Exam 3 Bio Study Guide
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Chromosome theory of inheritance
states that genes are located on chromosomes, and that the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis and fertilization accounts for inheritance patterns.
Homologous chromosome
chromosomes that are similar in shape, size, and genetic content
Sex Linked gene
a gene that is located on either chromosome
X linked gene
genes on the X chromosome
Recessive disorders are much more common in males than in females
have genes for many unrelated to sex
For a recessive __ trait to be expressed
A female needs two copies of the allele (homozygous)
A male needs only one copy of the allele (hemizygous)
Y linked gene
genes on the Y chromosome
- have genes help determine sex
Nondisjunction
pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate normally during meiosis I or sister chromatids do not separate during meiosis I or sister chromatids do not separate during meiosis II
As a result, one gamete receives two of the same type of chromosome, and another gamete recieves no copy
Aneuploidy
results from fertilization involving gametes in which nondisjunction occurred
Offspring with this condition have an abnormal number of a particular chromosome
Monosomic
a ___ zygote has only one copy of a particular chromosome
Trisomic
a ___ zygote has three copies of a particular chromsome
Polyploidy
a condition in which an organism has more than two complete sets of chromosomes
Triploidy (3n) is three sets of chromosomes
Tetraplody (4n) is four sets of chromosomes
Is common in plants but not in animals
Deletion
removes a chromosomal segment
Duplication
repeats a segment
Inversion
reverses orientation of a segment within a chromosome
Translocation
moves a segment from one chromosome to another
Character
distinct heritable features (such as flower color)
Trait
character variants (such as purple or white flowers)
True Breeding
plants that produce offspring of the same variety when they self-pollinate
P generation
the true breeding parents
F1
the hybrid offspring of the P generation
F2 generation
produced when F1 individuals self-pollinate/cross pollinate with other F1 hybrids
Law of Segregation
states that during gamete formation, each parent passes one of their two copies of a gene to their offspring at random
According to this law, only one of the two gene copies present in an organism is distributed to each gamete that it makes
The two alleles for a heritable character separate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes
Corresponds to the distribution of homologous chromosomes to different gametes in meiosis
Allele
alternative versions of a gene
Two of these are inherited, one from each parent
Dominant Allele
determines the organism’s appearance if two alleles at a locus differ
Recessive Allele
has no noticeable effect on appearance
Homozygous/ Homozygote
an organism with two identical alleles for a character is said to be ____ for the gene controlling that character
Homozygous dominant
two copies of the dominant form of a gene (TT)
Homozygous recessive
two copies of the recessive form of the gene (tt)
Heterozygous/heterozygote
two different genes (Tt): an organism that has two different alleles for a gene is said to be _____ for the gene controlling that character
Aren't true breeding
Phenotype
the physical appearance (tall or short)
Genotype
the letters that represent genetic makeup (TT, Tt, tt)
Test Cross
breeding the individual with a recessive homozygote is called a ____ because it can reveal the genotype of that organism
Monohybrid/monohybrid cross
the F1 offpspring produced in this cross were ____, individuals that are heterozygous for one character
A cross betwen such hetereozygotes is called a ____
Dihybrid/ dihybrid cross
produced by crossing two true breeding parents differing in two characters in the F1 generation, heterozygous for both characters
A cross between F1 ____, can determine whether two characters are transmitted to offspring as package or independently
Law of independent assortment
states that each pair of alleles segretgates independently of any other pair during gamete formation
Only applies to genes on chromosomes that are not homologous, or those far apart on the same chromosome
Genes located near each other on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together
Complete dominance.
