Chapter 8: Internal returns to scale
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:05 PM on 10/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Marginal Cost (MC)
The cost of producing one more unit, c
2
New cards
Improved competitive environment
More productive firms will stay in the market, and the less productive firms will exit the market
→ Surviving firms are more productive
→ Surviving firms are more productive
3
New cards
Market share
The amount of the market that one firm covers
4
New cards
Monopolistic competition
1) differentiated goods
2) technology exhibits increasing returns to scale (e.g., a firms needs a factory to produce)
3) many producers in the market
2) technology exhibits increasing returns to scale (e.g., a firms needs a factory to produce)
3) many producers in the market
5
New cards
Demand Curve
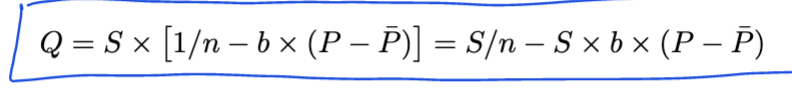
6
New cards
Inverse demand curve
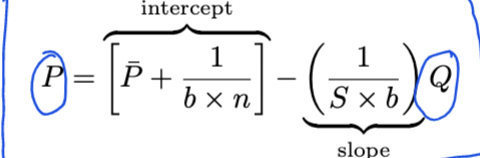
7
New cards
Operating profit
(P-c)*Q
8
New cards
Equilibrium
MR=MC
9
New cards
Firms optimal behaviour
10
New cards
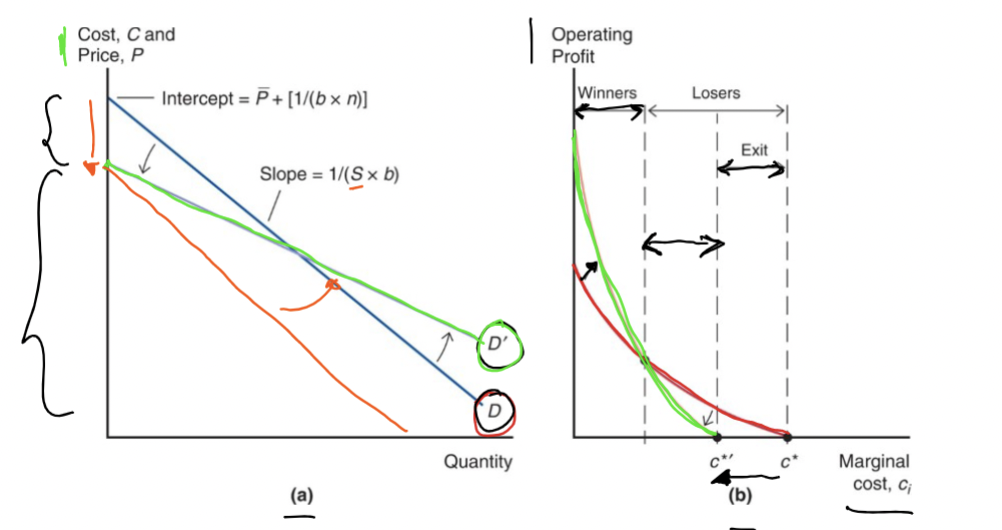
Who will exit the market?
Firms with c>c*
11
New cards
Who will stay in the market?
Firms with c*≥c
12
New cards
What happens when the market increases?
S increases → flatter slope
The Demand curve flattens. The intersect will be lower.
There will be more demand for any price.
n and p-bar changes
b stays the same
The operating profit curve will be steeper. Fewer firms will stay in the market as it pushes high-cost firms out
The Demand curve flattens. The intersect will be lower.
There will be more demand for any price.
n and p-bar changes
b stays the same
The operating profit curve will be steeper. Fewer firms will stay in the market as it pushes high-cost firms out
13
New cards
Slope
Slope=-1/(s*b)
14
New cards
Trade cost
a cost added to the cost of the product when exporting it to another market. Only the more effective firm will export.
