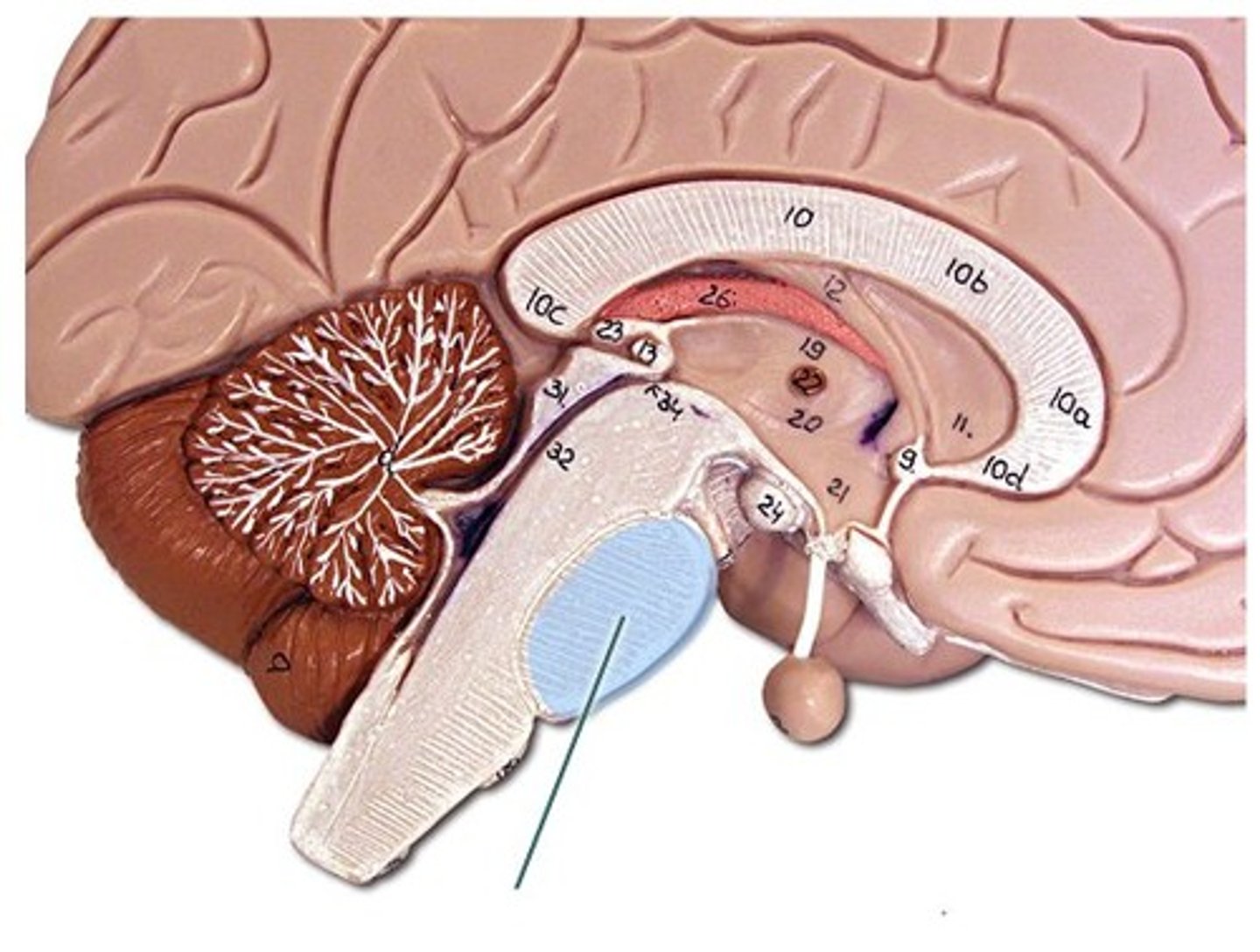
Pons function
-Reticular formation in pons contains additional nuclei concerned with sleep, respiration, and posture
-CN V, VI, VII and VIII
Pons sensory roles
-Hearing, equilibrium, taste, and facial sensation
Pons motor roles
-Eye movement, facial expressions, chewing, swallowing, urination, and secretion of saliva and tears
Cerebral peduncles pons