one form is completely dominant or completely recessive (red OR white)
Occurs when phenotypes of the heterozygote and dominant homozygote are indsitinguishable
Incomplete dominance
mix of two traits (red + white = maroon)
The phenotype of F1 hybrids is somewhere between the phenotypes of the two parental varietes
Codominance
both traits are dominant, meaning you can see them simaltaneously (commonly seen with coloration of animals and the ABO blood type system)
Two dominant alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinhuisable ways
epistasis
a gene at one locus alters the phenotypic expression of a gene at a second locus
Polygenetic inheritance
an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotype
Pedigree
a family tree that conmtains a family’s history for a particular trait
Carrier
heterzygous individuals who carry the recessive allele but are phenotypically normal
Multifactorial disorder
characters influenced by genetic and environmental factors collectively
Genes
The units of heredity and are made up of segments of DNA
Gametes
The reproductive cells that allow genes to be passed down
Sperm or egg; contains a single set of chromosomes and is haploid (n)
Only type of human cells produced by meiosis rather than mitosis
Fuse to form a diploid zygote that divides by mitosis to develop into a multicellular organism
Somatic Cell
the cells of the body except for gametes and their precursors
In humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes
Locus
specific locations for each gene on the chromosome
Asexual Reproduction
reproduction in which a single individual passes gene to its offspring without the fusion of gametes
Clone
a group of genetically identical individuals from the same parent, produced asexually
Sexual reproduction
reproduction in which two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from two parents
Karyotype
an ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
homologous chromosome
the two chromosomes in each pair
The chromosomes in a homologous pair are the same length and shape and carry genes controlling the same inherited characters
Sex chromosome
a package of DNA with part of/all of the genetic material
Determine the sex of the individual; called X and Y
Females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes (XX)
Males have one X and one Y chromosome
Autosome
the remaining pairs of chromosomes aside from the sex chromosomes
Diploid
(2n) an organism has two complete sets of chromosomes
23 from the mother; 23 for the father; total of 46
Haploid
an organism that has one set of unpaired chromosomes; 23n
Each set of 23 consists of 22 autosomes and a single sex chromosome
Fertilization
the union of gametes (the sperm and the egg cell)
Zygote (egg after union) has one set of chromosomes from each parent and so is diploid
Zygote produces somatic cells by mitosis
Meiosis
Takes place in two sets of cell divisions, which result in 4 daughter cells each of which only have half as many chromosomes as the parent cell
Produce gametes
Results in one set of chromosomes in each gamete
This, when combined with fertilization, maintain chromosome number
Reduces the number of chromosomes sets from two (diploid) to one (hapoloid), producing cells that differ genetically from each other and from the parent cell
Produces 4 new haploid cells
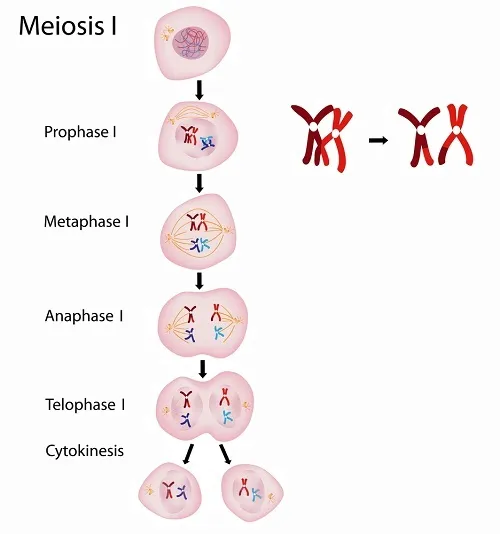
Meiosis I
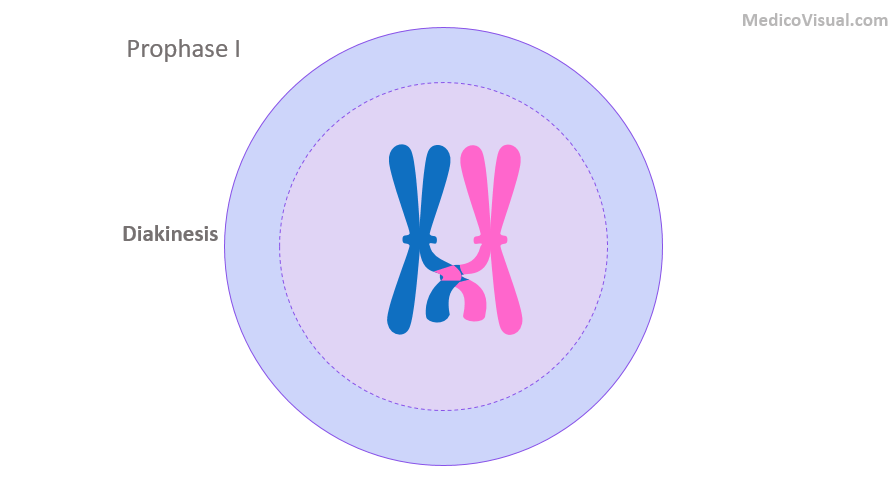
Prophase I: synapsis and crossing over
Homologous chromosomes physically connect and exchange genetic information
