bones
1/313
Earn XP
Description and Tags
it's bones!!!!! (recommended: set options to "answer with term" and open-ended, click on the pictures to zoom in)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
314 Terms
Bone
Structure used for structural support and protection
oste/o
Bone (combining form)
Muscle
Structure used for internal and external movement
my/o
Muscle (combining form, three letters)
Joint
Structure where bones (and other joints) come together (j_______)
Articulation
Another term for “joint”
Joint
Another term for “articulation”
arthr/o
Joint (combining form, six letters)
Tendon
Structure that connects muscle to bone
ten/o
Tendon (combining form, four letters)
tendin/o
Tendon (combining form, seven letters)
Ligament
Structure that connects bone to bone
ligament/o
Ligament (combining form)
-blast
Immature (suffix)
-clast
To break (suffix)
-cyte
Cell (suffix)
Ossification
Replacement of cartilage with bone
Osteoblast
Cell that produces immature bony tissue that replaces cartilage
Osteocyte
Cell that nourishes and maintains bone
Osteoclast
Cell that reabsorbs and digests bone (remodels bone)
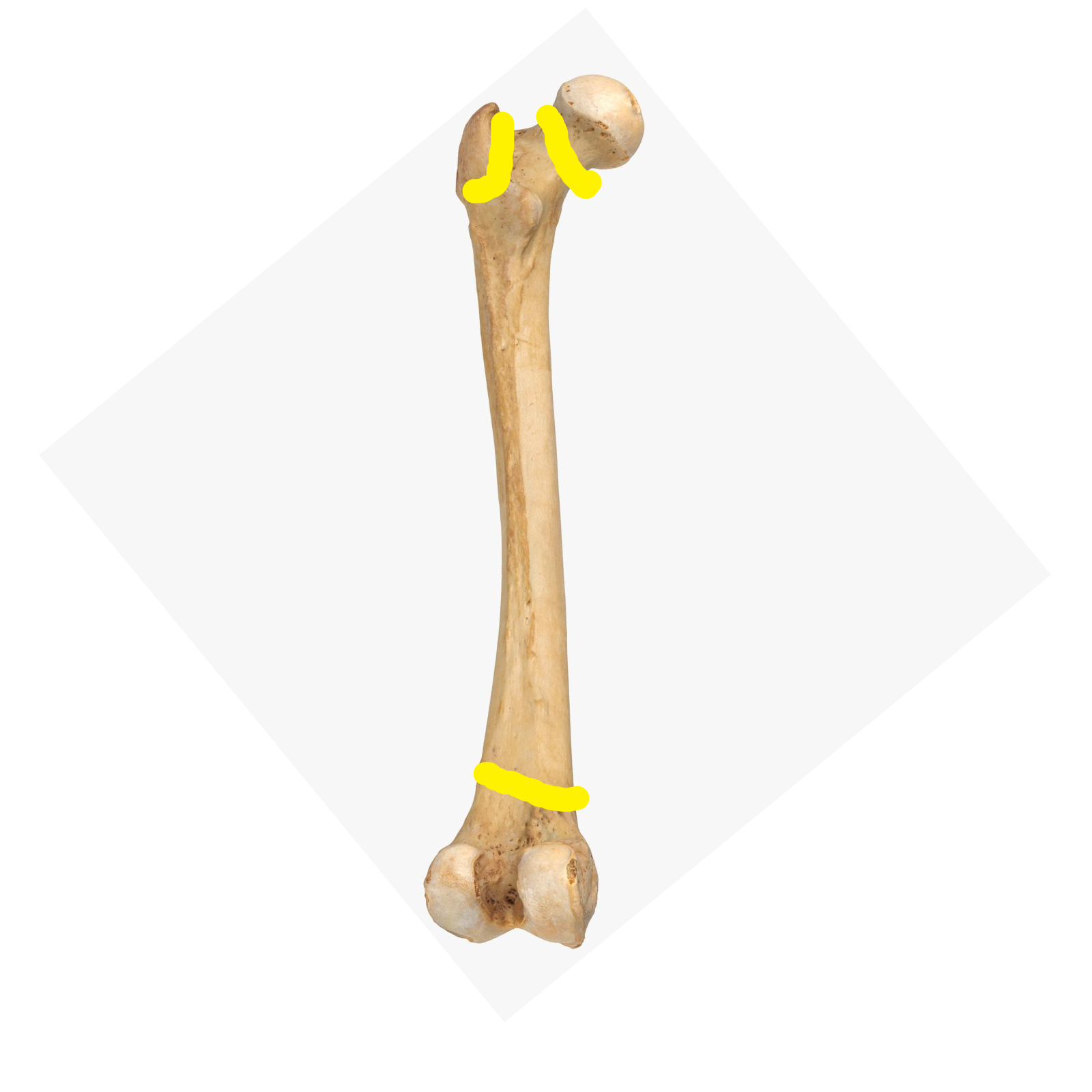
Diaphysis
Shaft of long bones
Diaphysis
Identify this bone part.