-Thick stalks on posterior pons that connect it (and the midbrain) to the cerebellum
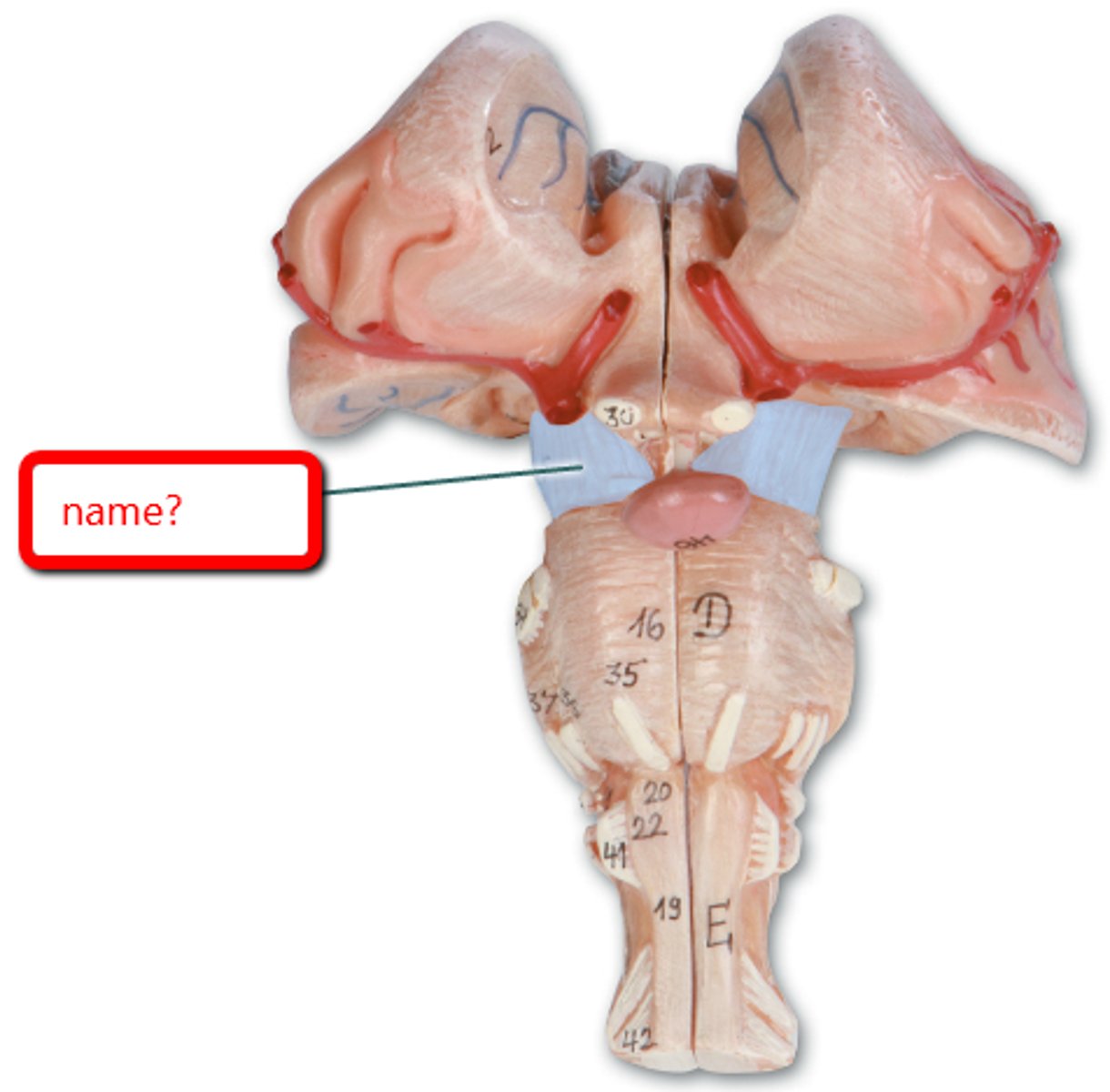
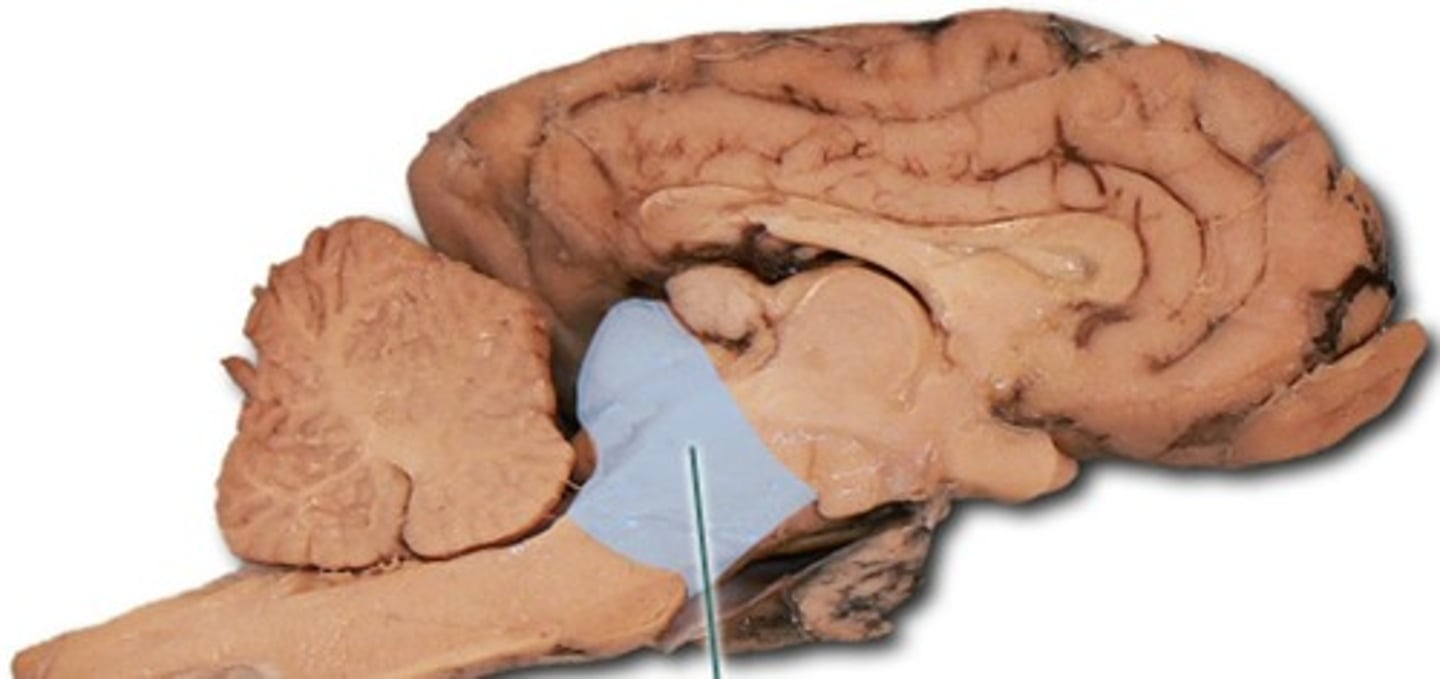
Midbrain function
-Short segment of the brainstem that connects hindbrain to the forebrain
-contains cerebral aqueduct
=Surrounded by central gray matter involved in controlling pain
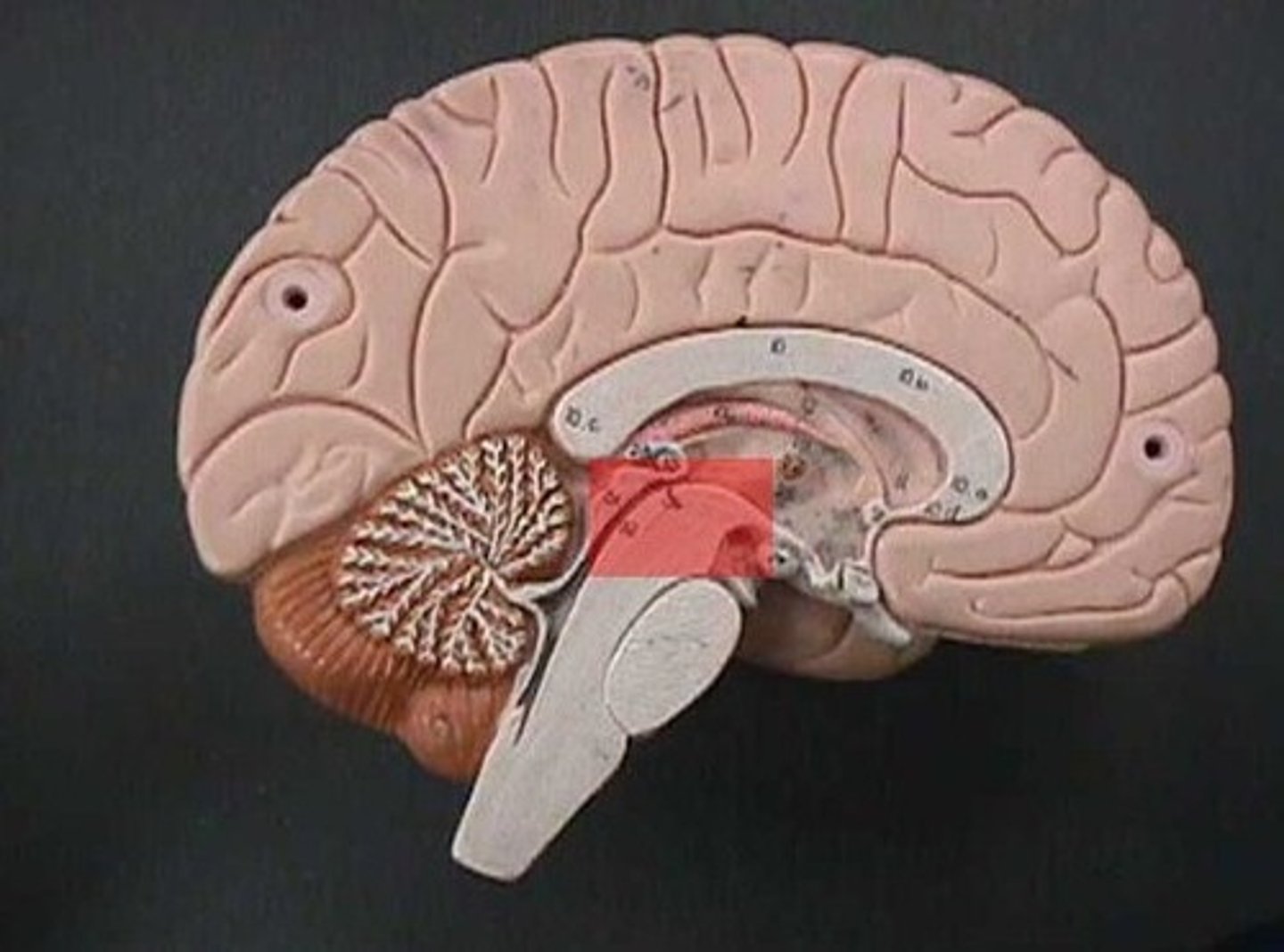
Midbrain
Contains...
