form 4 Biology chapter 14- Support and Movement in Humans and Animals
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Advantages & disadvantage if humans had an exoskeleton 外面的骨like an insect instead of an endoskeleton.
Ad : better protection for internal organ from physical damage
TDis : heavy & limit growth , requiring molting 蜕皮
Why do organisms need to maintain their body shapes?
for movement and support,
enables organs in the body to function properly.
State two functions of the skeletal system to humans.
To protect the internal organs
( Cth : the skull protects the human brain)
To produce red blood cells (in the bone marrow
For animals that move on the ground, what is the advantage of having legs below the body (for example, rats) compared to having legs at the side of the body (for example, crocodile)?
Animals with legs below the body lift their body mass above the ground to reduce friction while moving.身体离开地面,减少摩擦
This is more efficient for faster and longer running.
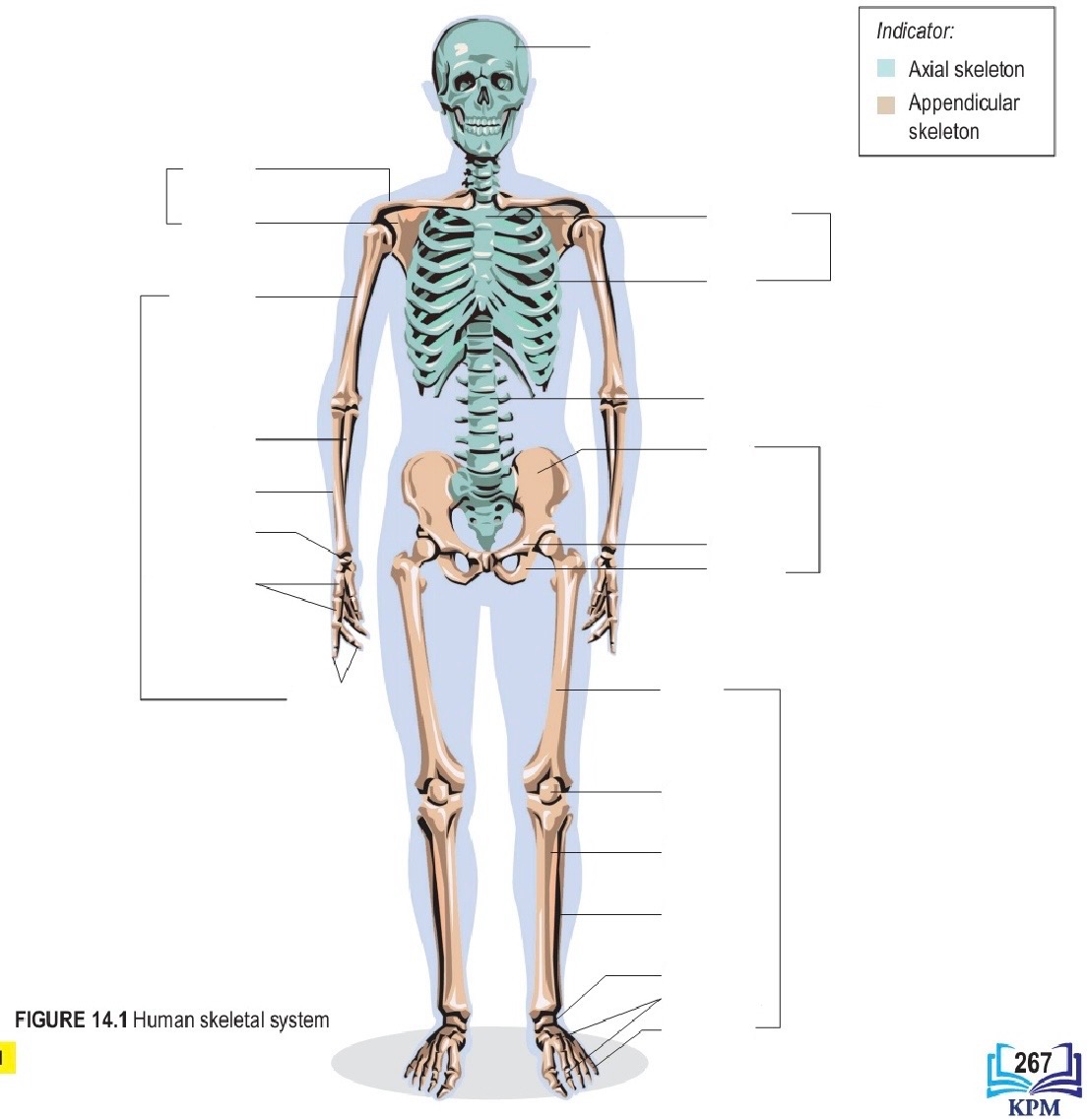
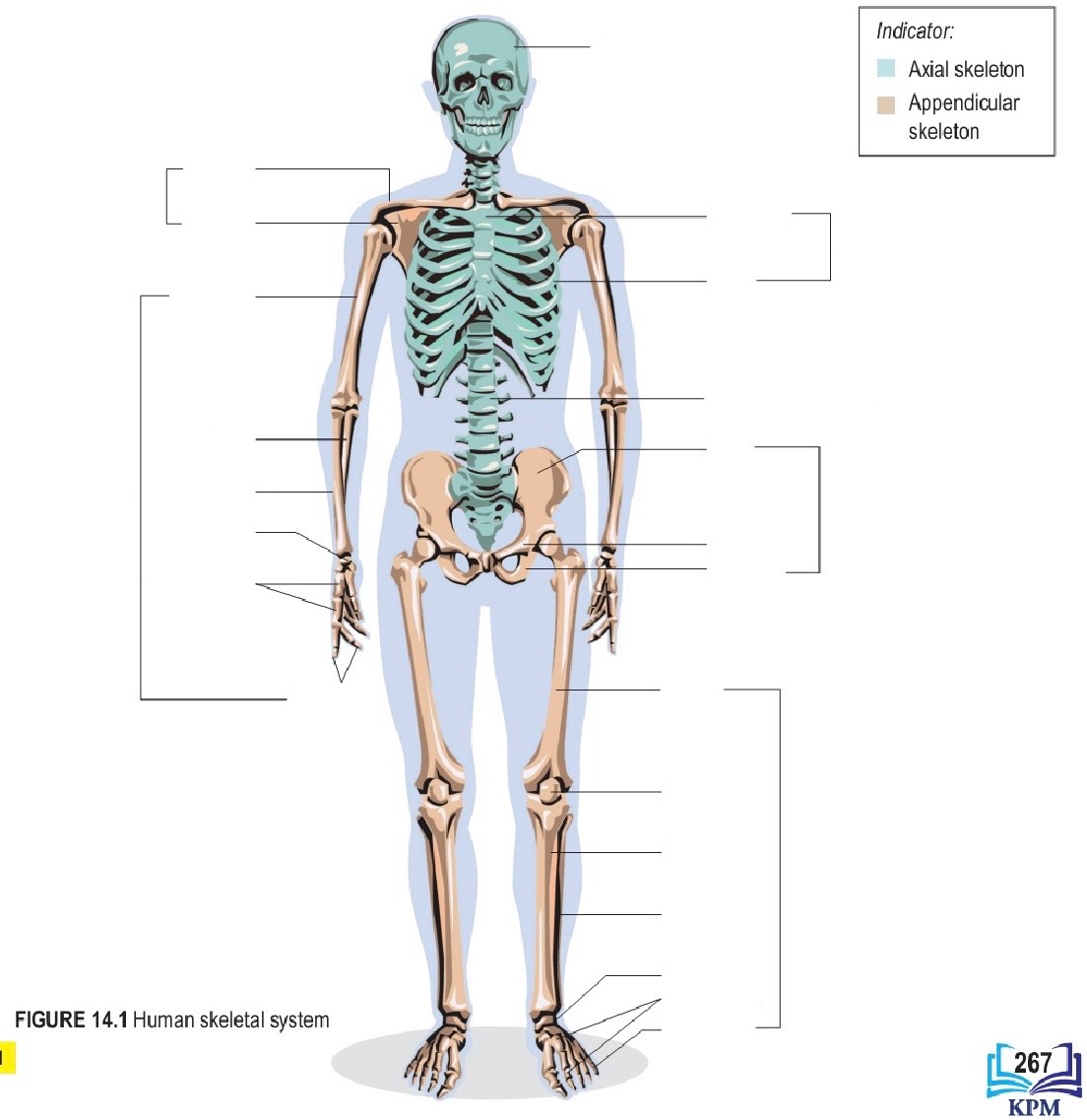
Axial skeleton include what part ? 4个
Skull , sternum , ribs , vertebral column
Appendicular skeleton included what part ?