Epiphysis
The end of long bones
Epiphysis
Identify this bone part.

Metaphysis
Cone-like flared portion between end and shaft
Metaphysis
Identify this bone part.
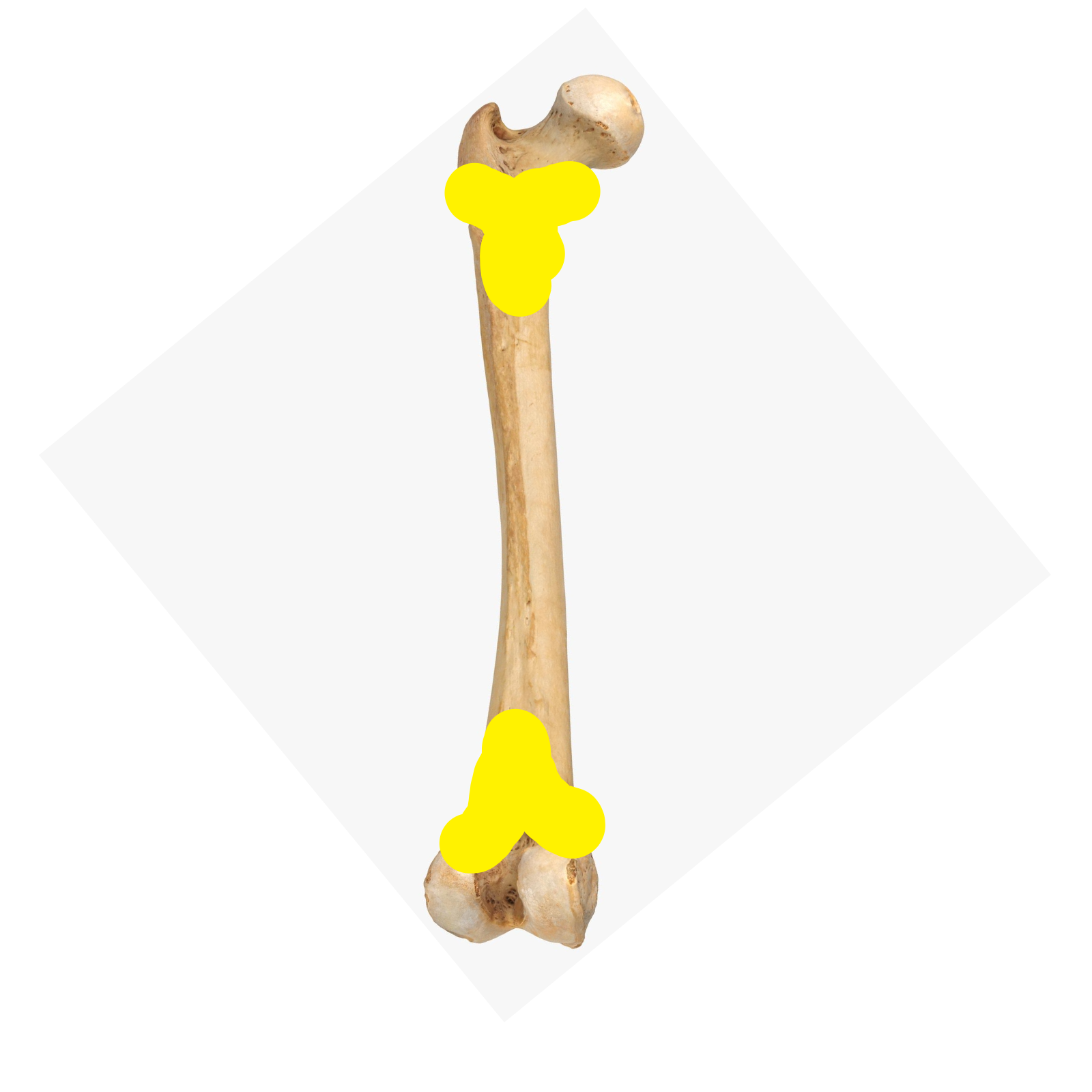
Epiphyseal plate
Growth plate where cartilage is replaced by bone for bone growth (in length) (________ p_______)
Epiphyseal line
Another term for “epiphyseal plate”
Epiphyseal
Identify this bone part (________ line)
-physis
To grow (suffix)
meta-
Change, beyond (prefix)
Compact
Contains Haversian systems for blood vessels, nerves, and yellow bone marrow (________ bone)
Articular cartilage
Cushions joints and allows for smooth movement, covers ends of bones
Cancellous
Spaces contain red bone marrow for elements for hematopoiesis (c_______ bone)
Spongy
Another term for “cancellous bone” (________ bone)
Cancellous
Another term for “spongy bone” (________ bone)
Hematopoesis
Process of blood cell creation
Yellow bone marrow
Part of the bone that is mostly fat
Red bone marrow
Ribs, pelvic bone, sternum, vertebrae, and the epiphysis of long bones are made up of ________ ________ ________.
Long
The femur, humerus, fibula, and tibula are ________ bones.
Short
The carpals and tarsals are ________ bones.
Flat
The scapula and sternum are ________ bones.
Sesamoid