-continuation of reticular formation
-Motor nuclei of two cranial nerves that control eye movement
-CN III and IV
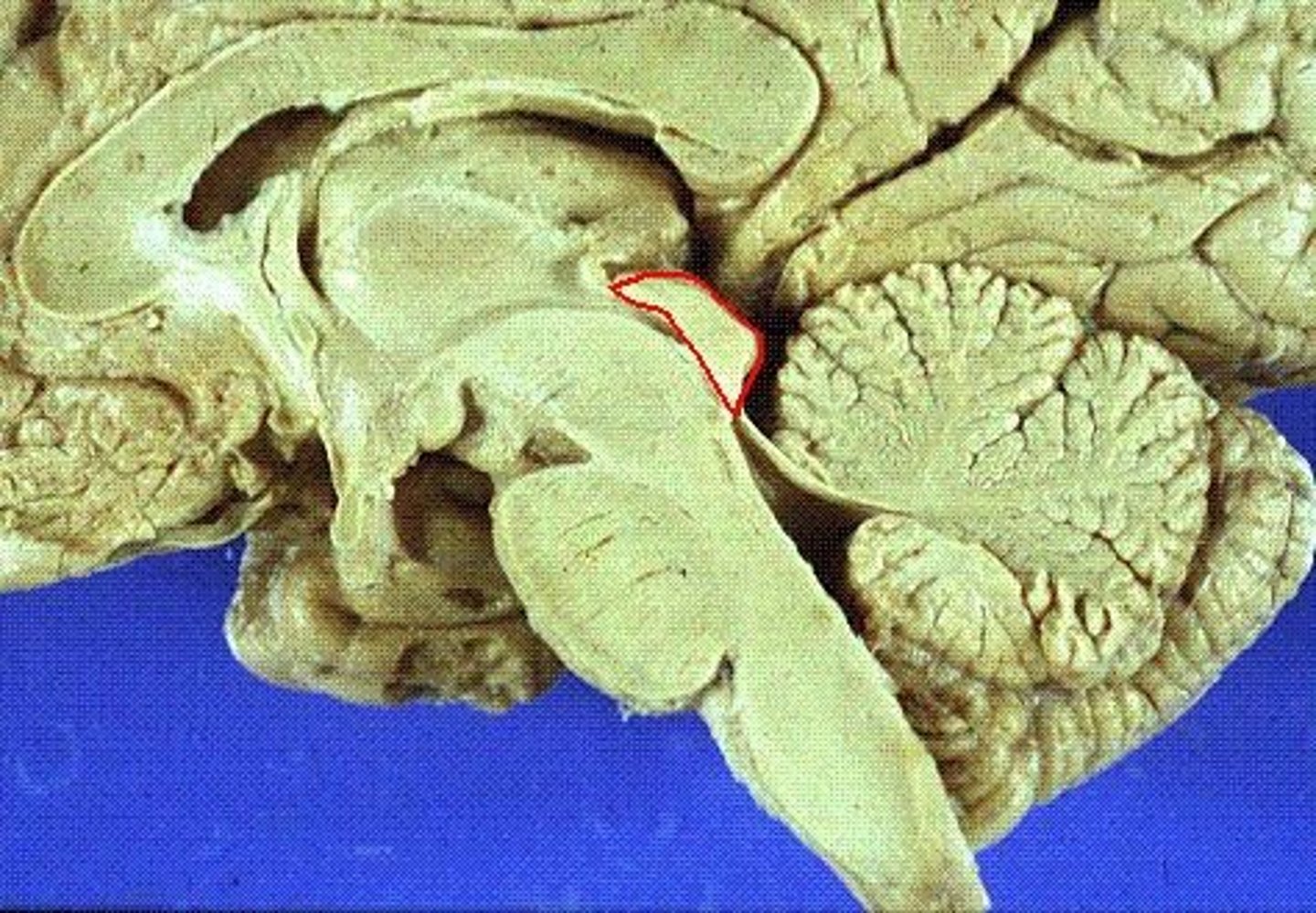
Tectum
-Roof-like part of the midbrain posterior to cerebral aqueduct
-contains corpora quadrigemina
=Superior and inferior colliculi
Superior colliculi
-Upper pair of corpora quadrigemina
-Function in visual attention, tracking moving objects, and some reflexes
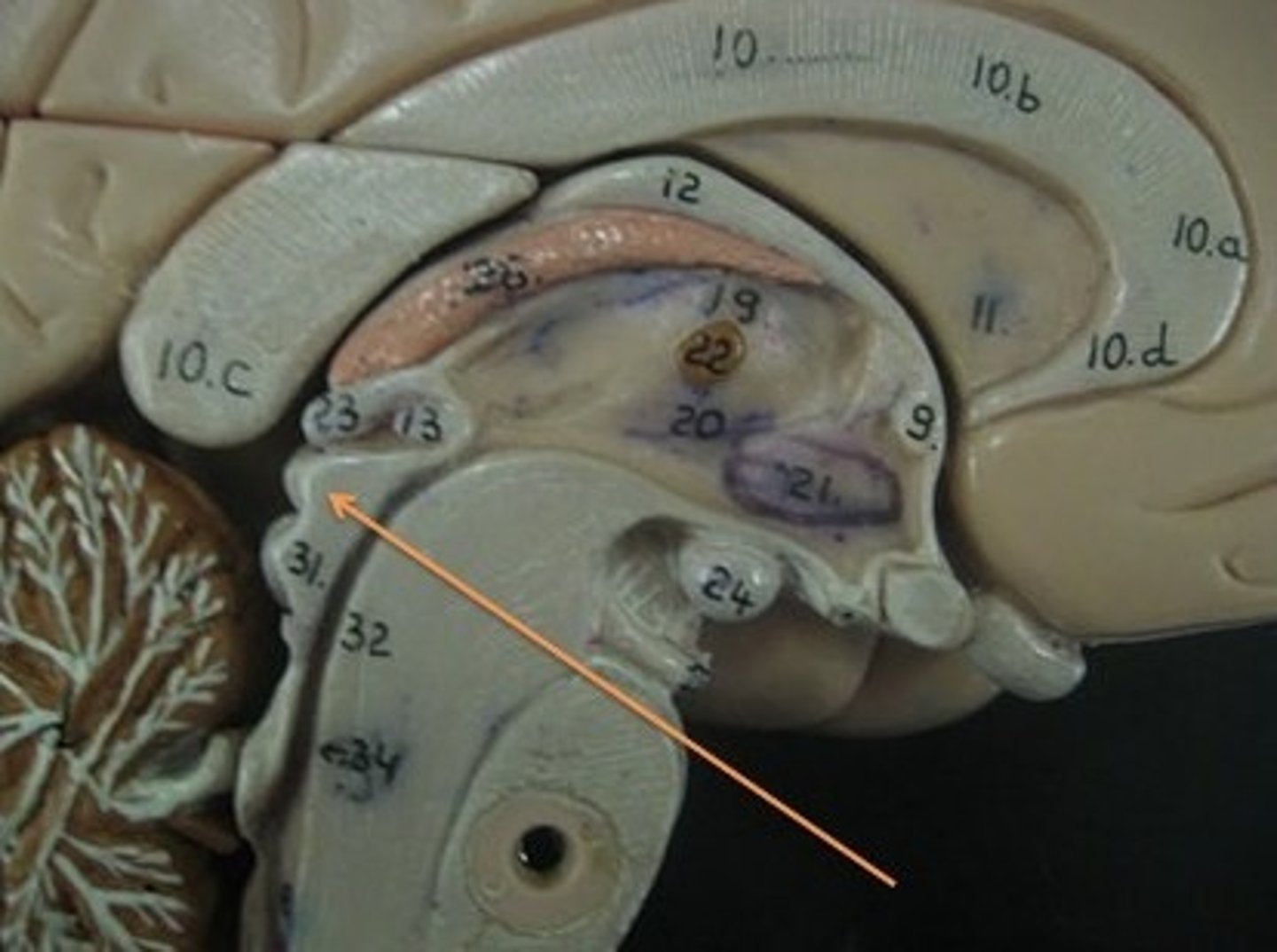
Inferior colliculi
-Lower pair of corpora quadrigemina
-Receives signals from the inner ear and relays them to other part of the brain, especially thalamus
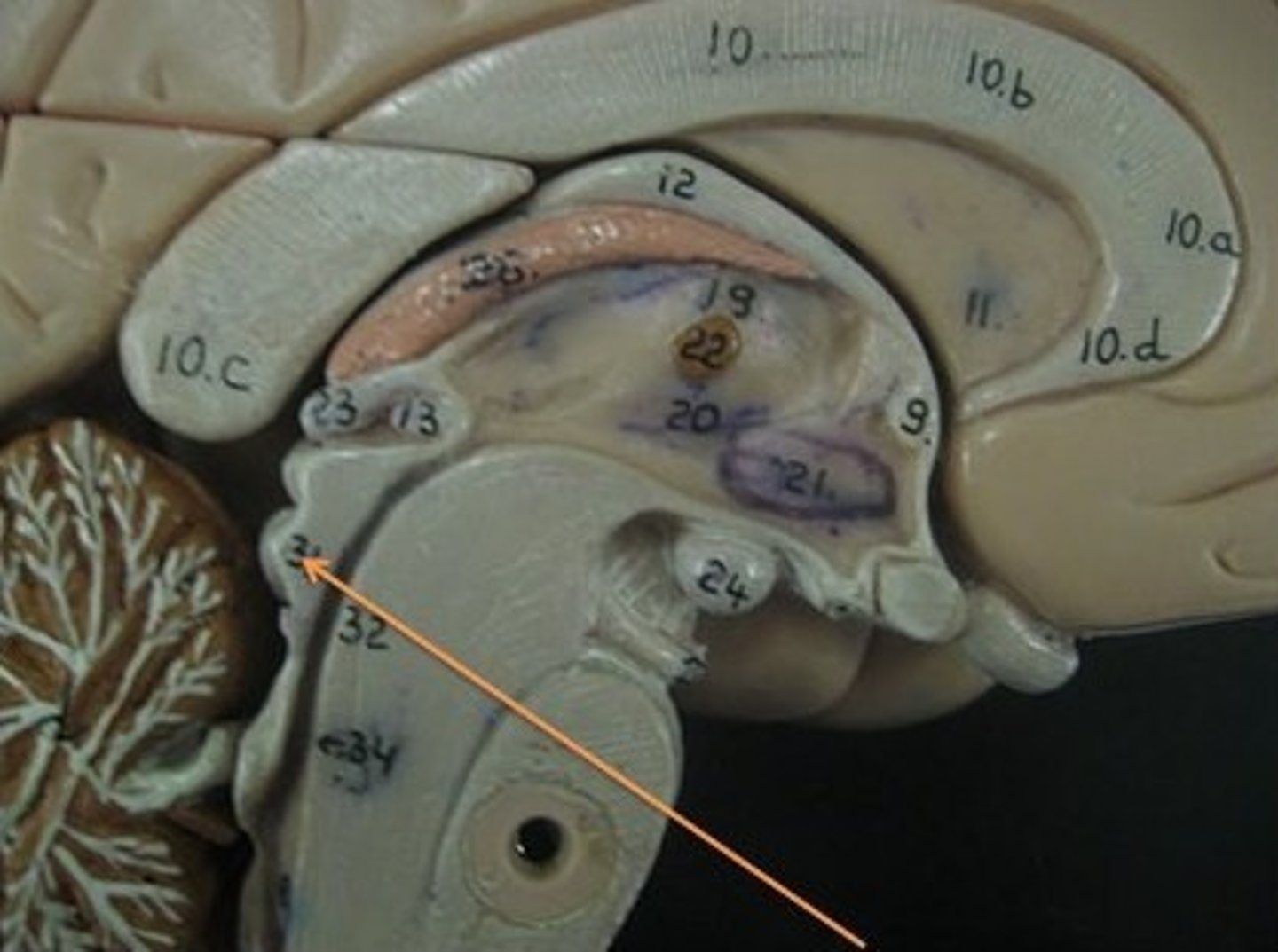
Cerebral peduncles midbrain