全部除了那4个
three bones fuse together to form the pelvic girdle 髋带
Ilium , pubis , ischium
Types of skeleton
exoskeleton
Endoskeleton
Hydrostatic skeleton ( tissue fluid , earthworm )
Hmm fill in the blank
Skull
Clavicle 锁骨
Scapula 肩胛骨
Humerus 大臂的骨
Ulna 小臂旁边的骨
Radius 小臂的骨
Carpus 腕骨
Metacarpals 掌骨
Phalanges 指甲的骨
Sternum 胸骨
Ribs 一条条
Vertebral column 脊椎骨
ilium 髋骨
Pubis 连着髋骨的
ischium 那个洞
Femur 大腿的骨
Patella 大腿和小腿之间的球
Tibia 小腿的骨
Fibula 旁边小腿的骨
Tarsals 跗骨(像腕骨)
Metatarsals 脚掌骨
Phalanges 指甲的骨
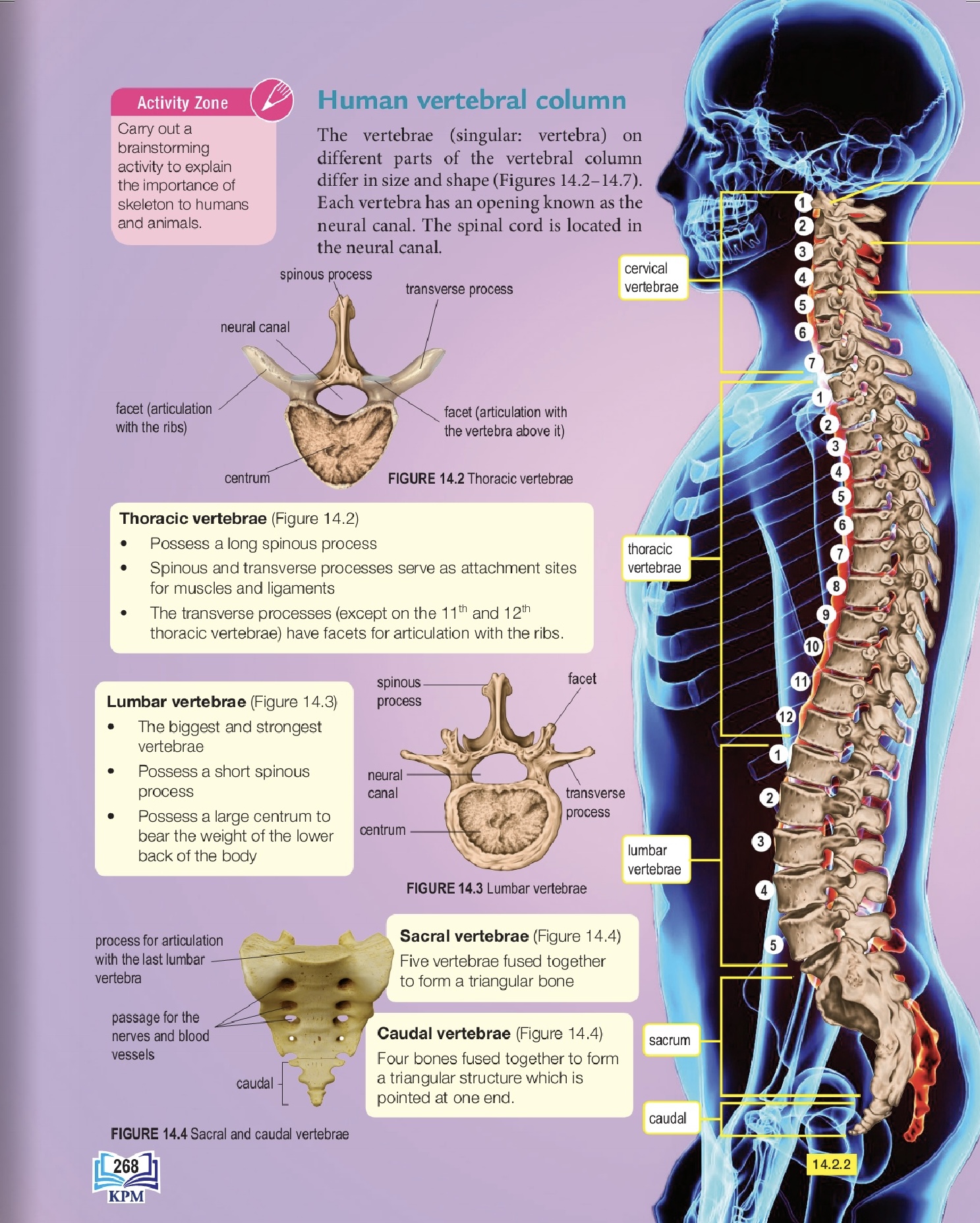
Type of Vertebrae 椎骨类型 | Key Characteristics 特征 | Function 功能 |
Cervical/ 颈椎 | Small centrum, short spinous process, transverse foramen 椎体小,棘突短,有横突孔 | Support the head, allow neck movement 支撑头部,允许颈部运动 |
Thoracic /胸椎 | Long spinous process, facets for rib attachment 棘突长,有关节面与肋骨连接 | Form the thoracic cage (chest) with the ribs 5与肋 骨形成胸廓 |
Lumbar/腰椎 | Large, strong centrum, short spinous process 椎体大而坚固,棘突短 | Bear most of the body's weight 承受身体的大部 分重量 |
Sacral/骶椎 | 5 fused vertebrae 5块融 合的椎骨 | Form the sacrum, connects spine to pelvic girdle 形成骶骨,连接脊柱和骨盆带 |
Caudal/尾椎 | 4 fused vertebrae 4块融 合的椎骨 | Forms the coccyx (tailbone) / 形成尾骨 |
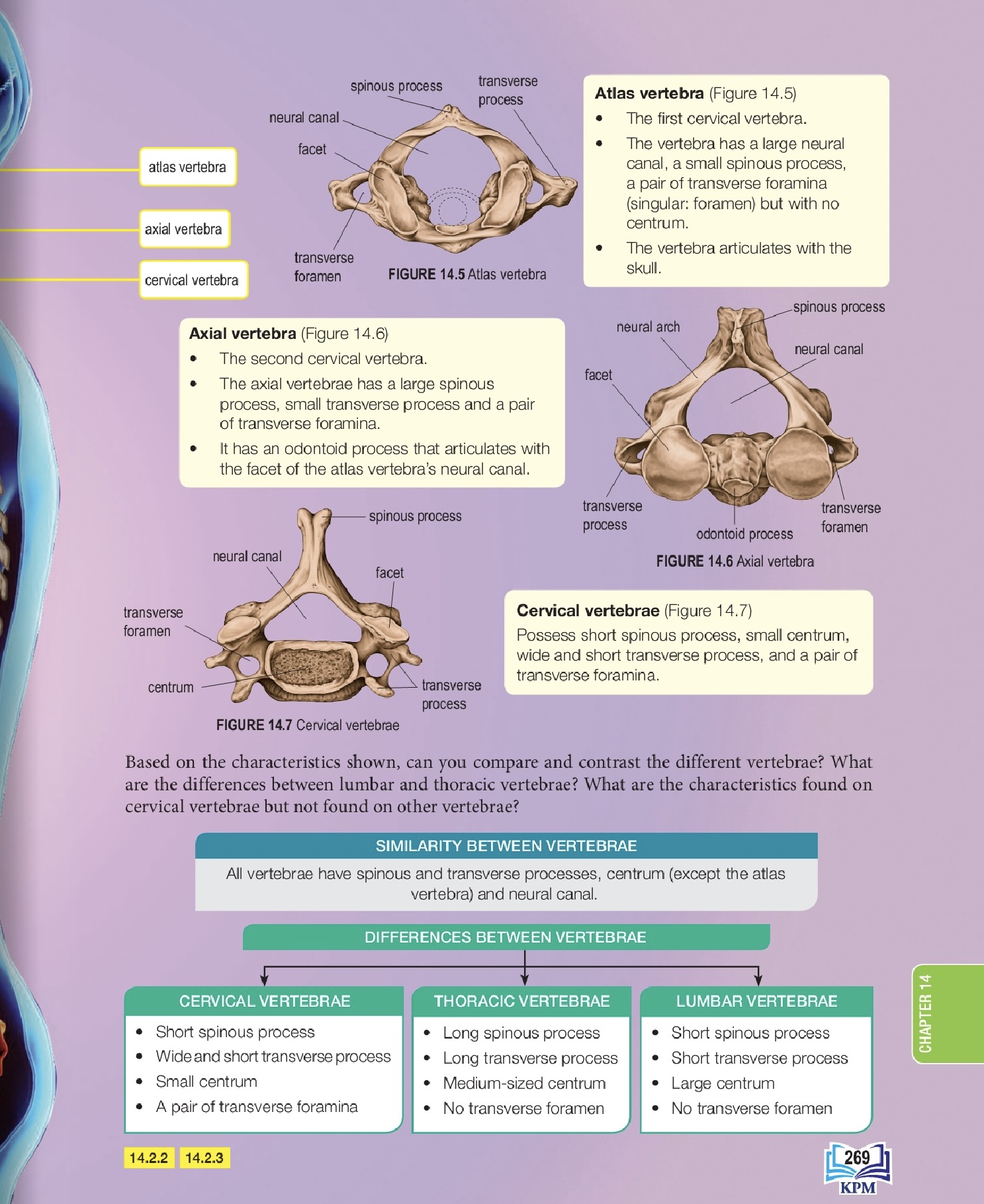
Atlas (C1)/寰椎 | No centrum, articulates with the skull / 没有椎体,与头骨连接 | Allows the "yes" nodding motion / 允许"点头"动作 |
Axis (C2) | Has an odontoid process (dens) that pivots with the atlas 有一个齿突,与寰椎形成枢轴关节 | Allows the head to rotate ( shake no ) |