The patella is a s_______ bone.
Floating
Another term for sesamoid bone (________ bone)
Sesamoid
Another term for floating bone (________ bone)
Irregular
The vertebrae are made up of ________ bones.
Process
Attachment for muscles, tendons, and ligaments
Depression
Opening or hollow region; passageway for nerves and/or vessels
Bone head
Process - Round end of the bone
Condyle
Process - round, knuckle-like
Epicondyle
Process - used for tendon attachment (small rounded process)
Trochanter
Process - used for tendon attachment
Femur
Trochanters are only found in the ________. (greater trochanter, lesser trochanter)
Tuberosity
Process - used for tendon attachment (small rounded elevation, 10 letters)
Tubercle
Another term for “tuberosity”
Tuberosity
Another term for “tubercle”
Fissure
Depression - narrow, slit-like
Fissure
The eye socket is an example of a(n) ________ depression.
Foramen
Depression - opening for blood vessels and nerves
Foramen
The foramen magnum is an example of a(n) ________ depression.
Fossa
Depression - shallow cavity in or on a bone
Fossa
The olecranon fossa is an example of a(n) ________ depression.
Sinus
Depression - hollow cavity within bone (example: found in the skull)
Cranial
The frontal bone is a(n) ________ bone.
Frontal
This bone is the ________ bone.