-Two anterior midbrain stalks that anchor the cerebrum to the midbrain
-Each peduncle has three parts
=Tegmentum, substantia nigra, other (not important)
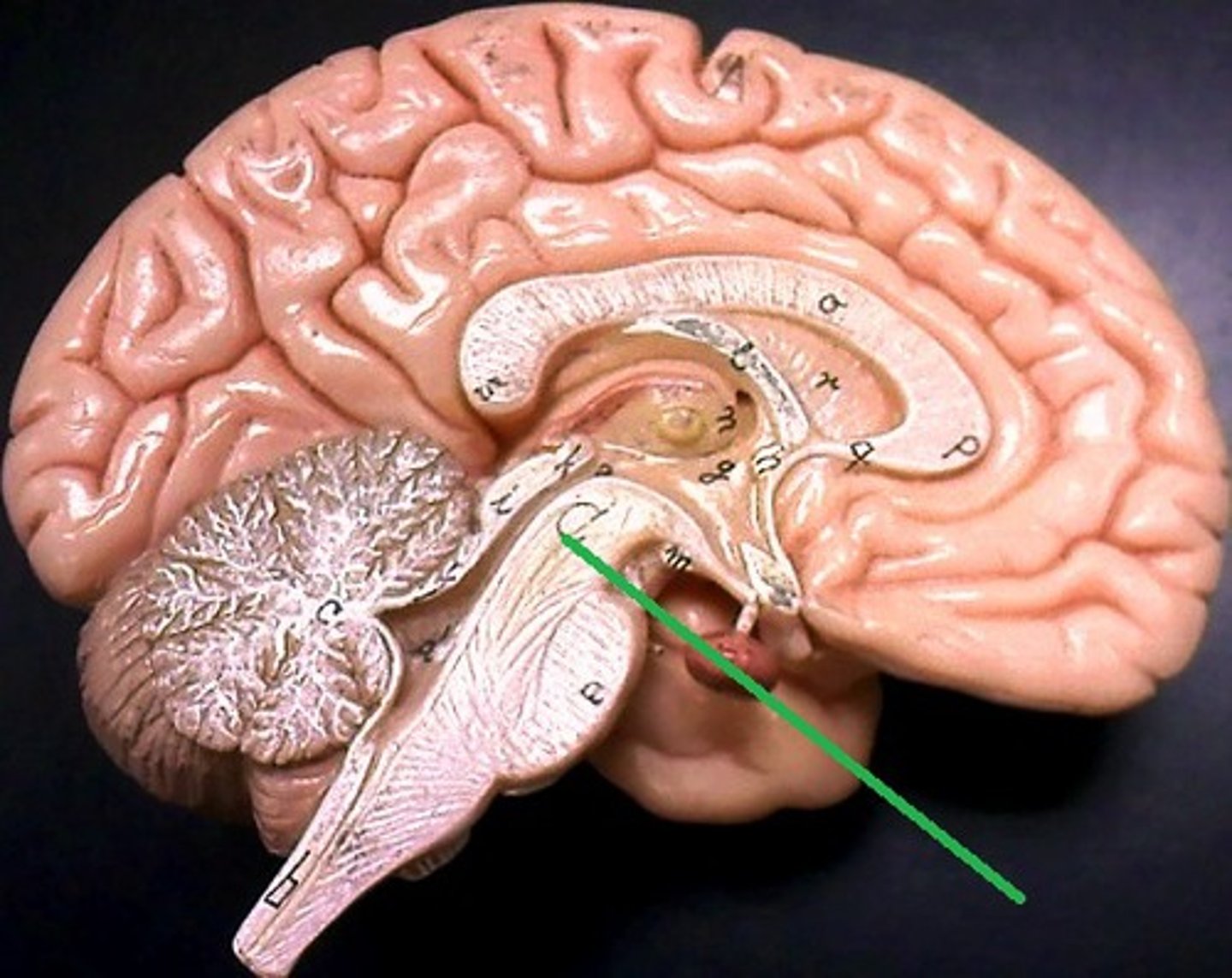
Tegmentum
-Dominated by red nucleus
-Pink color due to high density of blood vessels
-Connections go to and from cerebellum for motor controls
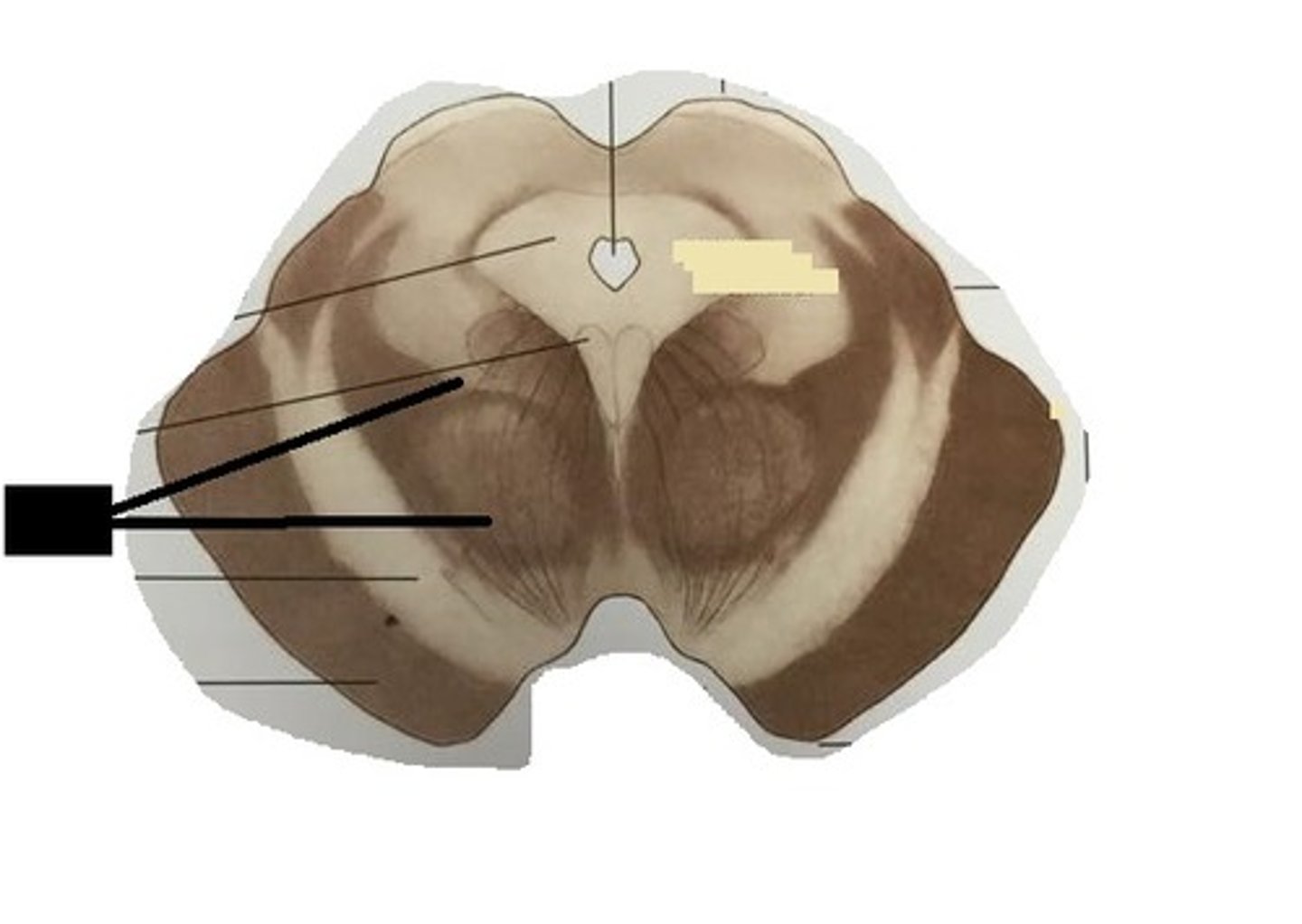
Substantia nigra
-Motor center that relays inhibitory signals to thalamus and basal nuclei preventing unwanted body movement
-Black nucleus pigmented with melanin
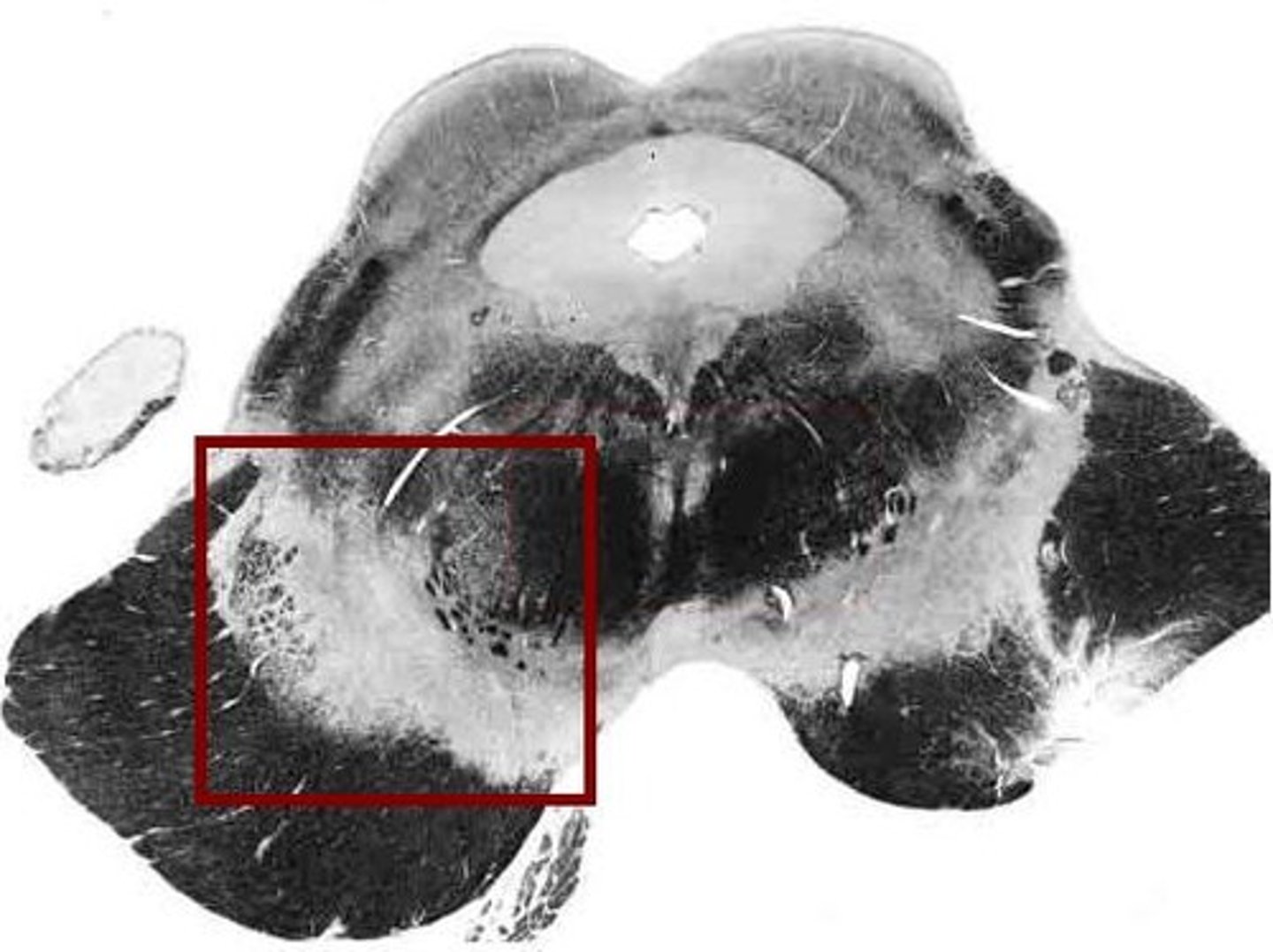
Substantia nigra senescence
-Degeneration of neurons leads to tremors of Parkinson disease
Reticular formation
-Loose web of gray matter that runs vertically though all levels of the brainstem
