CHEM 51A FINAL review cards
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prof Vanderwal 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Resonance effect / conjugation
for C=O IR absorption goes down by 25-30cm-1 for conjugation to alkene alkyne and benzene
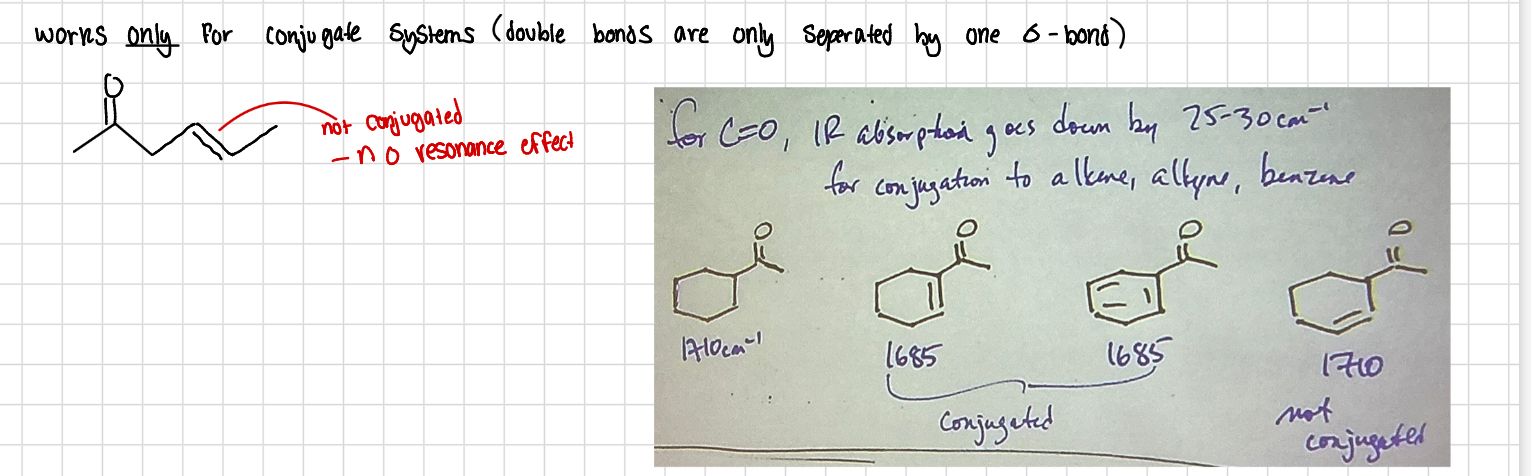
For the bond to be conjugated, they have to be separated by one sigma bond only
Resonance Effect Esters + Amides
Minor Contributors weaken C=O bond
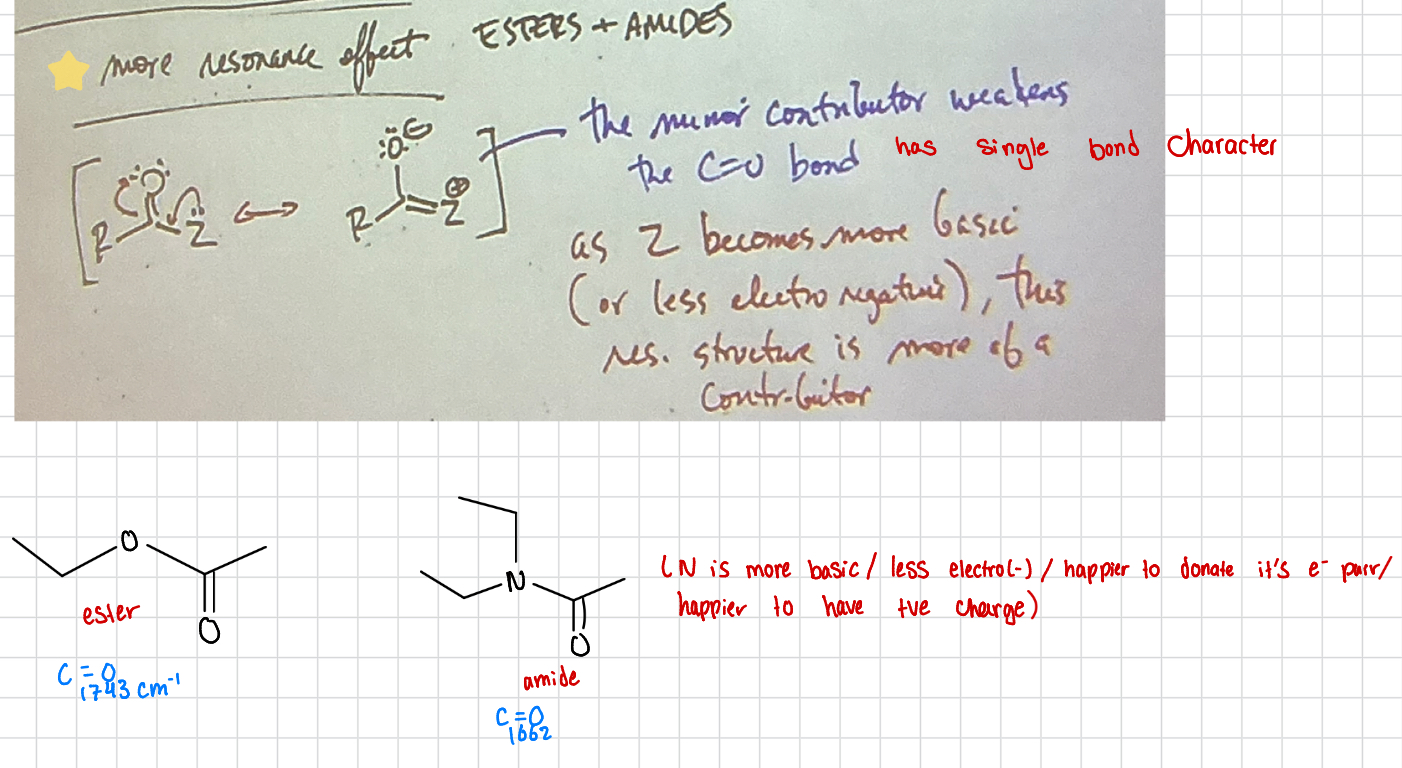
S- charachter
increases sp3=25% —> sp2 = 33% —> sp = 50%
when is entropy not a large contributor to the overall free energy of a rxn

Dihedral Angles for gauche, eclipsed, anti
Anti | 180° | Lowest |
Gauche | 60° | Medium |
Partially Eclipsed | 120° / 240° | High |