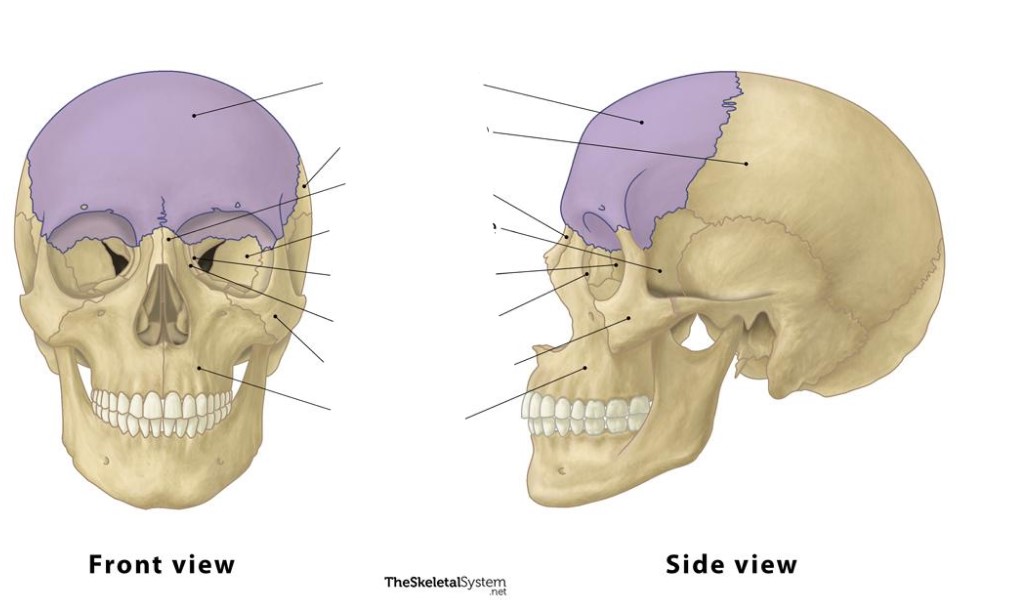
Cranial
A parietal bone is a(n) ________ bone.
Parietal
This bone is the ________ bone.
Cranial
A temporal bone is a(n) ________ bone.
Temporal
These bones are the ________ bones.
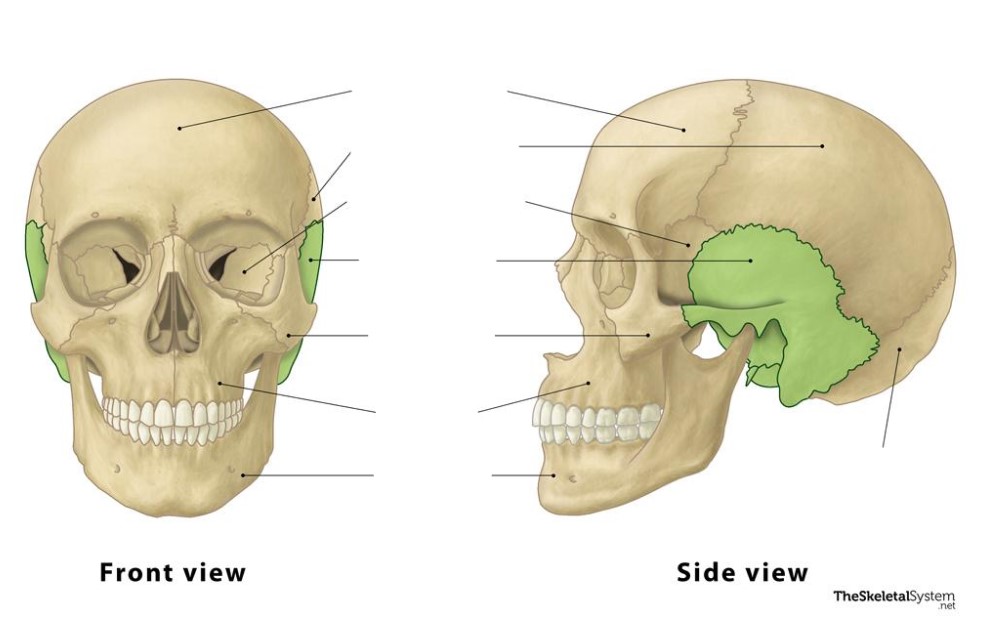
Mandibular, temporal
The temporomandibular (TMJ) is located on the m_______ bone and the ________ bone (separated by commas)
Temporomandibular joint
Joint between a temporal bone and the lower jaw (________ ________)
TMJ
Abbreviation for “temporomandibular joint”