Types of Joints 关节类型
Immovable Joint 不动关节( cth : sutures in the skull 头骨的骨缝)
Slightly Moveable Joint 微动关节( cth : discs between vertebrae 椎骨间的椎间盘)
Freely Moveable Joint 可动关节(cth: 滑膜关节) - Allow free movement
Type of Vertebrae 椎骨类型 | Key Characteristics 特征 | Function 功能 |
Cervical/ 颈椎 | Small centrum, short spinous process, transverse foramen 椎体小,棘突短,有横突孔 | Support the head, allow neck movement 支撑头部,允许颈部运动 |
Thoracic /胸椎 | Long spinous process, facets for rib attachment 棘突长,有关节面与肋骨 连接 | Form the thoracic cage (chest) with the ribs 5与肋 骨形成胸廓 |
Lumbar/腰椎 | Large, strong centrum, short spinous process 椎体大而坚固,棘突短 | Bear most of the body's weight 承受身体的大部 分重量 |
Sacral/骶椎 | 5 fused vertebrae 5块融 合的椎骨 | Form the sacrum, connects spine to pelvic girdle 形成骶骨,连接脊柱和骨盆带 |
Caudal/尾椎 | 4 fused vertebrae / 4块融 合的椎骨 | Forms the coccyx (tailbone) / 形成尾骨 |
Atlas (C1)/寰椎 | No centrum, articulates with the skull / 没有椎体,与头骨连接 | Allows the "yes" nodding motion / 允许"点头"动作 |
Axis (C2) | Has an odontoid process (dens) that pivots with the atlas 有一个齿突,与寰椎形成枢轴关节 | Allows the head to rotate ( shake no ) |
Parts of a Synovial Joint 滑膜关节的组成部分
Cartilage 软骨:Cushions the joint, reduces friction缓冲关节,减少摩擦
Synovial Membrane 滑膜:Produces synovial fluid 产生滑液
Synovial Fluid 滑液:Lubricates the joint 润滑关节
Ligament 韧带:Connects bone to bone. Strong and elastic
连接骨与骨。坚固且有弹性。
Capsule 关节霧:Fibrous tissue enclosing the joint 包裹关节的纤维组织
Types of Synovial Joints / 滑膜关节的类型