Fully Eclipsed | 0° | Highest |
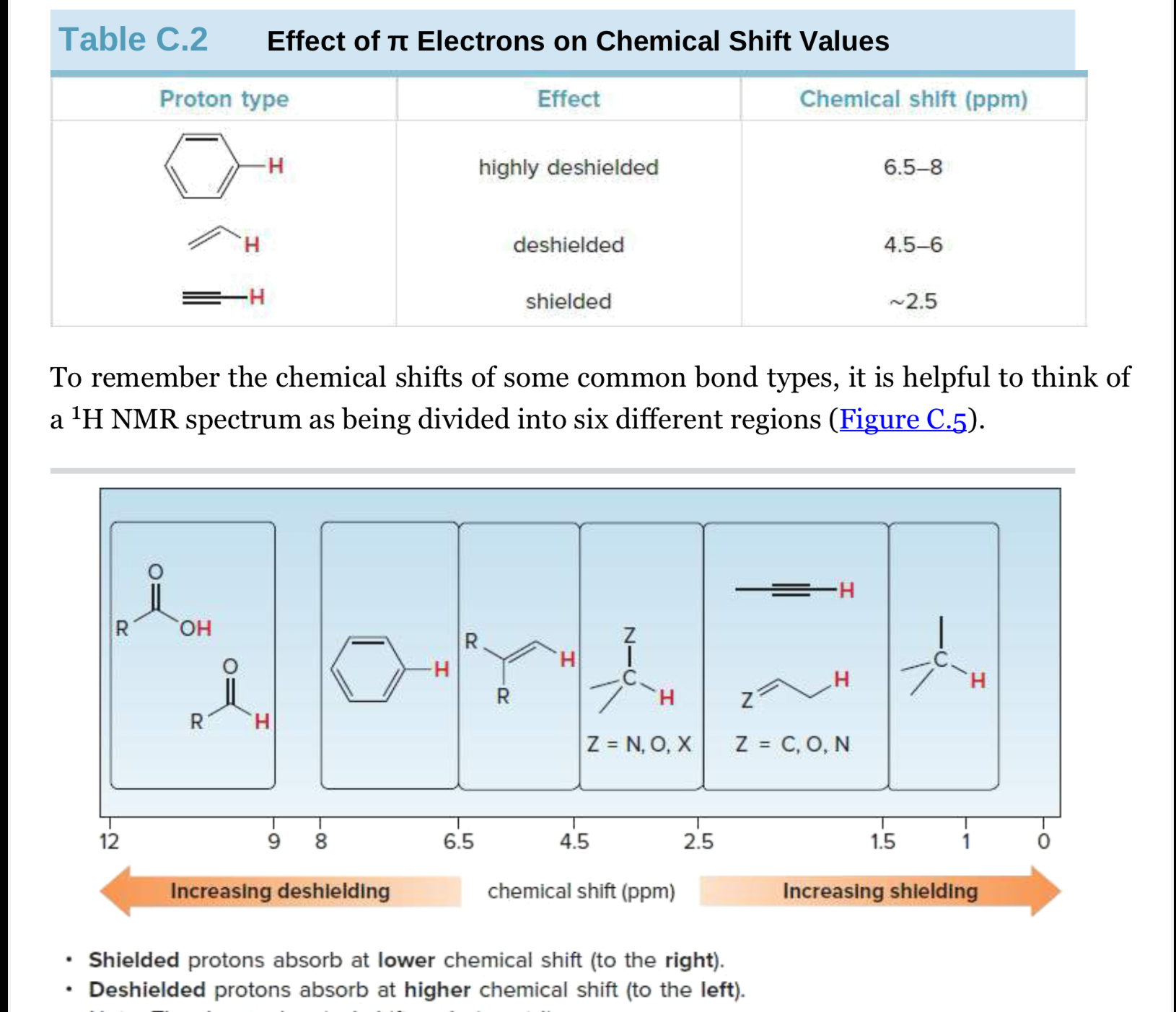
General trend for chemical shifts

ΔG overall free energy
Thermodynamically favored = spontaneous = ΔG < 0
Thermodynamically not favored = ΔG > 0 (positive)
wavenumber trend
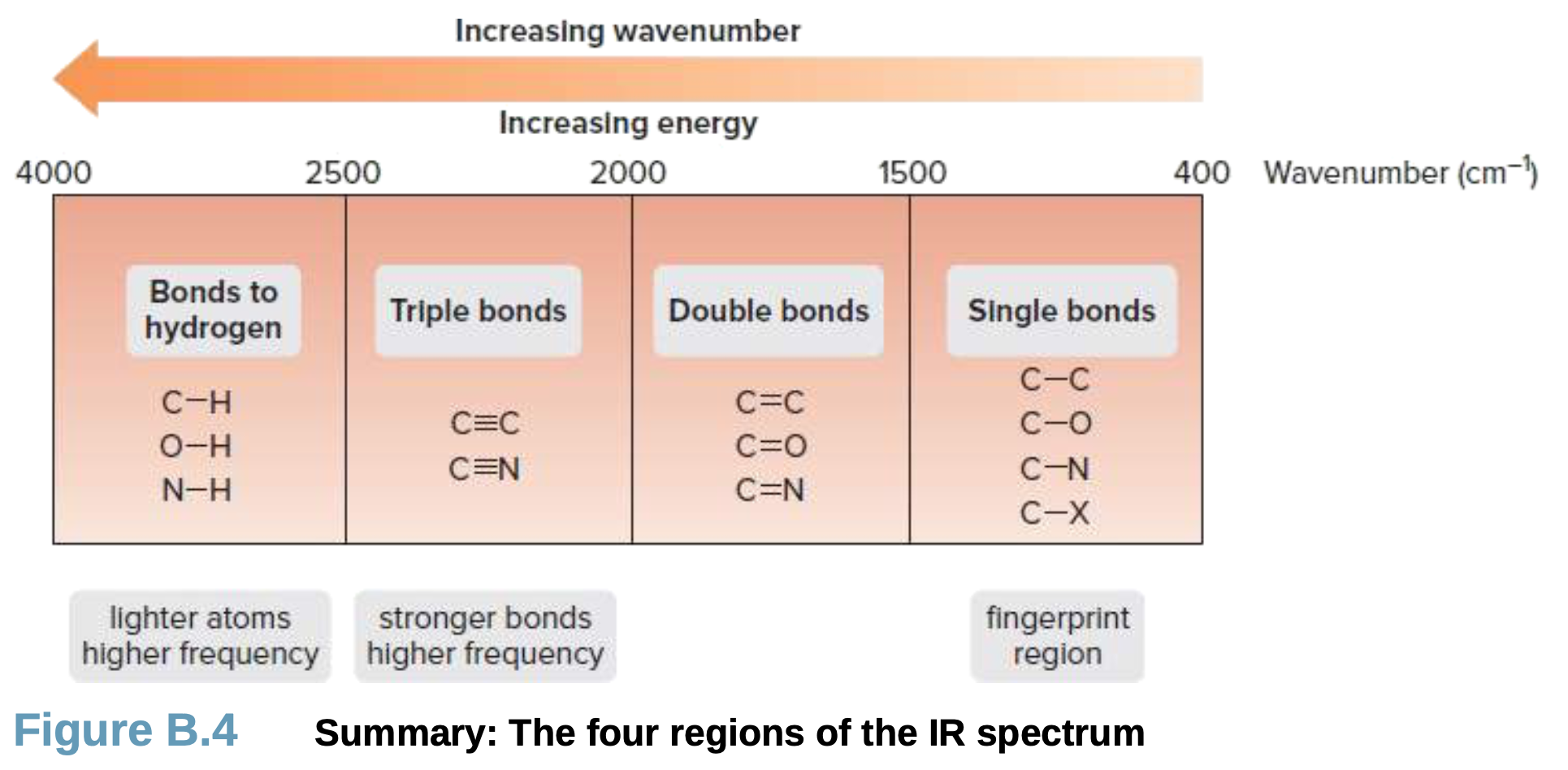
Bond strength: stronger bonds vibrate at higher frequency, so they absorb at higher Wavenumber
Atom mass: bonds with lighter atoms vibrate at higher frequency, so they absorb at higher Wavenumber
inductive vs element
element = attached to H
inductive = attached to C
topocity
Nucleophile
“nucleus loving” species that donates an electron pair to form a chemical bond. ( has high electron density)
Nucleophilic sites have
lone pair
pi bond
negative charge
Electrophile
“electron loving” species that accepts an electron pair to form a chemical bond. (have low electron density)
element effect
looks at the element to which the proton for X-H is attached where X is a main group element. Due to the ability of atom X to attract/hold negative charge
Electronegativity trend ( element effect)
across second row electronegativity increases = more acidic ———>
Atomic radius trend (element effect)
down a group atomic radius increases = more acidic
bigger atoms are better @ accommodating -ve charge b/c spread out over large space (Less charge density = more stability)
acidity increases down a group due to significant differences in bond dissociation energies
only true for when the hydrogen (proton) is attached to the heteroatom.