Temporomandibular joint
Long version of “TMJ”
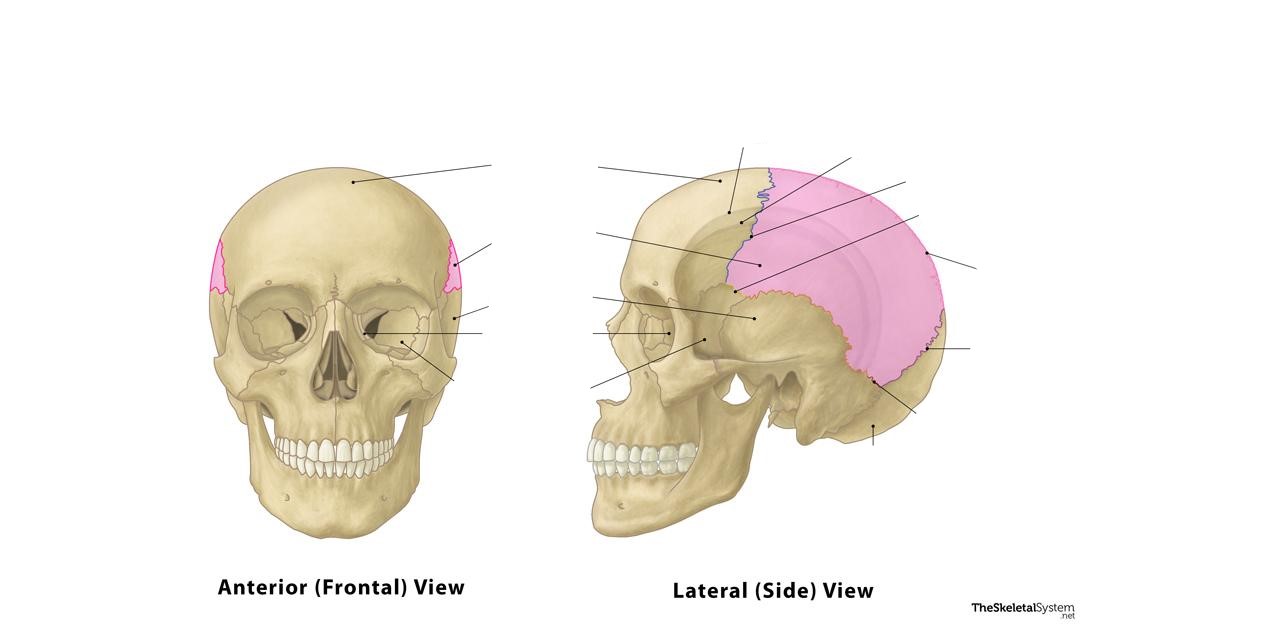
Temporal
The mastoid process is located on a(n) ________ bone.
Mastoid process
Joins a temporal bone to neck muscles (________ ________)
Temporal
The styloid process is located on a(n) ________ bone.
Styloid process
Allows for the movement of several structures, such as the tongue and the pharynx (________ ________)
Cranial
The occipital bone is a(n) ________ bone.
Occipital
This bone is the ________ bone.
