Anatomy and Physiology Chemistry Book
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
1
New cards
a chemical element is...
the simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties
2
New cards
How many naturally occurring elements are there on earth? How many play normal roles in humans?
91
24
24
3
New cards
What elements take up 98.5% of the body's weight?
Oxygen (O) 65%
Carbon (C) 18%
Hydrogen (H) 10%
Nitrogen (N) 3%
Calcium (Ca) 1.5%
Phosphors (P) 1%
Carbon (C) 18%
Hydrogen (H) 10%
Nitrogen (N) 3%
Calcium (Ca) 1.5%
Phosphors (P) 1%
4
New cards
What elements take up 0.8% of body's weight
Sulfur (S) .25%
Potassium (K) .20%
Sodium (Na) .15%
Chlorine (Cl) .15%
Magnesium (Mg) .05%
Iron (Fe) .006%
Potassium (K) .20%
Sodium (Na) .15%
Chlorine (Cl) .15%
Magnesium (Mg) .05%
Iron (Fe) .006%
5
New cards
What elements take up 0.7% of body's weight
Chromium (Cr)
Cobalt (Co)
Copper (Cu)
Fluorine (F)
Iodine (I)
Manganese (Mn)
Molybdenum (Mo)
Selenium (Se)
Silicon (Si)
Tin (Sn)
Vanadium (V)
Zinc (Zn)
Cobalt (Co)
Copper (Cu)
Fluorine (F)
Iodine (I)
Manganese (Mn)
Molybdenum (Mo)
Selenium (Se)
Silicon (Si)
Tin (Sn)
Vanadium (V)
Zinc (Zn)
6
New cards
What are the elements that take up 0.7% of weight known as
trace elements
7
New cards
Define minerals