Two members of a homologous pair associate along their length, allele by allele
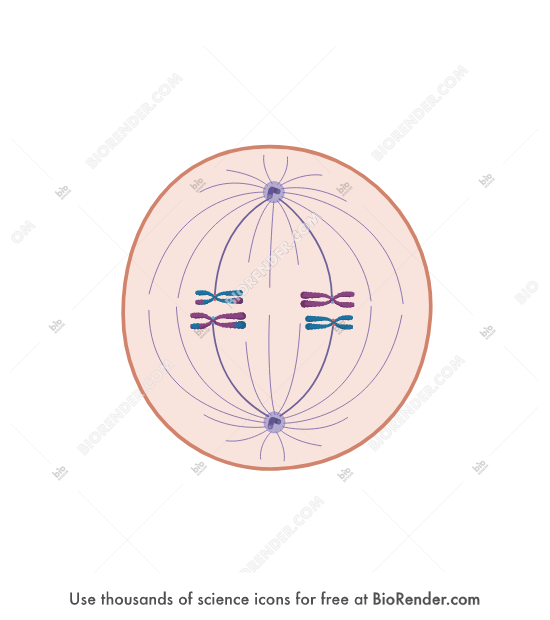
Metaphase I: alignment of homologous pairs; homologous pairs of chromosomes are positioned there in the first phase of this
Homologous pairs line up at the platem with one chromosome facing each pole
Microtobules from one pole are attatched to the kinetochore of one chromosome of each tetrad
Anaphase I: Separation of homologs
One chromosome moves toward each pole, guided by the spindle apparatuus
Telophase I: at the beginning of this stage, each half of the cell has a haploid set of chromosomes
Each chromosome still consists of two sister chromatids
Cytokinesis usually occurs simultaneously, forming two haploid daughter cells
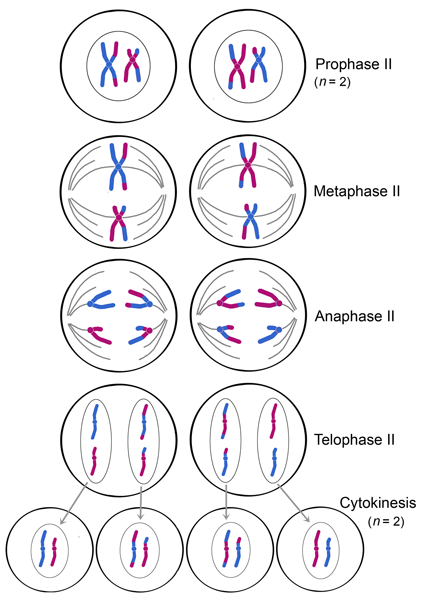
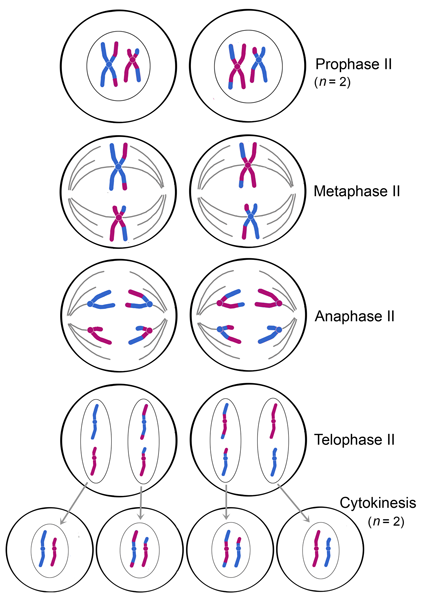
Meiosis II
Occurs in four phases:
Prophase II:
Spindle apparatus forms
Later in this stage chromosomes (each still comprised of two chromatids) move toward the metaphase plate
Metaphase II: the sister chromatids are arranged at theplate
Because of crossing over in in the first version of this stage, the two sister chromatids of each chromosome are no longer genetically identical
The kinetochores of sister chromatids attatch to microtubles extending from extending opposite poles
Anaphase II:
In this stage, the sister chromatids separate
The sister chromatids of each chromosome now move as two newly individual chromosomes toward opposite poles
Telophase II + cytokinesis
Nuclei form, and the chromosomes begin decondensing
At the end of meiosis, there are four daughter cells, each with a haploid set of unduplicated chromosomes
Each daughter cell is genetically distinct from the others and from the parent cell
Chromosomes
Each one replicated consists of two identical sister chromatids
Sister chromatid
identical copies of a chromosome that are joined together by a centromere
Crossing Over
nonsister chromatids exchange DNA segments
Produces recombinant chromosomes- combine DNA inherited from each parent
Contributes to genetic variation by combining DNA, producing chromosomes with new combinations of maternal and paternal alleles
Independent Assortment
one of the mechanisms that contributes to genetic variation
Homologous pairs of chromosomes orient randomly at metaphase I of meiosis
Each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal and paternal homologs into daughter cells independetly of the other pairs
Number of combinations possible when chromosomes assort independently into gametes is 2n
Recombinant Chromosome
combine DNA inherited from each parent
Random Fertilization
adds to genetic variation because any sperm can fuse with any ovum (unfertilized egg)
Each zygote has a unique genetic identity
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
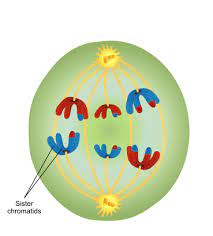
Telophase
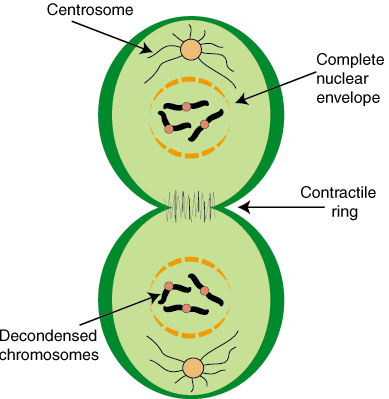
Meiosis II
Polymer
long molecule consisting of many buildings' blocks; composed of monomers
Monomer
The subunit that serves as the building block of a polymer.
Dehydration Synthesis
occurs when 2 monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule
Hydrolysis
polymers that are disassembled to monomers through the process of adding water
Enzyme Section
speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the reaction
Polypeptide
A polymer of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Amino Acid
are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
Protein
biologically functional molecule that consists of one or more polypeptides
Peptide Bond