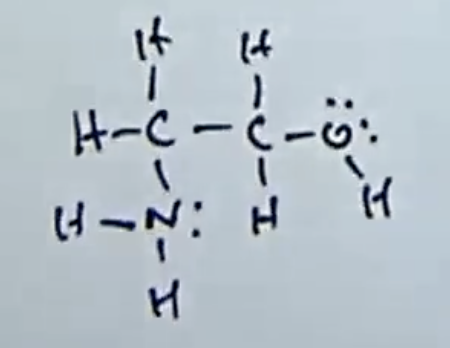
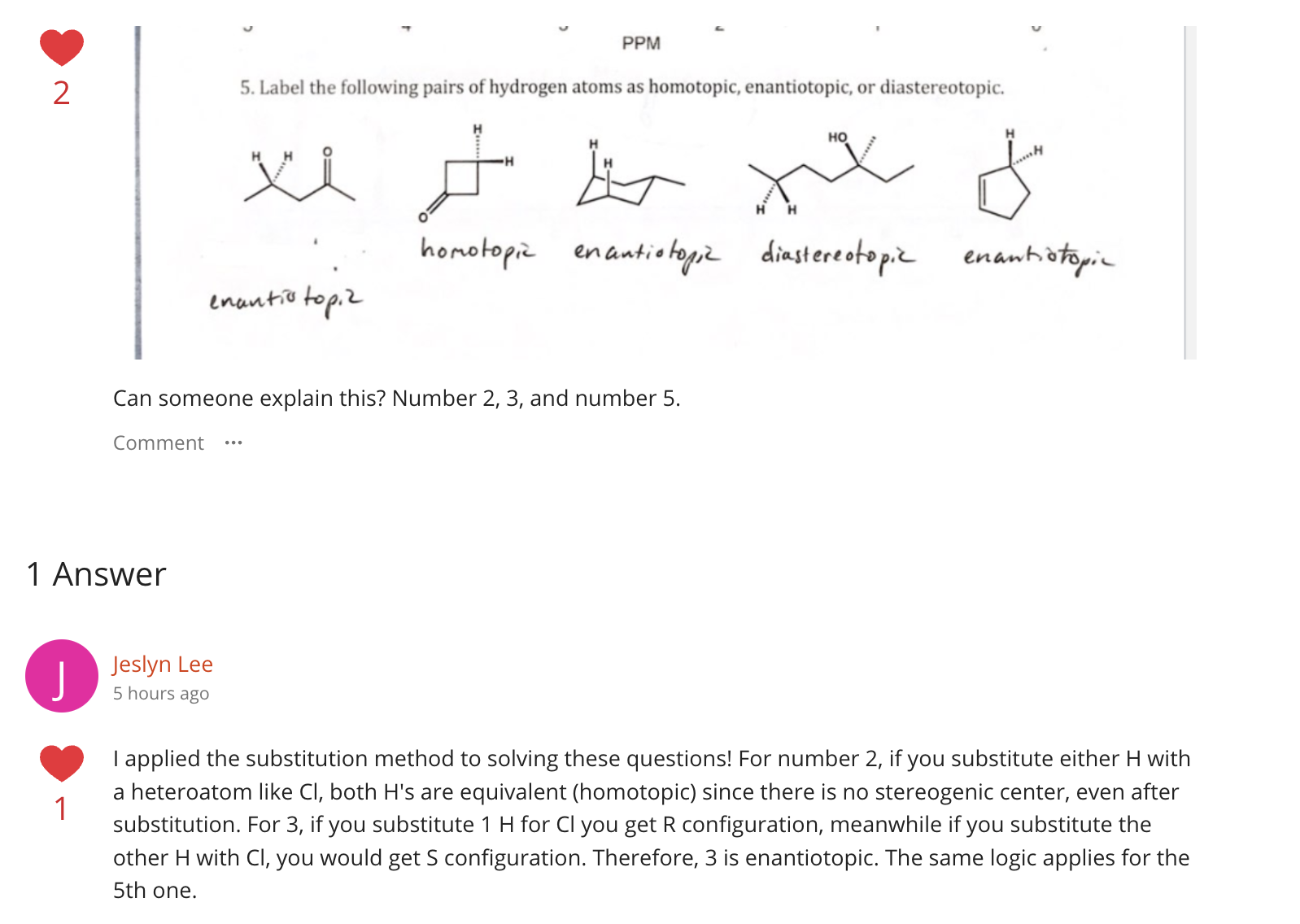
Which element will be removed (deprotonated) first by a base?
3 types of 2nd row elements present in the molecule [N,O,C]
Electronegative of the atoms holding the charge (O > N > C)
O-H is most acidic thus gets removed first
![<ul><li><p>3 types of 2nd row elements present in the molecule [N,O,C] </p></li><li><p><strong>Electronegative of the atoms</strong> holding the charge (O > N > C)</p></li><li><p>O-H is most acidic thus gets removed first</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a07278e3-441e-44ca-959c-867fc596e3a1.png)
Inductive effect (polar effect)
explains why acidity changes as more polar groups are added
(ex: adding more “F” to a carboxylic acid increases molecule acidity as they help stabilize negative charge of conjugate base)
acidity increases when electronegative atoms are added
the effect is affected by distance ( closer = more acidic)
the farther the electronegative group is from the site of the negative charge (or acidic hydrogen), the less it can pull or push electron density.
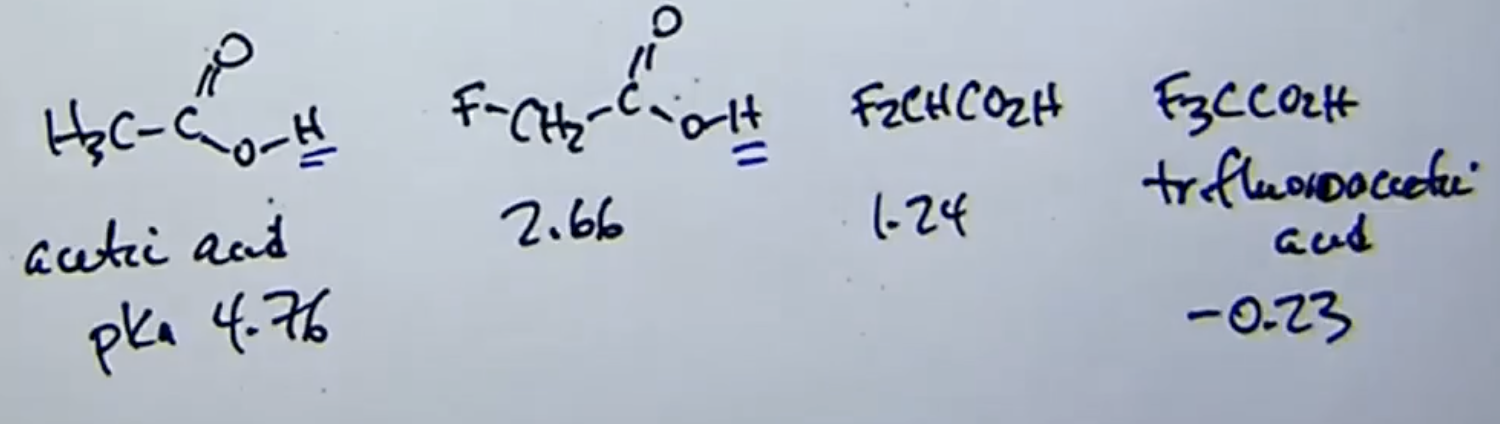
How does distance affect the inductive effect?