-Has connections with many areas of cerebrum
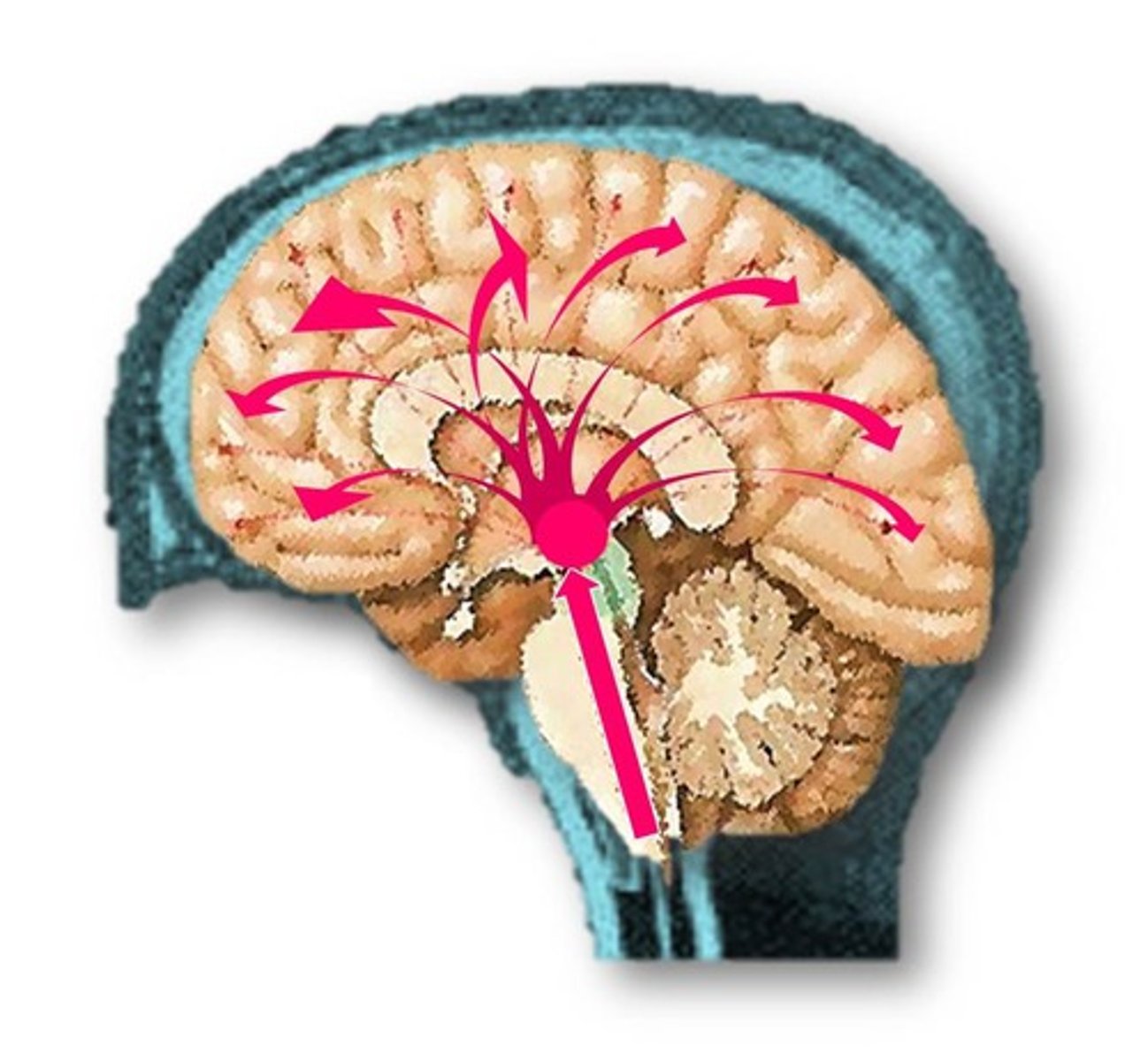
reticular formation location
-Occupies space between white fiber tracts and brainstem nuclei
-Has more than 100 small neural networks without distinct boundaries
reticular formation function
-Somatic motor control
-Adjust muscle tension
-Cardiovascular control
-Pain modulation
-sleep and consciousness
-Habituation
-Gaze center
-Central pattern generators
-Integrate visual, auditory, balance and motion stimuli into motor coordination
Adjust muscle tension
-Reticular formation
-To maintain tone, balance, and posture, especially during body movements
Gaze centers
-Reticular formation
-Allow eyes to track and fixate on objects