substances extracted from the soil by plants and passed up the food chain to humans and other organisms
8
New cards
How much weight do Minerals count as in the body
4%
9
New cards
What minerals count as three quarters of the 4%
Calcium (Ca) and Phosphorus (P)
10
New cards
What other minerals constitute the weight for the 4%
Chlorine (Cl)
Magnesium (Mg)
Potassium (K)
Sodium (Na)
Sulfur (S)
Magnesium (Mg)
Potassium (K)
Sodium (Na)
Sulfur (S)
11
New cards
What do minerals contribute significantly to
body structure
12
New cards
each chemical is composed of a unique type of...
atom
13
New cards
what are the electrons called that are in the outermost shell
valence electrons
14
New cards
what function does a valence electron have
determines the formation of chemical bonds
15
New cards
All elements have two or more varieties called...
isotopes
16
New cards
What makes elements differ from each other
number of neutrons
17
New cards
What is the decay of unstable isotopes by giving off radiation called
radioactivity
18
New cards
what are the unstable isotopes called
radioisotopes
19
New cards
radioactivity is a form of
ionizing radiation (UV radiation, X-rays)
20
New cards
Ionizing radiation can be damaging because
it can cause cancer, birth defects, or immediate death
21
New cards
Ionizing radiation can be beneficial in controlled settings like
radiography, PET scans, and cancer radiation therapy
22
New cards
Define ions
charged particles with unequal number of protons and electrons
23
New cards
What is the process of ionization
electrons transferring from one to the other and turn both of them into ions
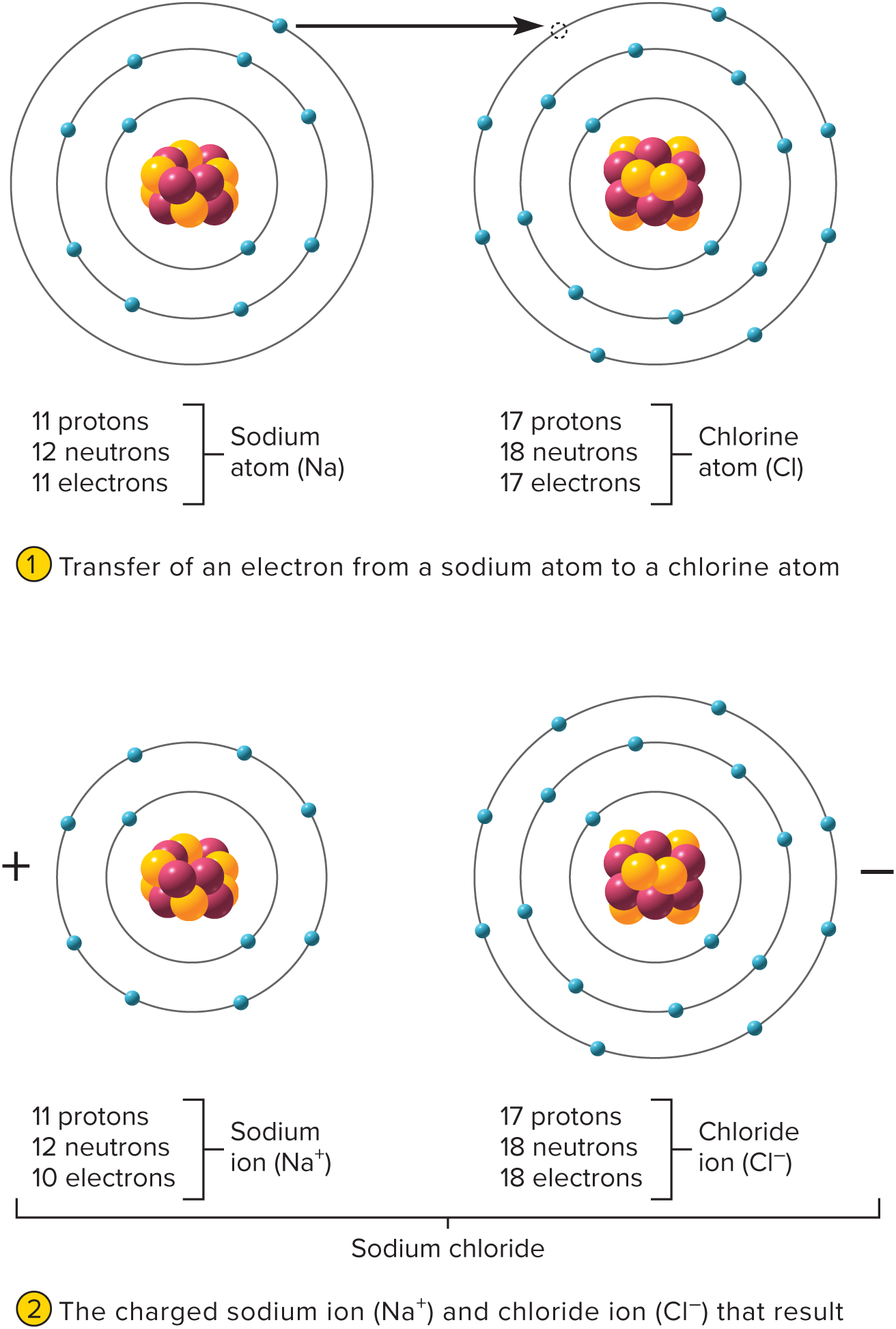
24
New cards
anion
a negatively charged ion
25
New cards
cation
a positively charged ion
26
New cards
Ions with ___ charges are strongly ____ to each other and unite in ____ bonds.
opposite
attracted
ionic
attracted
ionic
27
New cards
Define Electrolytes
A salt that ionizes in water and produces a solution that conducts electricity
28
New cards
What is electrolytes important for
chemical reactivity, osmotic effects, and electrical effects
29
New cards
______ balance is on of the most important considerations in patient care
Electrolyte
30
New cards
Define free radicals
A particle derived from an atom or molecule, having an unpaired electron that makes it highly reactive and destructive to cells;
31
New cards
What do antioxidants do to free radicals
neutralize and limit their destruction
32
New cards
How do molecules form
two or more atoms are united by a chemical bond
33
New cards
Define compound
