Small animal GI case studies
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Hypovolemia is a fluid deficit in the
Intravascular space
Dehydration is a fluid deficit in the
Extravascular space
Hypovolemia signs
Weak pulse
Tachycardia
Dehydration signs
^ PCV/ TP
Tacky mm
^ CRT
^ Skin tent
^ eye sunken
An 8-year-old, female, spayed American domestic shorthair cat is brought to the clinic by her owner for further evaluation. One week prior, the owner found the cat hiding and observed that the cat was not well; she appeared lethargic and not interested in food, and her skin and mucus membranes appeared yellow. She was taken to the referring veterinarian's clinic, and laboratory studies showed anemia and increased serum liver enzymes. She was treated with IV fluids, broad-spectrum antibiotics, a blood transfusion, and steroids for 4 days. The patient improved somewhat and was discharged. At home the patient relapsed and was referred for further evaluation.
General: Unwilling or unable to stand
Skin: Slightly yellow skin color
HEENT: Mucus membranes slightly yellow
Gastrointestinal: Anorectic Gut sounds absent.
Neurologic: Depressed mentation
Medical history: Recently unwell and treated by referring DVM for anemia and dehydration.Surgical history: Spayed at a young age.
Medications: None. Vaccinations current.
General appearance: Lethargic and unwilling or unable to standVital signs:
Temperature: 36.4° C (97.6° F)
Pulse: 190 beats/min
Respirations: 90/min
Weight: 4.9 kg (10.8 lb)
Genitourinary: Urination not observed; small bladder palpated.
Mental status: Quiet and uninterested in surroundings.
What initial diagnostics do you want to do?
CBC, Chem, UA, Abd U/S
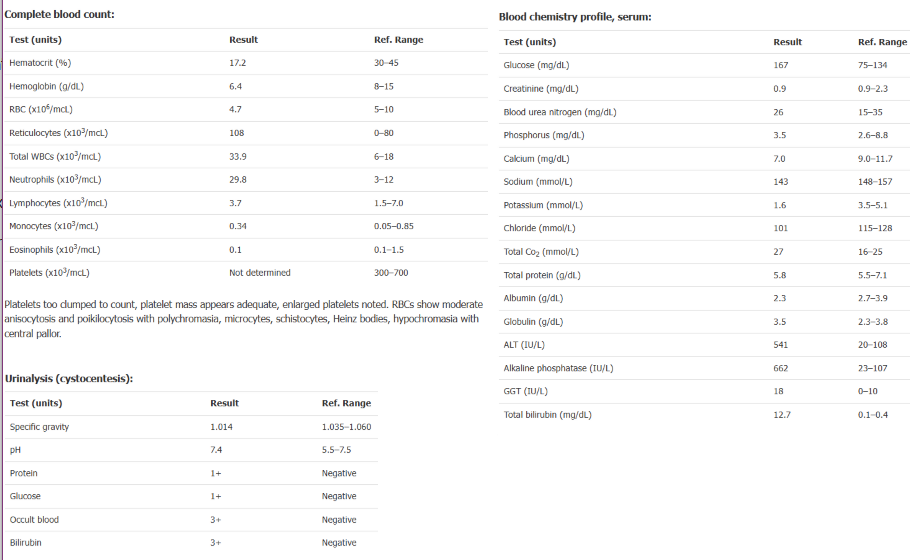
Which of these lab diagnoses is most important in guiding treatment in this patient? What other tests should you do?
Moderate regenerative anemia→ hemolysis→ blood transfusion needed
Mod- marked hypokalemia → needs to be corrected
Mod increased serum liver enzymes and bilirubin → hepatocellular/ cholestasis
Abdominal U/S, Coag profile, Liver biopsy + cytology
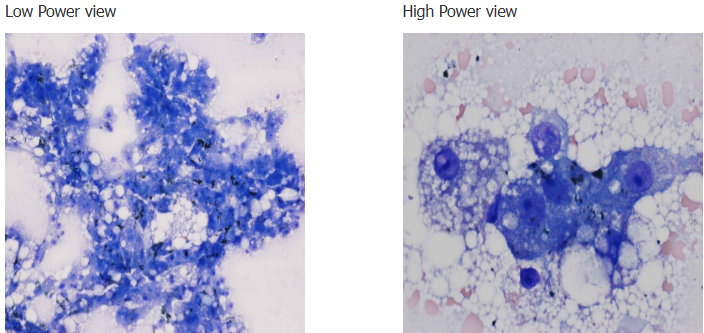
Liver cytology shows these highly cellular samples containing highly vacuolated hepatocytes and extracellular bile casts. Based on the lab results and cytology findings, name 2 differentials to consider
Hepatic lipidosis w/ cholestasis
Metabolic disease
Based on your top differential— name some appropriate management/ treatment plans for this cat. What critical secondary disease needs to be considered and treated with what?
Blood transfusion
IV fluid therapy to correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
Nutritional support
Antiemetic drugs
Hepatic encephalopathy→ lactulose, amoxicillin or metronidazole