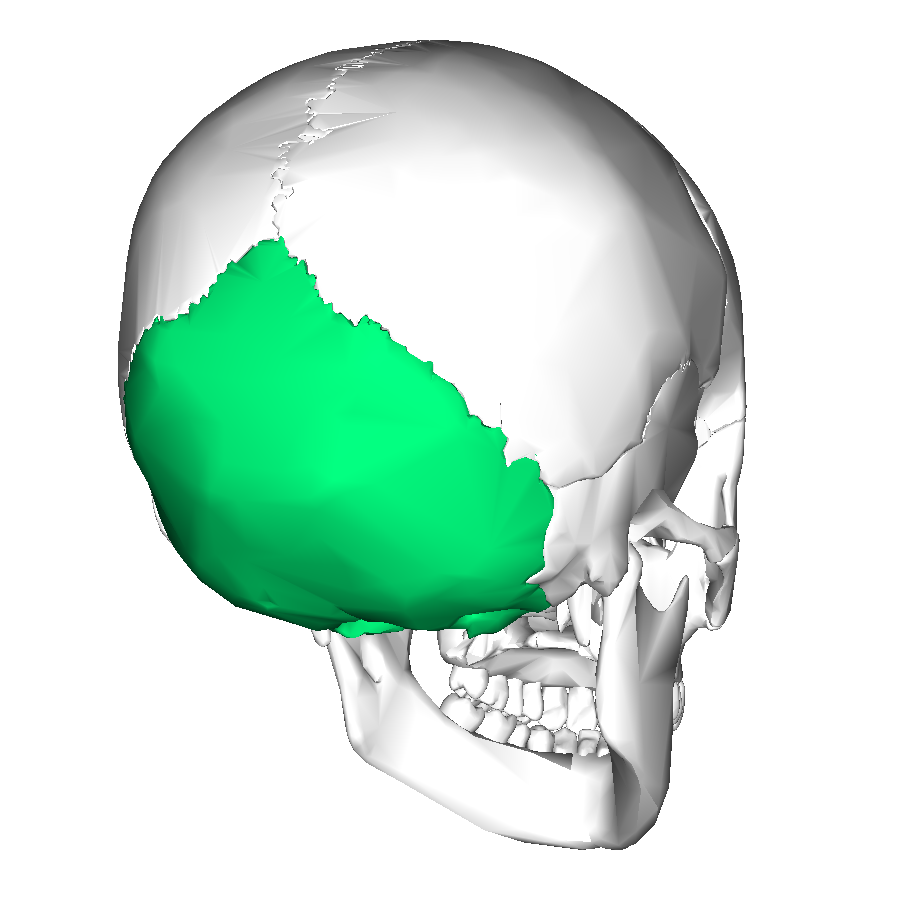
Occipital
The foramen magnum is located on the ________ bone.
Foramen magnum
Foramen that spinal cord passes through (_________ ________)
Cranial
The sphenoid bone is a(n) ________ bone.
Sphenoid
This bone is the ________ bone.
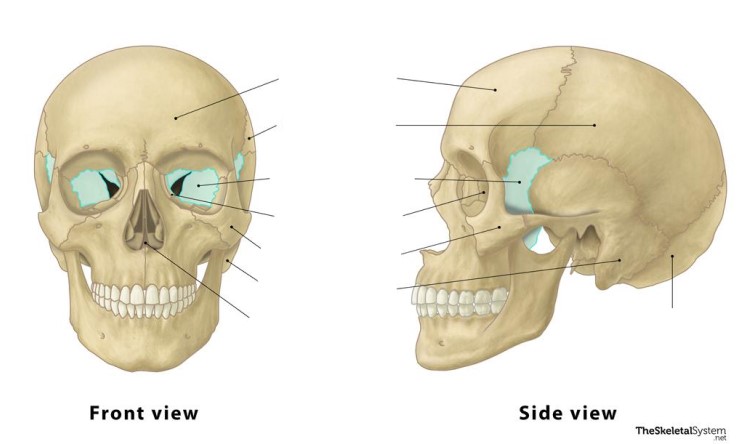
Sella turcica
Depression in the sphenoid bone, containing the pituitary gland
Cranial
The ethmoid bones are ________ bones.
Ethmoid
These bones are the ________ bones.