molecules composed of two or more different elements
34
New cards
How are molecules represented
molecular formulae
35
New cards
Define isomers
molecules with identical formulae but different arrangements
36
New cards
ionic bond
a chemical bond in which one atom loses an electron to form a positive ion and the other atom gains an electron to form a negative ion
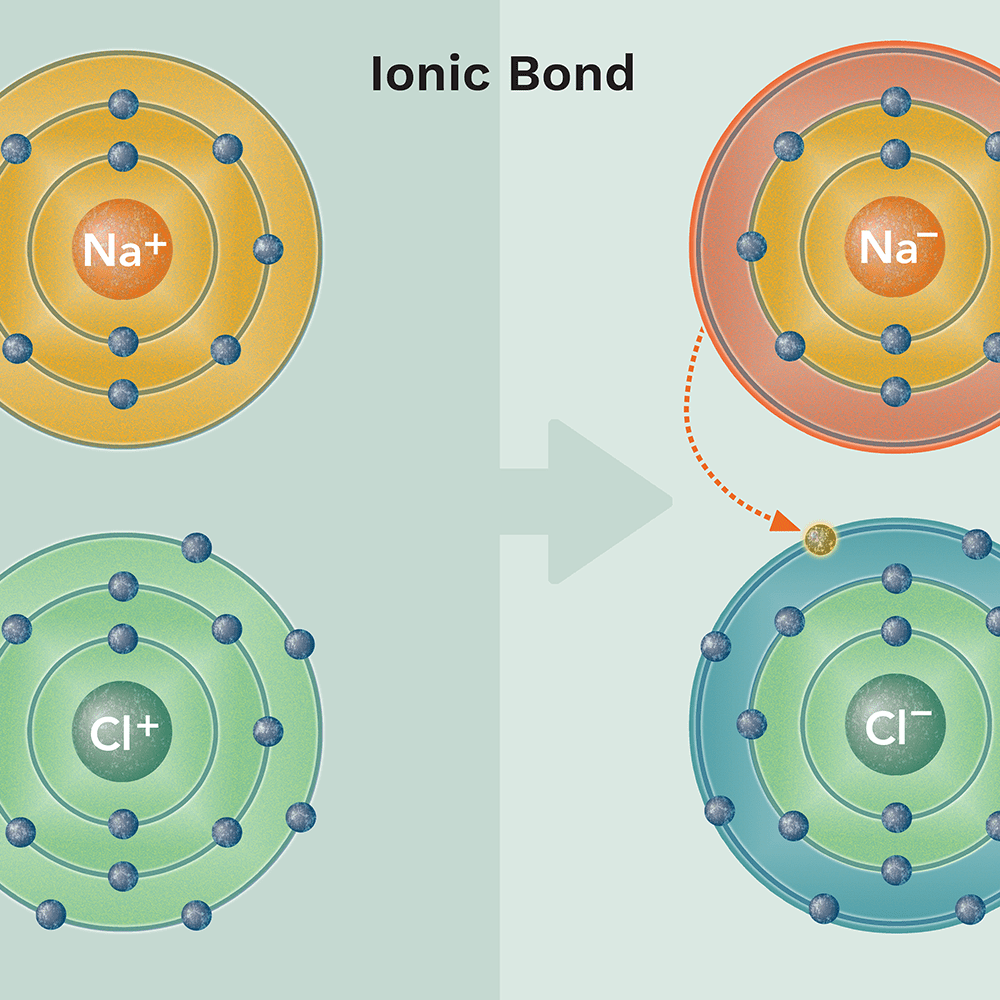
37
New cards
describe ionic bond
weak
easily dissociate (break up)
easily dissociate (break up)
38
New cards
Covalent bond
a chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
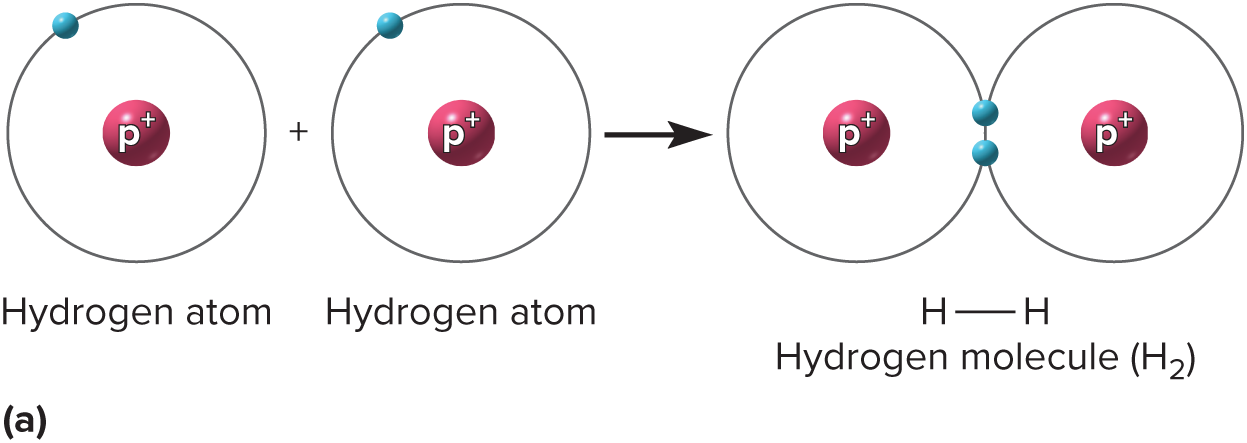
39
New cards
nonpolar covalent bond
electrons spend equal time around each nucleus
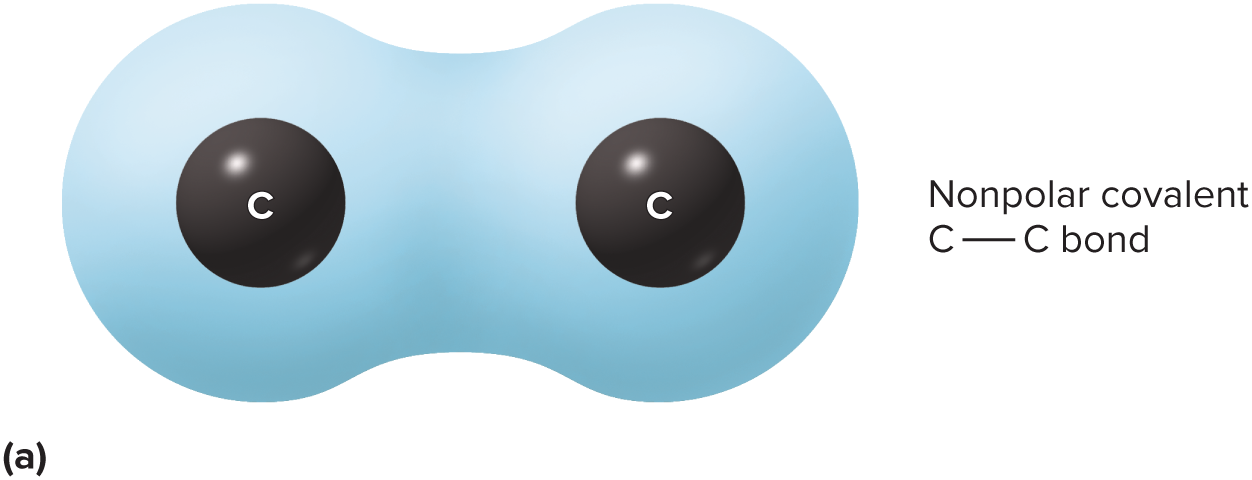
40
New cards
polar covalent bond
shared electrons spend more time orbiting one nucleus. They lend their negative charge where the spend most time
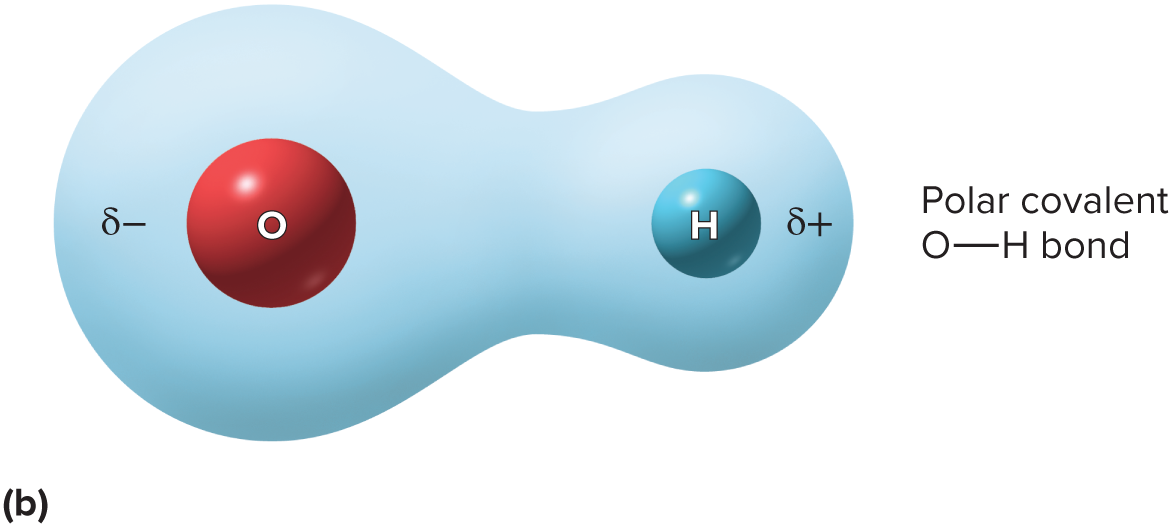
41
New cards
hydrogen bond
A weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom on one molecule and a slightly negative oxygen or nitrogen atom on another molecule
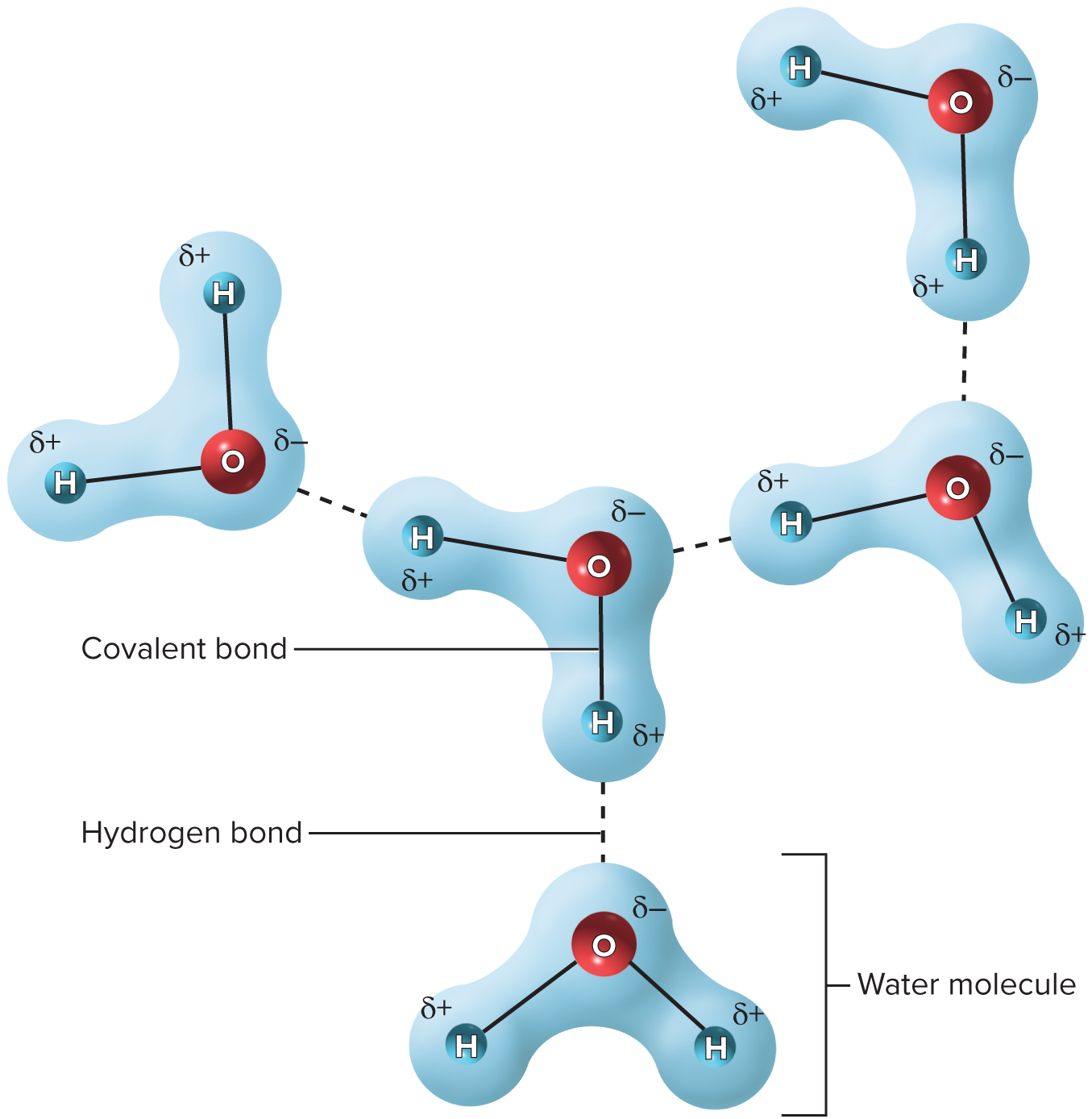
42
New cards
single covalent
sharing one electron pair
43
New cards
double covalent
sharing two electron pairs
44
New cards
what easily disrupts an ionic bond
water
45
New cards
What is the strongest chemical bond
nonpolar covalent
46
New cards
What is the weakest chemical bond
hydrogen bond
47
New cards
What percent of our bodies is water
50% to 75%
48
New cards
What is the universal solvent
water
49
New cards
substances that dissolve are
solutes
50
New cards
hydrophilic
having a strong affinity for water; tending to dissolve in, mix with, or be wetted by water
51
New cards
hydrophobic
lacking affinity for water; tending to repel and not absorb water; tending not to dissolve in or mix with or be wetted by water
52
New cards
Functions of water
Universal solvent
Adhesion
Cohesion
thermal stability
chemical reactivity
Adhesion
Cohesion
thermal stability
chemical reactivity
53
New cards
adhesion
tendency to cling to other substances
54
New cards
cohesion
attraction of its molecules to each other
55
New cards
thermal stability
resistance to temperature change
56
New cards
chemical reactivity
ability to participate in chemical reactions
57
New cards
concentration
how much solute is present in a given volume of water
58
New cards
acid
A proton (H+) donor; a chemical that releases protons into solution
59
New cards
base
A chemical that binds protons from solution; a proton acceptor.
