Unit 4: Heart and Circulatory System
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Pericardium
Fibrous sac that encloses the heart.
Myocardium
Cardiac muscle.
Endocardium
Epithelial tissue lining the internal chambers of the heart.
Base
Area where great vessels attach to the heart (Aorta, Pulmonary Trunk, Superior Vena Cava).
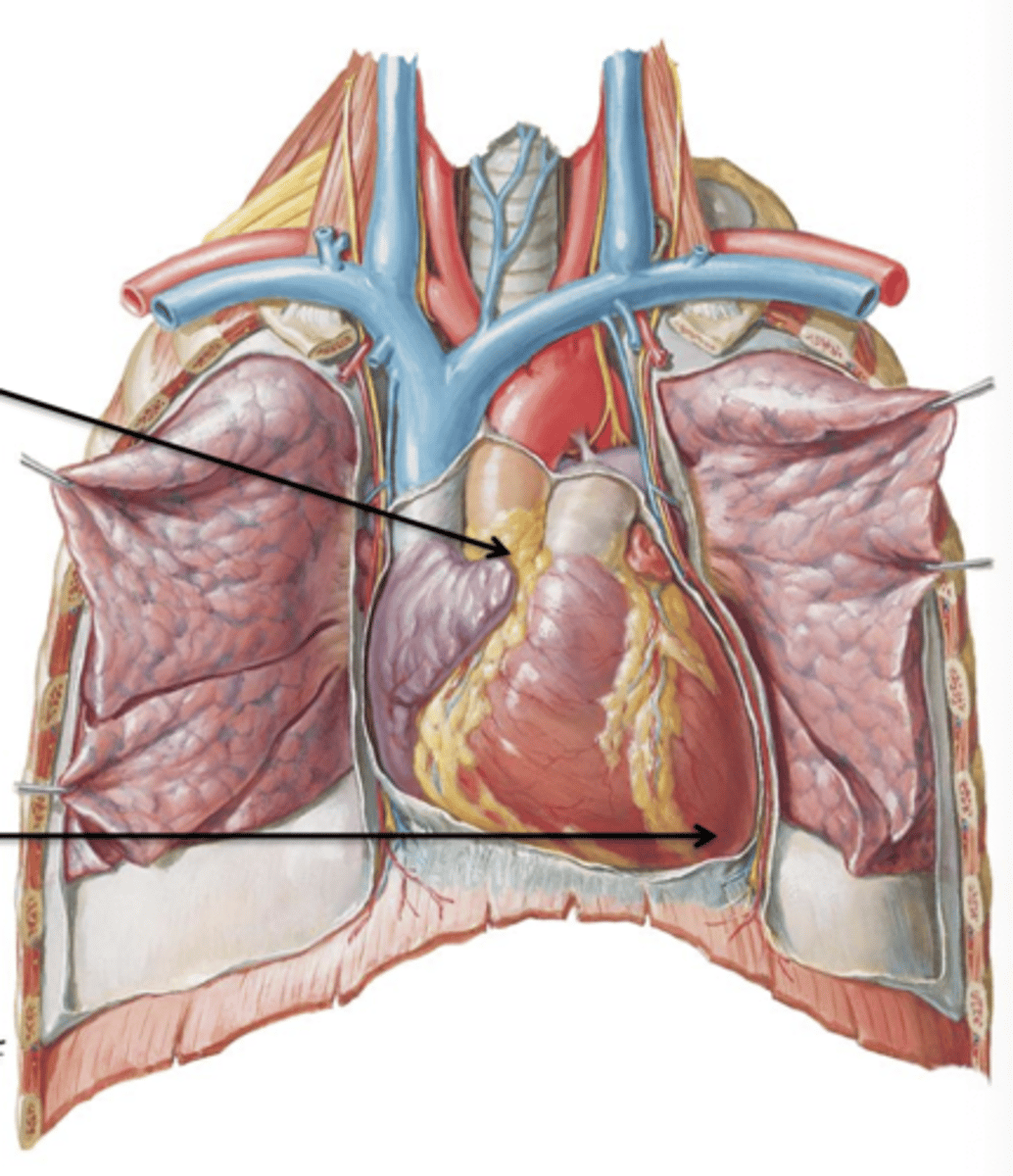
Apex
Rounded projection of the heart that points inferiorly and to the left. It lies at the level of the left 6th costal cartilage.
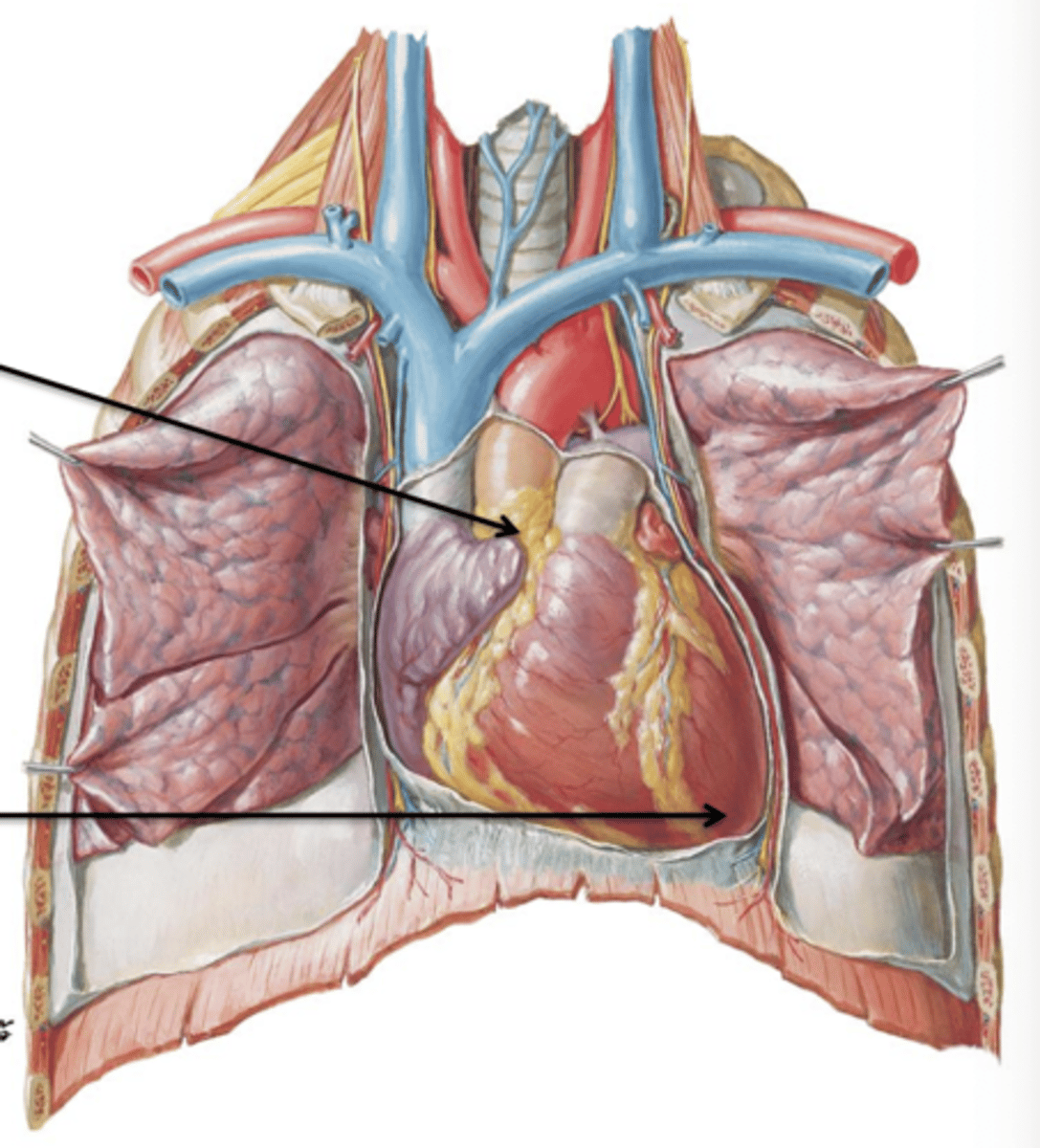
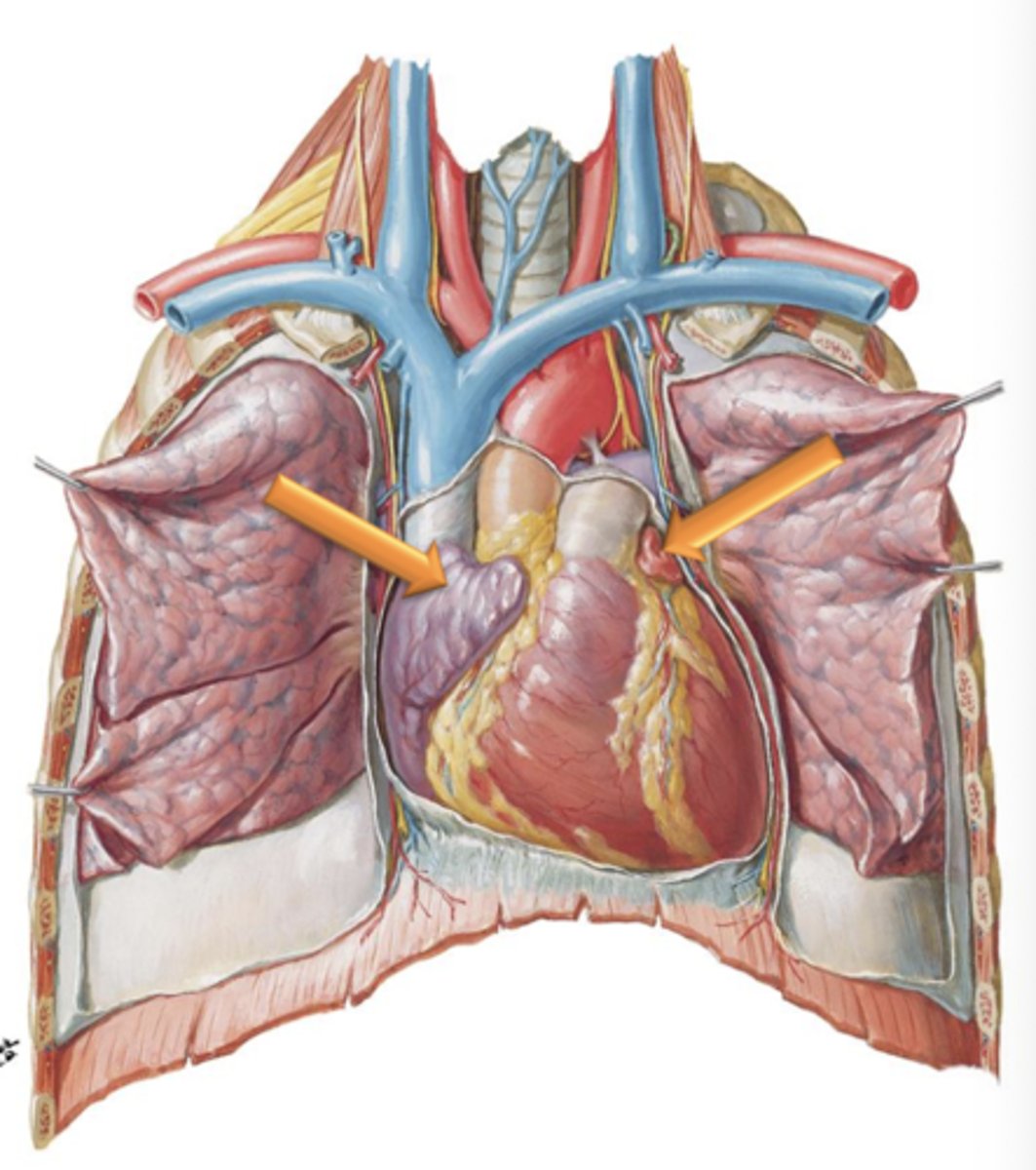
Left and Right Auricles
Appendages attached to the lateral surfaces of the atria. They increase internal surface area of the left and right atria.
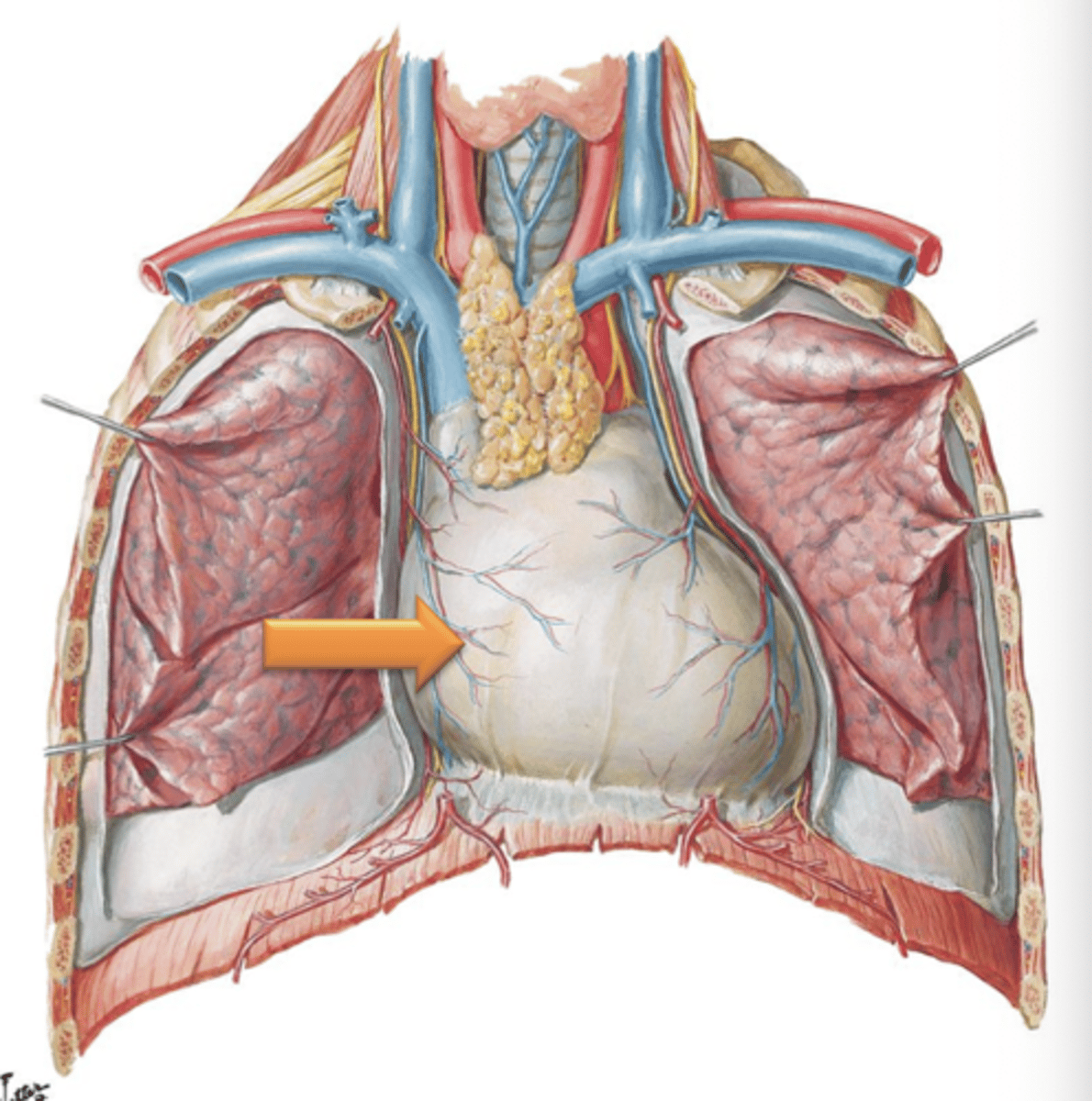
Superior Vena Cava
Major Vessel that drains the head, neck, and upper limbs.
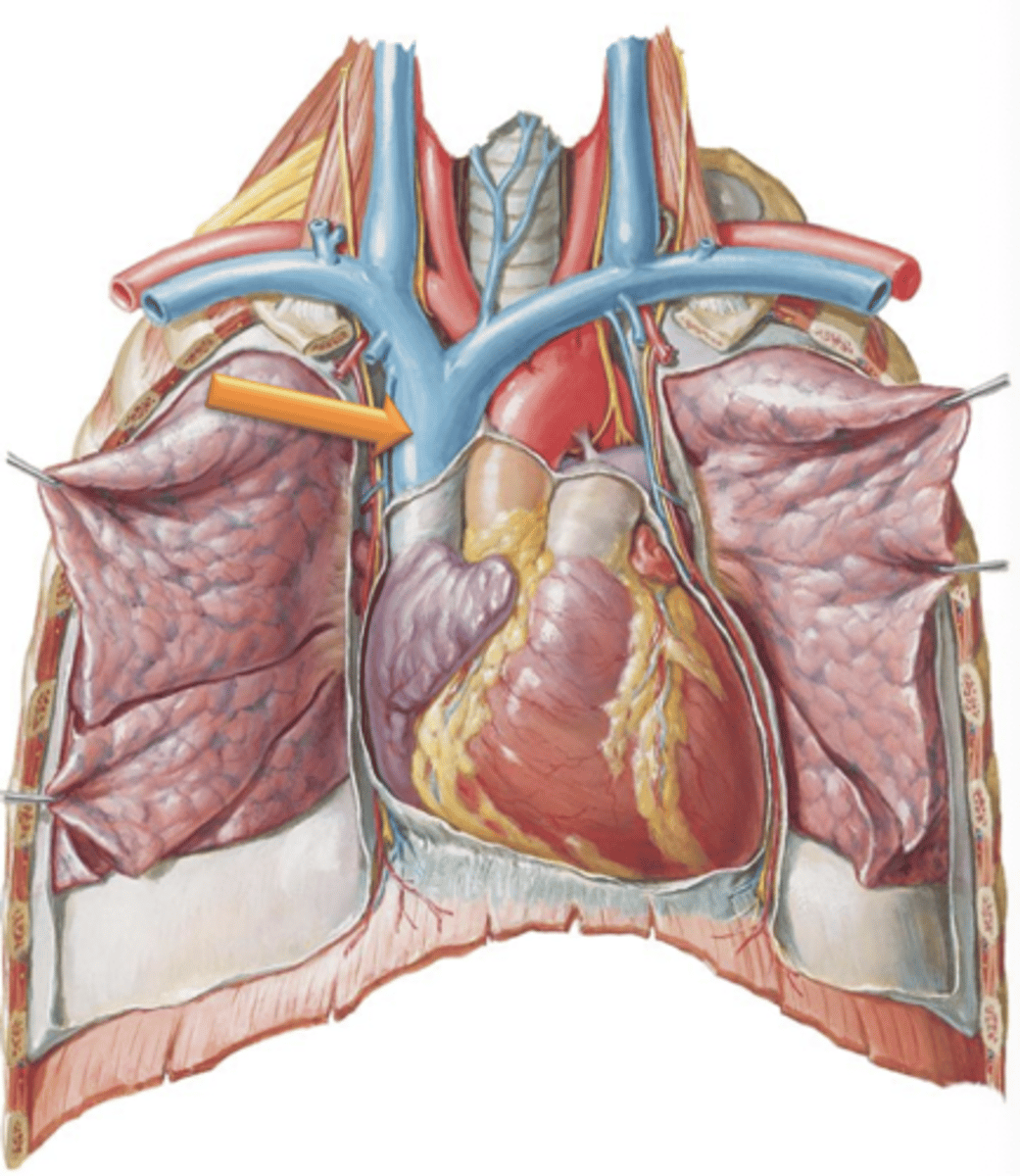
Brachiocephalic Veins
Superior Vena Cava is formed as left and right ___ ___ join together and empties into the right atrium.
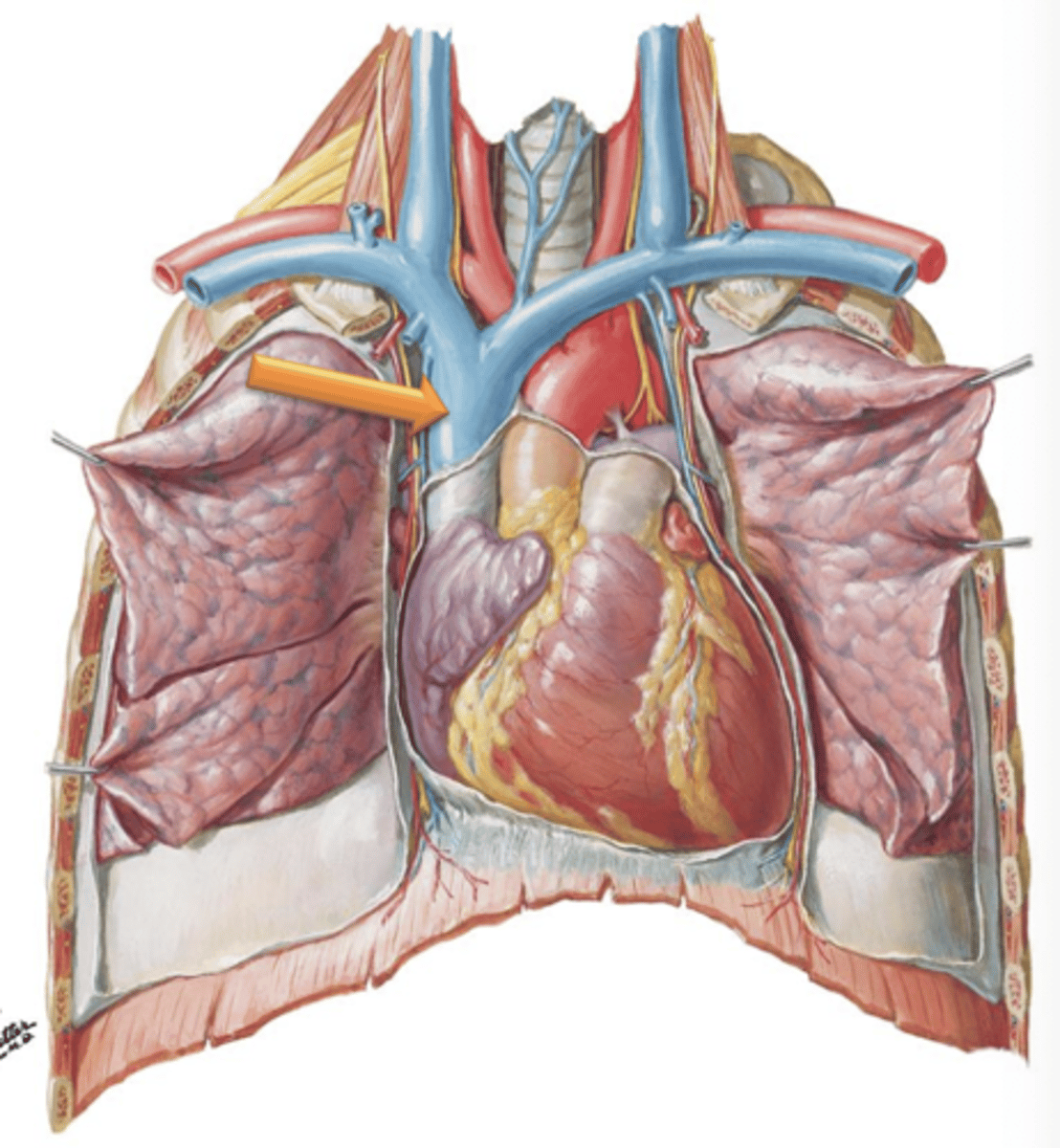
Aorta
Major vessel that supplies the entire body with blood and originates at the aortic semilunar valve within the left ventricle of the heart.