the closer the electronegative atom is to the proton the stronger the acid
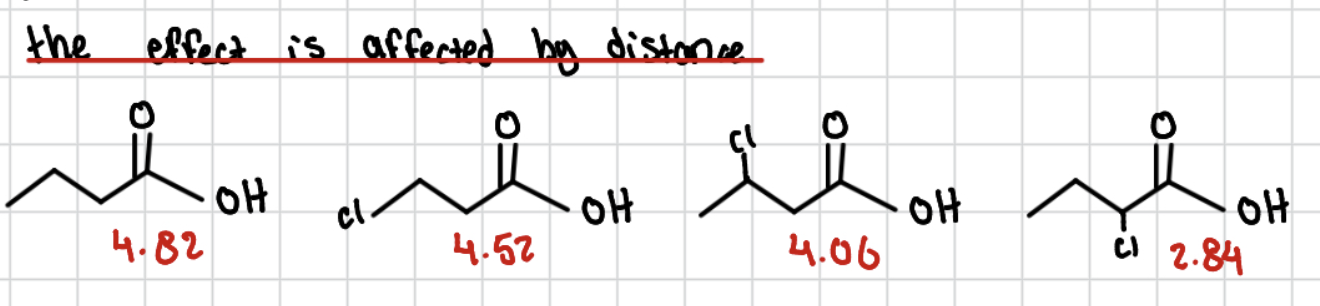
Pka trend
Lower Pka = more acidic
Higher Pka = less acidic
resonance effect
spreads out negative/positive charge over multiple atoms stabilizing the molecule
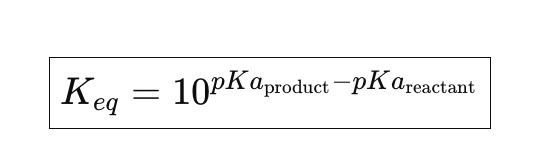
Acid Base Equilibria Equation
Functional groups
name them
Bronsted Lowry Acid
a species that donates a proton (H+)
Bronsted Lowry Base
a species that accepts a proton (H+)
must be able to form a bond to a proton
must contain an available electron pair that can easily be donated to form a new bond. These include lone pairs or electron pairs in π-bonds
curved arrow
shows movement of an electron pair
The tail of the arrow always begins at an electron pair (such as non-bonding electrons or a covalent bond) and the head points to where that electron pair moves.
Relationship btwn strong acid/base & conjugate
**STRONG ACIDS HAVE WEAK CONJUGATE BASES*
* WEAK ACIDS HAVE STRONG CONJUGATE BASES
