CSE 110 Midterm 1 Flashcards
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Waterfall Method
Top Down, break up a software development projects into a set of steps running through designing, planning, executing, verifying and maintaining.
4 values of RAIL model
(response, animation, idle, load)
the concept of working from the code first and requiring it to emit pages but do so letting the user know they have messed up or provide them a different version is called:
graceful degradation
the concept of working upwards from the markup to the code in web development is called:
progressive enhancement
web sites or web apps should generally employ graceful degradation?
web apps
web sites or web apps should generally employ progressive enhancement?
web sites
generally fast but inherently insecure
client-side
generally slow but can be controlled
server-side
double diamond
design process which will allow us to expand and contract our thinking as our team builds our product
What are key points of solo development?
developing focus and discipline
avoid complexity
being meticulous with our work
what is pair programming?
two developers working together on the same code synchronously either locally or remotely.
what is the role of a driver in pair programming?
writes the code
what is the role of an observer/navigator in pair programming?
learning and improving the code as we go along and coming to a consensus so it is our code not the driver’s code.
what the ideal pair for pair programming and why?
senior and junior - is a great way to share knowledge and even out a team often eliminating bus factor for created code.
what is a flaw of pair programming?
depends on interpersonal skills and it is quite easy for it to become toxic when one participant judges the other, checks out, etc.
what is mobbing / mob programming and what is its structure?
where the entire Agile team works together on the code. means we have a single driver and many observers, researchers, editors, etc.
what are two benefits of mobbing / mob programming?
good at the start of a project to work out live coding styles and get agreement on code shape and approach.
build some team cohesion in a technical setting.
what is a flaw of mobbing / mob programming that pair programming also has?
exposes poor team social dynamics
key mistake people make in Agile teams?
not formally defining your DoD or Definition of Done.
what is the idea of DoD or Definition of Done?
understand that a task isn’t finished until all the aspects of the task have been addressed. includes unit tests, documentation, other team member review, linting, etc.
what is the 5 points of the Tuckman model (and their specific order)?
forming
storming
norming
performing
adjourning
what is the idea of “Thinking in Bets”?
the idea that the process models and estimation aspects of SE suggest a certain amount of prediction.
Is thinking of "1 / 0 certainty of pass or fail" an example of "Thinking in Bets"?
No, adopt more a percentage outcome of pass fail like 86%/14% or something
Is thinking of "86%/14% pass fail" an example of "Thinking in Bets"?
Yes, adopt more a percentage outcome of pass fail like 86%/14% or something
True or false: if the outcome is bad, it is guarenteed we made a bad decision somewhere
False - Decisions are bets on the future, and they aren't "right" or "wrong" based on whether they turn out well on any particular iteration
True or false: the vast majority of skills are acquired through practice instead of innate ability
true
True or false: one day in the near future we'll finally have a "golden hammer" tool that we can use for most every project
false
True or false: learning a new language or tool initially increases the team's productivity
false
what is not the first step in writing a program?
a) designing
b) architecture
c) research
d) coding
d) coding
What is the most influential factor that affects the success of a software engineering team?
a) product complexity
b) personnel / team capability
c) technology used
d) time constraints
b) personnel / team capability
True or false: There is usually one true perfect solution to most problems that novice programmers are unable to see
false
what does it mean to be a T shaped Engineer
It mean to be a balanced devs who have breadth and depth within reason
What characteristics in a person let them make better decisions?
a) Equal amount of breadth and depth in multiple subjects
b) More depth in one subject and less breadth in multiple subjects
c) All depth in multiple subjects
d) More breadth in multiple subjects and less depth in one subject
a) Equal amount of breadth and depth in multiple subjects
Which of the following is not an example of the new values of software engineering?