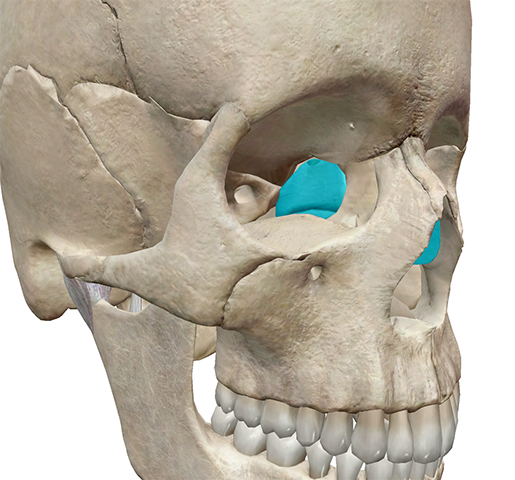
Facial
The nasal bones are ________ bones.
Nasal
These bones are the ________ bones.
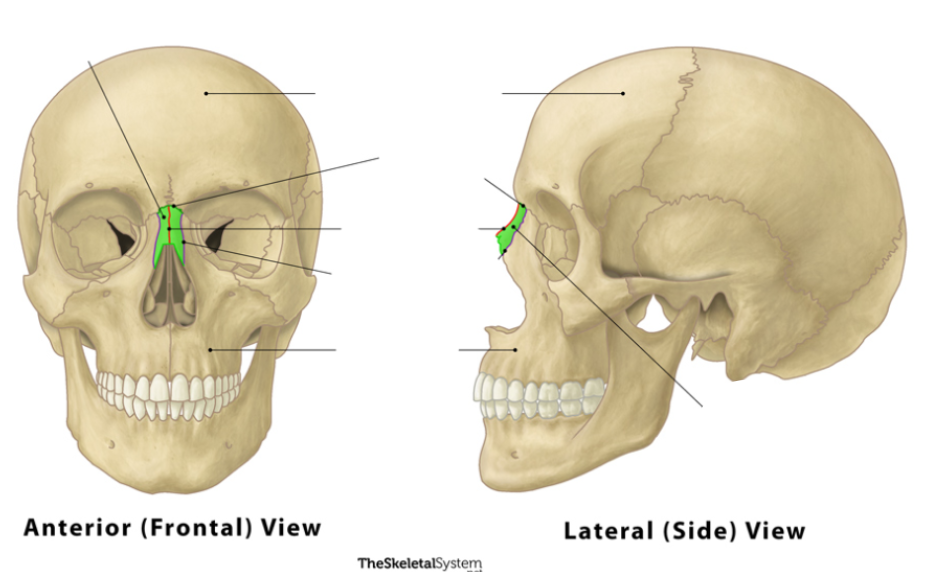
Facial
The lacrimal bones are ________ bones.
Lacrimal
These bones are the ________ bones.
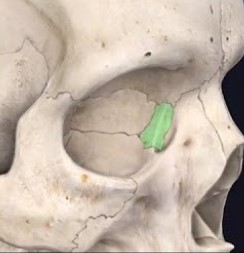
Facial
The maxillary bones are ________ bones.
Maxillary
These bones are the ________ bones.
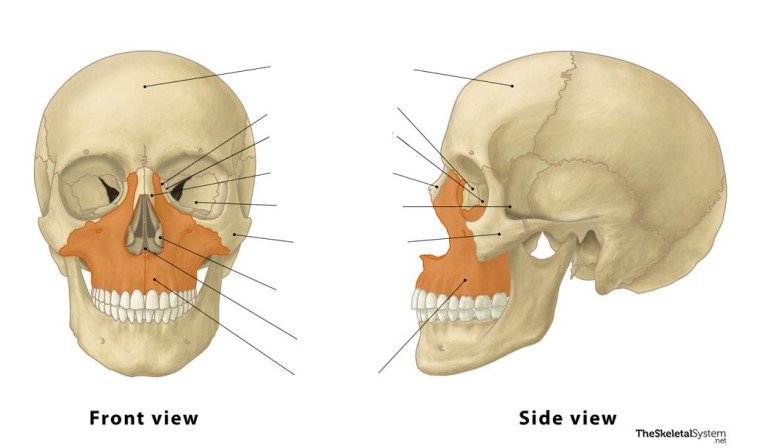
Facial
A mandibular bone is a(n) ________ bone.