amphoteric
act as both acids & bases.
what makes a good resonance
more bonds and fewer charges = more stable
every atom has an octet = more stable
negative charge on more electronegative atom = more stable
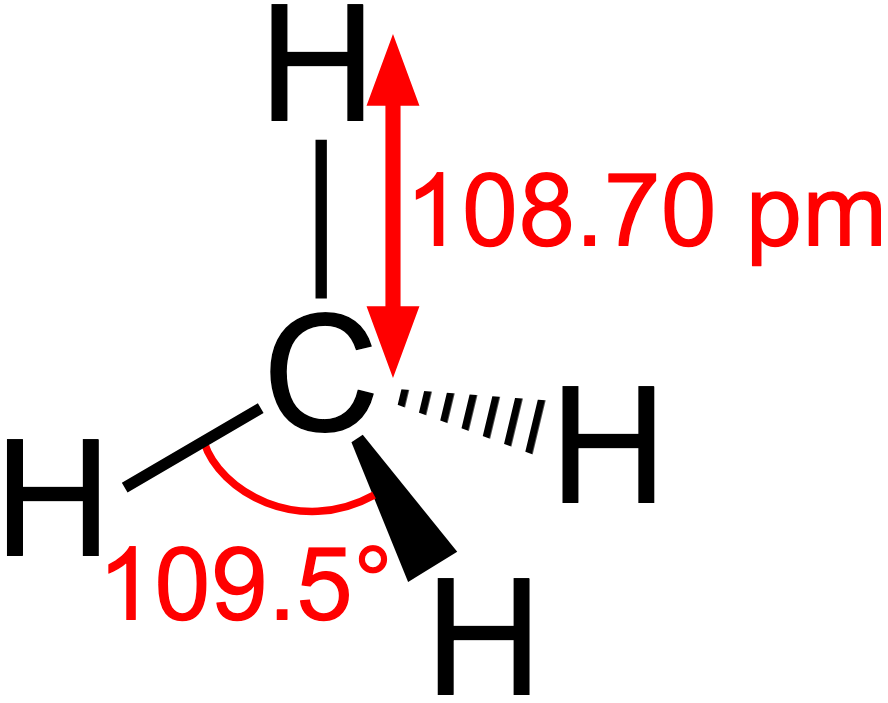
methane
SP3
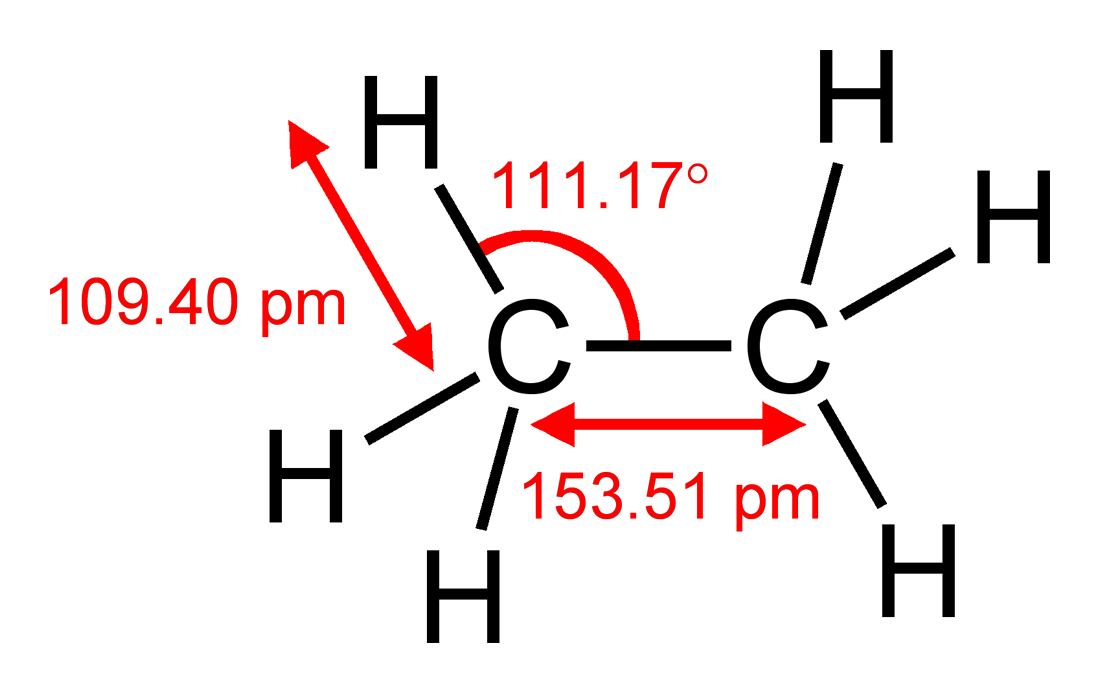
ALKANES (ex: ethane)
SP3
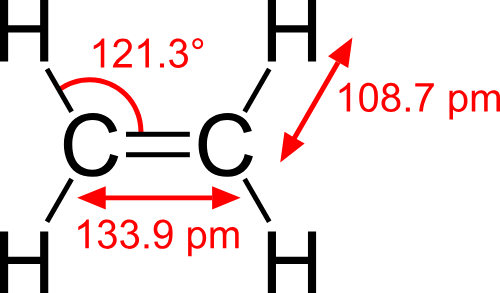
ALKENES (ex: ethylene)
SP2
ALKYNE (ex: Acetylene)
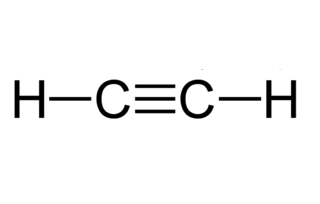
SP
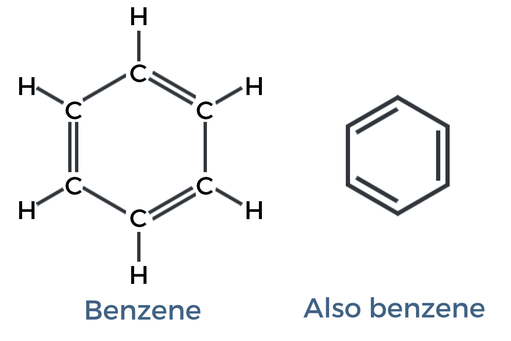
Aromatic (ex: BENZENE)
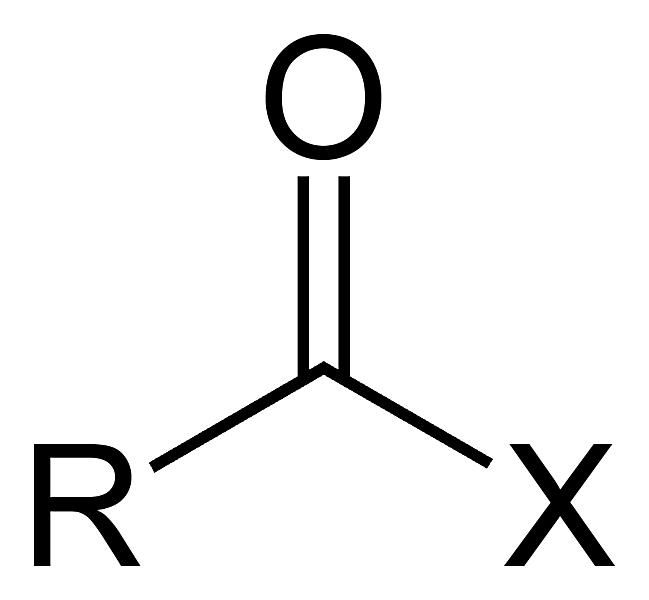
HALO group (alkyl halide) C-Z σ bond
short for halogens F,Cl, Br, I
general structure R - X
Functional group. -X
HYDROXY ( alcohol) C-Z σ bond
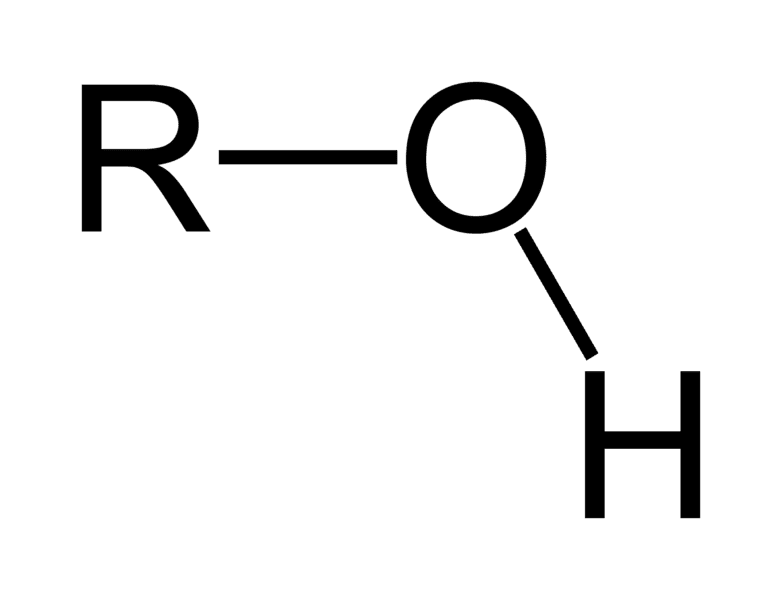
functional group -OH
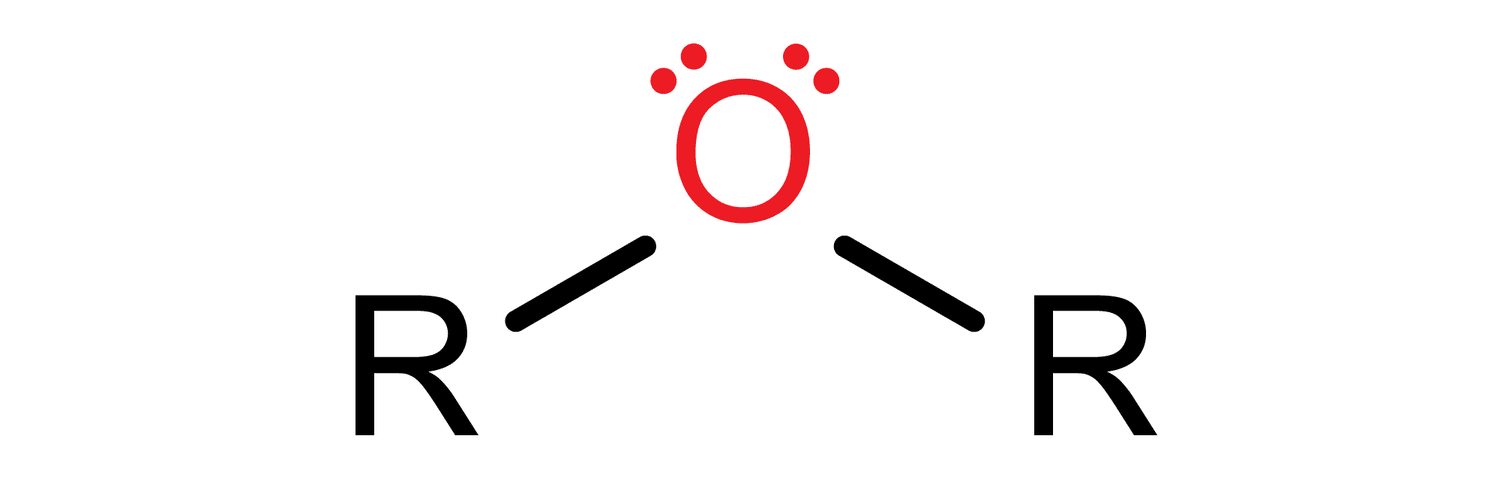
ALOXY (ether) C-Z σ bond
functional group -OR
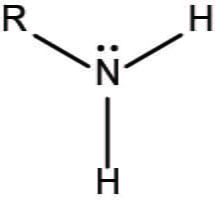
AMINO (amine) C-Z σ bond
functional group -NH2