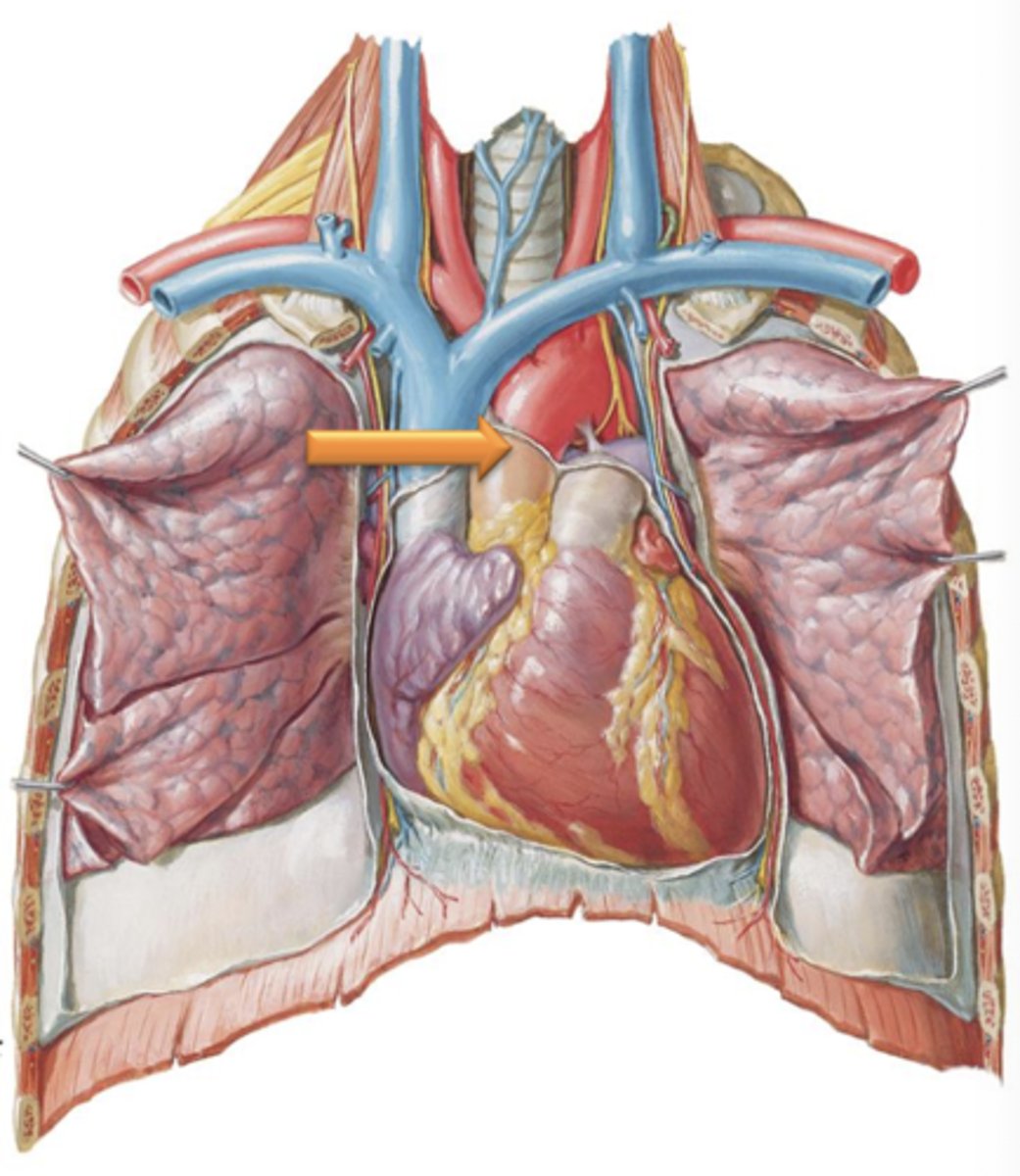
Ascending Aorta
Region of aorta that leads from the heart and courses superiorly.
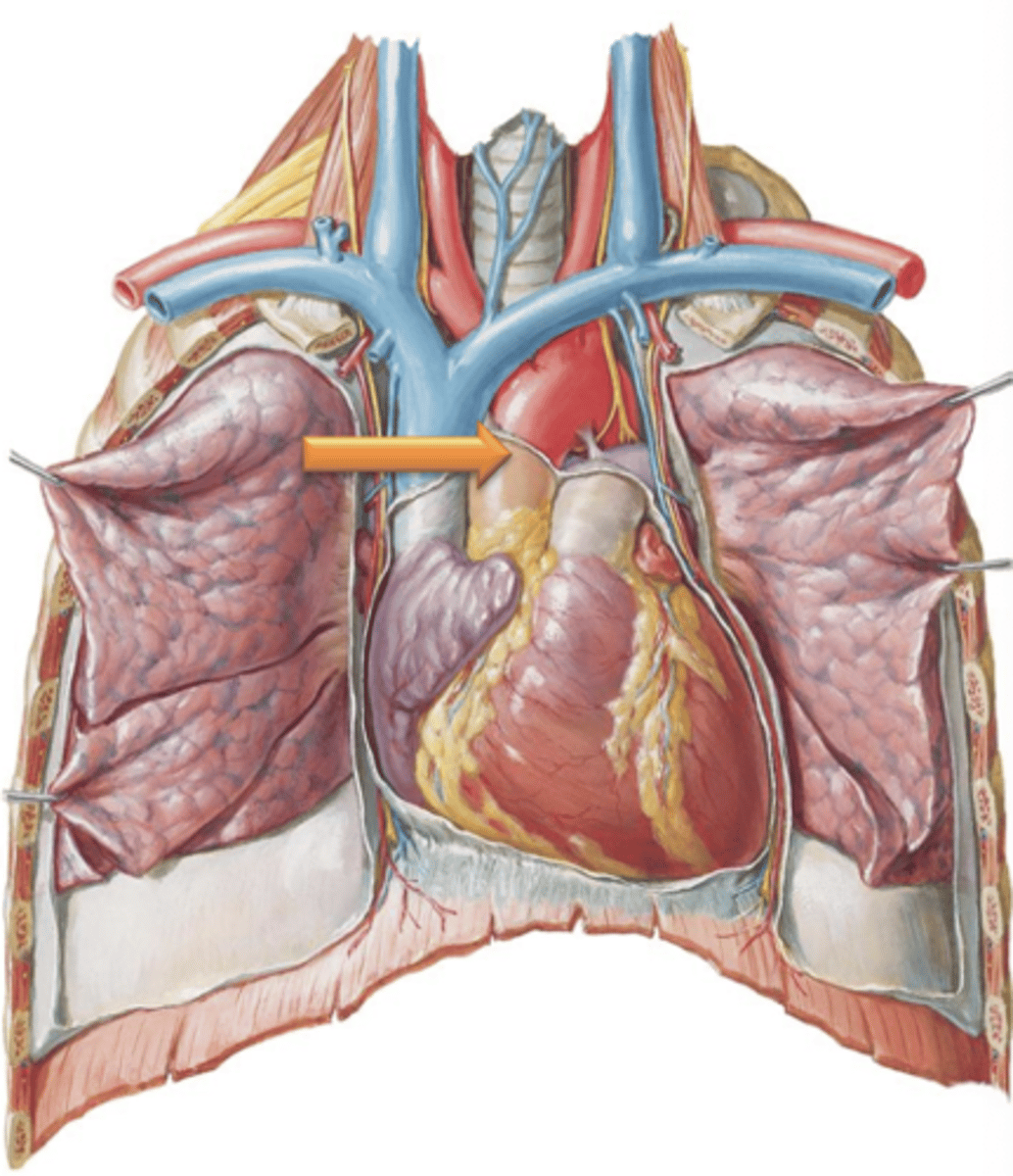
Aortic Arch
Region of aorta that courses posteriorly and to the left giving off its major branches
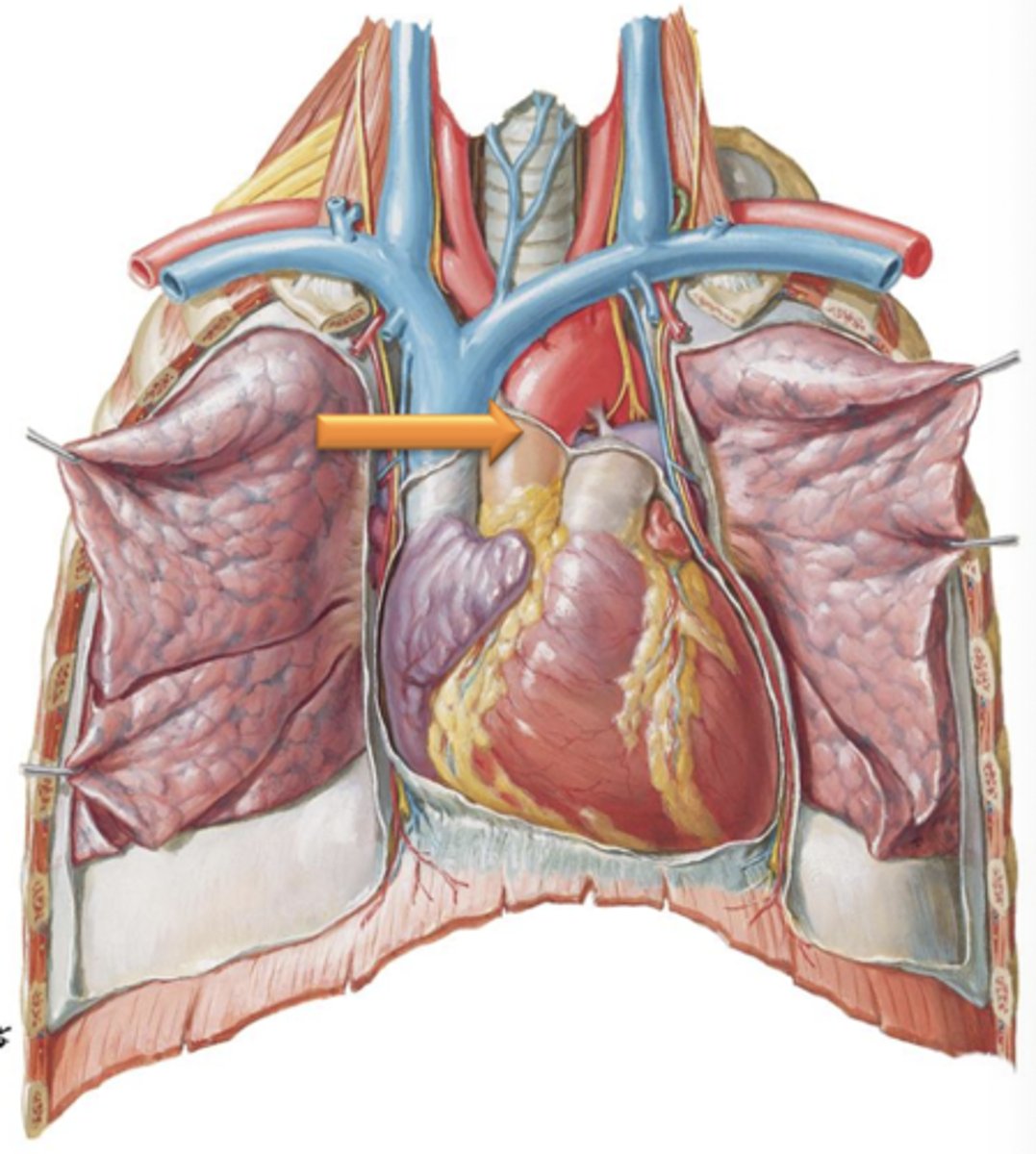
Descending Aorta
Region of aorta that courses posterior to the heart as it descends through the thorax.
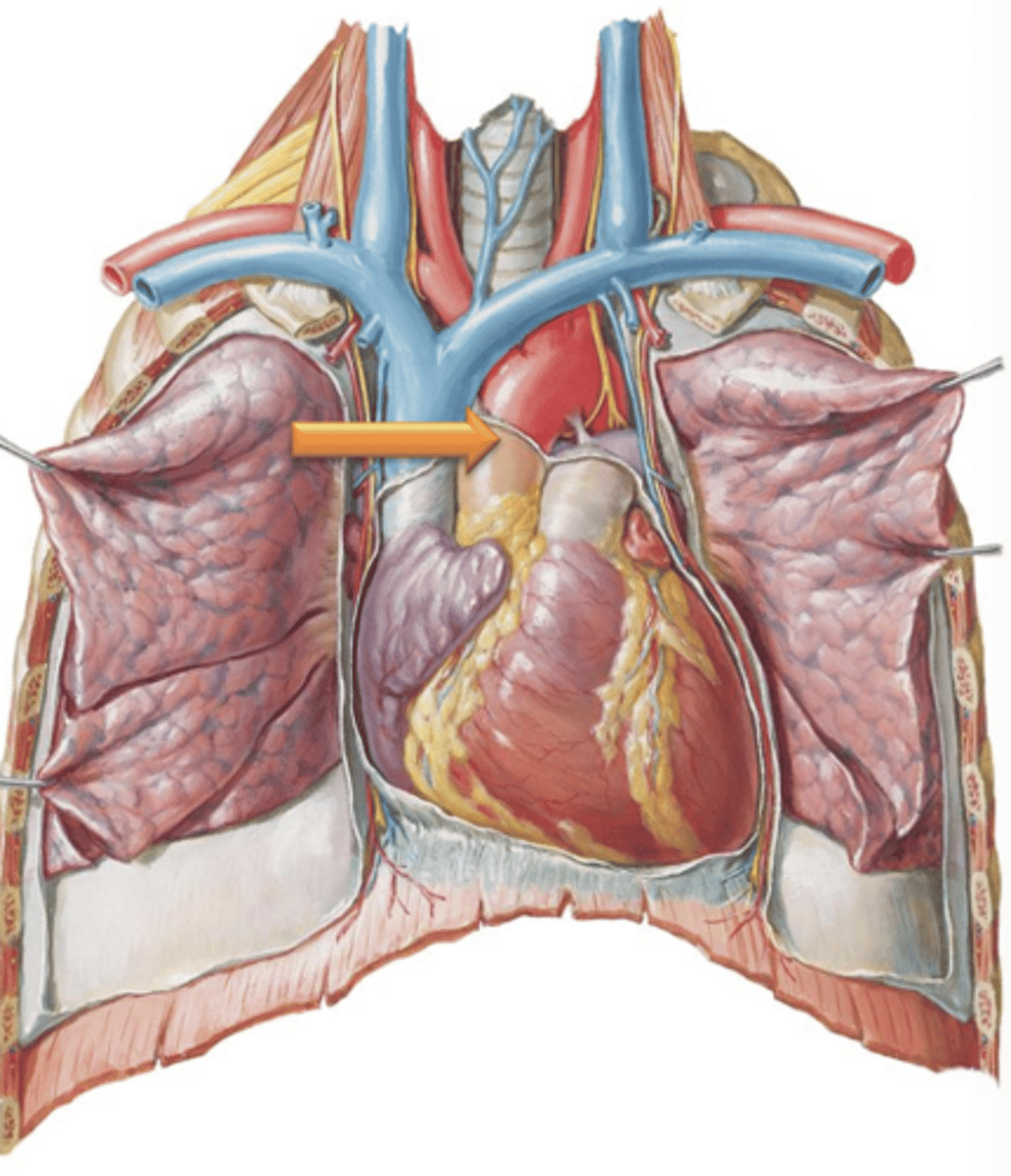
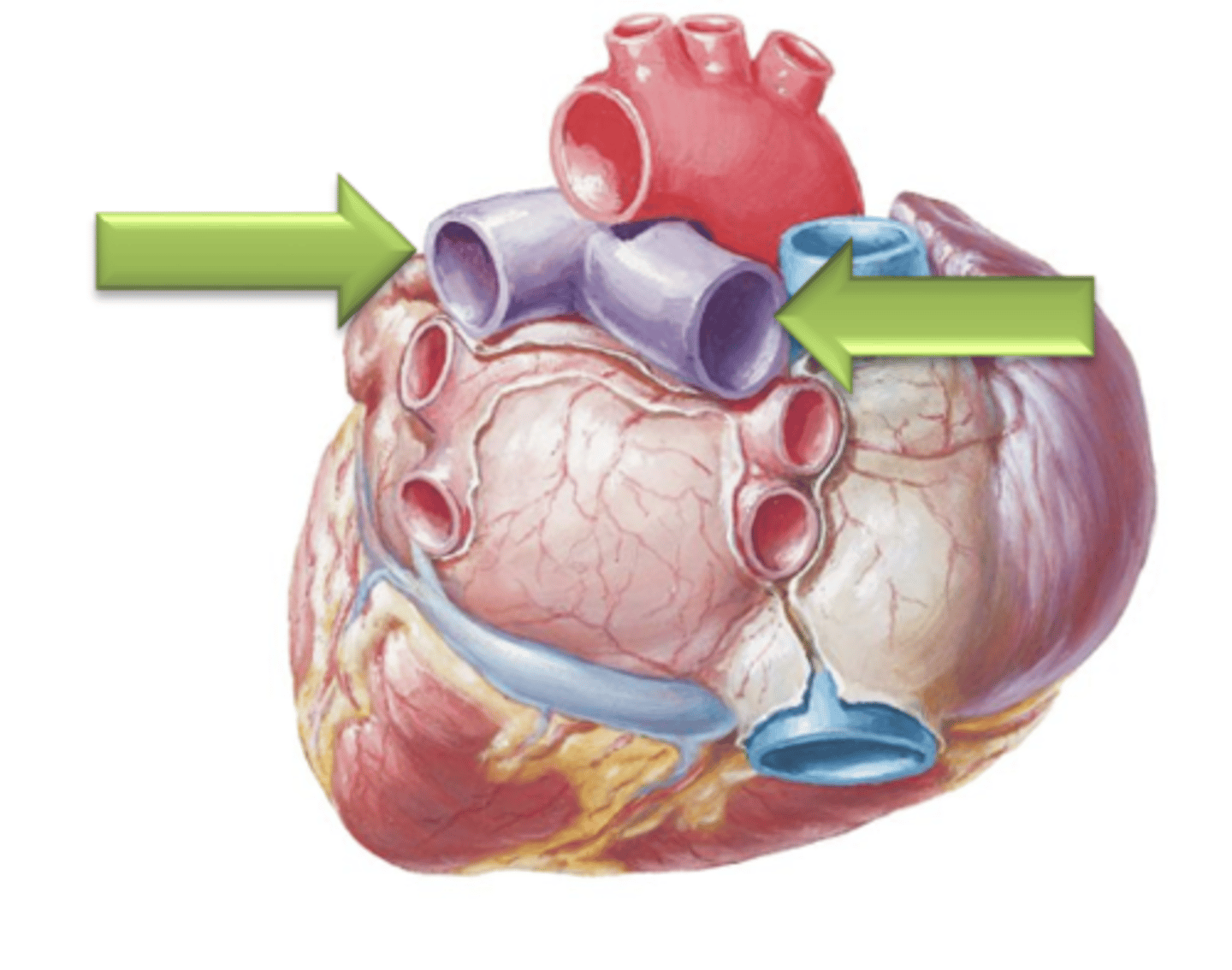
Pulmonary Trunk
Major vessel that leads from the right ventricle and carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for reoxygenation.
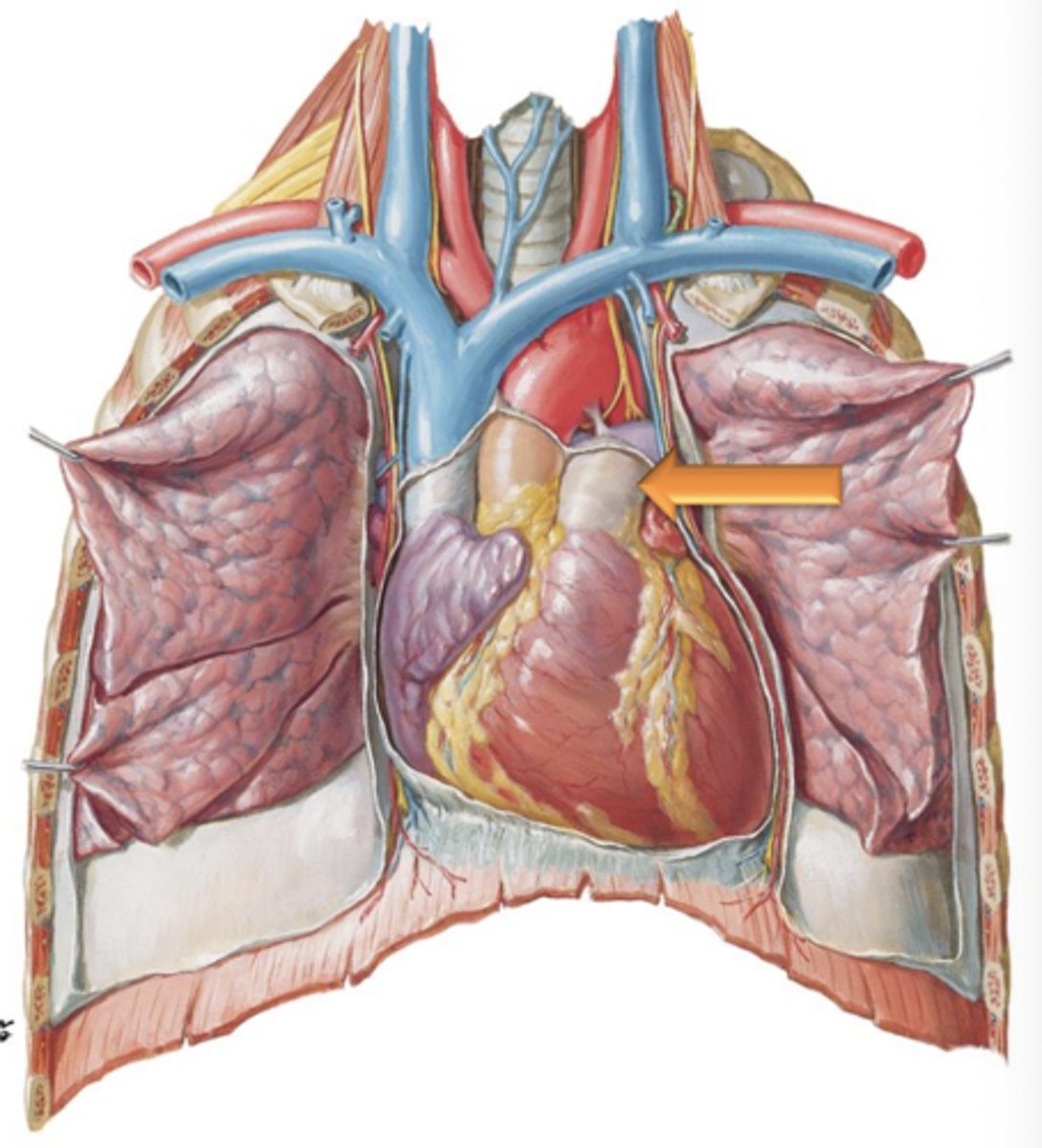
Inferior Vena Cava
Major vessel that receives blood from the lower limbs, pelvis and abdomen and enters the right atrium of the heart inferiorly.