60
New cards
Acidity is expressed in terms of...
pH
61
New cards
Describe pH scale
0.0-14.0
pH 7.0- neutral
pH below 7- acidic
pH greater 7- basic (alkaline)
pH 7.0- neutral
pH below 7- acidic
pH greater 7- basic (alkaline)
62
New cards
organic compound
any compound of carbon and another element or a radical
63
New cards
organic chemistry
the chemistry of compounds containing carbon
64
New cards
biochemistry
subdiscipline of organic chemistry that relates organic compounds to the processes of life
65
New cards
4 organic molecules of life
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
66
New cards
macromolecule
any very large complex molecule; carbon forming chains
67
New cards
polymers
A molecule that consists of a long chain of identical or similar subunits, such as protein, DNA, or starch.
68
New cards
monomers
One of the identical or similar subunits of a larger molecule in the dimer to polymer range; for example, the glucose monomers of starch, the amino acids of a protein, or the nucleotides of DNA.
69
New cards
Living cells use a process called ____ ____ to join monomers together to form polymers
dehydration synthesis
70
New cards
Describe process of dehydration synthesis
remove hydrogen (-H) from one monomer and a hydroxyl group (-OH) from another, producing water as a by-product. Two monomers become joined by a covalent bond. This is repeated for each monomer added to the chain
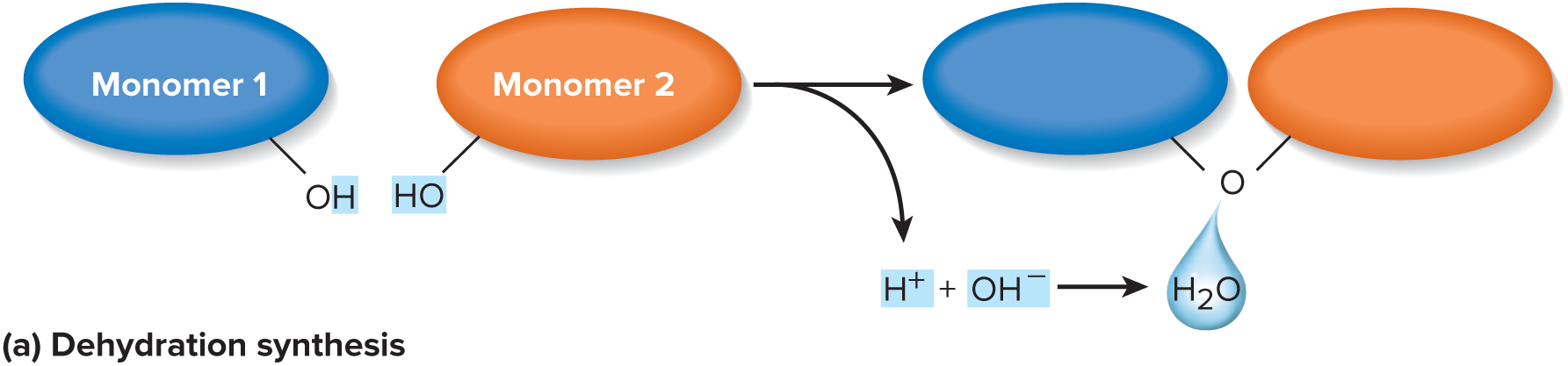
71
New cards
hydrolysis
A chemical reaction that breaks a covalent bond in a molecule by adding an —OH group to one side of the bond and —H to the other side, thus consuming a water molecule.