a) learning
b) competition
c) cooperation
d) inclusion
e) humility
b) competition
what is top-down design
start with high level and break down towards small pieces. The common reductionist style
what is bottom-up design
using interactions, data, etc. to grow upwards
what is middle-out design
a surprising concept that has us trying things sometimes completely out of order and still finding value via exploration
Using the Iron Triangle theory, what happens if we increase the number of features?
cost and time increases
True or false: the best teams are the ones where everyone is a 10x developer.
false
True or false: You should pick one of "Top-Down", "Bottom-Up", "Middle-Out" and stick with it to reduce complexity in your design
false
True or false: You should use all of "Top-Down", "Bottom-Up", "Middle-Out" in one project depending on the situation
true
what is the defintion of software engineering?
the study of an application of engineering to design, development and maintenance of software.
what is a 10x Developer?
the idea of high performing developer
How does one become a 10x developer?
It takes long long journey that involves significant commitment and practice.
Why do you think developers get imposter syndrome so commonly?
due to the rapid pace of technological change, high standards, constant learning requirements and a culture of comparison that makes them doubt their abilities and feel like fake despite their skills.
what are the key points of incremental solutions?
focus on doing pieces at a time
provide more safety
utilize feedback
True or False: all at once solutions are now obsolete
false
what is the idea of “all at once solution”
we do the whole thing in one go and release, ie space probe software
True or false: communication is a mostly learned skill rather than an innate ability
true
What is the most important (by a wide margin) factor in making a successful team?
a) psychological safety
b) structure and clarity
c) meaning of work
d) dependability
e) impact of work
a) psychological safety
True or false: in order for a team to feel psychologically safe, they have to know that those who under perform / make big mistakes are punished accordingly.
false
True or false: good teams make sure everyone points out the member who has made a big mistake, and make sure to mention that they're ok with it so that the member feels psychologically safe
false
True or false: you generally want a higher bus factor so that your team is less reliant on any one individual
true
True or false: the technologies used will be more important than the processes we use when developing the project.
false
what are the three key points of the HRT (HEART) method?
Humility, Respect, Trust
True or false: everyone should be able to be leaders of their domain within the team
true
True or false: project Leaders / Managers tend to bog down projects and over-insert themselves, they don't really serve a purpose outside of micromanaging
false
Which of the following is not a stage of group development?
a) warming
b) storming
c) adjourning
d) norming
e) forming
f) performing
a) warming
True or false: diagramming using Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standardized method used to visualize and communicate system design and user interactions.
true
True or false: users will not always read your use cases and instructional manuals to figure out how to use your software.
true
True or false: users will judge your products based on the “-ilities”
true
True or false: software == code
false
True or false: the build process should be so quick and simple that the CEO can do it
true
a famous developer once said: "The hardest single part of building a software system is deciding ____."
precisely what to build
True or false: it is our job as developers to take the vague requirements of our clients and turn them into specific requirements and goals
true
True or false: programming doesn't translate well to writing since programmers think in code and not words
false
According to Spolsky's cardinal axiom of UI design: A UI is well designed when the program behaves ________
exactly how the user thought it would
What three things make up the Iron Triangle?
Scope, Cost, Schedule
True or false: with proper planning and following a process, we can avoid tradeoffs
FALSE, tradeoffs cannot be avoided, and should be embraced (Iron Triangle)
In the Iron Triangle, do we focus on acceptable quality or pull points?
focus on the acceptable quality. Without defining quality we are somewhat lost
How many points in the Iron Triangle should you be fixing?
1 point. If you set more, plans become hard to follow.
what are pull points for the iron triangle?
the parts of the iron triangle that you try to increase / keep high. You should only have one at a time.
True or False: If other companies are using a technology, then you should adopt it too
False, when you encounter Fashion Based Problem Solving you need to work at how to describe and explore these fashionable solutions to see if there are novel or just trendy.
Describe the balance between security and usability / ux
more security tends to degrade ux and inversely ease of use might sacrifice security.
what is Postel’s law
the robustness principle that drives much of how the internet works. it states be permissive in what you accepts, and strict with what you emit ("be conservative in what you do, be liberal in what you accept from others")
With a fixed deadline, what tends to happen to quality and features?