The covalent bond between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on another, formed by a dehydration reaction.
Catalyst
A chemical agent that selectively increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Protein Structure
A protein’s structure determines its function
Have 4 levels of structure:
Primary: protein’s unique sequence of amino acids
Secondary: consists of coils and folds in the polypeptide chain
The result of hydrogen bonds between constituents' of the polypeptide backbone
Include the α helix and the β pleated sheet
Tertiary: the overall shape of a polypeptide
Determined by interactions among various side chains (R groups)
Quaternary Structure: arises when a protein consists of two or more polypeptide chains
Results from interactions between multiple polypeptide chains
Denaturation
the loss of a protein’s native structure
Is biologically inactive
Nucleic Acids
2 Types
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Provides directions for its own replication
Directs synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) ad, through mRNA, controls protein synthesis, a process called gene expression
Contains thymine
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Contains uracil
Polypeptide
molecules made up of nucleotides that are linked together by covalent bonds to form a chain
Ribose
the sugar in RNA
Deoxyribose
the sugar in the DNA
Double Helix
formed by DNA molecules have two polynucleotides spiraling around an imaginary axis
Carbohydrate
macromolecules are polysaccharides, polymers composed of many sugar building blocks
Monosaccharide
The simplest carbohydrates; AKA simple sugars serve as major nutriets for cells and as raw materials for building molecules
Disaccharide
formed when a dehydration reaction occurs joins two monosaccharides
Glycosidic Linkage
Positions determine the structure and function of a polysaccharide are determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of its glycosidic linkages
Polysaccharide
the polymers of sugars, have storage and structural roles
The structure and function of a ____ are determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of its glycosidic linkages
Starch
a storage polysaccharide of plants, consists entirely of glucose monomers
Plants store surplus as granules
Most animals have enzymes that can hydrolyze this, making glucose available as a nutrient
Glycogen
is a storage polysaccharide in animals
Lipid
do not form true polymers
Has little to no affinity for water
Are hydrophobic because they mostly consist of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds
Most biologically important forms are fats, phospholipids, and steroids
Fat
type of lipid; constructed from two types of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids
separate from water because water molecules hydrogen bond to each other and exclude the fats
Primary function is energy storage
Fatty Acid
consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton
Two tails tails are hydrophobic; the phosphate group and its attachments form a hydrophilic head
Saturated fatty acid
have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds
Unsaturated fatty acid
have one or more double bonds
Phospholipid
two fatty acids and a phosphate group are attached to glycerol
are major constituents of cell membranes
When are added to water, they self- assemble into a bilayer, with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the interior
This feature results in the bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes
bilayer forms a boundary between a cell and its external environment