Central pattern generators
-Reticular formation
-Neural pools produce rhythmic signals to the muscles of breathing and swallowing
Cardiovascular control
-Reticular formation
-Cardiac and vasomotor centers of medulla oblongata
Pain modulation
-Reticular formation
-some pain signals ascend though the reticular formation
-Some descending analgesic pathways begin in the reticular formation
=End in the spinal cord where they block transmission of pain signals
Sleep and consciousness
-Reticular formation
-Plays a role a central role in consciousness, alertness and sleep
-Injury here can result in irreversible coma
Habituation
-Reticular formation
-Activating system modulates activity in cerebral cortex so that it ignores repetitive, inconsequential stimuli
Cerebellar peduncles
-Three pairs of stalks that connect brainstem and cerebellum
-Fibers carry signals to and from cerebellum
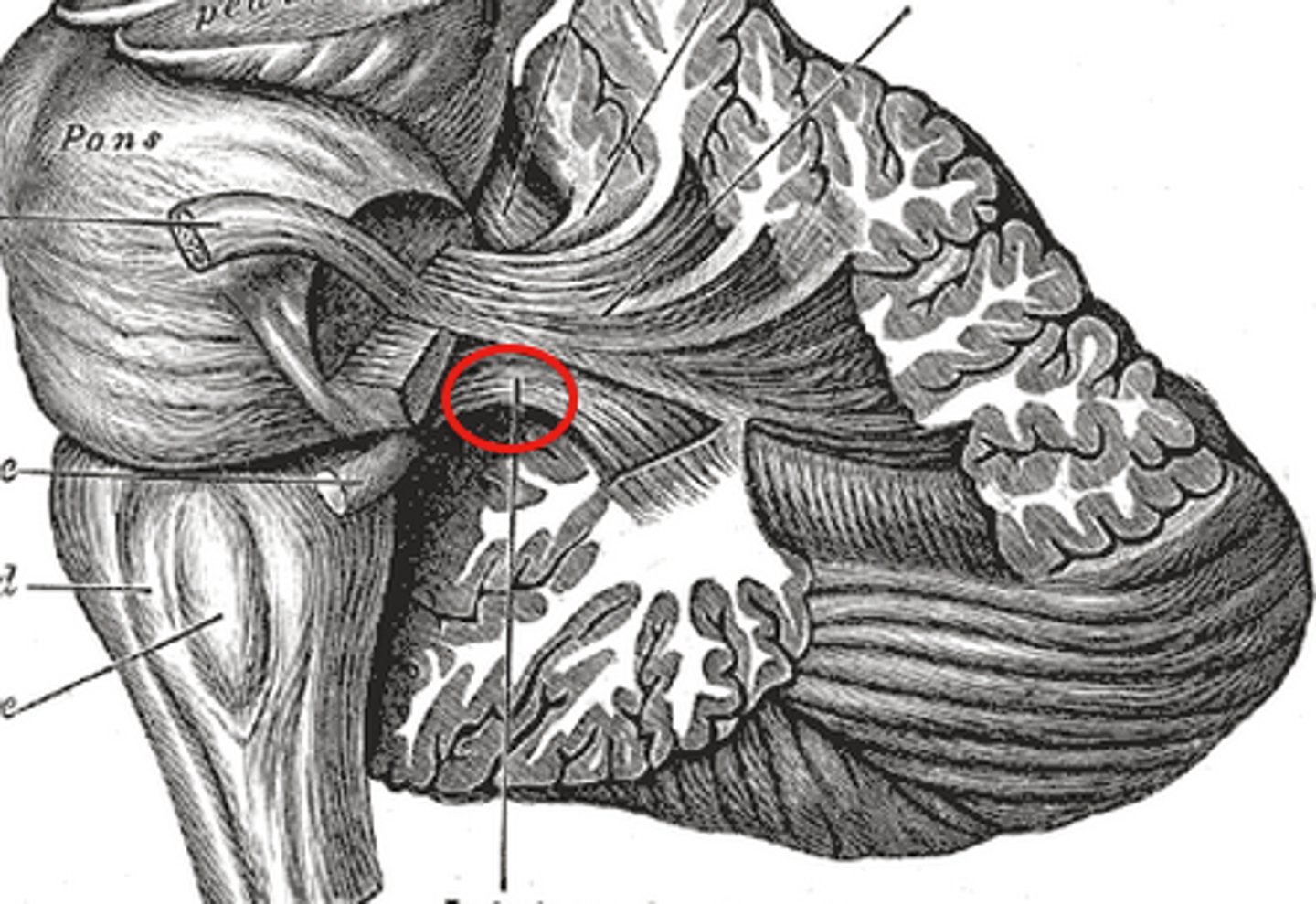
Inferior peduncles
-Connected to medulla oblongata
-Most spinal input enters the cerebellum through here
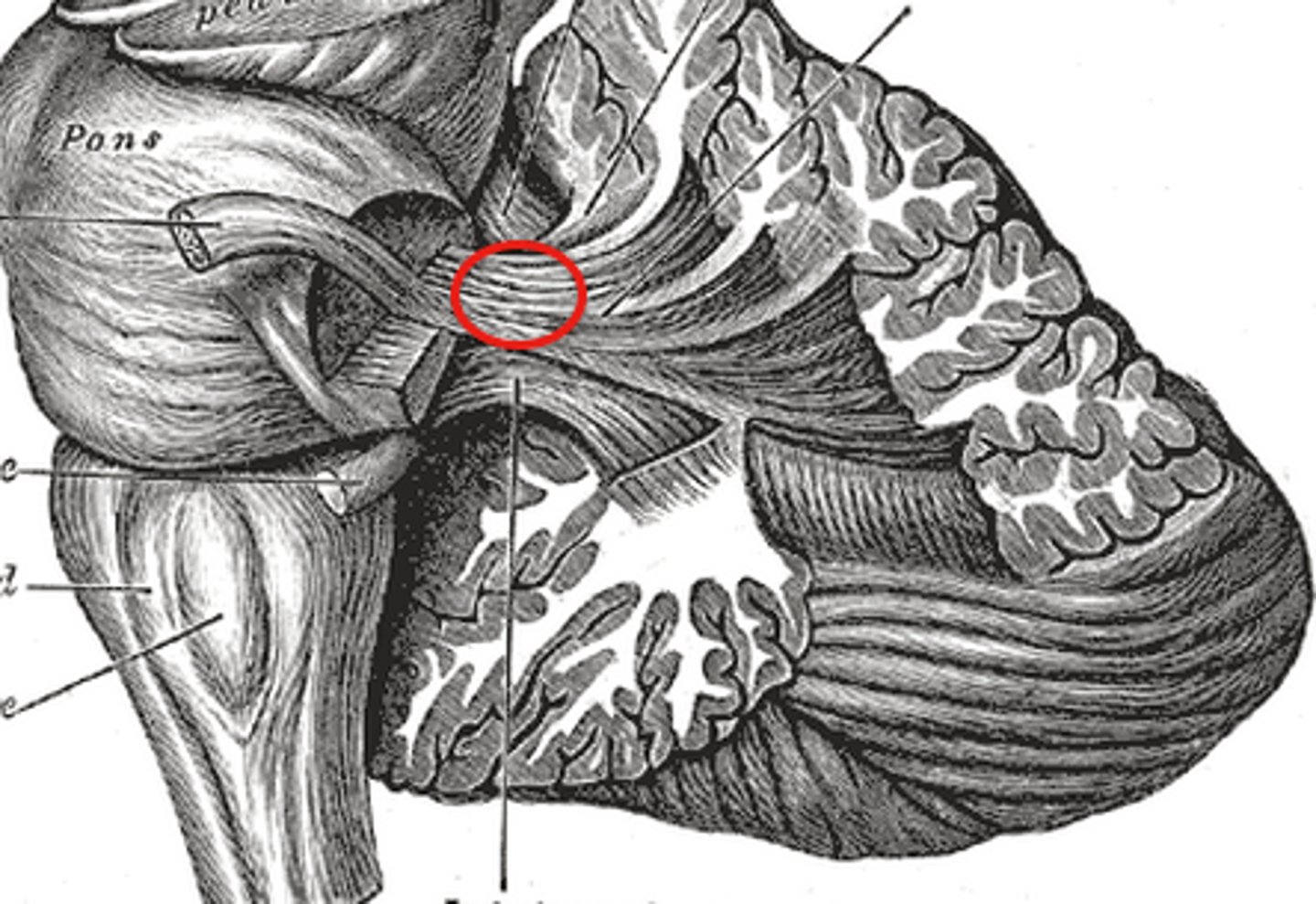
Middle peduncles
-Connected to medulla oblongata
-most input from rest of the brain enters here
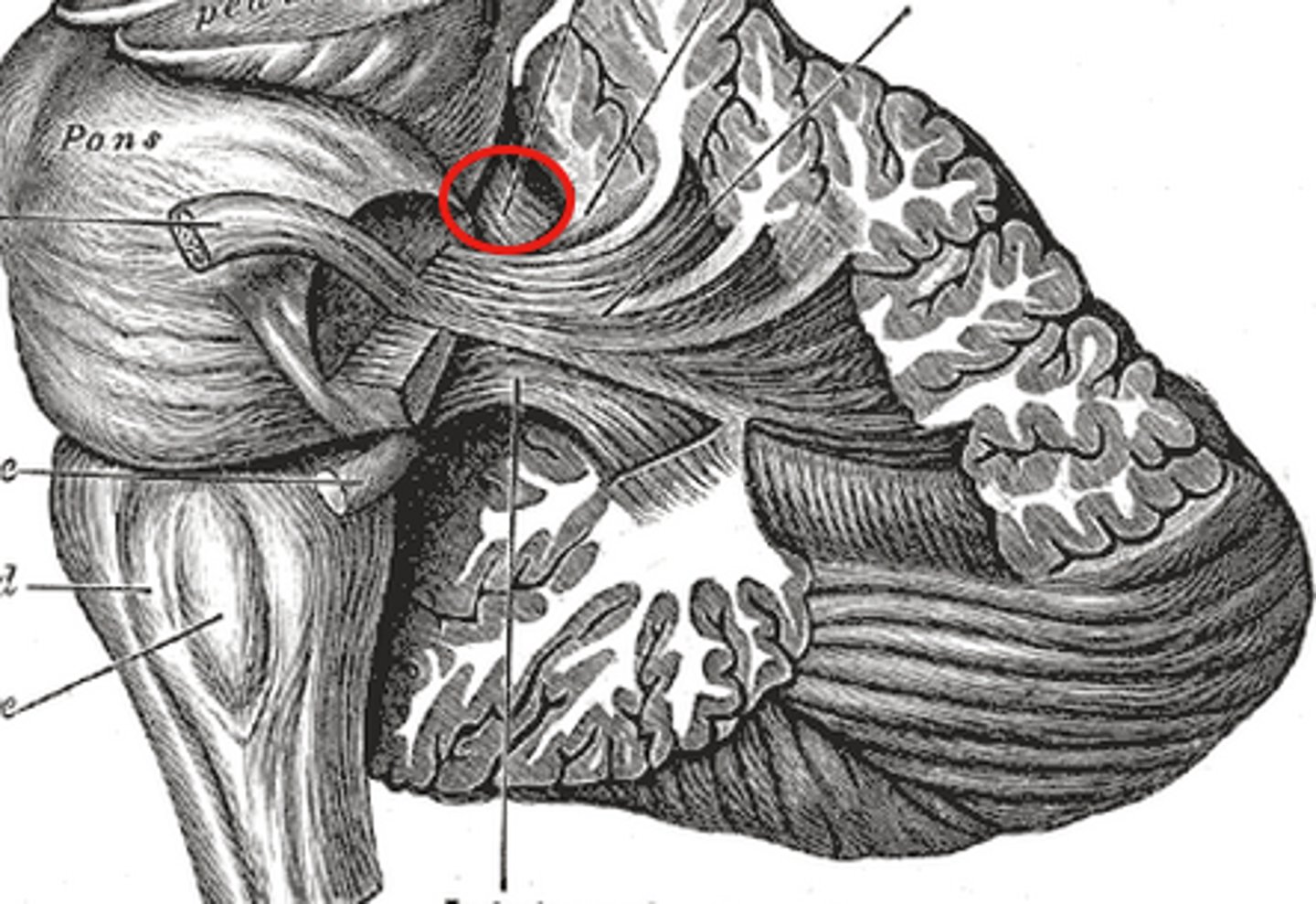
Superior peduncles
-Connected to the midbrain
-Carries cerebellar output
Motor coordination
-Cerebellum has long been known to be important for this and locomotor ability
Cerebellum and nonmotor functions