Mandibular
This bone is the ________ bone.
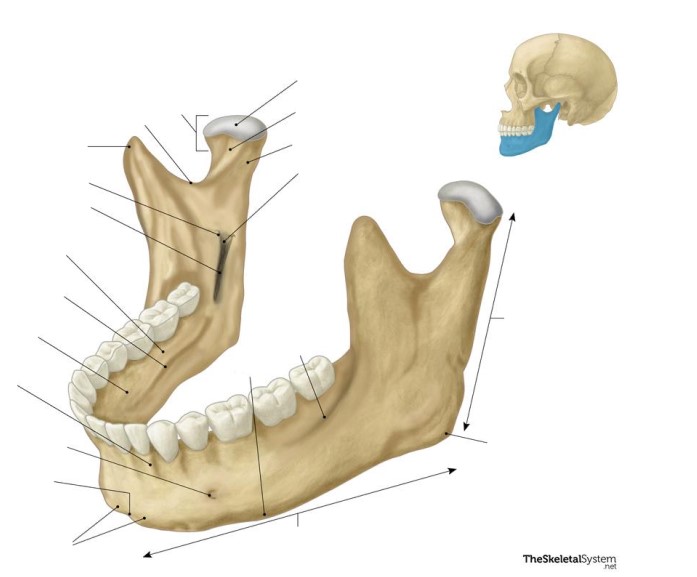
Facial
The zygomatic bones are ________ bones.
Zygomatic
These bones are the ________ bones.
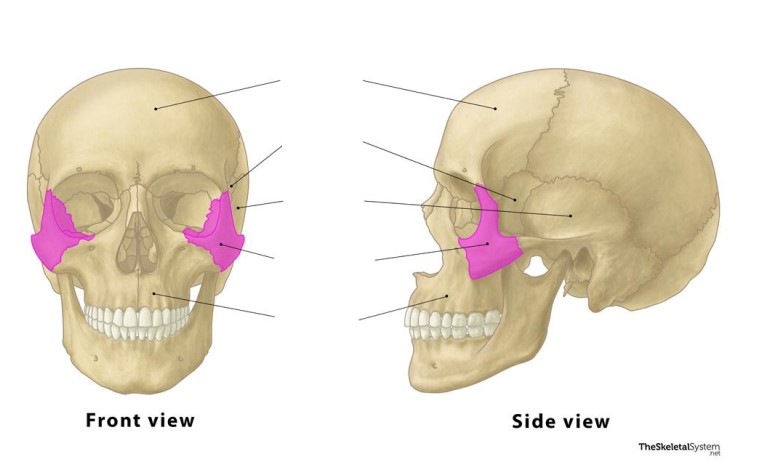
Facial
The vomer bone is a(n) ________ bone.
Vomer
This bone is the ________ bone.
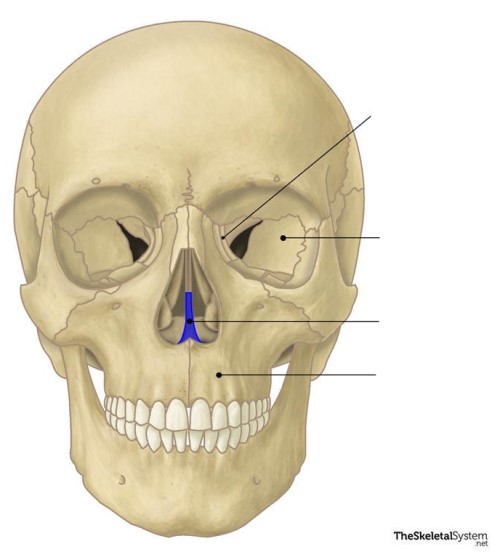
Cranial, facial
In what bones are the skull sinuses located? (c________, f________)
Sinus
Structure that lightens the skull