KON7 Risk management
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Project goals and risk management
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is Risk management
Not about avoiding risks, but deciding which risks are acceptable and not acceptable and need to be monitored.
What is uncertainty?
Known events that will have different outcomes if it happens
Types of risks:
Operational, contextual, random
Contextual, programmatic, institutional
What is operational risk about
Will it work technically or not
Focuses on difference and gap between what you know and what you will need to know, and how to manage the gap
What is contextual risks about
Focuses on difference between what you know and what you will need to know, and how this will affect planning and execution
Operate within social contexts such as current laws, legislations, morals, norms
What is institutional risks about
Do we have resources?
Will we be part of the decision making process?
Will important stakeholders contribute in the right time?
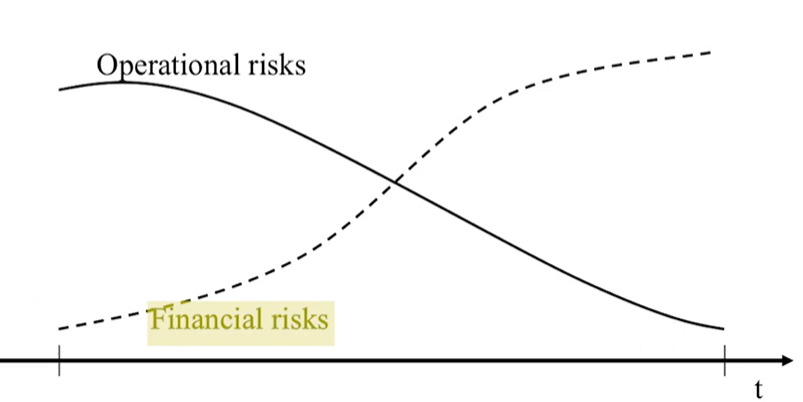
Difference between operational and financial risks:
High operational risks and low financial risks in the beginning. After the intersection, it will cost you too much to make changes!
Phases of risk management process
Identify risk - How often will risks occur, what’s the impact outcome? Talk with stakeholders to identify.
Analyze risk - Is the value of the risk based on the project or the company?
Prioritize risk
Plan how to prevent risk
Monitor risk
PMI:s Risk Classification
External - unpredictable: Law changes or natural disaster
External - predictable: Financial changes, raw material access changes
Internal - non-technical: Security, working time agreement
Internal - technical: Design changes, technical issues
Legal: Issues with licenses, patents, rights, lawsuits
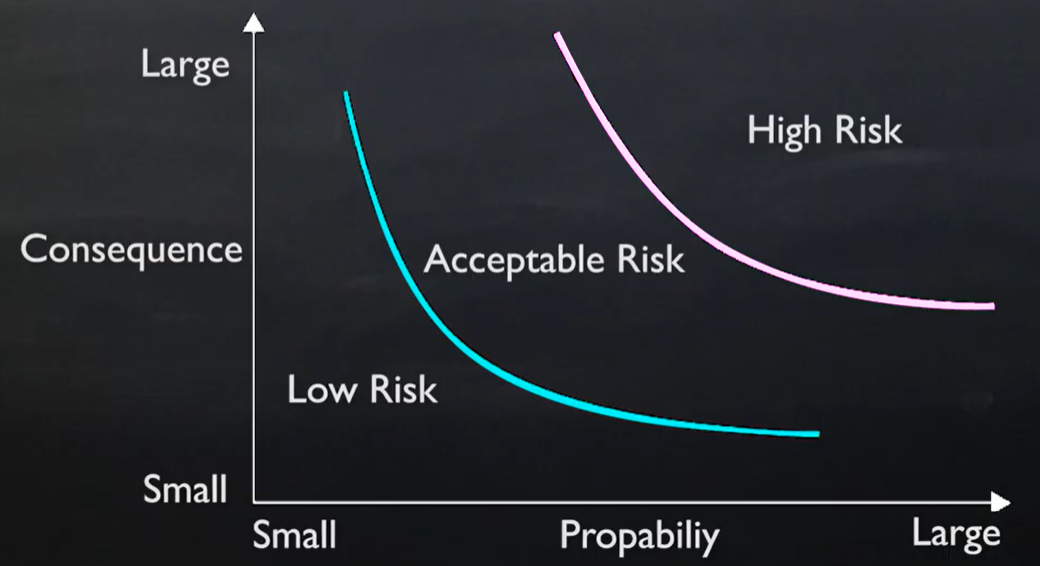
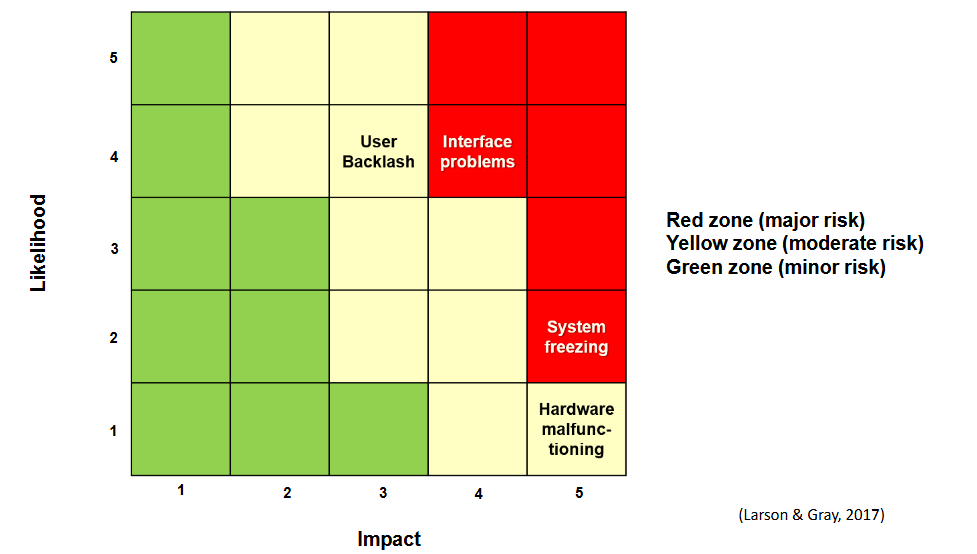
Risk map
Categorize risks.