Ball-and-Socket Joint 球窝关节
Allows movement in all directions (rotation)
exp : shoulder and hip 肩关节和髋关节。
Hinge Joint / 屈成关节(铰链关节)
Allows movement in one plane only (back & forth )
exp : elbow and knee 肘关节和膝关节。
Muscles, Tendons, Ligaments /肌肉、肌腱、初帯
Skeletal Muscle 骨骼肌
Contracts to pull on bones and cause movement. Works in
antagonistic pairs (exp : biceps and triceps)
Flexor/ 屈肌
Bends a joint (exp : Biceps )
Extensor / 伸肌
Straightens a joint (exp : Triceps)
Tendon /肌腱
Connects muscle to bone. Strong, not elastic
Ligament /初帯
Connects bone to bone. Strong and elastic
What is the main function of the neural canal in a vertebra?
椎骨中神经管的主要功能是什么?
To house and protect the spinal cord.
Which vertebrae have facets for articulation with the ribs?
The Thoracic vertebrae.
What is the key structural difference between the Atlas (C1) and other cervical vertebrae?
The Atlas vertebra has no centrum (body).
Name two structures found in a synovial joint and state their function.
Cartilage: Cushions joints and reduces friction.
Synovial Fluid: Lubricates the joint.
Ligament: Connects bones and provides stability.
Synovial Membrane: Produces synovial fluid.
Capsule: Encloses and protects the joint.
What type of joint is the knee? What movement does it allow?
The knee is a hinge joint. It allows movement in one plane
Does a tendon connect muscle-to-bone or bone-to-bone? Is it elastic?
tendon connects muscle to bone, strong , flexible , not elastic.