15
New cards
Horizontal FDI
when firms expand their sales horizontally → located and sell their products in more markets
To sell abroad
- produce at home and pay trade costs, t, to ship the goods
- start production abroad by paying a fixed cost, F, to open a factory
To sell abroad
- produce at home and pay trade costs, t, to ship the goods
- start production abroad by paying a fixed cost, F, to open a factory
16
New cards
Vertical FDI
Invest in developing countries to lower their production costs by moving some parts of production from home to foreign
scale-fixed cost tradeoff
The most productive firms are more likely to do Vertical FDI, as they produce more and can therefore lower their MC
scale-fixed cost tradeoff
The most productive firms are more likely to do Vertical FDI, as they produce more and can therefore lower their MC
17
New cards
Price dumping
When a firms sells a product at a lower price (net trade cost) on a foreign market
18
New cards
Who will export with trade cost?
the firms with c+t
19
New cards
Who will no longer export with trade cost?
the firms with c+t>c*
20
New cards
Imperfect competition
Firms can influence the prices
21
New cards
Marginal revenue
The demand curve with double the slope
(demand curve equation)*Q and take first order derivative
MR=P-(Q/B)
P-MR=Q/B
(demand curve equation)*Q and take first order derivative
MR=P-(Q/B)
P-MR=Q/B
22
New cards
Slope parameter
B (will be given)
23
New cards
Firms total cost
C=F+c*Q
24
New cards
AC
AC=C/Q=F/Q+c
25
New cards
c
Marginal cost, cost of producing one extra unit
26
New cards
F
Fixed cost, the intersect of the supply curve
27
New cards
Demand in monopolistic competition
The larger the Q, the larger the S
When P increases, quantity increases
when "P-bar" increases, the quantity increases (if the price of other firms increases, more people will buy our product)
When P increases, quantity increases
when "P-bar" increases, the quantity increases (if the price of other firms increases, more people will buy our product)
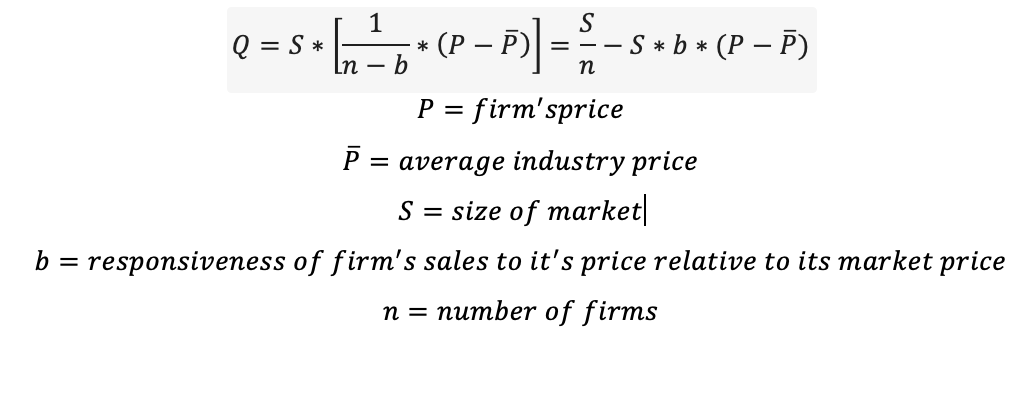
28
New cards
Competitive market
More competition from other firms will lower the sales from any firm at any price (given a fixed market size)
29
New cards
Assumptions for the model
1) firms are symmetric