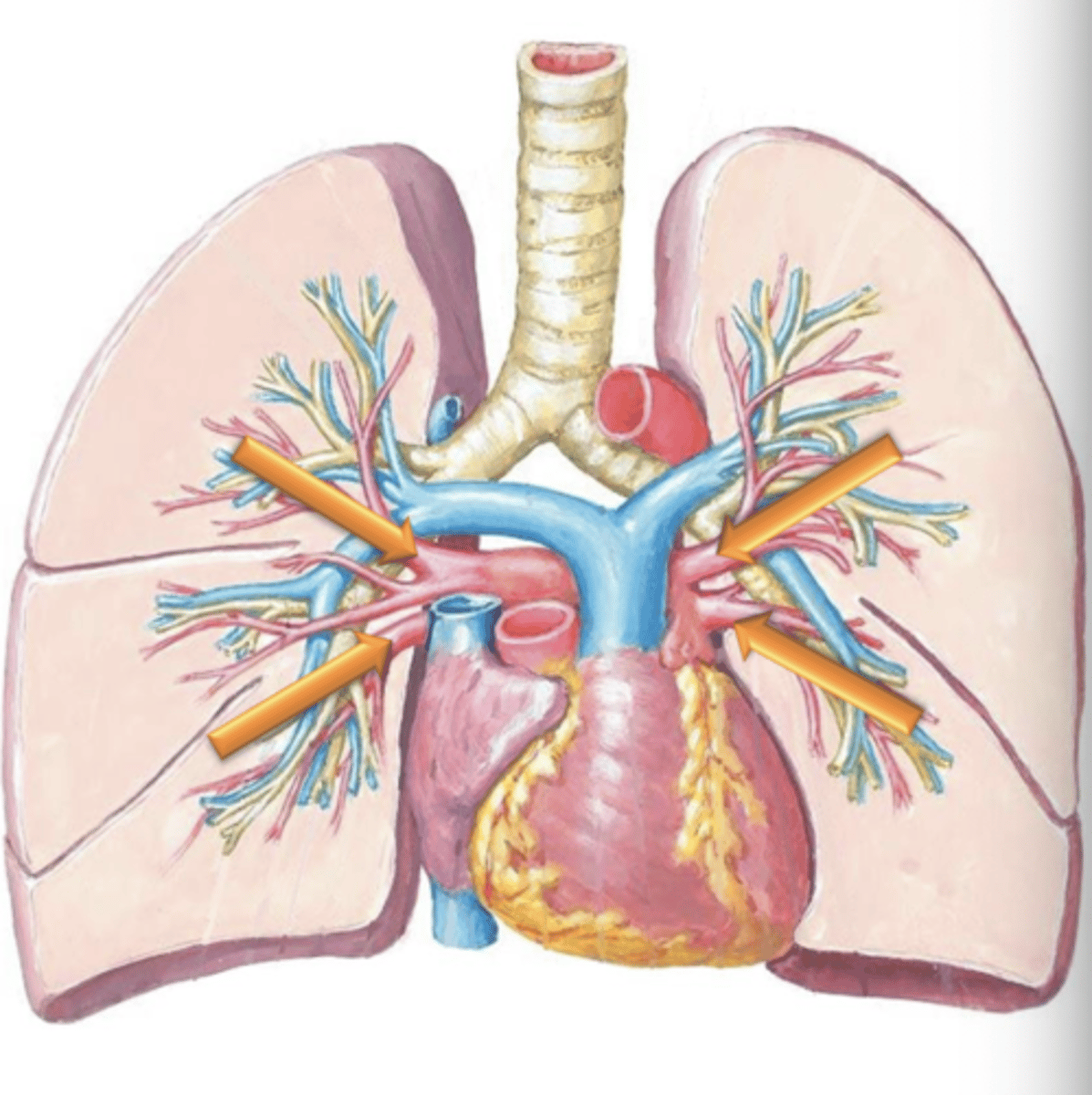
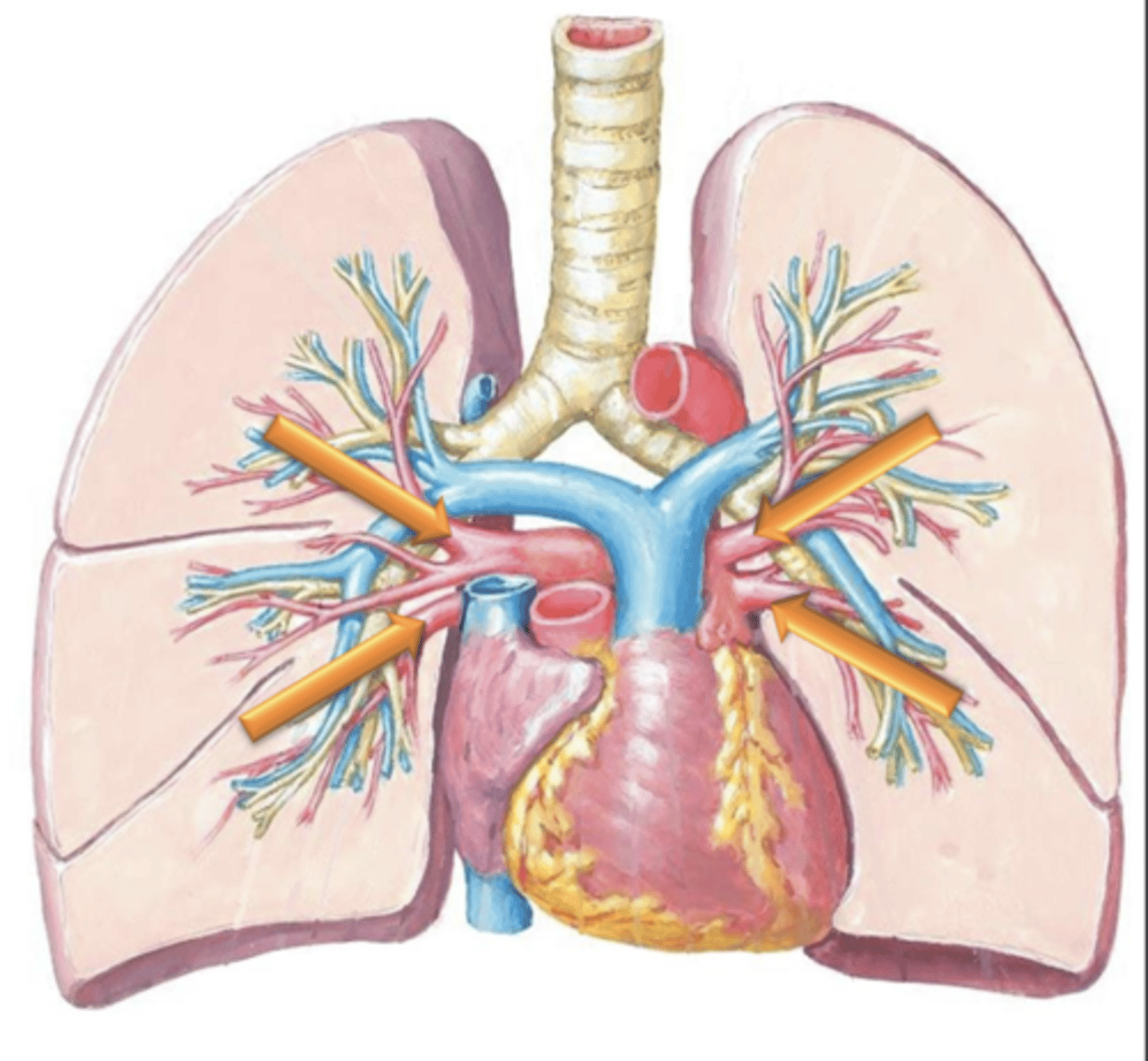
Pulmonary Arteries
Blood will flow through the Pulmonary Trunk which bifurcates into the left and right ___ ___.
deoxygenated
Pulmonary arteries are the only arteries in the body which carry ___ blood.
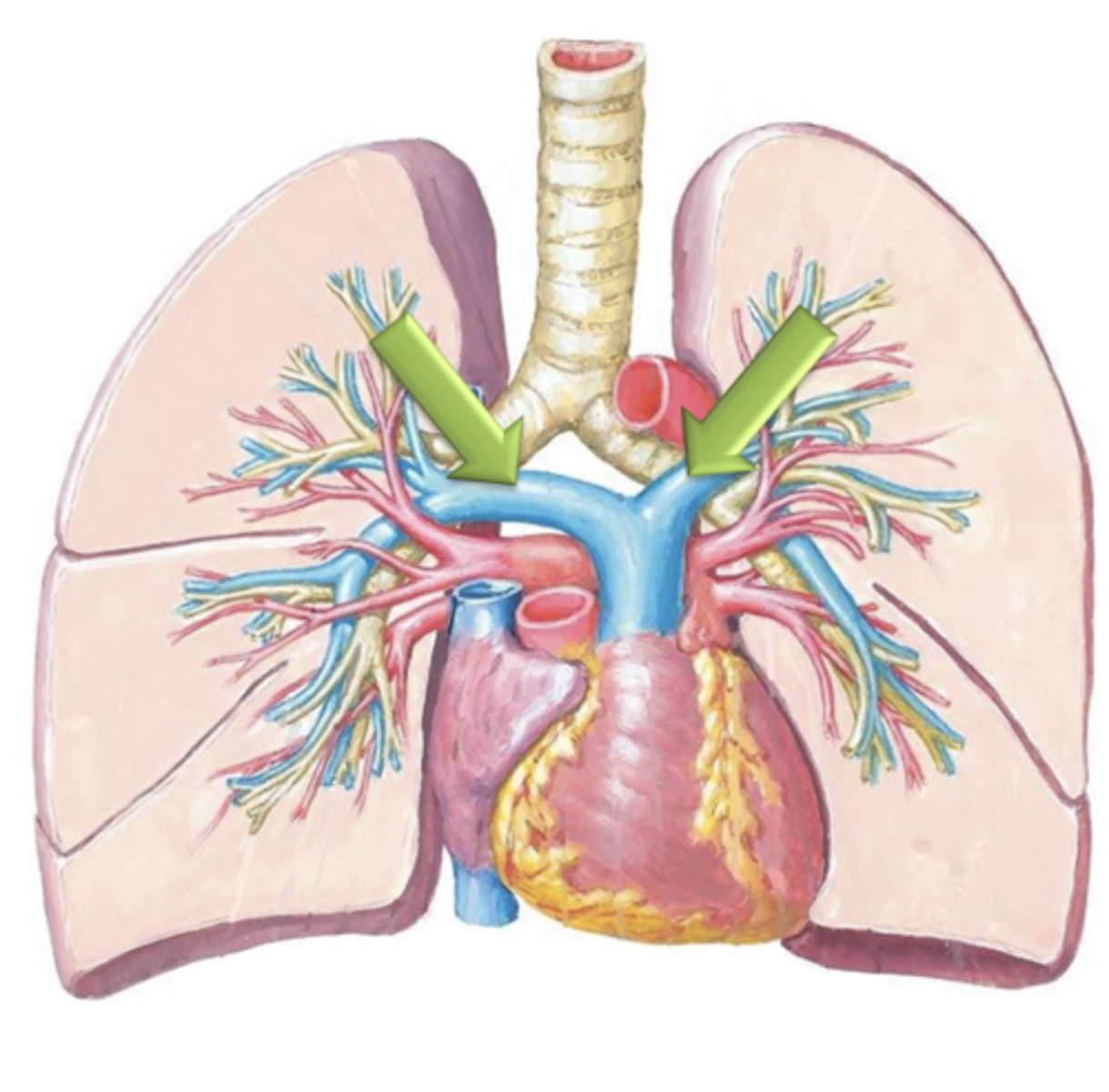
Pulmonary Veins
Once the blood has been reoxygenated in the lungs, it returns to the left atria of the heart via the four ___ ___.
oxygenated
Pulmonary Veins are the only veins in the body which carry ___ blood.
Coronary Circulation
Blood supply to the myocardium of the heart itself is termed
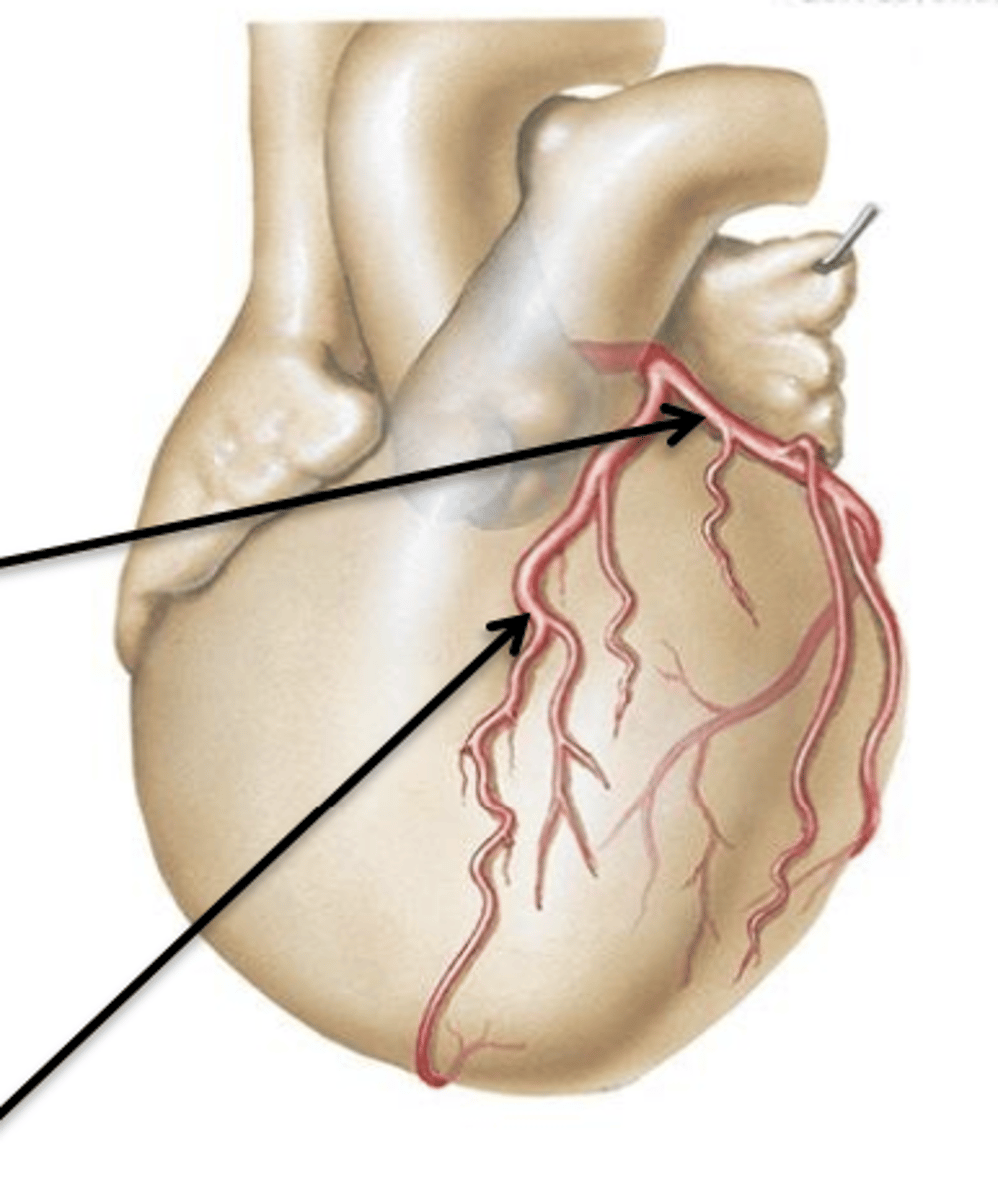
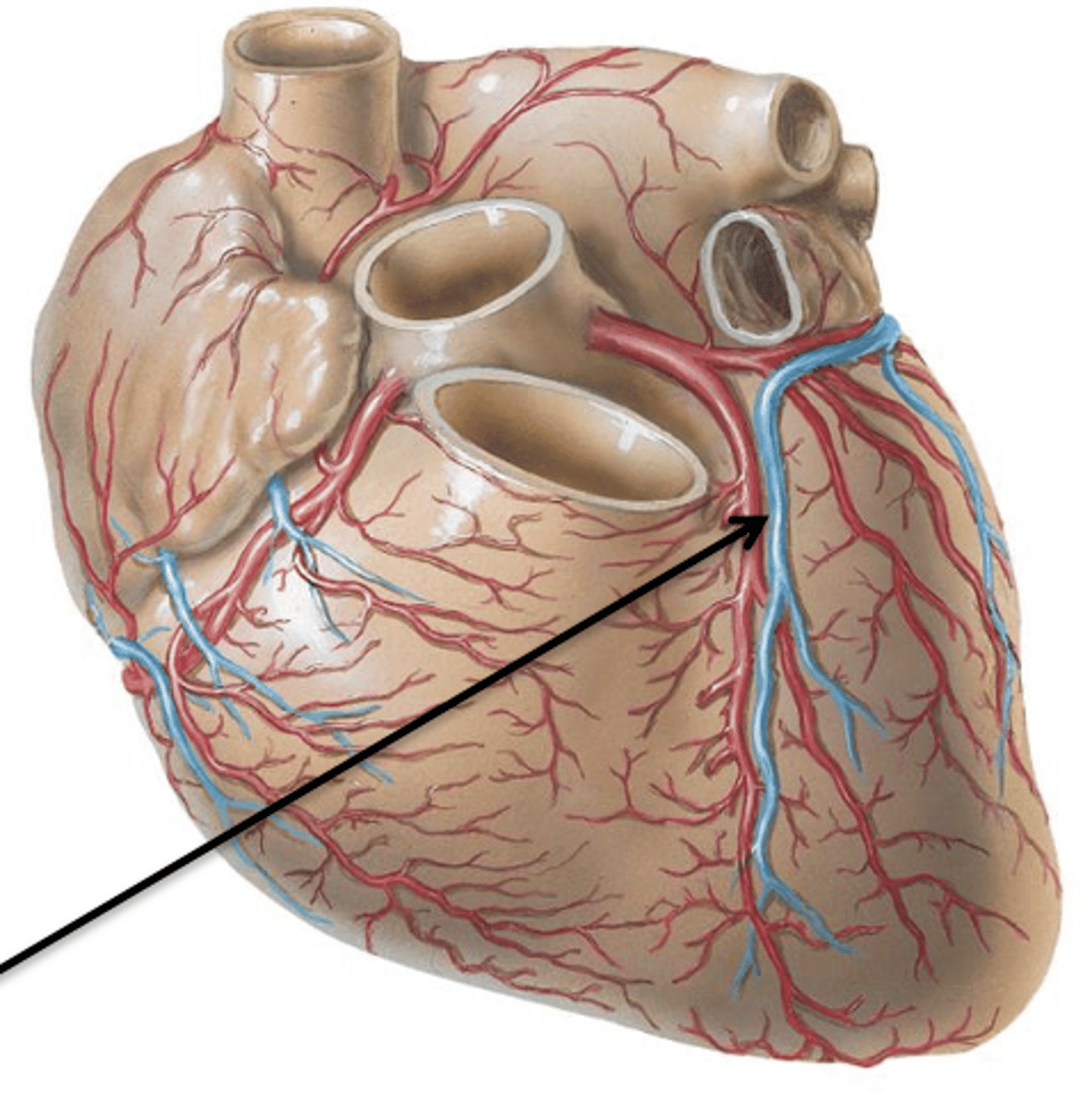
Left and Right Coronary Arteries
Arteries that lead to the left and right sides of the heart respectively.
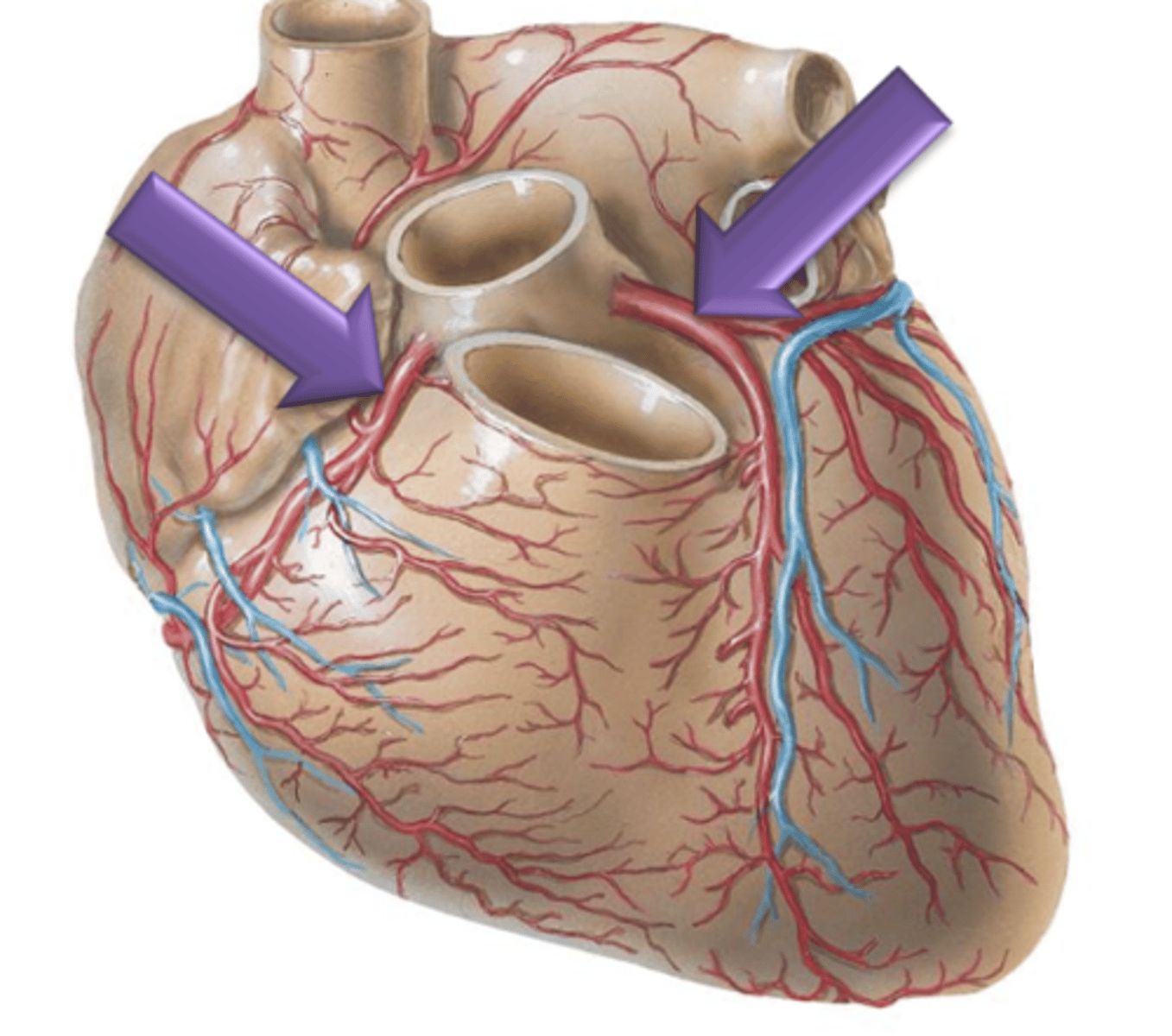
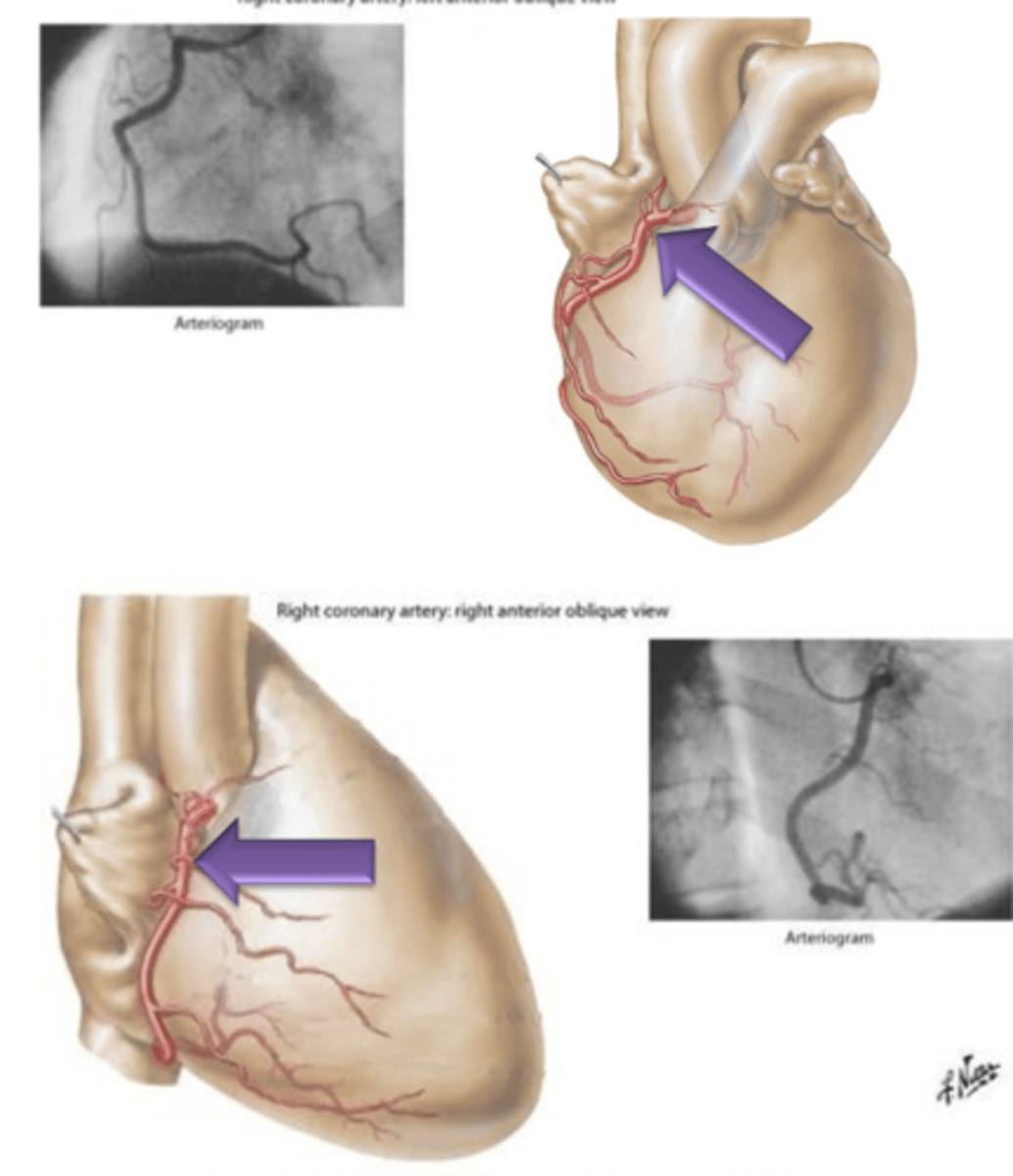
Right Coronary Artery
Artery that originates from the right side of the aorta, courses underneath the right auricle and continues to the posterior surface of the heart.