when does a rxn favored to products vs reactants and the relationship btwn Keq</> 1
Keq > 1 → Products favored
Keq < 1 → Reactants favored
Keq = 1 → Neither side favored (equal stability)
what does more S character mean
the more “s” character a hybrid orbital has, the closer to the nucleus and the more tightly held are its electrons
sp: 50% s character, linear geometry 180 degrees
sp²: 33.3% s character, trigonal planar geometry 120 degrees
sp³: 25% s character, tetrahedral geometry 109.5
polarity
higher electronegativity = greater attraction for electrons
the greater difference in electronegativity the greater the polarity of a bond
why does acidity increase down a column?
b/c positive or negative charge is stabilized when it is spread over a larger volume
only true for when the hydrogen (proton) is attached to the heteroatom.
heteroatom: any atom other than carbon or hydrogen in an organic compound
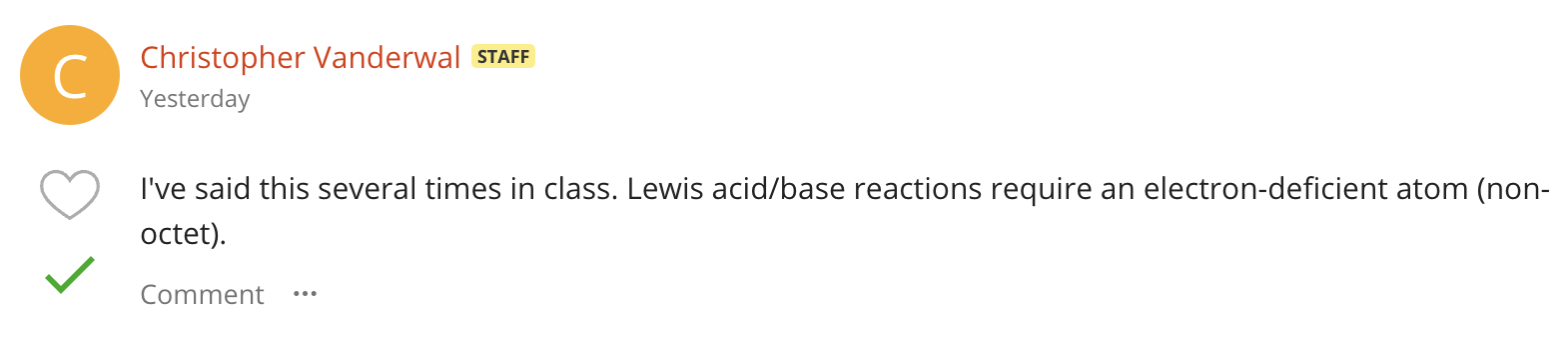
when does an electron displacement reaction take place?