Quality and features are sacrificed, may result in lower user-acceptance or profit
True or False: when people schedule deadlines for their projects, they tend to get to their desired quality within that time frame
False. The truth of estimating and completion when you don’t have a fixed date is that deadlines tend to shift to hit the desired quality mark.
what is Conway’s Law?
a law that suggests software architecture and team structure will often be a function of the organizational structure.
If Conway’s Law is a strict rule and we discover that the software architecture is bad, in order to address the poor architecture what might we need to do outside of just focusing on the code itself?
We should be able to compare it to organization size or type
What are the main forces in Software Engineering?
a) 10x developers
b) tech stack
c) the people
d) the money
c) the people
what is the cone of uncertainty
a useful way to remind ourselves that when starting something we are mostly uncertain and the longer time or examination continues especially as we build software the more certain and specific we get.
What does DUF stand for?
Design Up Front
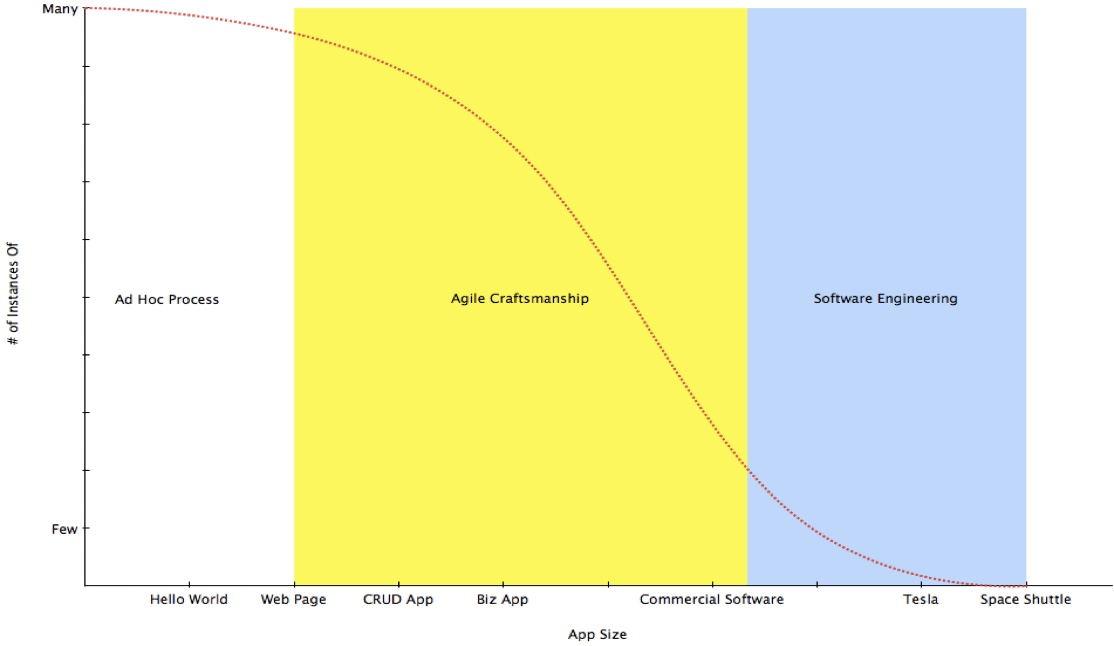
What does this image refer to?
The Spectrum of Process
What factors should influence the decision to use a certain process (ie AGILE or waterfall, there are 5 points to consider)?
1) Risk appetite
2) project type
3) time availability
4) team maturity
5) organization needs
and such as opposed to one particular right or wrong way.
