CHE 161 Midterm - Lipids
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This deck focuses more on lipids explanations.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are lipids mainly made of?
Lipids are mainly composed of long chains of hydrocarbons
Are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophilic, and what are they soluble in?
Lipids are hydrophobic and are soluble in organic solvents but not in water.
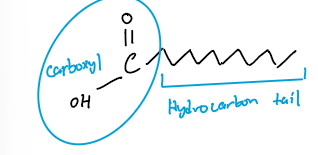
What is a fatty acid? What does a fatty acid look like
A fatty adid is made of a carboxyl group attached to a hydrocarbon tail. Fatty acids are combined with other molecules - glycerol - via their carboxyl group.
What are triglycerides made of?
Triglycerides are made up of a glycerol molecule bonded to three separate fatty acids via an ester bond. (OH-OH condensation reaction)
What is a triglyceride’s (fat) primary function?
A triglyceride’s primary function is long-term energy storage and insulation. They provide more energy that carbohydrates on a per gram basis because the carbons in the long chains are only bonded to hydrogens so they are more reduced than the carbons in carbohydrates are bonded to oxygens.
Why are triglycerides for long term energy storage and not short term storage?
Triglycerides are hydrophobic and repel water. Therefore, it makes it harder for enzymes to reach the fats to break them down.
What is an ester bond?
An ester bond is a bond through the interaction of a carboxyl group and an alcohol (OH). It bonds fatty acids to the glycerol molecule.
Compare saturated and unsaturated fats.
Saturated fats have fatty acids that contain no double bonds, meaning the fat molecules are packed closely together, and have higher melting points. Unsaturated fats have double bonds, meaning they are less compact and are liquid are room temperature.
Describe and draw the structure of phospholipids.
Phosholipids contain two fatty acids bonds to a glycerol molecule, plus a phosphate group which is bonded to the third OH on glycerol.
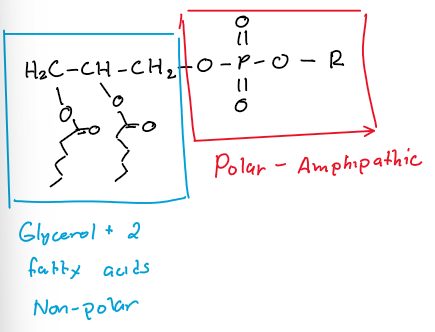
What do phospholipids do when they are added to water?
When phospholipids are added to water they assemble themselves into liposomes, micelles, or bilayer sheets. By doing this their hydrophobic tails are hidden from the water while the hydrophilic heads point out.
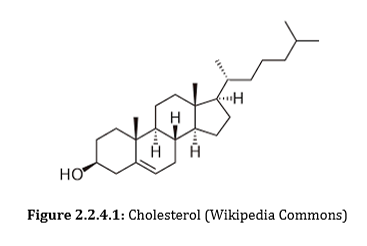
Describe the structure of steroids.
Steroids have a four ring structures with varying functional groups.
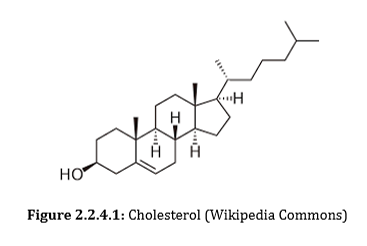
How does cholestrol’s (steroid) shape impact its role
Cholestrol will interfere with the closely packed structure of saturated fats, allowing for increased fluidity. It can also fill in gaps in phospholipids with unsaturated/short tails. It will keep the membrane fluid while maintaining the rigidity of the membrane.