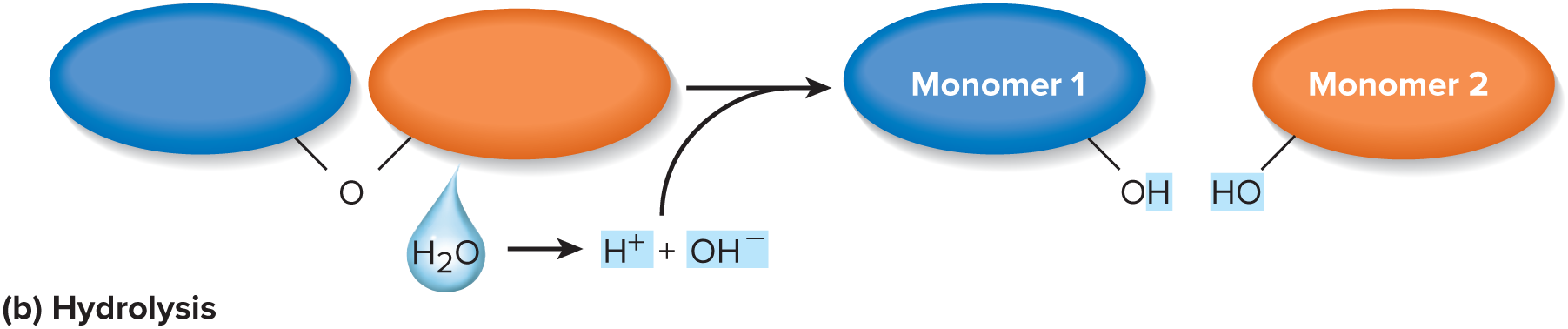
72
New cards
Carbohydrates
A hydrophilic organic compound composed of carbon and a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen; includes sugars, starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
73
New cards
what are the simplest carbohydrates
monosaccharides, simple sugars
74
New cards
examples of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, and galactose
75
New cards
Disaccharides
A carbohydrate composed of two simple sugars (monosaccharides) covalently bonded together;
76
New cards
examples of disaccharides
lactose, sucrose, and maltose
77
New cards
Polysaccarides
A polymer of simple sugars
78
New cards
examples of polysaccharides
glycogen, starch, and cellulose
79
New cards
Glycogen
an energy-storage polysaccharide.
80
New cards
Glucose
blood sugar- energy source for most cells
81
New cards
Galactose
converted to glucose
82
New cards
Fructose
converted to glucose
83
New cards
Sucrose
Cane Sugar- digested to glucose and fructose
84
New cards
Lactose
Milk sugar- digested to glucose and galactose; important in infant nutrition
85
New cards
maltose
Malt sugar- product of starch digestion, further digested to glucose
86
New cards
cellulose
structural polysaccharide of plants; dietary fiber
87
New cards
Starch
Energy storage in plant cells; dietary source of energy for humans
88
New cards
Glycogen
energy storage in animal cells (liver, muscle, uterus)
89
New cards
Lipids
A hydrophobic organic compound composed mainly of carbon and a high ratio of hydrogen to oxygen
90
New cards
Triglycerides Functions
Energy storage; thermal insulation; filling space; binding organs together; cushioning organs
91
New cards
Fatty acid functions
precursor of triglycerides; source of energy
92
New cards
phospholipids function
major component of cell membranes
93
New cards
cholesterol function
component of cell membranes; precursor of other steroids
94
New cards
steroid hormones
chemical messengers between cells
95
New cards
bile acids
steroids that aid in fat digestion and nutrient absorption
96
New cards
Triglycerides are called ___ if solid and ___ if liquid
fats
oils
oils
97
New cards
saturated fatty acid
a fatty acid whose carbon chain cannot absorb any more hydrogen atoms; found chiefly in animal fats
98
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
a fatty acid whose carbon chain can absorb additional hydrogen atoms
99
New cards
polyunsaturated fatty acid
an unsaturated fatty acid whose carbon chain has more than one double or triple valence bond per molecule
100
New cards
difference between triglycerides and phospholipids
phospholipids have a phosphate group instead of one fatty acid