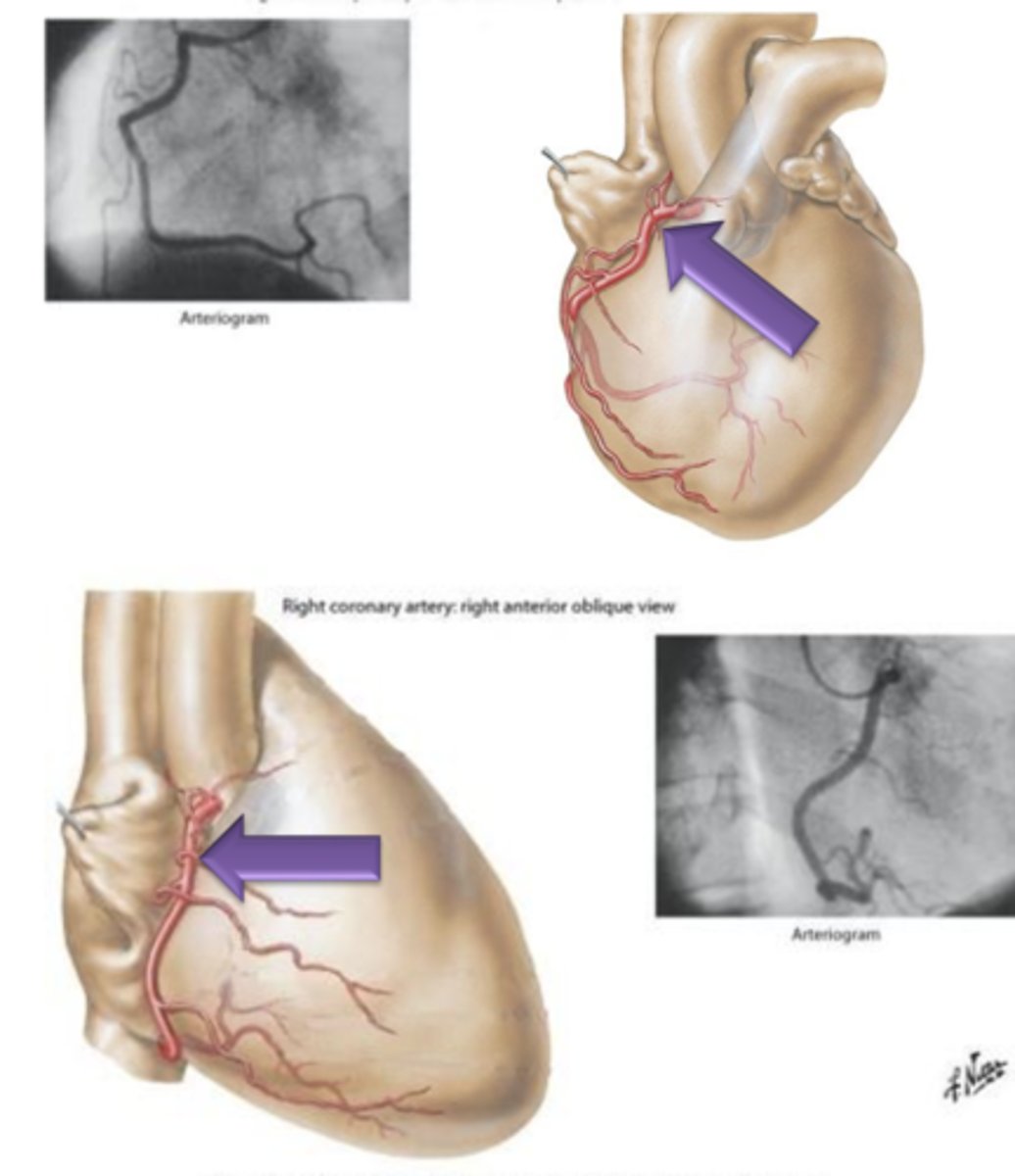
Right Marginal Branch, Posterior Interventricular Branch
What 2 structures does Right Coronary Artery give off?
Left Coronary Artery
Artery that originates from the left side of the aorta.
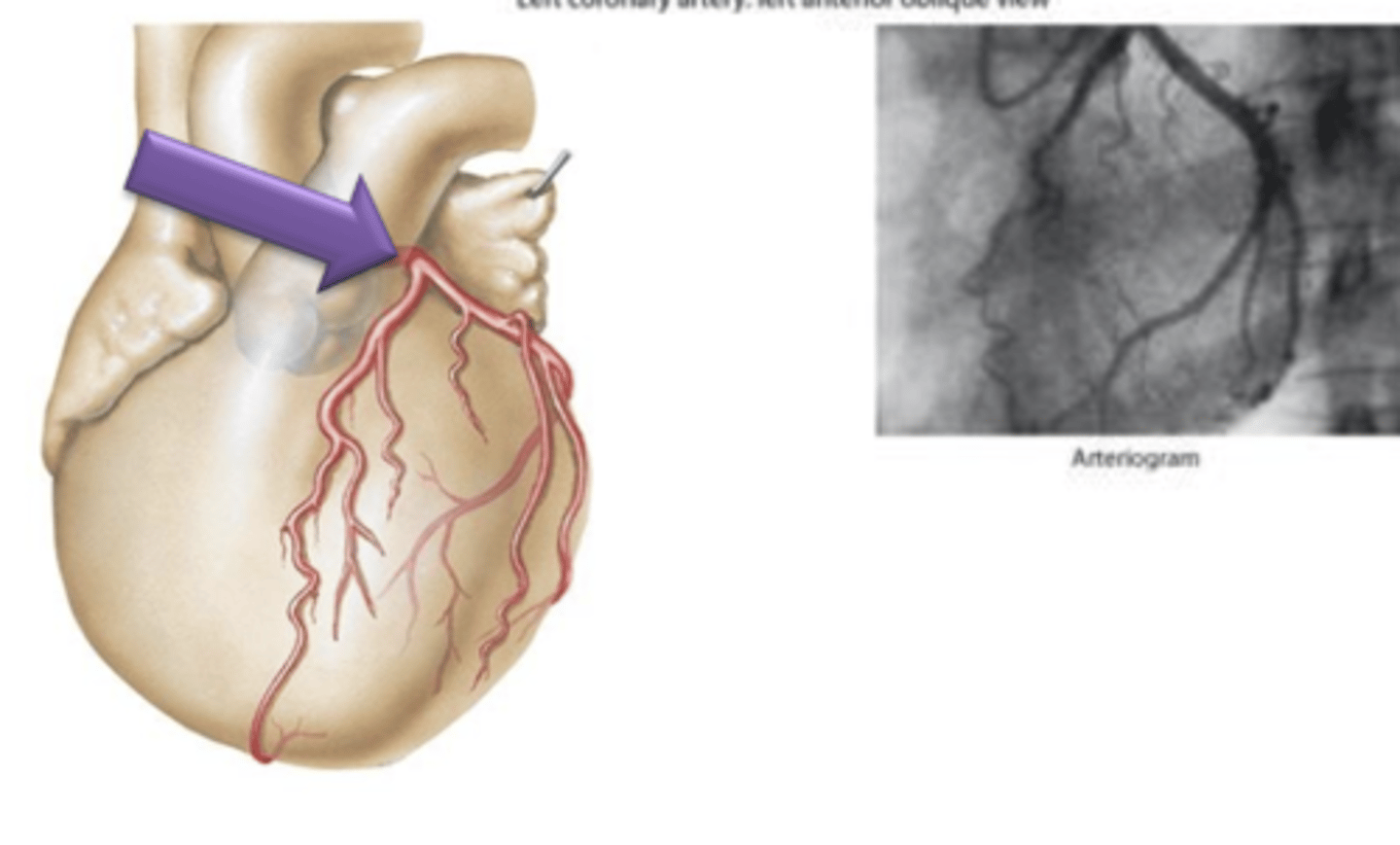
Circumflex Branch, Left Anterior Descending Artery (Anterior Interventricular Branch)
What 2 structures does Left Coronary Artery give off?
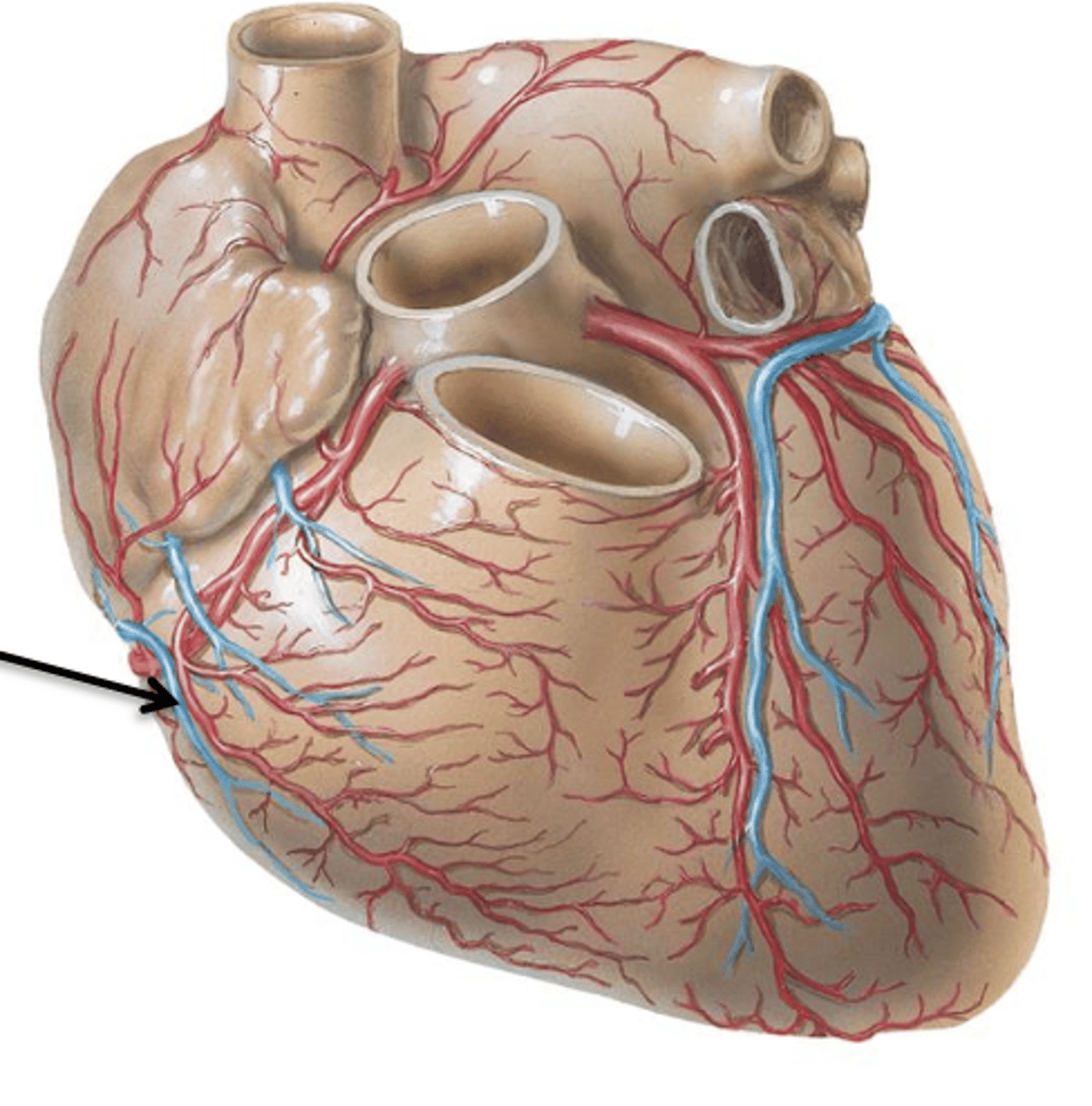
Cardiac Veins
Veins draining the myocardium of the heart.
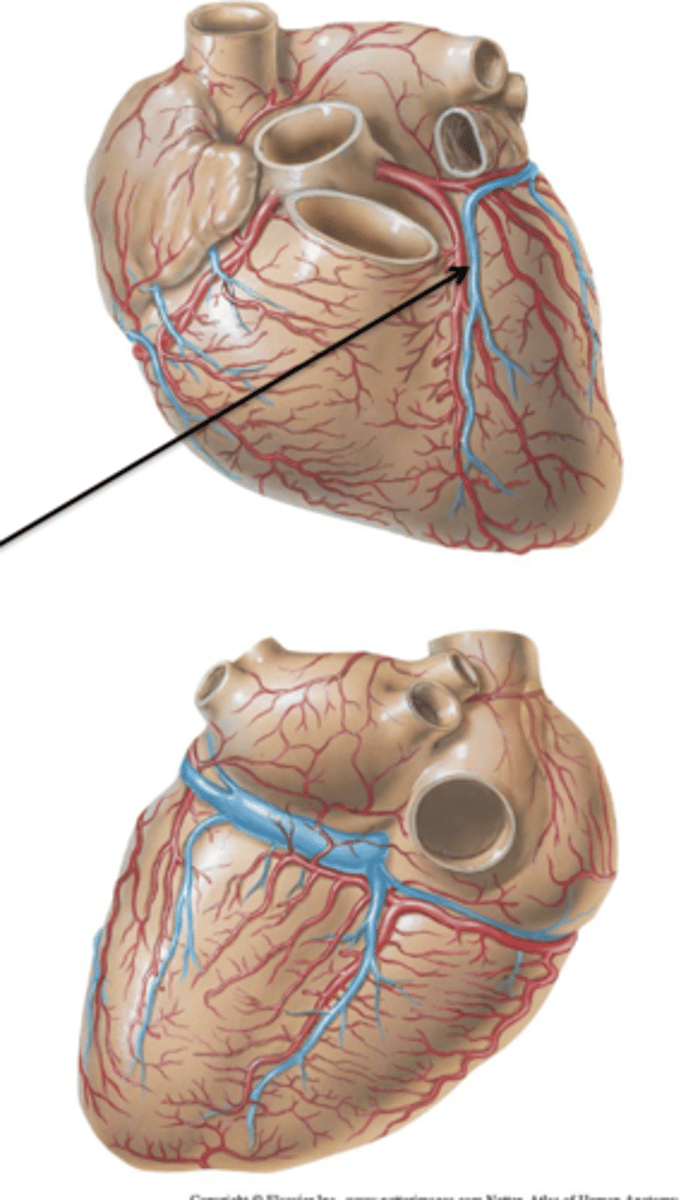
Coronary Sinus
All 3 major cardiac veins drain into ___ ___. It is a short, wide vessel that receives all 3 cardiac veins and empties directly into the right atrium.
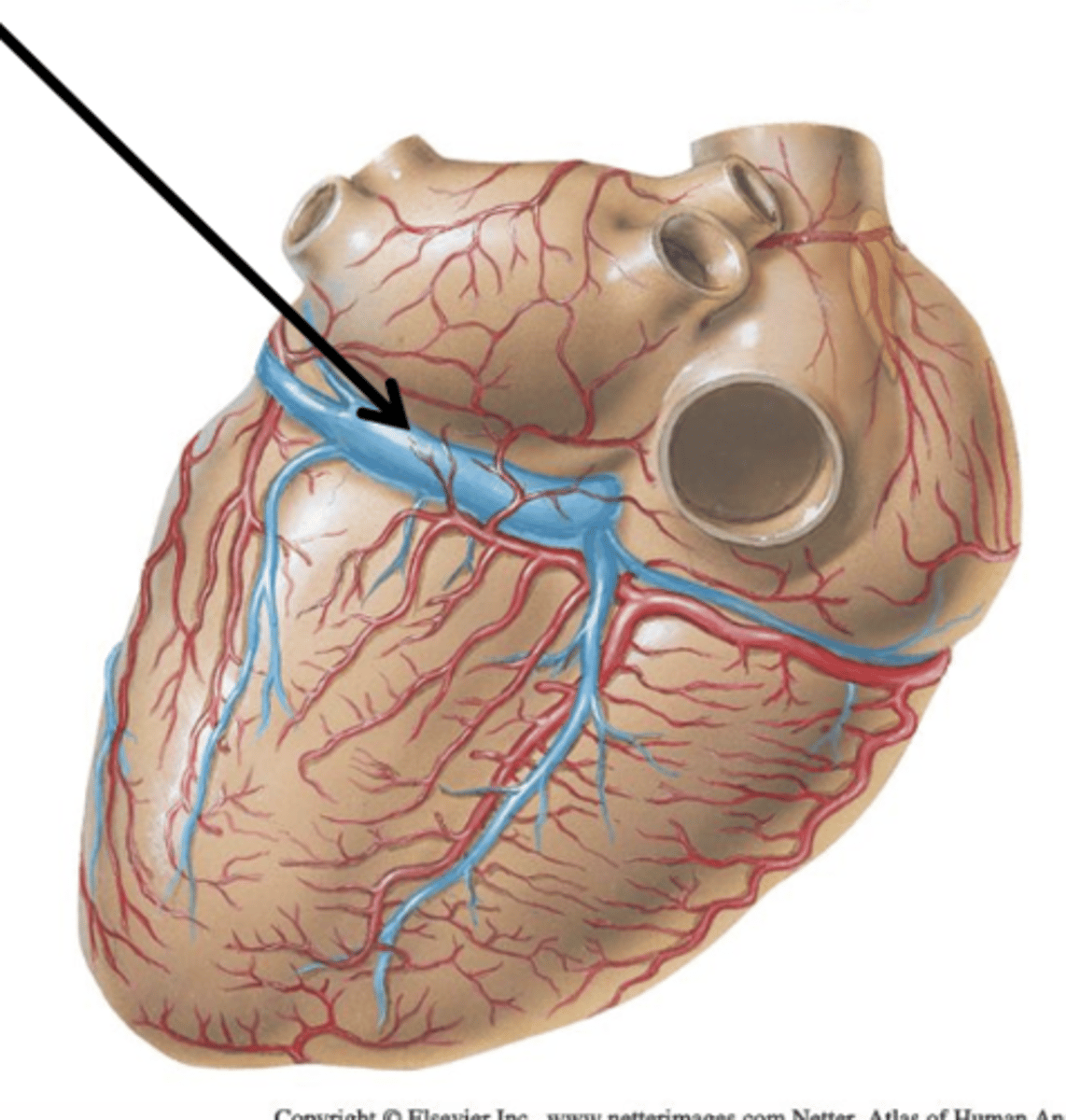
Great Cardiac Vein
Cardiac Vein that courses with the anterior interventricular artery and circumflex branch. It continues on the back of the heart as the coronary sinus.
Small Cardiac Vein
Cardiac Vein that courses with the marginal artery and drains into the coronary sinus.
Middle Cardiac Vein
Cardiac Vein that courses with the posterior interventricular artery and drains into the coronary sinus.$
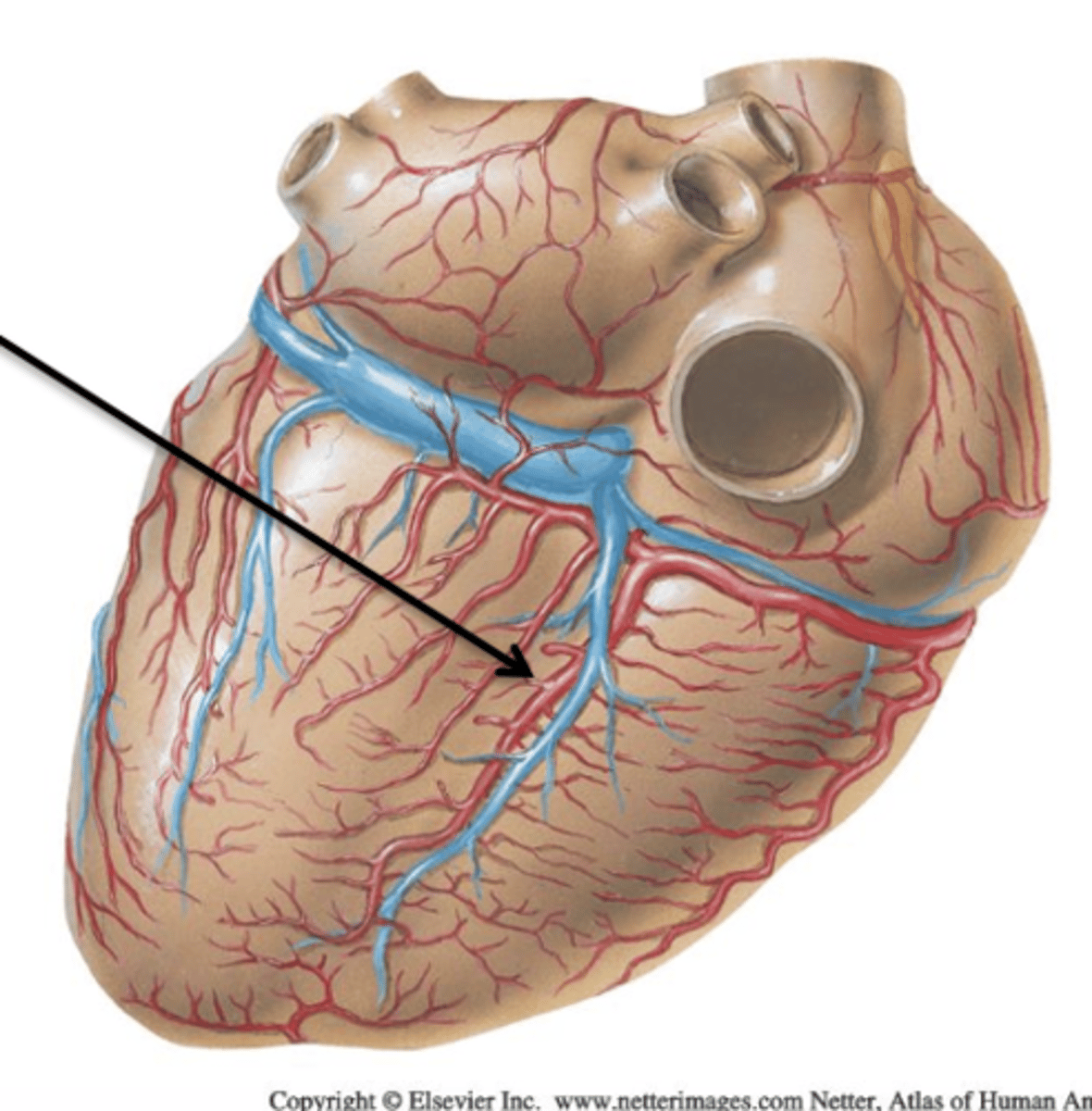
Anterior Cardiac Veins
2 or 3 small vessels which drain the right ventricle and end directly in the right atrium.