-Comparing textures
-Perceiving space
-Recognizing objects from different views
-Maintaining judgment of time and Rythm
-directing eye movement that compensates for head movement
-Judging pitch and tone
-Verbal association
-Planning, scheduling, and emotional control
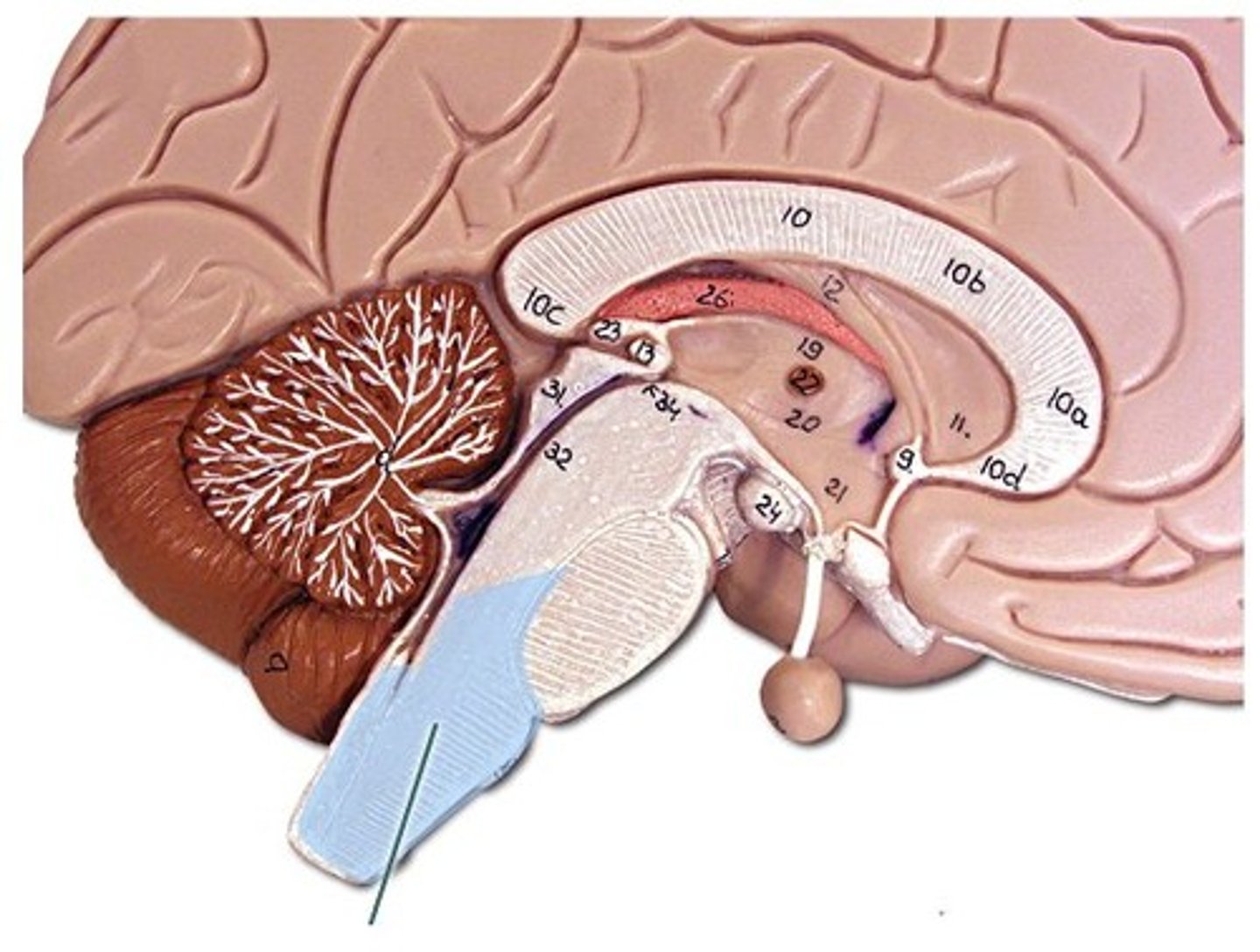
Forebrain
-Diencephalon
-Telencephalon
Diencephalon
-Encloses third ventricle
-Most rostral part of the brainstem
-hypo/thalamus, and epithalamus
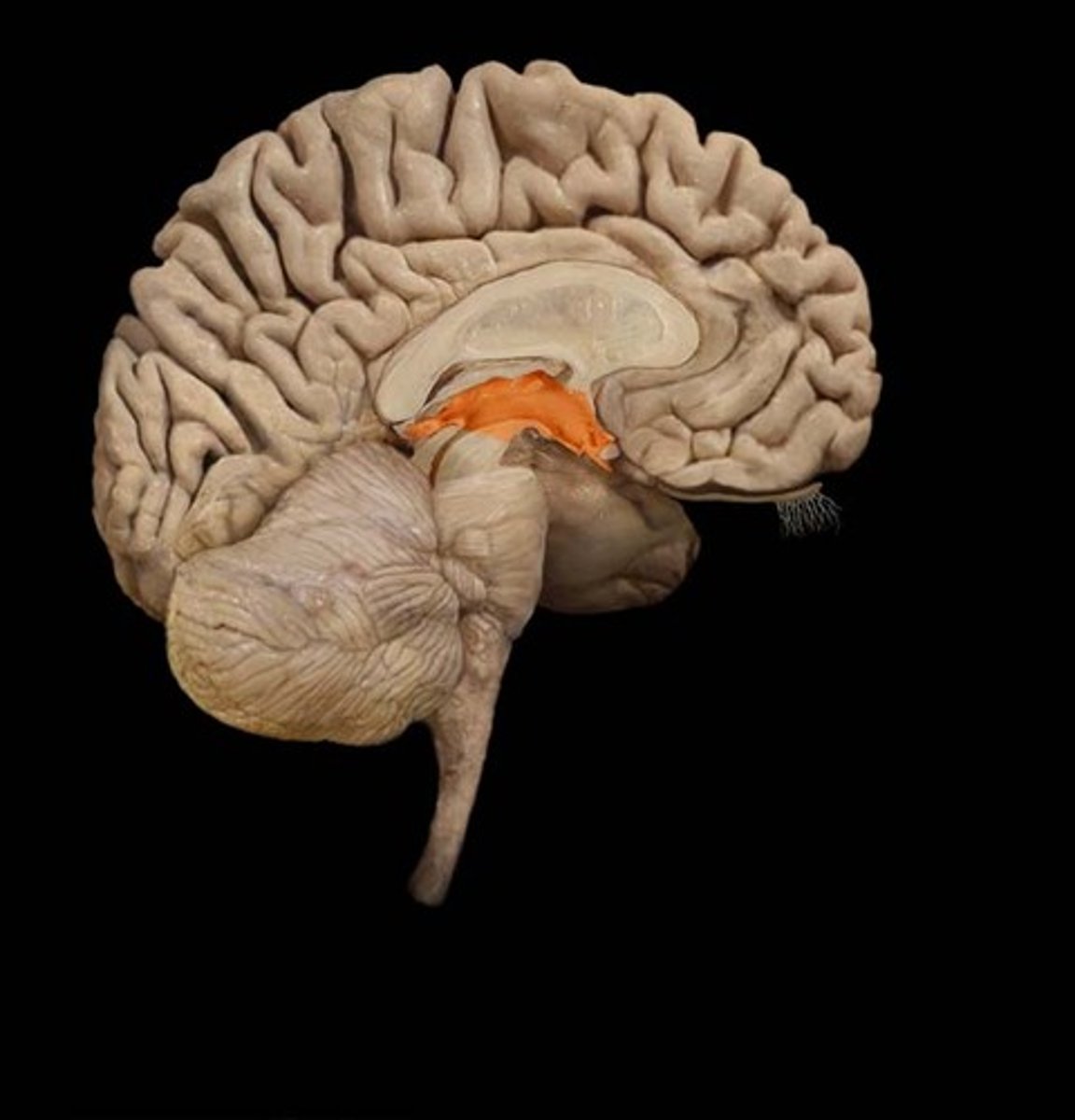
Telencephalon
-Develops chiefly into the cerebrum
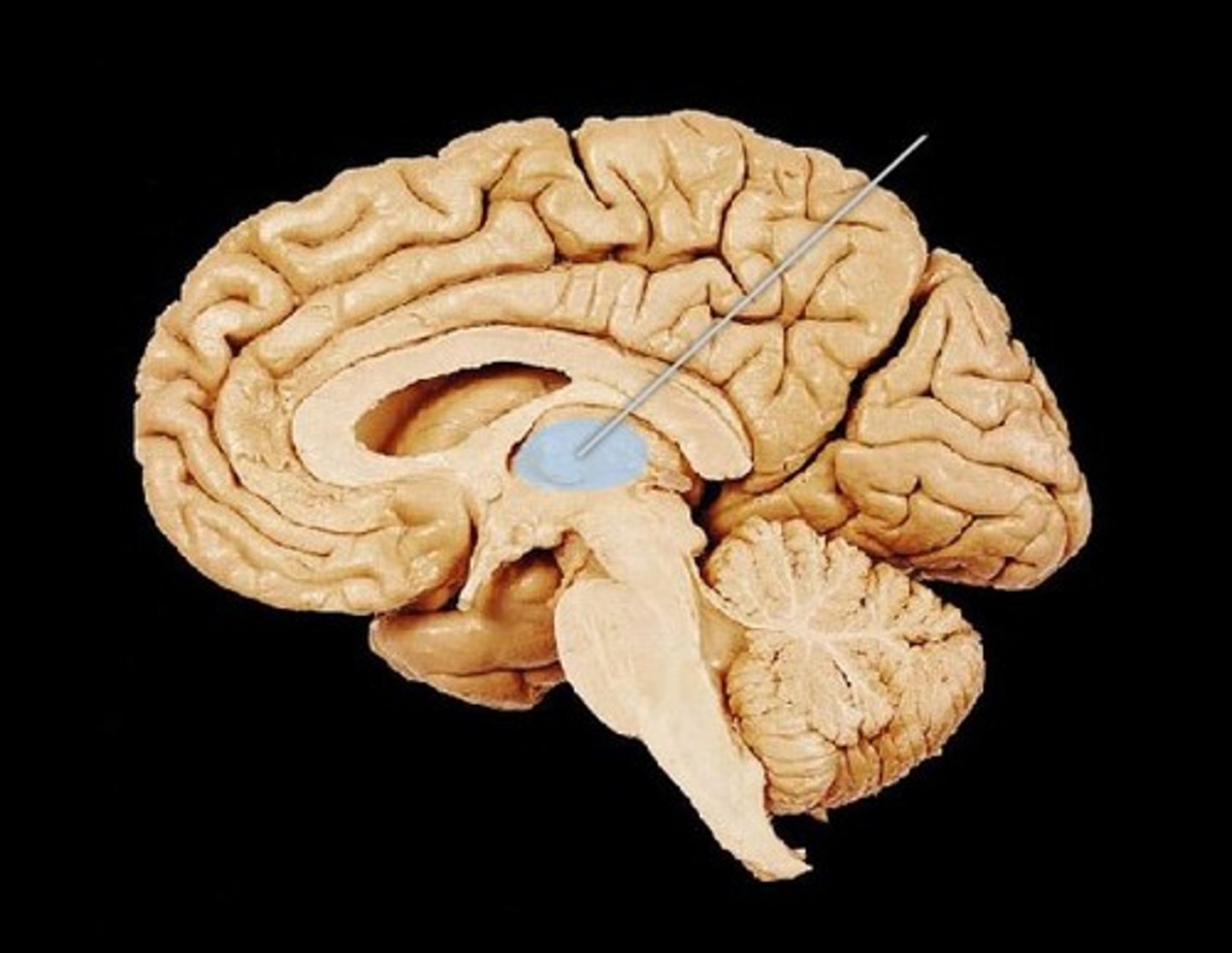
Thalamus location
-Ovoid mass on each side of the brain perched at the superior end of the brainstem beneath the cerebral hemispheres