If an electron pair is being used to fill an octet of a Lewis acid, then there is no electron pair departing (being displaced).
If there's only one arrow, there is no electron pair being displaced
Lewis ACID
NONOCTET
chair conformation stability
if you have one group on the ring the more stable chair will be the one with the group in an equatorial position
two groups best if they occupy equatorial position
if only one can be equatorial in either chair then the more stable will be the one with the larger group in the equatorial position
wedge and dash
wedged = up
dash = down
*no correlation between up/down and axial/equatorial
newman
most stable is staggered specifically anti
cis
two groups are up or down
trans
one group is up and the other is down
gauche interactions in in cyclohexane rings
2 guache interactions for each axial groups in cyclohexane ring
1 guache interaction for each equatorial in cyclohexane ring
methane
1
ethane
2
propane
3
butane
4
pentane
5
hexane
6
heptane
7
octane
8
nonane
9
decane
10
H-H eclipsing
0.9kcal/mol
H-CH3 eclipsing
1.4kcal/mol
dihedral angle
chiral
objects that exist as enantiomers
all molecules w/ exactly one stereogenic center are chiral
a molecule w/ no stereogenic center are usually not chiral
OPTICALLY ACTIVE
achiral
molecules contain a plane of symmetry
stereogenic center
only 3° and 4° carbons can be stereogenic
any c with 4 diff substituents
DONT GET FOOLED BY THE RING
drawing enantiomers
draw mirror image
OR
exchange any 2 substituents dash/wedge
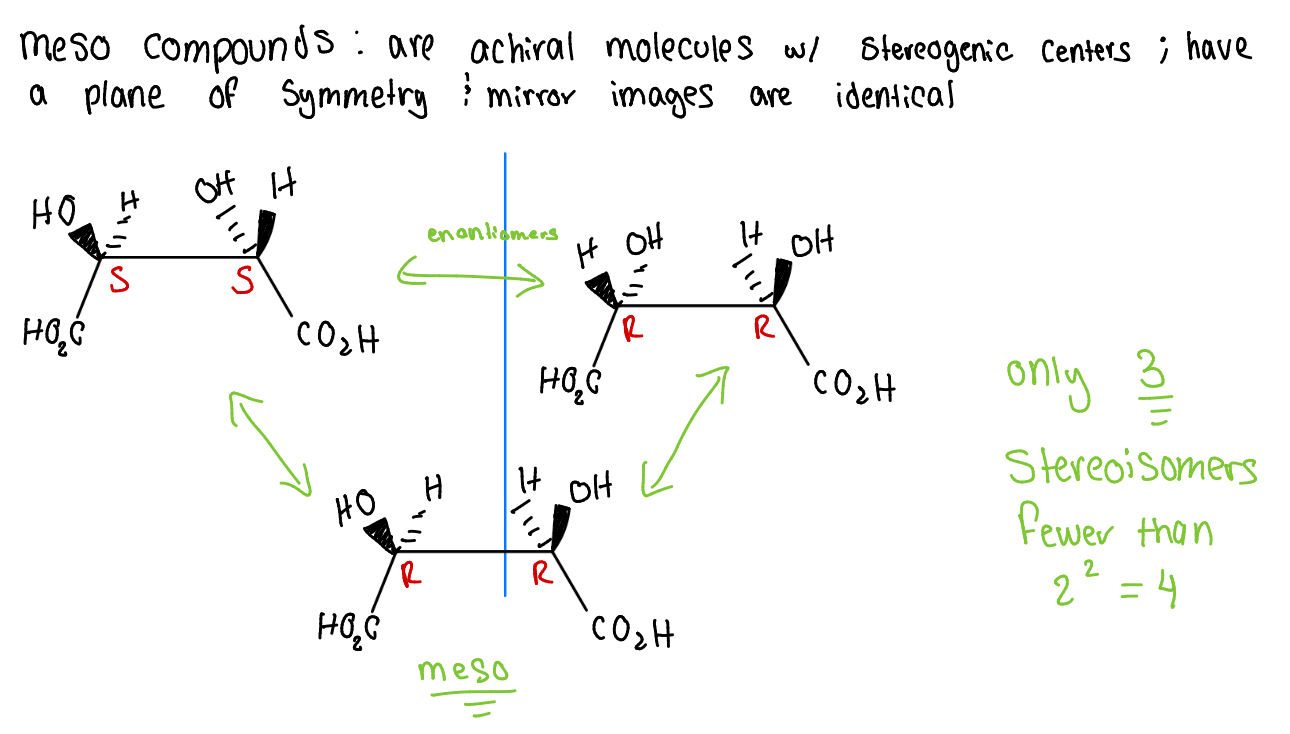
meso compounds
molecules w/ stereogenic centers; have a plane of symmetry & mirror images are identical
mus thave at least two stereogenic centers
racemic mixture
an equal amount of two enantiomers
optically inactive
no rotation (=0°) is observed b/c two enantiomers rotate PPL to an equal extent in opp directions
roation of polarized clockwise vs counterclockwise
clockwise = d or +
counterclockwise = l or -
two enantiomers rotate plane polarized light to an equal extent but in opposite directions
physical properties of isomers
Constitutional isomers and diastereomers have different physical properties.
enantiomers have the same physical properties
can not be separated by physical properties
enantiomeric excess