Low risks don’t need action plan.
Acceptable risks need situational plan to know what to do if it happens.
High risk need plan to eliminate or plan to reduce impact
Examples of risk measures
avoid
move
reduce risks or consequences or probability
accept
integrate risk planning into project planning
build risk analysis and risk management into all life cycle phases - good for controlling and monitoring risk.
take potential problems seriously
keep your eyes open after new circumstances
accept that you can’t identify and resolve all risks
How do we do risk response control
Implement risk strategy
Monitor and adjust plan for new risks
Change management
Document and write lessons learned after project
General project risk management principles
Effective project risk allocation and ownership
Adequate level of effort
Proactive approach
Example of risk assessment form
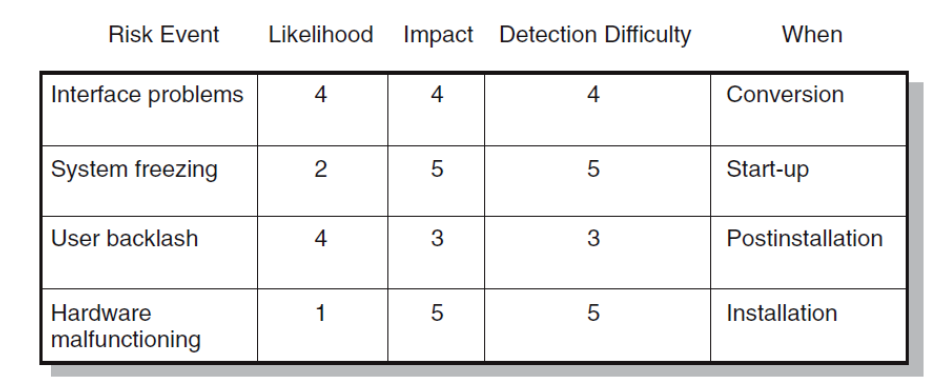
Example of risk matrix
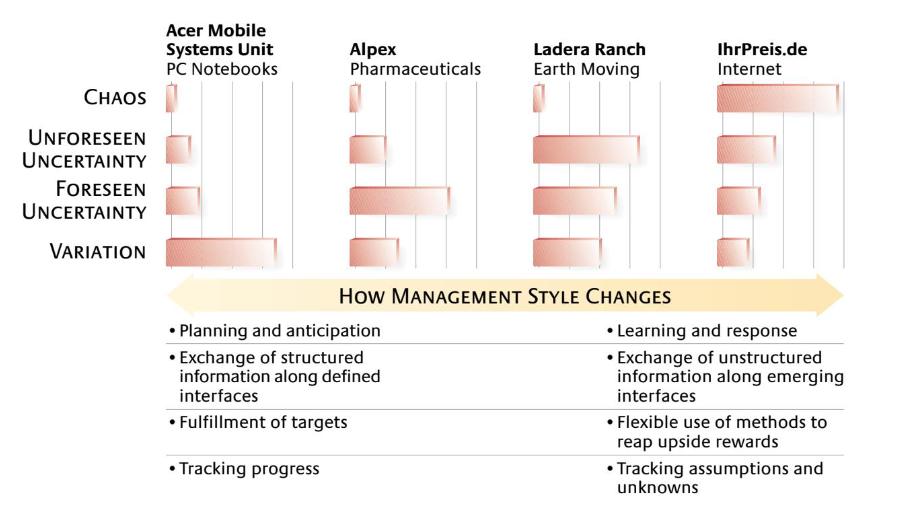
Uncertainty profile and its implications
Chaos, unforeseen uncertainty, foreseen uncertainty, variation