Venae Cordis Minimae
Numerous small veins that drain the myocardium itself and empty separately into all 4 chambers of the heart.
Superior Vena Caval opening, Inferior Vena Caval Opening, opening of Coronary Sinus
What are the 3 openings that the 3 major veins drain into the right atrium?
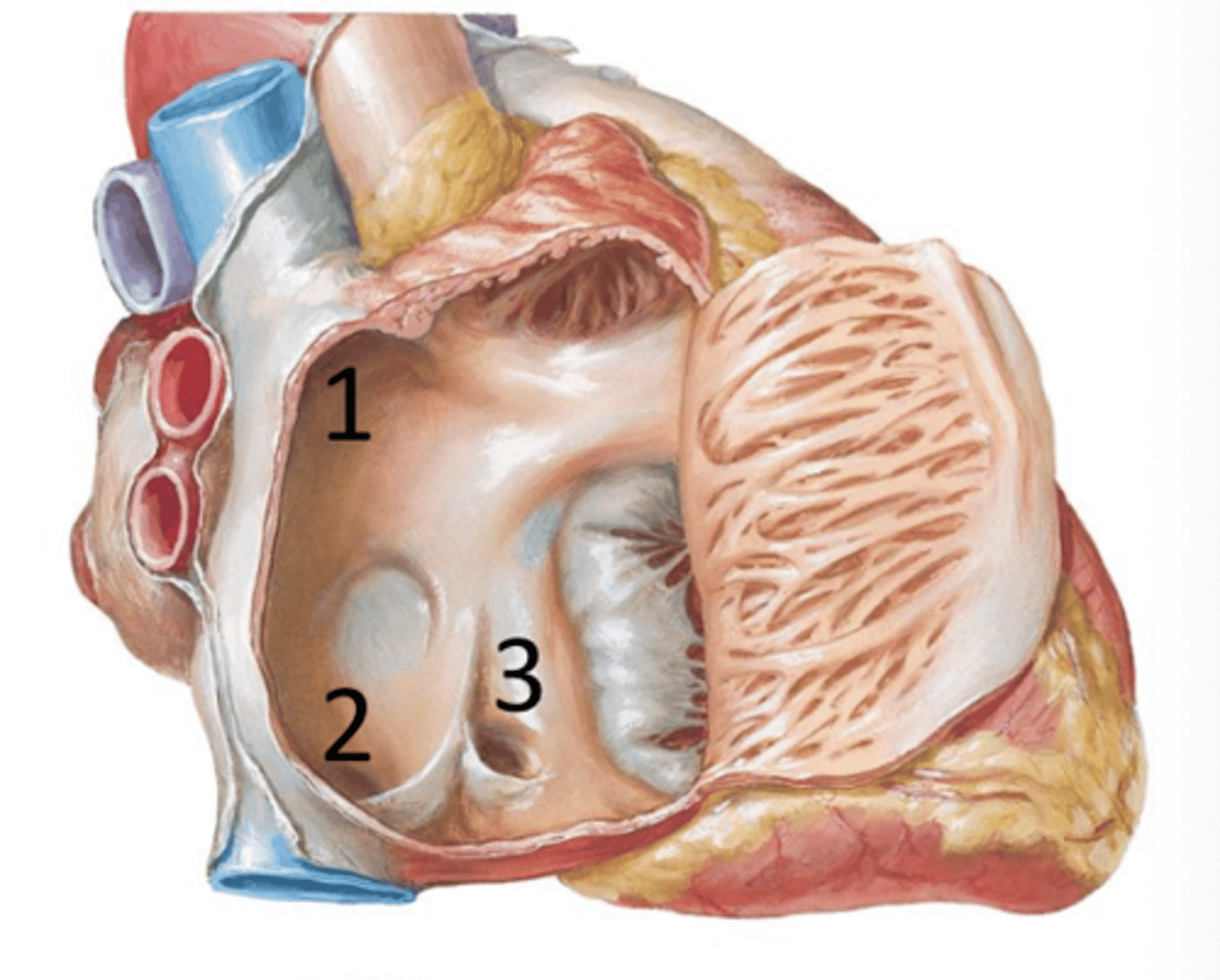
Crista Terminalis
A vertical muscular ridge on the posterior wall of the right atrium.
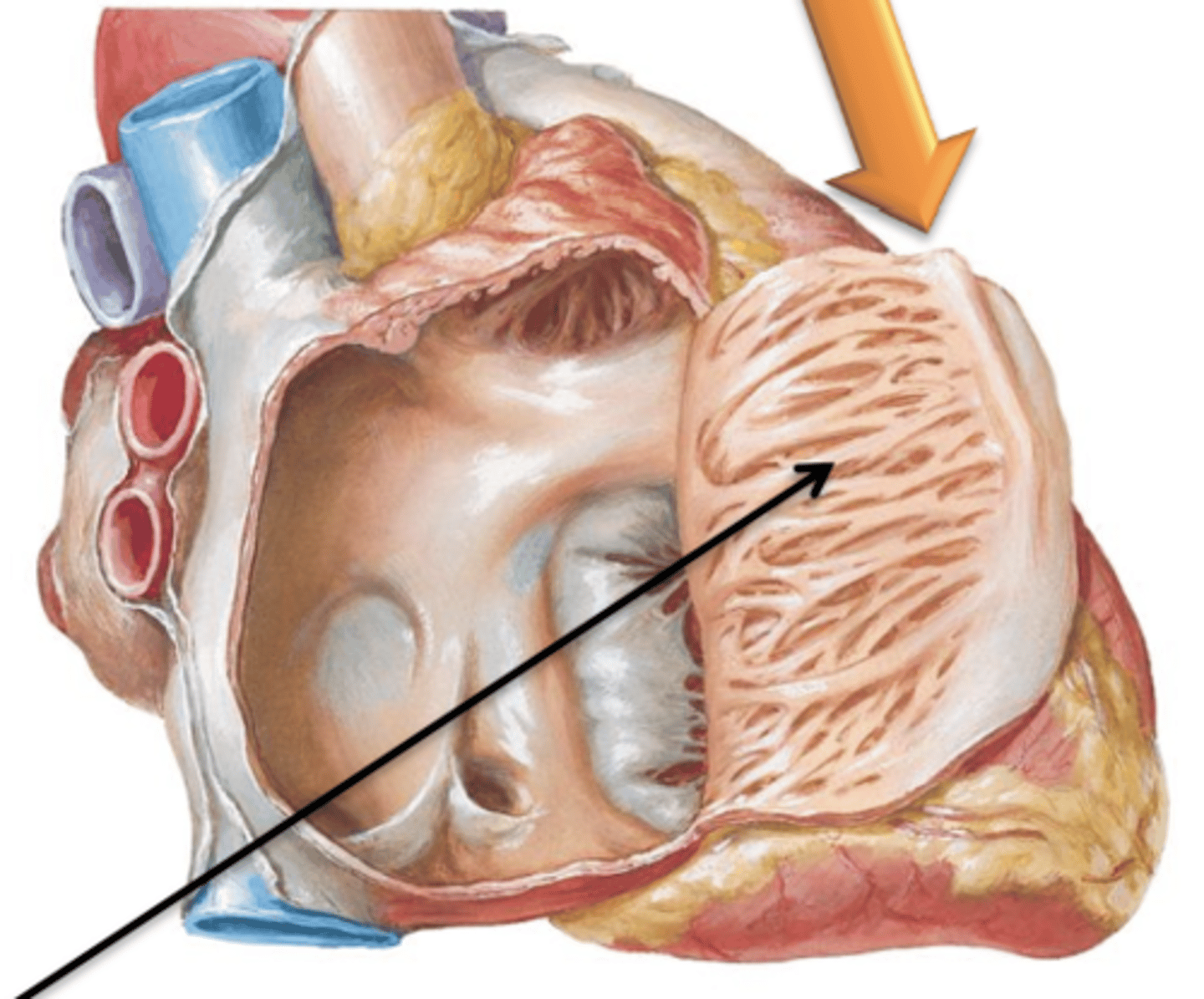
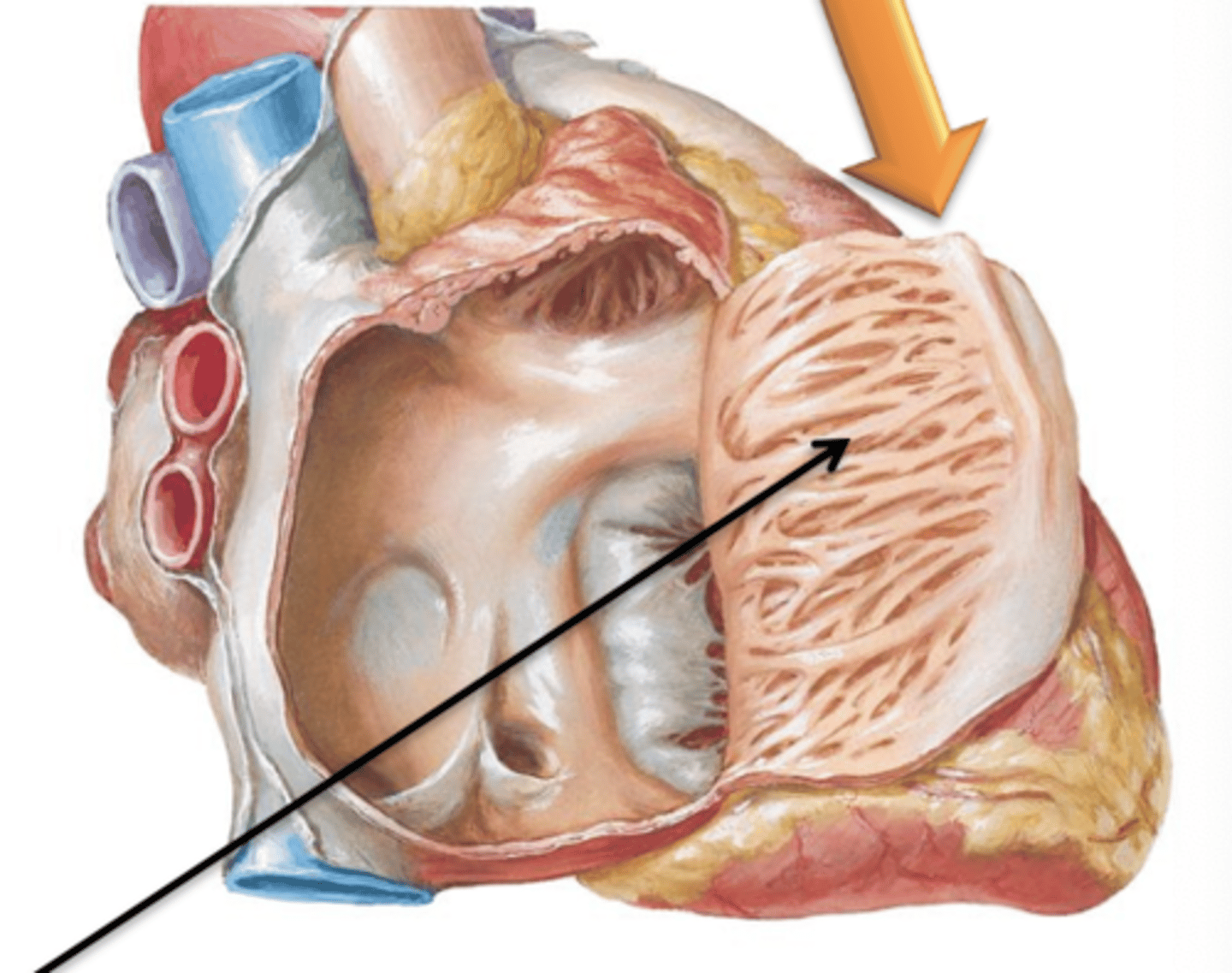
Musculi Pectinati (Pectinate Muscle)
Muscular ridge-like projections extending from the crista terminalis. Found within the right atrium and in right and left auricles.
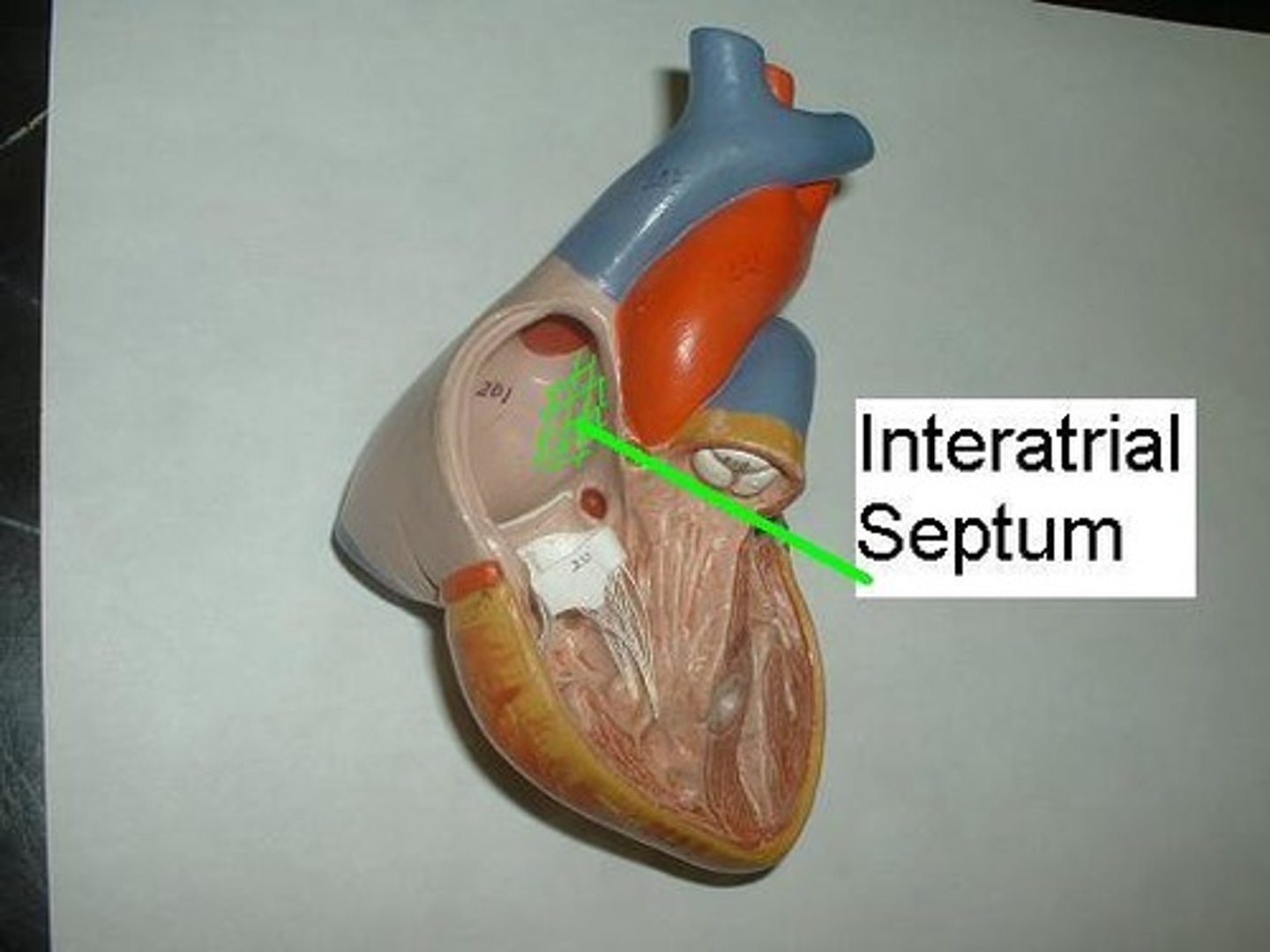
Interatrial Septum
Partition between right and left atria.
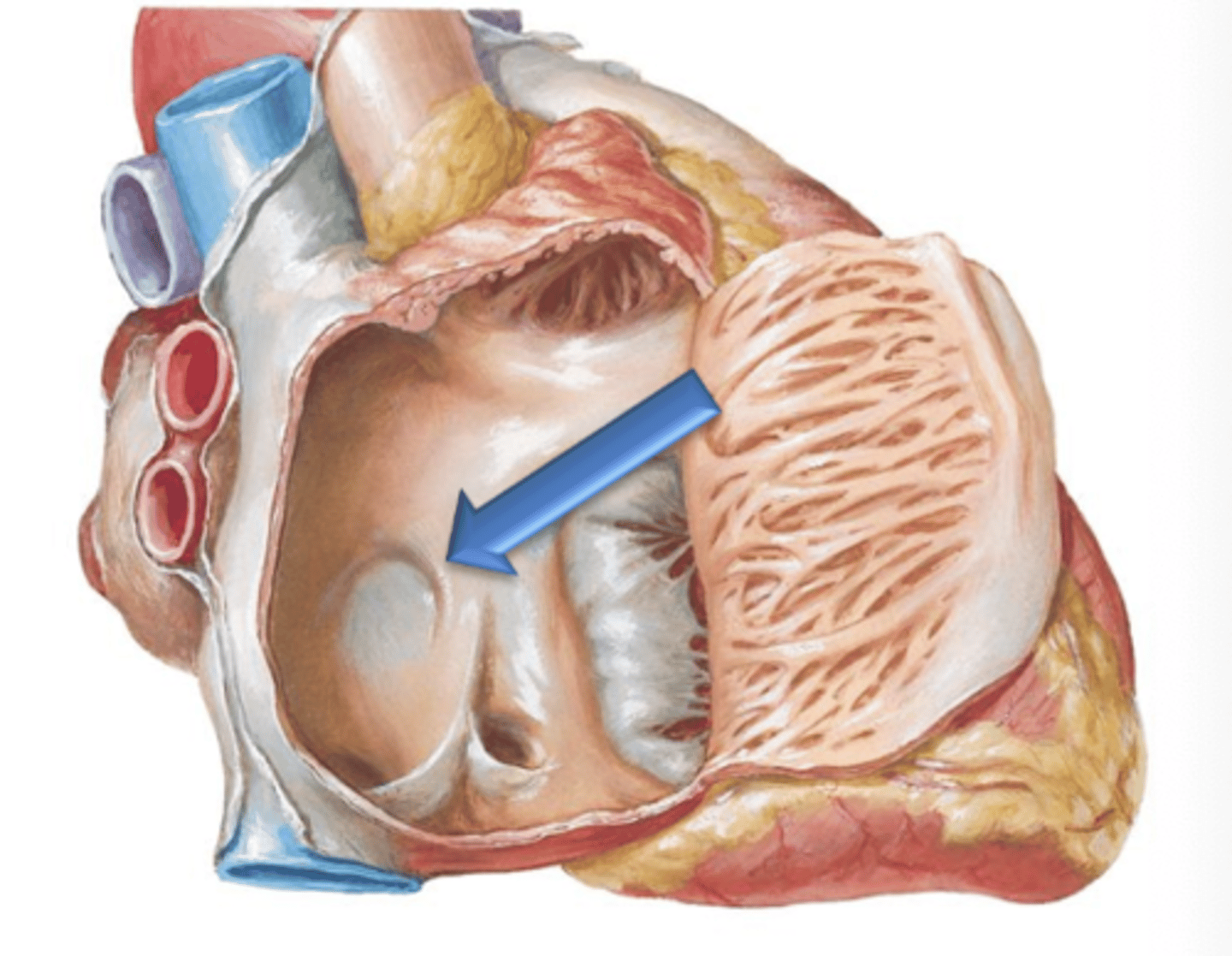
Fossa Ovalis
Oval depression on the interatrial septum in the right atrium.
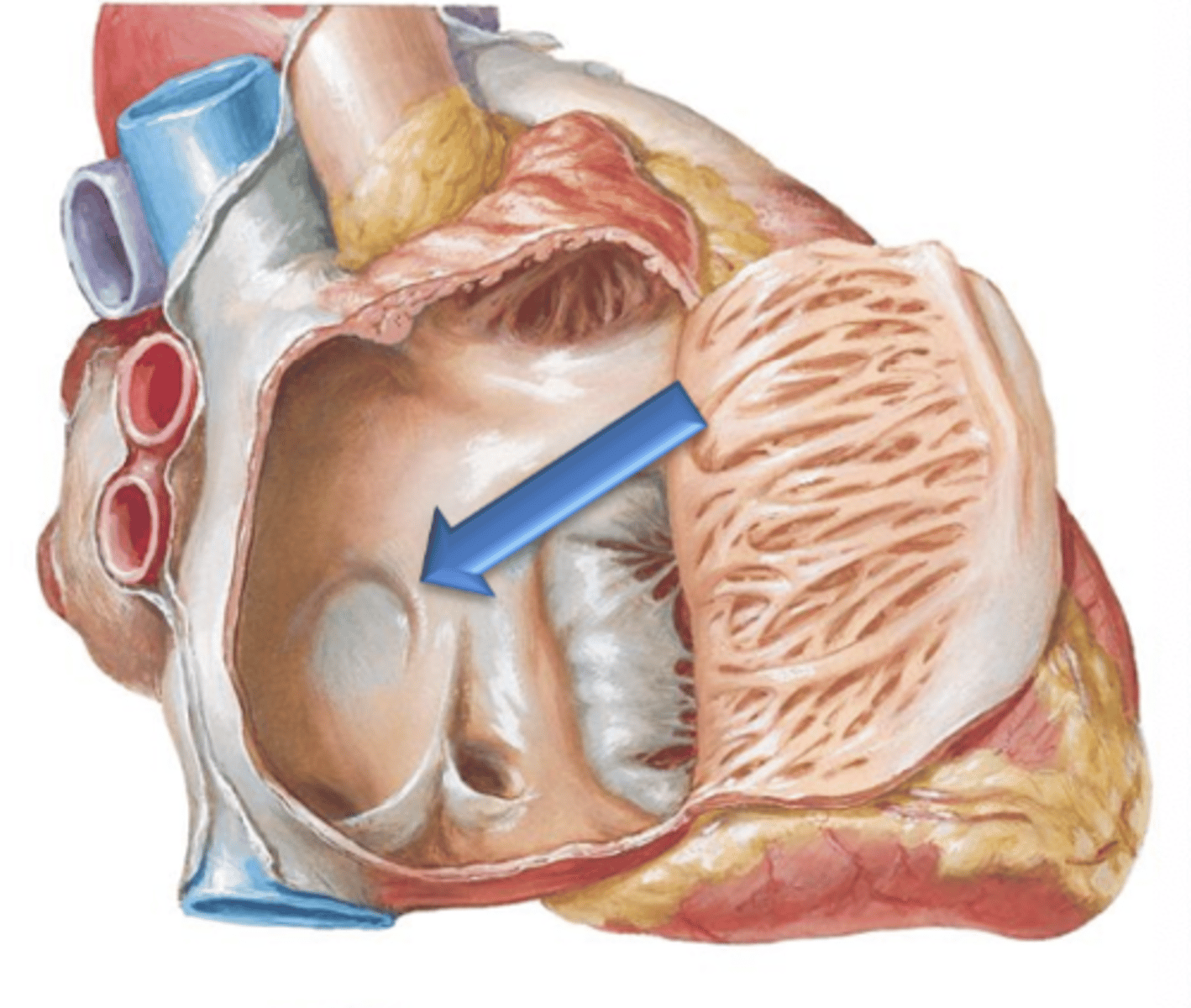
Limbus Fossa Ovalis
The fossa ovalis is surrounded at its peiphery by a ridge called the ___ ___ ___.