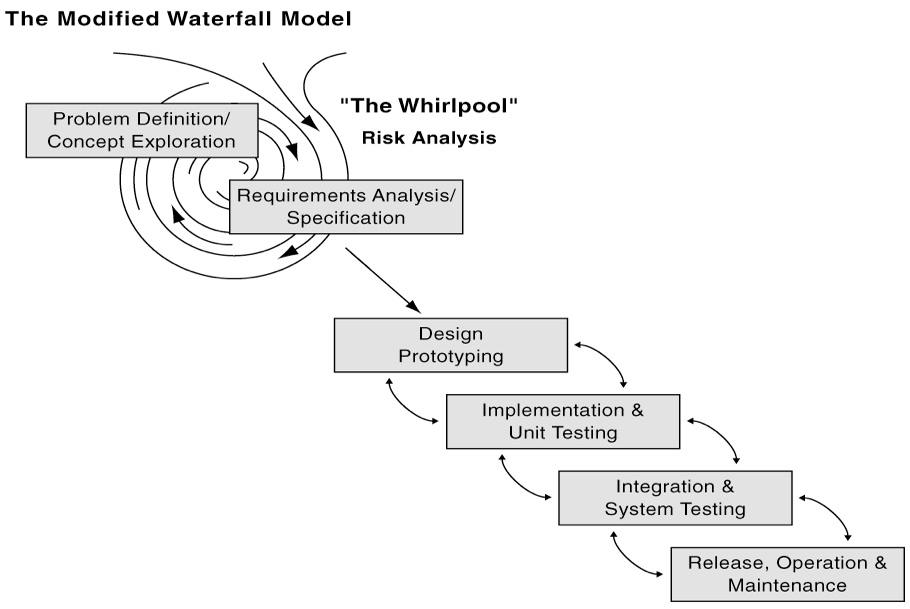
What modifications do the professor like to make to the Waterfall Method?
Arrows that point to previous steps if warranted.
Design whirlpool effor before entering build process.
Disadvantages of waterfall include?
1) does not handle change well
2) often do not get user feedback early and often enough without modification (ex. whirlpool idea)
3) may delay progress or gratification in a world that demands to see that
Define bus factor
How many team members "can be hit by a bus" before the entire project is at risk.
describe the concept of user centered design or UCD (and what are two laws to remember for UCD)
We call a strong emphasis on user during the constructive process
Law: You are != your users
Law: Users cannot be your designer
Some of -ilities like security, reliability, etc. are not user focused, but many include:
The system provides the required functions - Utility
Ability to access the systems and its function - Availability
Ability to access the systems within acceptable time - Performance - ility :-)
Ability to be able to use the functions - Accessibility
Ability to be able to use the functions successfully - Usability
Ability to enjoy the functions - Satisfaction (Satisfiability)
What is one example of an over engineered solution
formal model for hello world
what is an example of under engineered solution
cowboy hacking or rapid iteration for a life and limb application like a heart monitor or autonomous driving system
True or False, software engineering process models provides unique challenges that make it unique from other disciplines and prevent the adoption of process models from elsewhere
False. We’ve known many of the problems with process for a long time, but struggle as an industry to get consensus.
True or false, there is one true way for different aspects of software engineering
False, there is no one true way to do things within software engineering
What mindset should we employ as Software Engineers (SE)?
focus less on perfect eternal solutions and more on situational appropriate solutions.
What are four key values of Extreme Programming (XP)
communication
Feedback
Simplicity
Courage
what is agile software development all about?
it is about speed, user focus, communication, self organization, good tech and design, keeping it simple and dealing with change.
describe daily standups in Agile software development
quick meetings of what you did, what you want/need to do, and any blockers to be cleared
describe user stories in Agile software development
user stories help us write user needs in a manner that we might translate them into the requirements for our project
what is a backlog in Agile software development
a collection of tasks (user stories, bug fixes, etc) that have been defined for the product.
what do backlogs contain, and why do we want small backlogs?
backlogs contain what you will eventually do. The smaller they are, the better since it reflects that we have smaller work in progress tasks