a) Produce differentiated goods
b) They have the same demand directed at their product
c) They operate with the same technology
2) properties of firms' demand
3) properties of firms' technology
a) Produce differentiated goods
b) They have the same demand directed at their product
c) They operate with the same technology
2) properties of firms' demand
3) properties of firms' technology
30
New cards
The CC-curve
When there's firm symmetry (Q=S/n, P=P-bar)
AC=(n*f)/S +c
AC increases with number of firms
S is fixed, when n increases, AC increases as each firm produces less
AC=(n*f)/S +c
AC increases with number of firms
S is fixed, when n increases, AC increases as each firm produces less
31
New cards
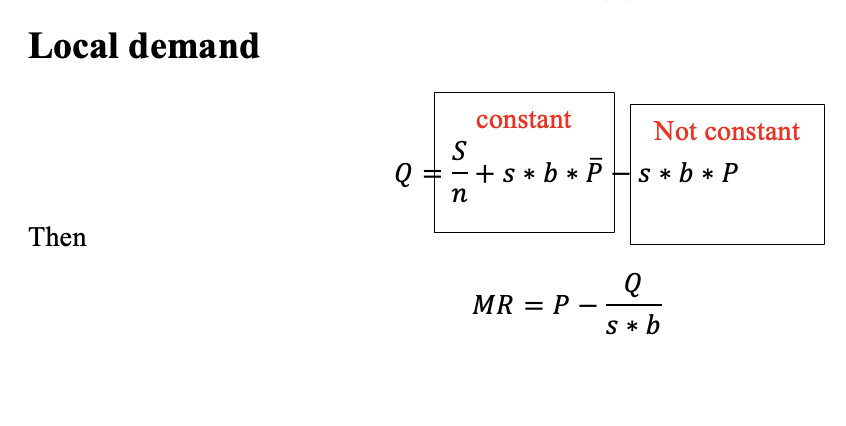
PP-curve
Firm acts as local monopolies
32
New cards
mark-up
P-c=1/(n*b)
measures a firms market power
measures a firms market power
33
New cards
International trade
In market with economies of scale, the market size (S) constraints:
1) number of operating firms,n, i.e., the number of product varieties
2) The quantity produced bt each firm S/n which affects AC
1) number of operating firms,n, i.e., the number of product varieties
2) The quantity produced bt each firm S/n which affects AC
34
New cards
Integrated market
1) each country can produce less variaties → lower AC
2) consumers enjoy greater variety
2) consumers enjoy greater variety
35
New cards
The effect of market size
CC: When S increases, AC decreases
PP: Nothing happens
mark-ups will not change directly with market size
Reward low-cost firms → expand demand = more consumers
Penalise high-cost firms
PP: Nothing happens
mark-ups will not change directly with market size
Reward low-cost firms → expand demand = more consumers
Penalise high-cost firms
36
New cards
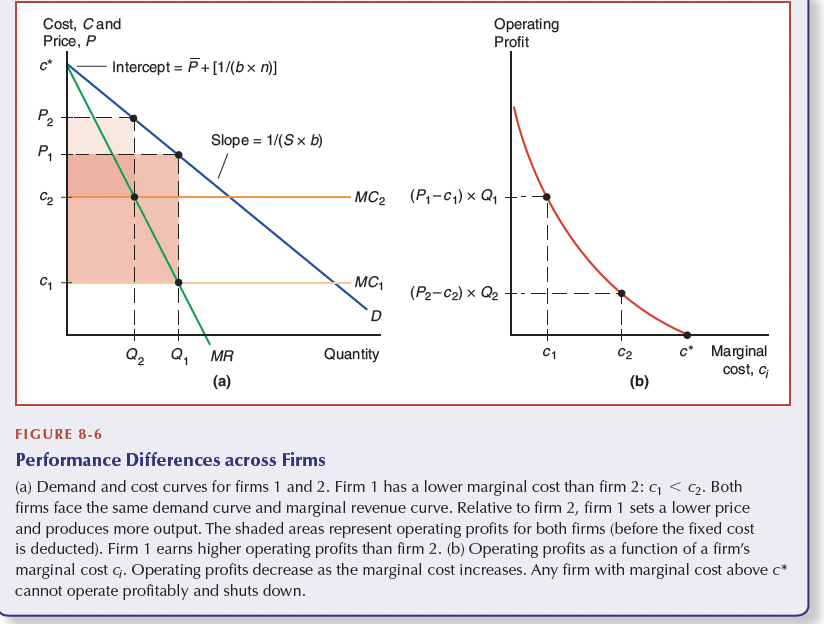
Optimal behaviour
In the long run firms produce up until the point where Profit=0
37
New cards
International trade with external economies to scale
→ Trade increases market size, which lowers
→ intersept of inverse demand (and decreases marginal cost cutoff, c*)
→ Slope of the inverse demand (increase demand for each price level)
→ intersept of inverse demand (and decreases marginal cost cutoff, c*)
→ Slope of the inverse demand (increase demand for each price level)