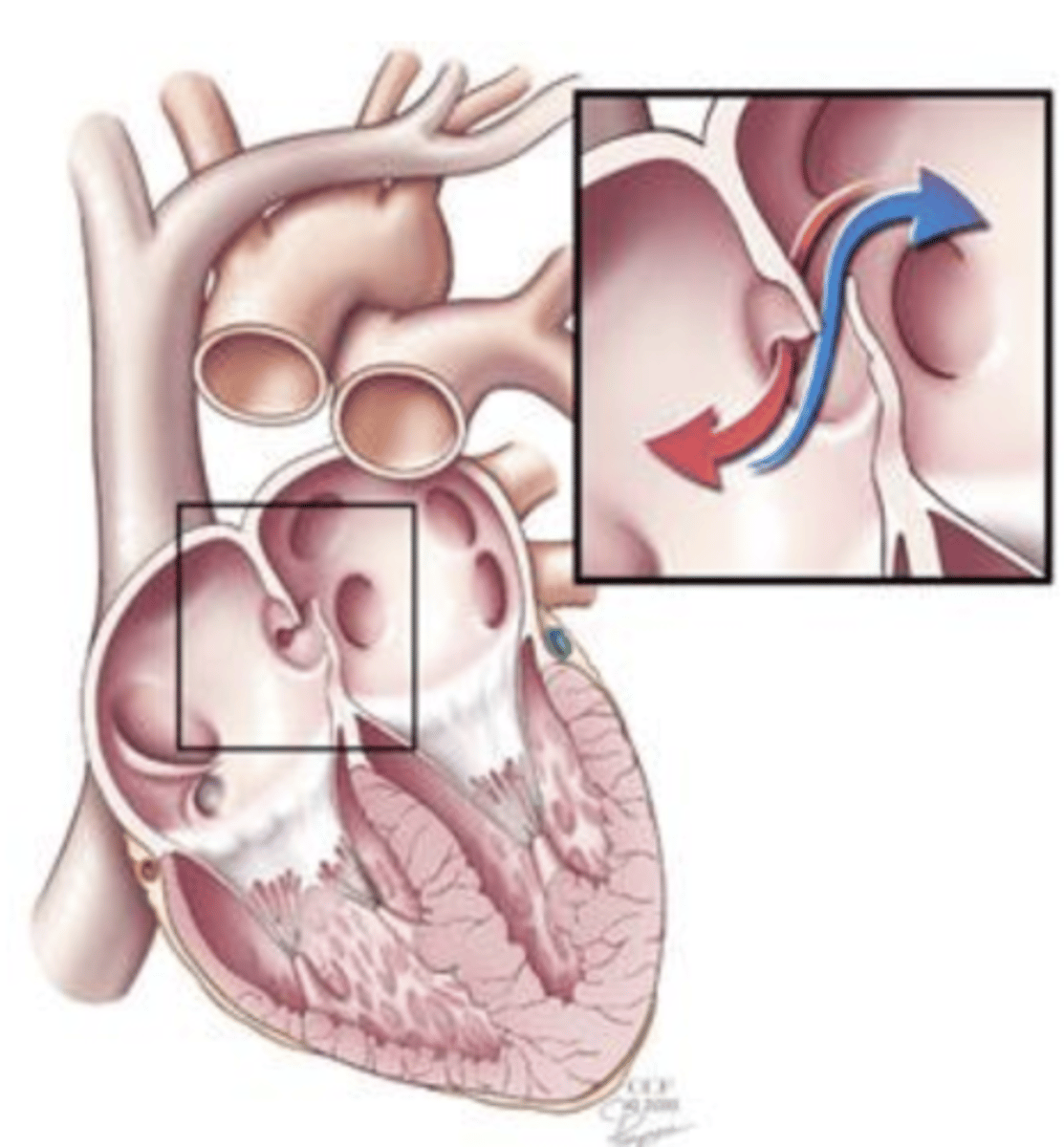
Foramen Ovale
The fossa ovalis is a remnant of a foramen that, in the fetal stage of development, existed between the right and left atrium called the ___ ___ that normally closes at birth.
Right Atrioventricular Opening, Right Atrioventricular, Tricuspid
Anteriorly, the right atrium opens to the right ventricle via the ___ ___ ___ which is guarded by the ___ ___ Valve or ___ Valve which consists of 3 cusps.
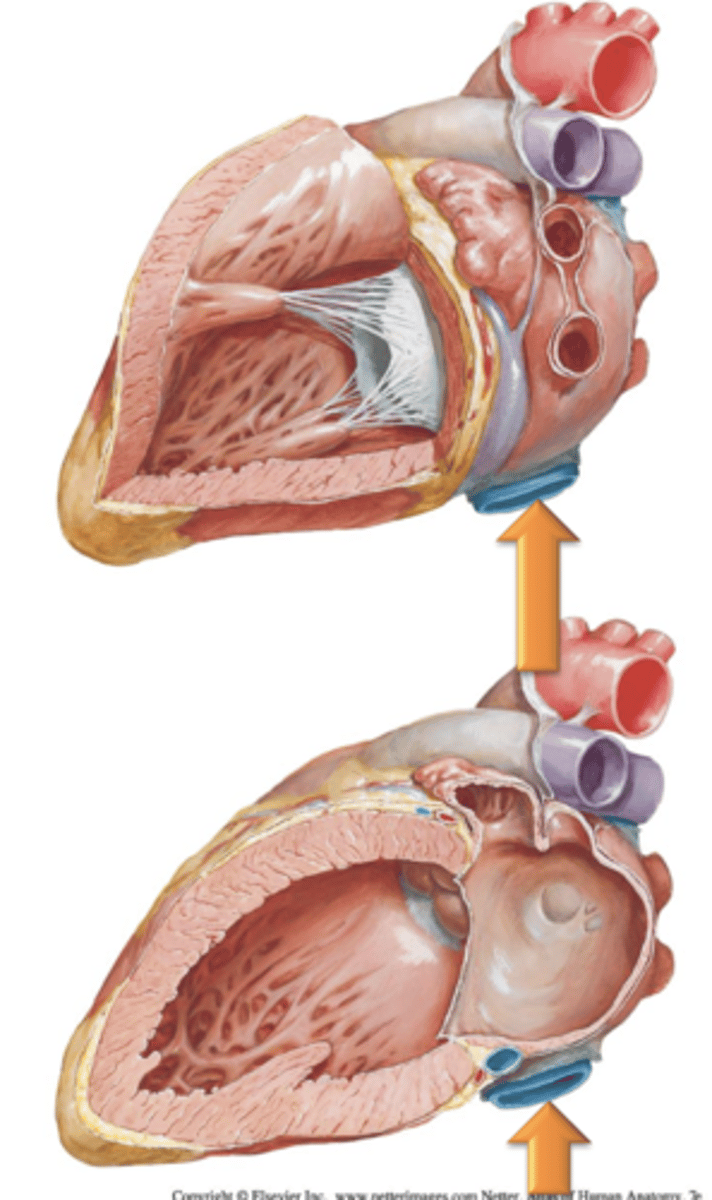
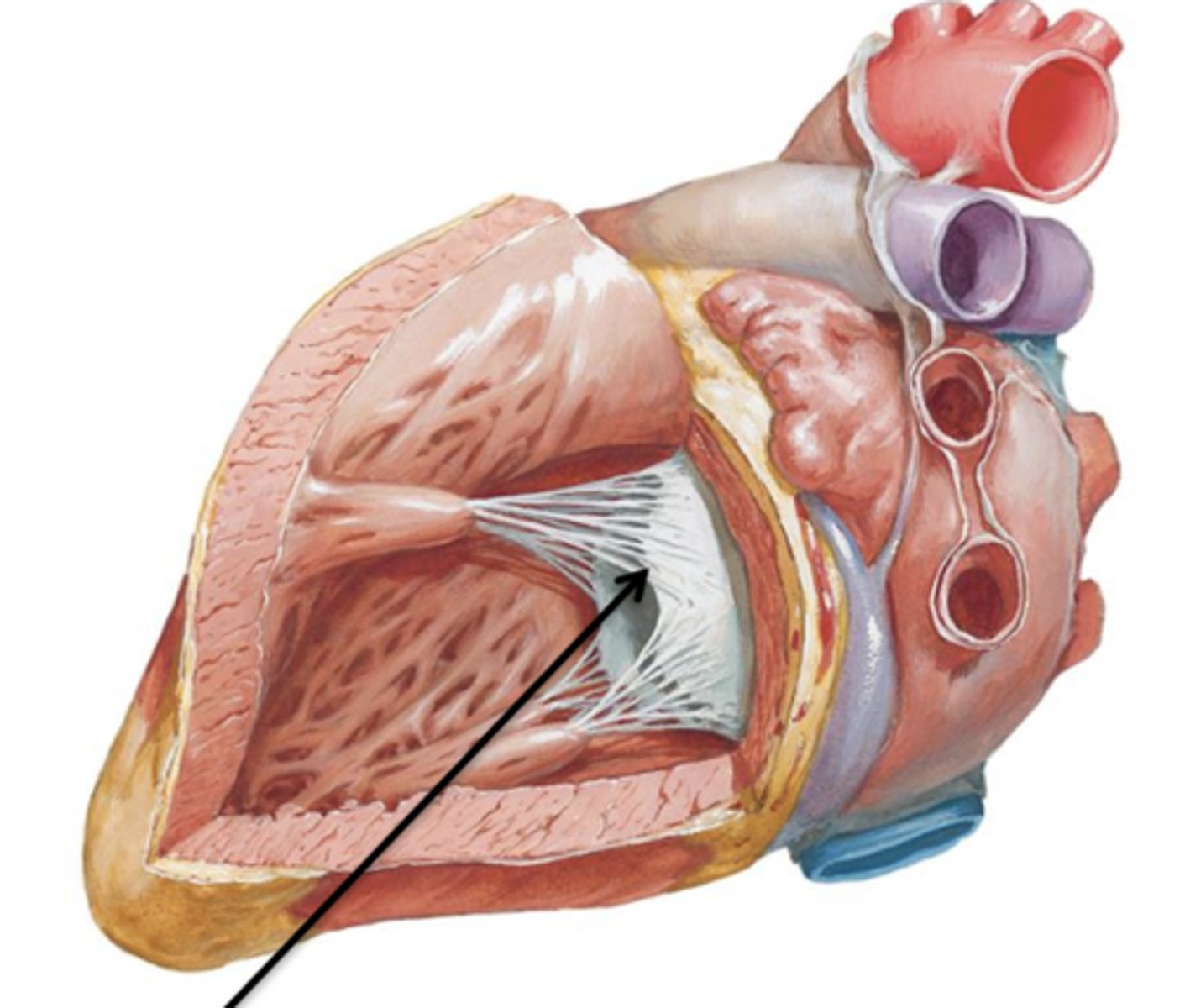
Cusps, Chordae Tendineae, Papillary Muscles
What are the 3 parts of atrioventricular valves?
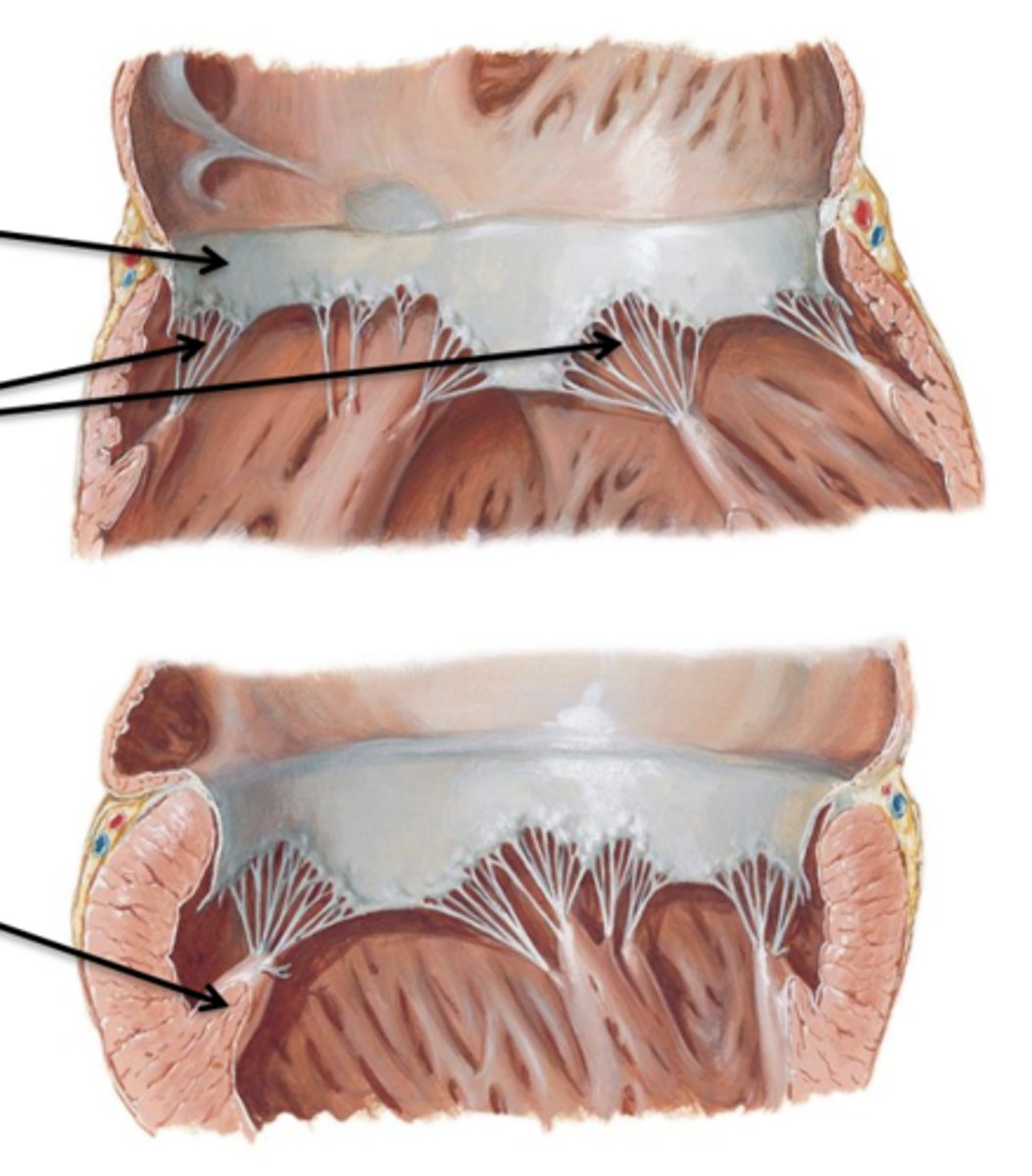
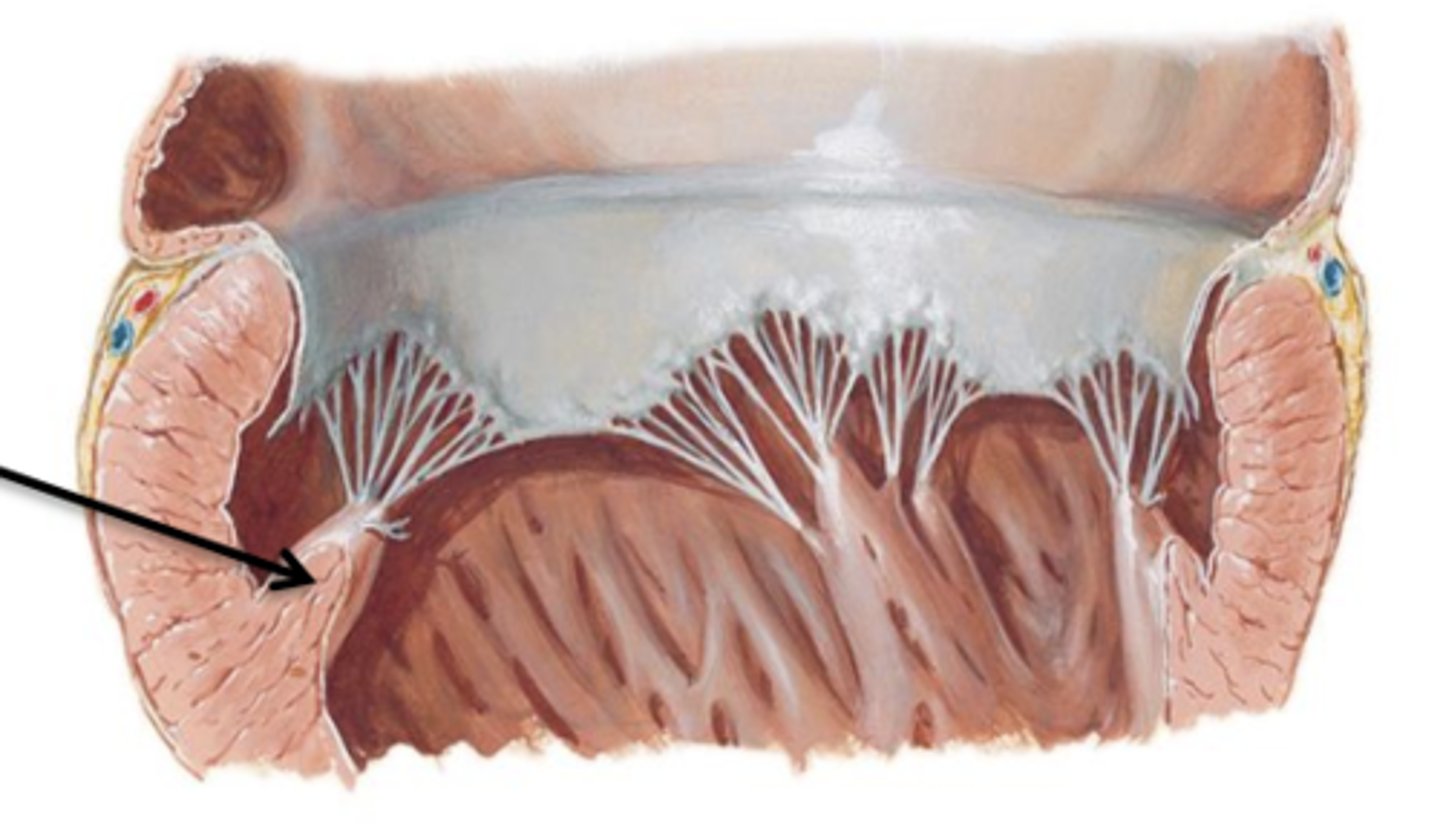
Cusps
Flaps of connective tissue.
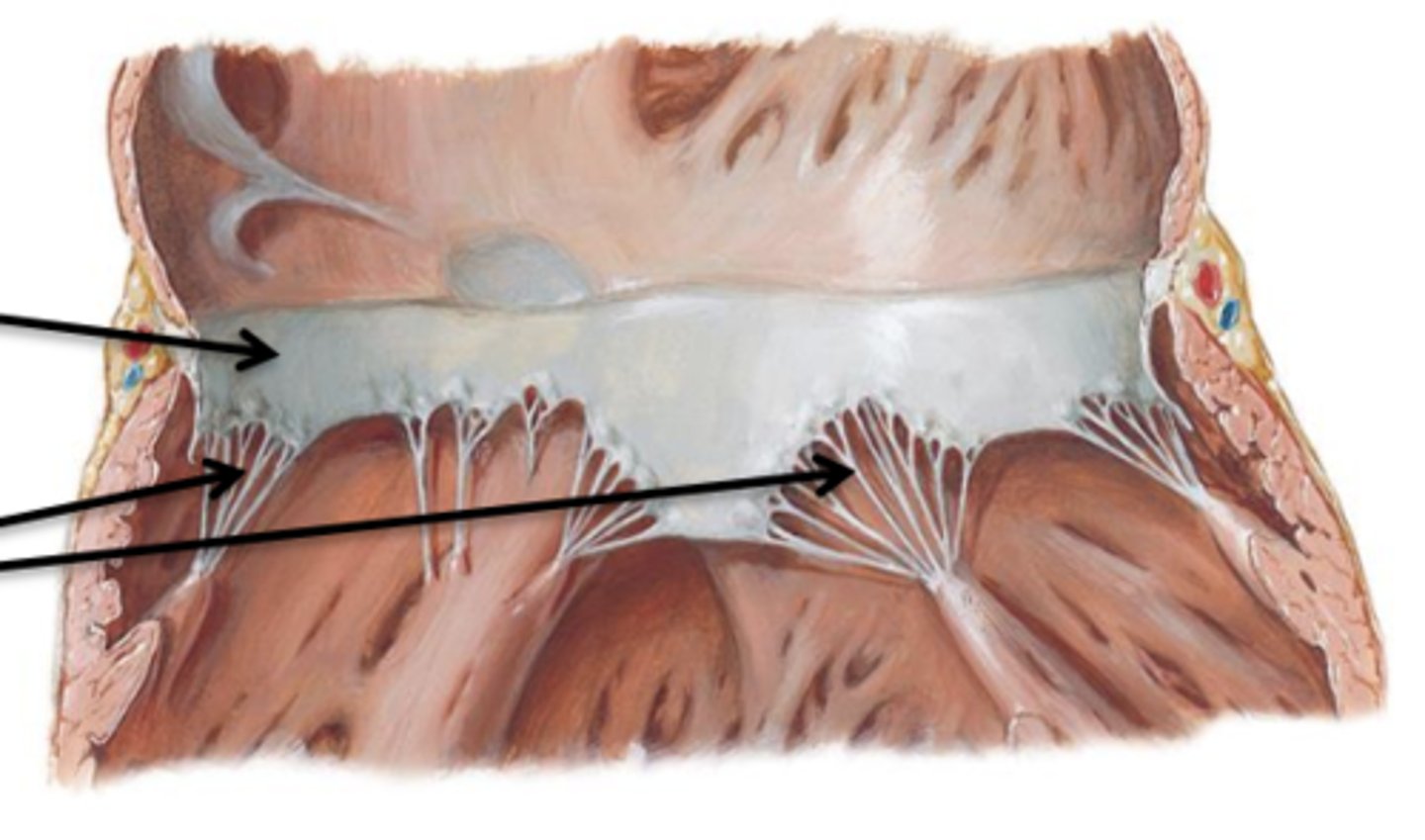
Chordae Tendineae
Connective tissue cords that attach to the lower surface of the cusps.
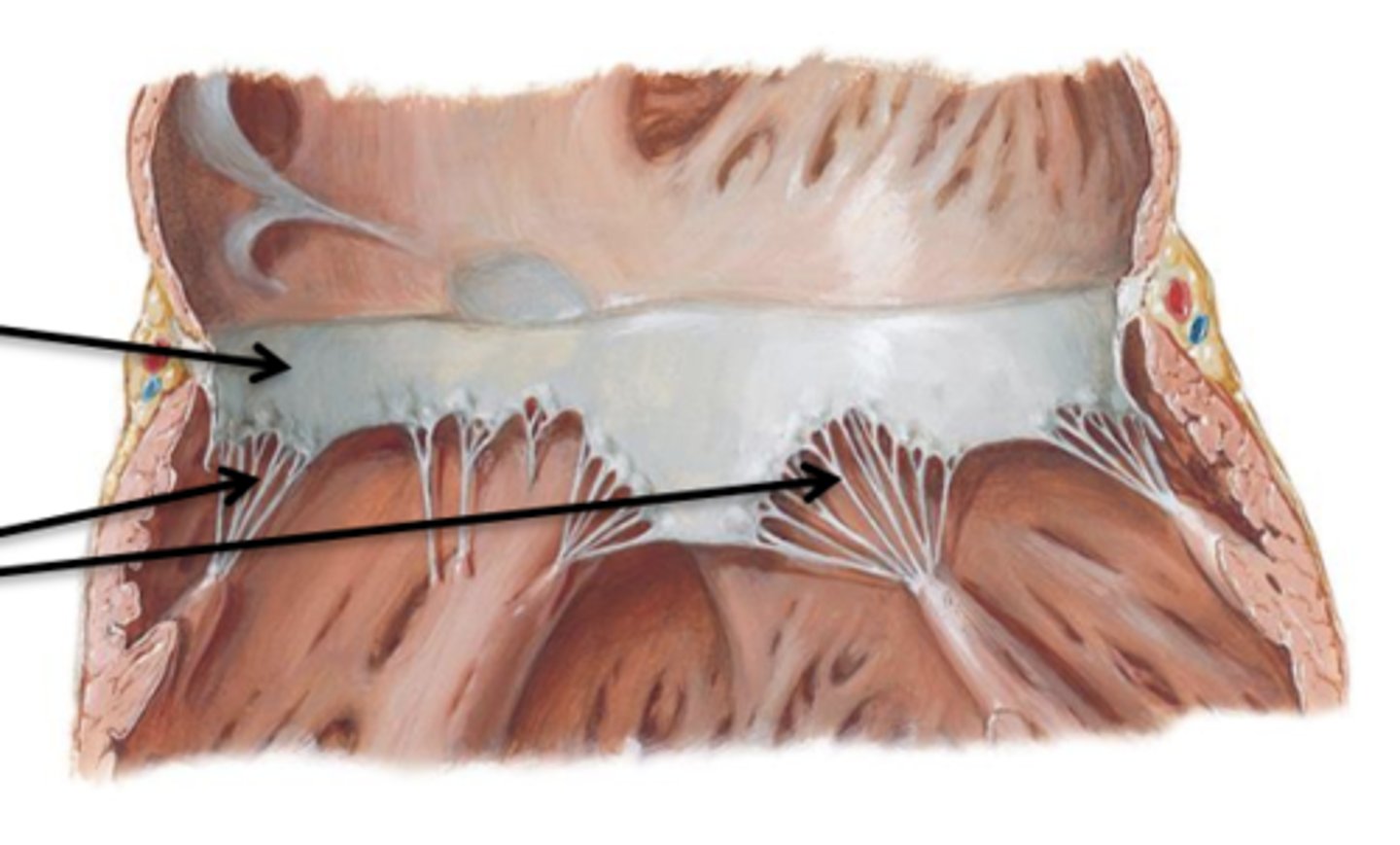
Papillary Muscles
Internal folds of ventricular muscle that give off attachments to the chordae tendineae.

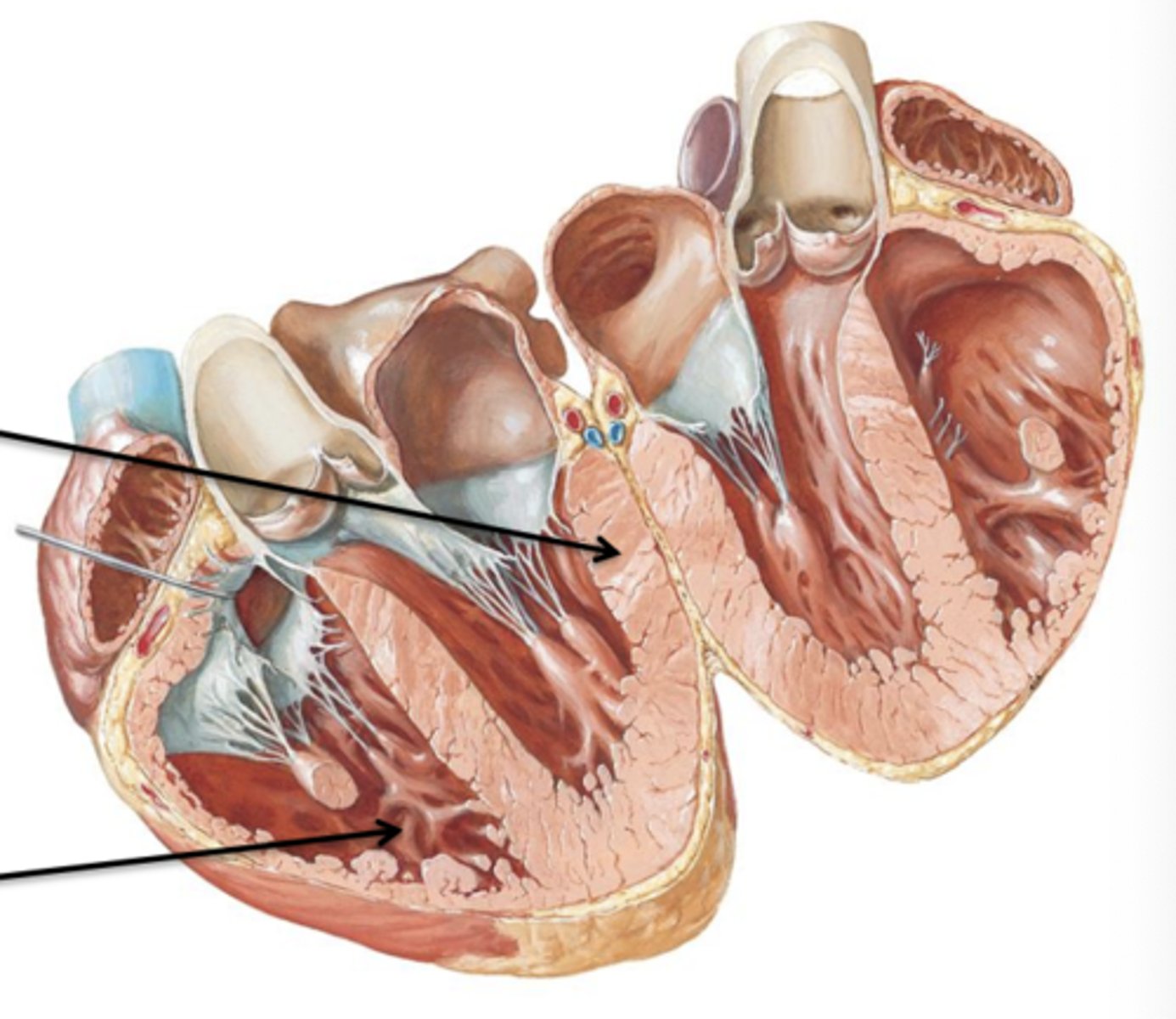
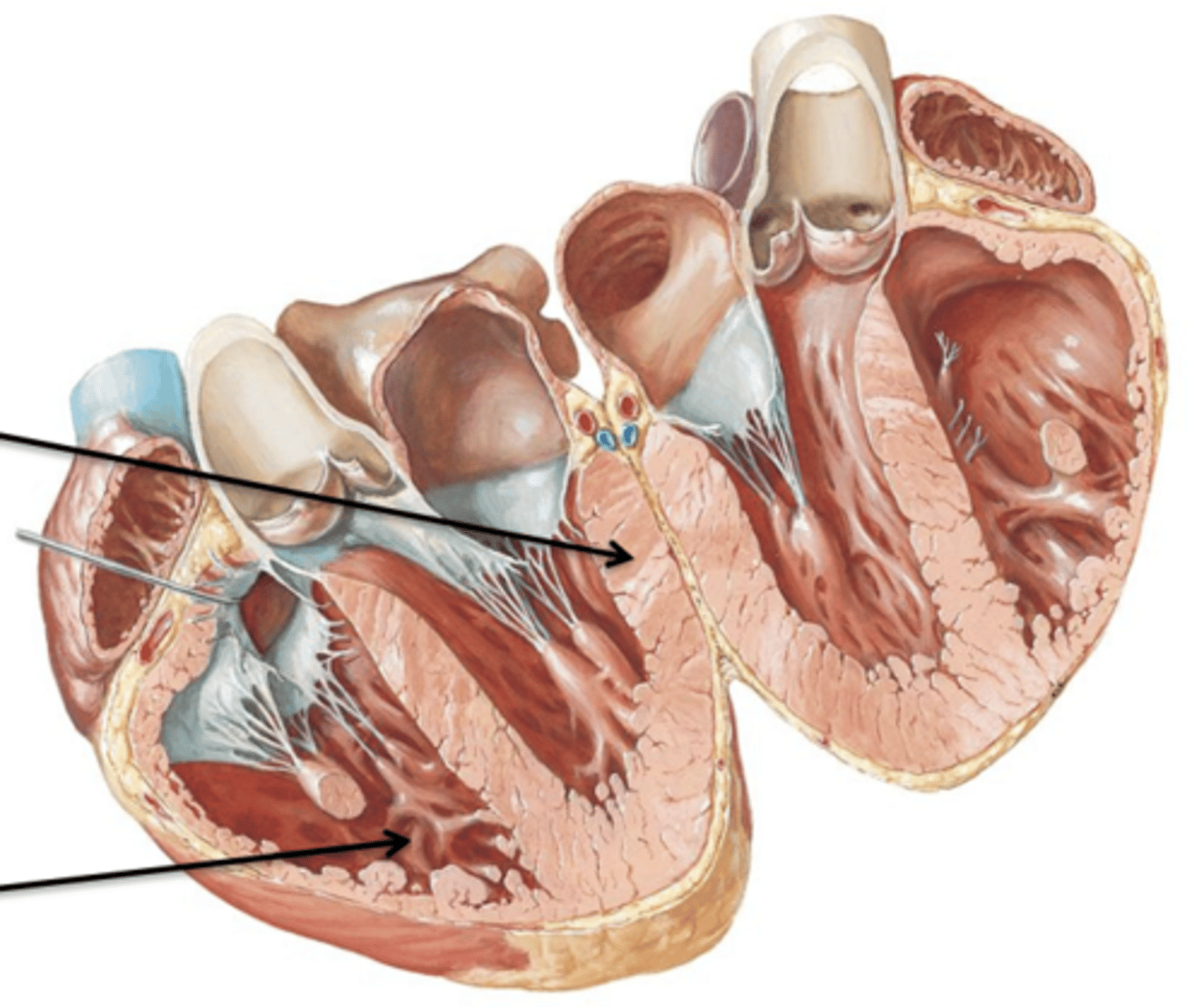
Trabeculae Carneae
The internal surface of the ventricle consists of irregular projections of muscle called ___ ___.
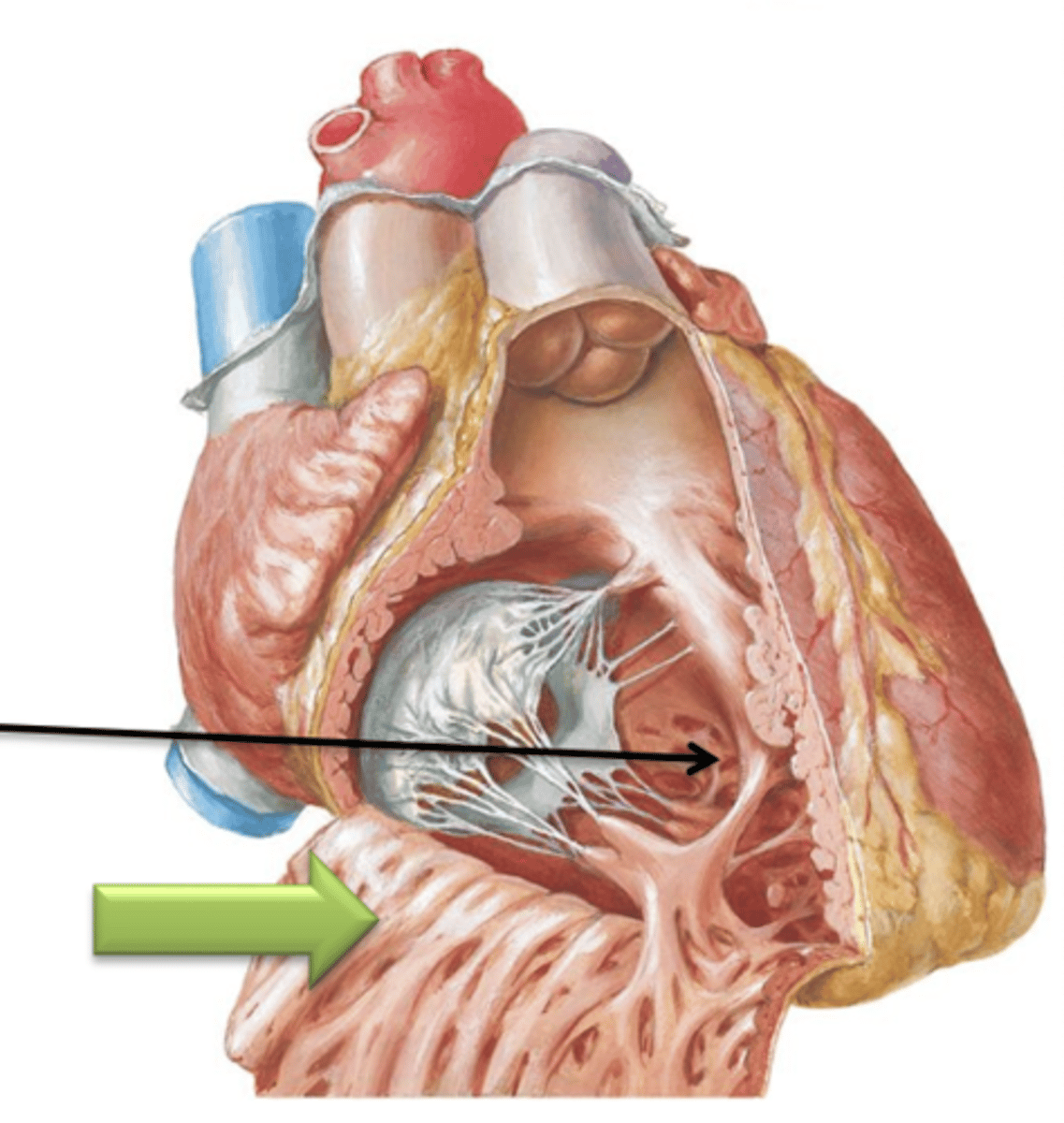
Septomarginal Trabeculae
Another type of trabeculae carneae that is a band of tissue that attaches the interventricular septum to the papillary muscle. It contains important nerve fibers of the conduction system of the heart.
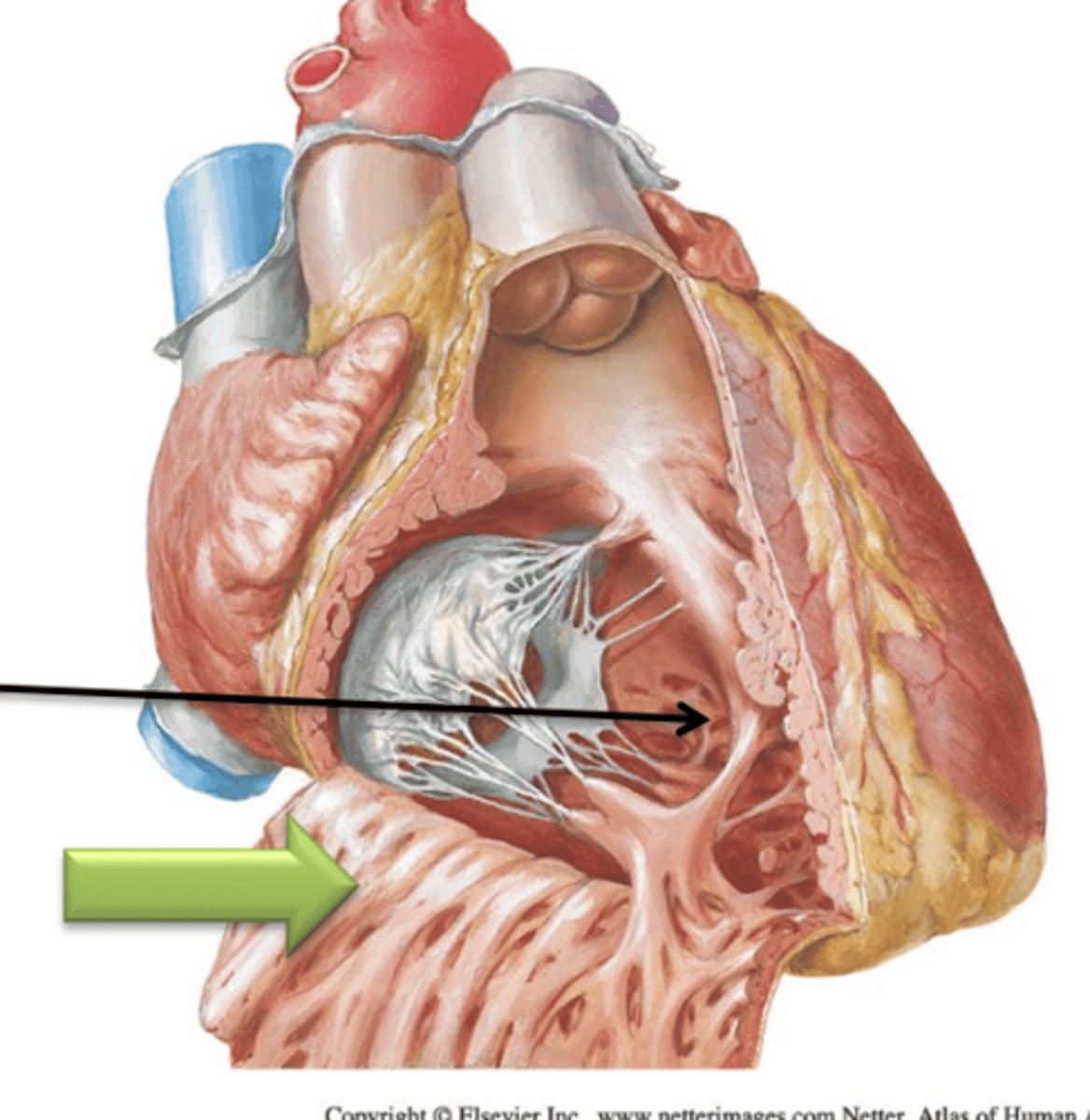
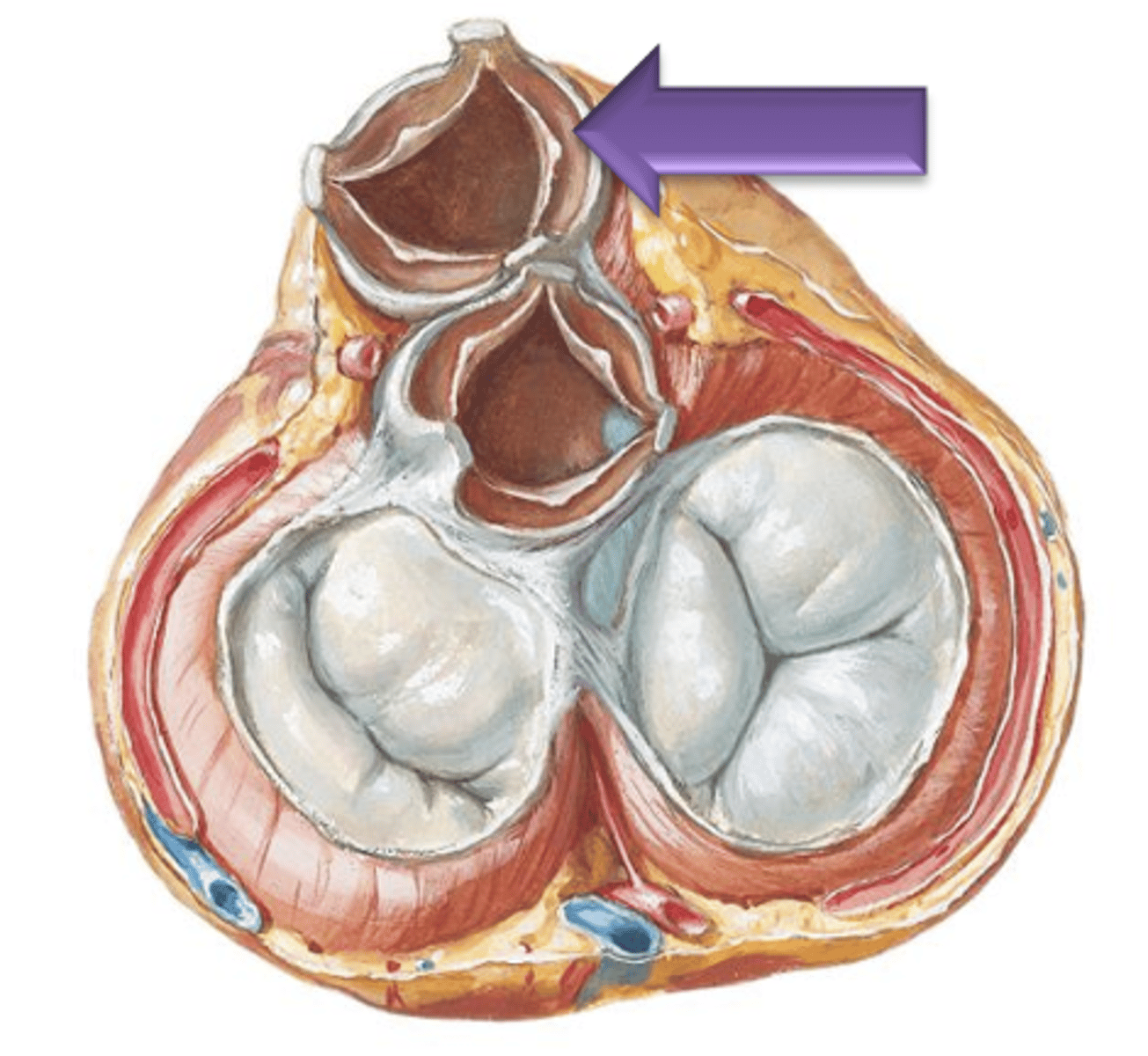
Pulmonary Semilunar
Blood will leave the right ventricle and enter the pulmonary trunk by passing through the ___ ___ Valve.
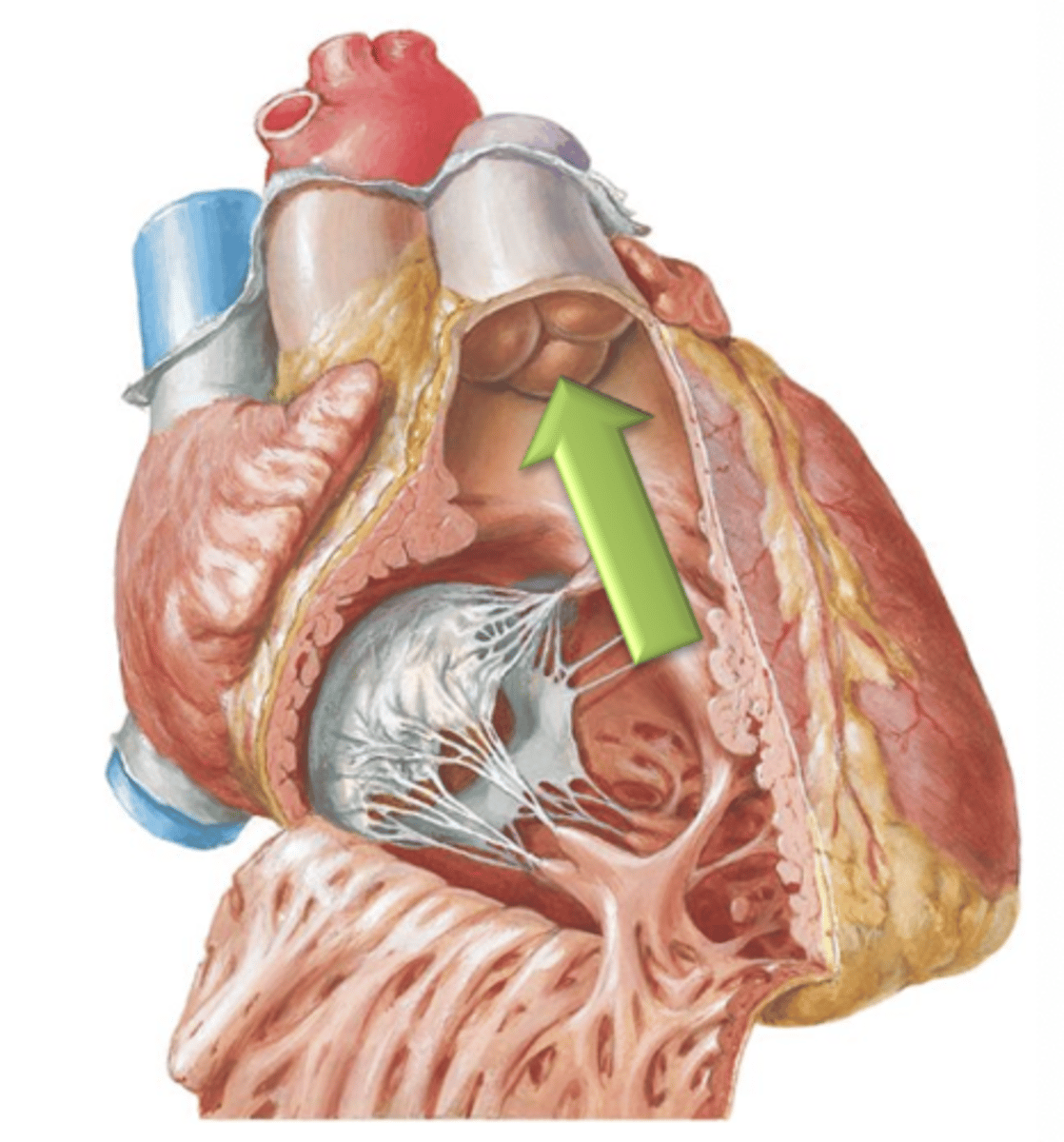
3
For each semilunar valve, there are ___ cusps.
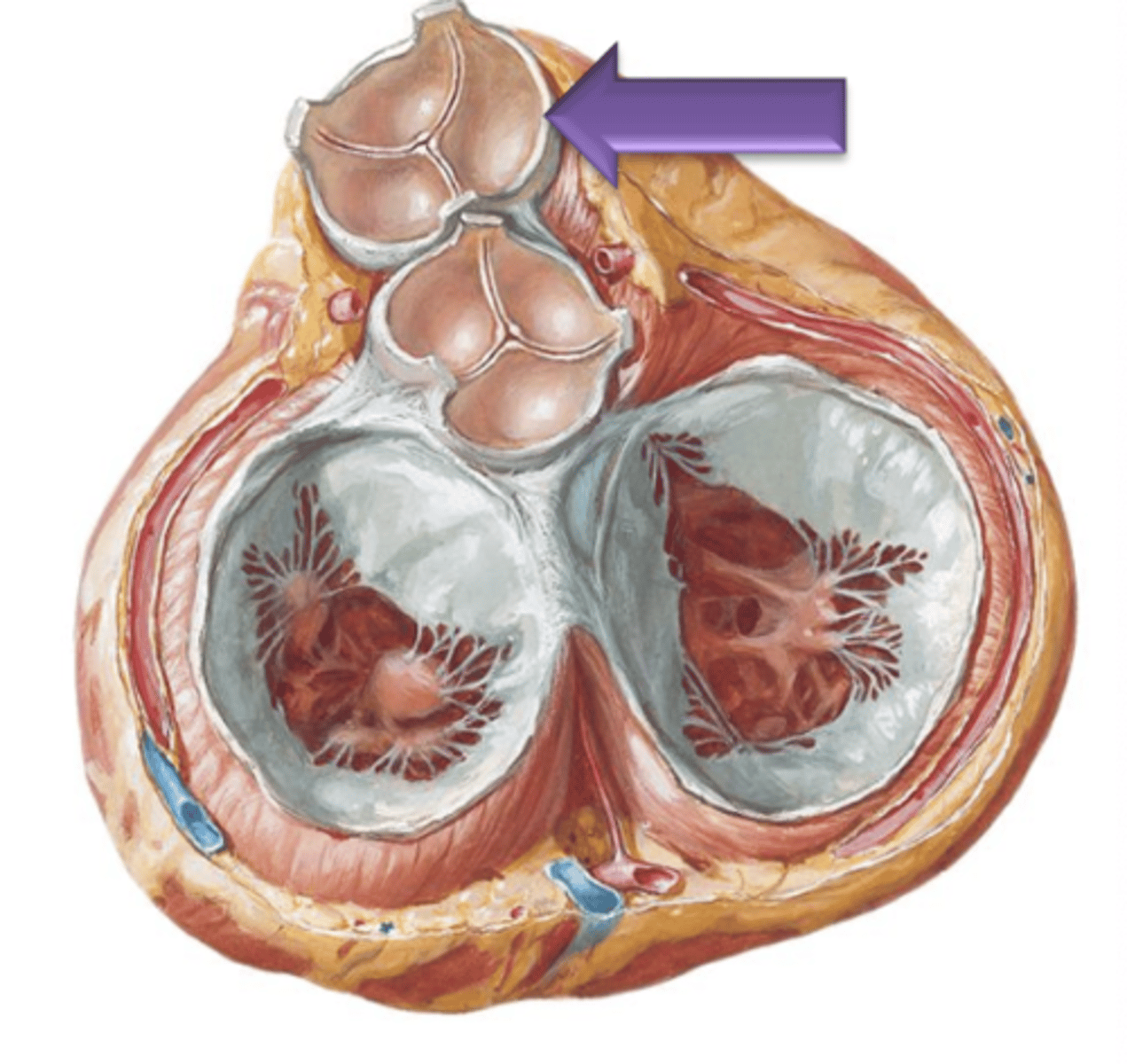
Nodule
The small central thickening of fibrous tissue on the free edge of the cusp.
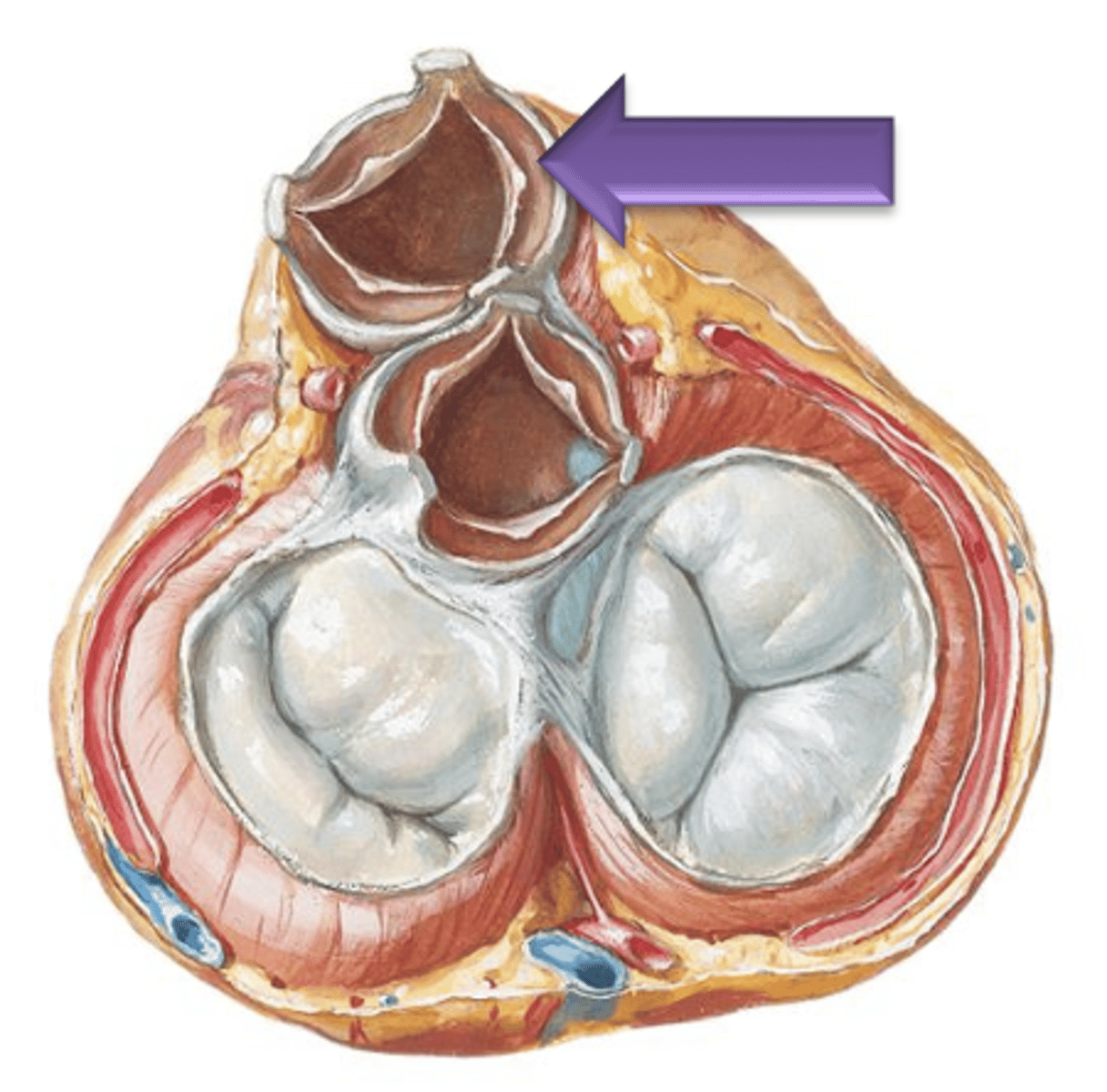
Lunula
Narrow thin crescent area extending from each side of the nodule on the cusp.
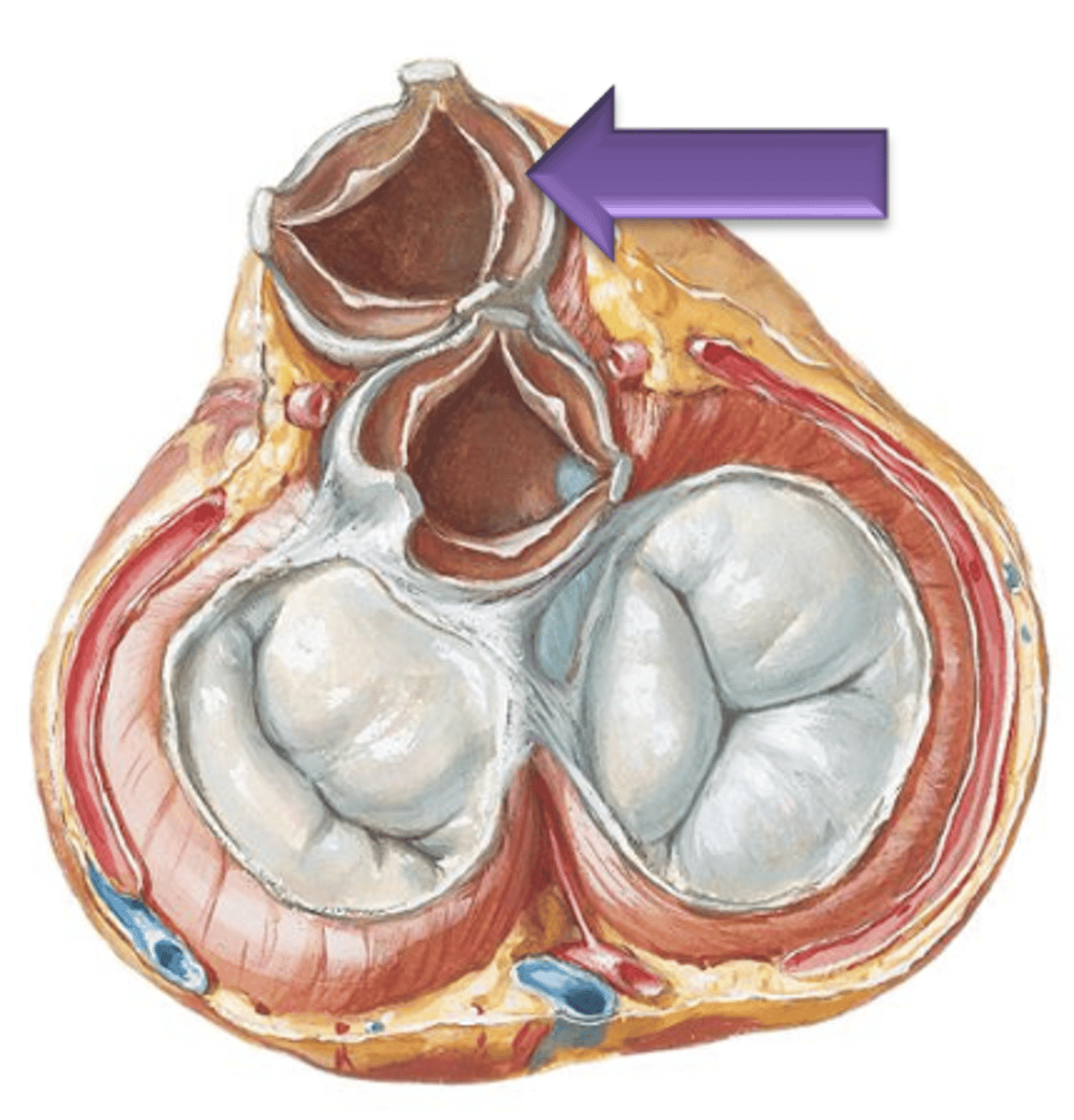
Sinuses
The spaces between the cusps and the wall of the vessel.
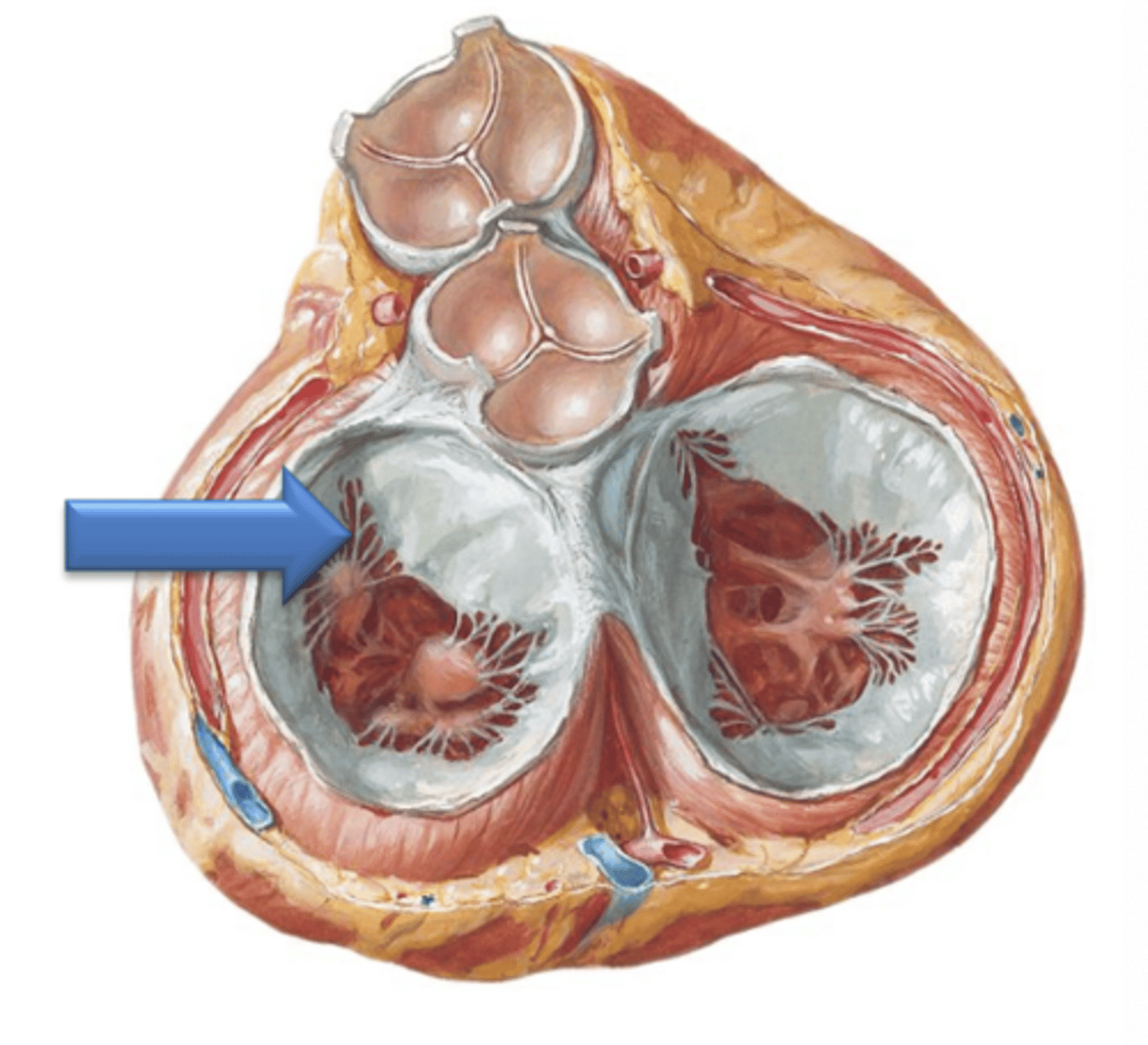
Left Atrium
Has musculi pectinati located within the left auricle only; the rest of its internal surface is smooth.
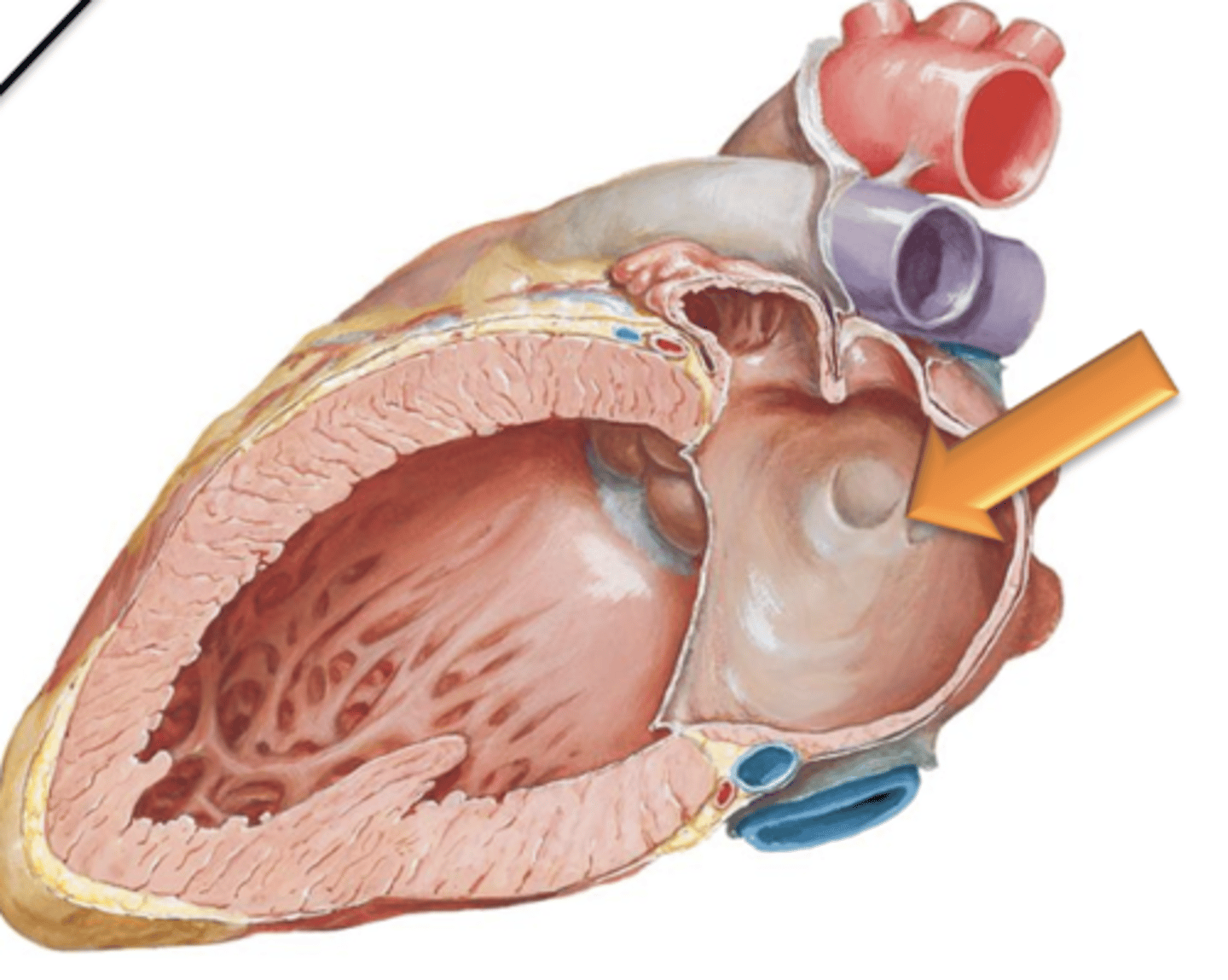
Left Atrioventricular Opening
the majority of the surface area of the left atrium is taken up by the 4 separate openings of the pulmonary veins. The only other opening of the left atrium is the ___ ___ ___.
Bicuspid Valve (Mitral Valve, Left Atrioventricular Valve)
The left atrioventricular opening is guarded by what?
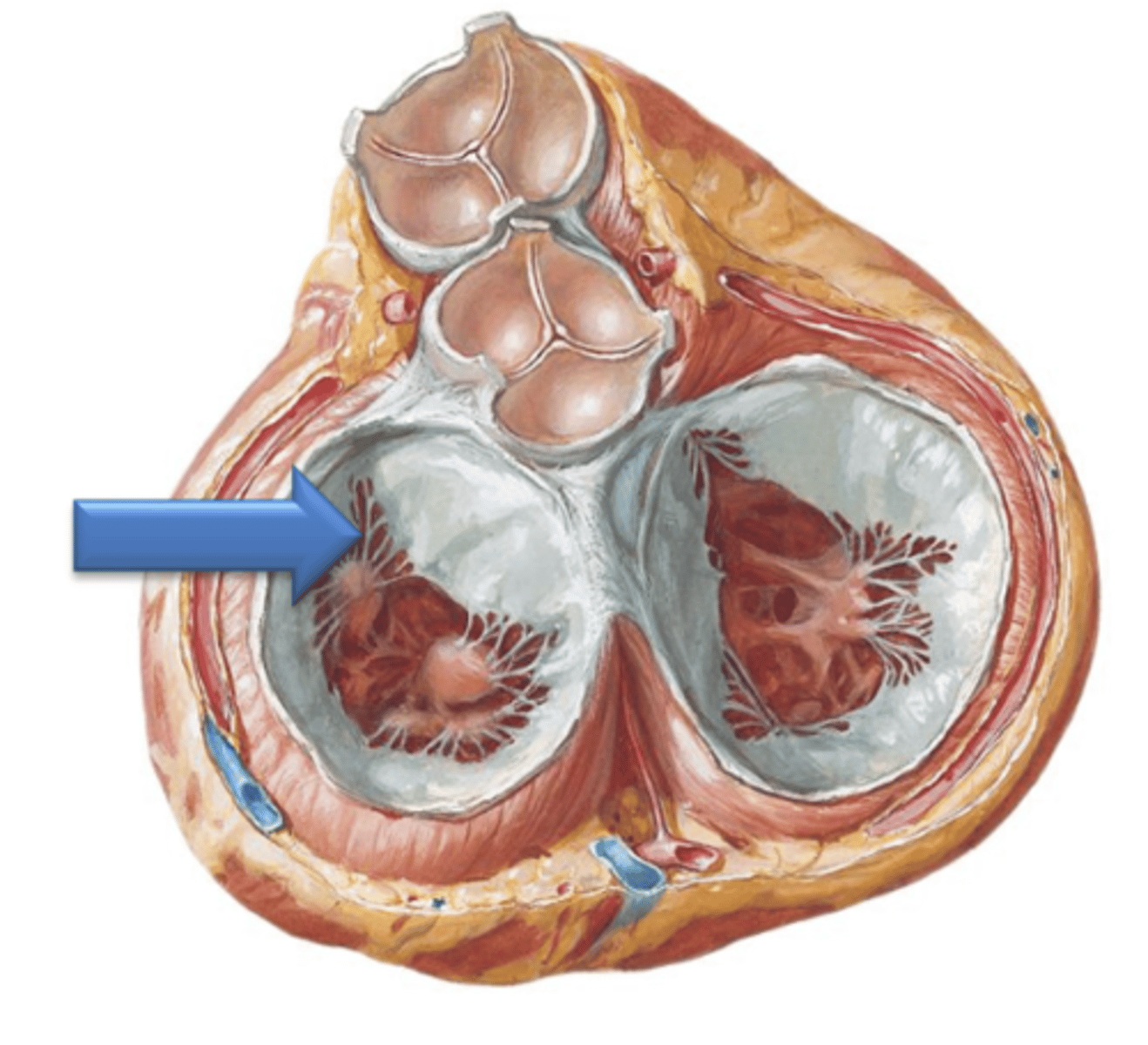
2
The bicuspid valve has how many cusps?
Left and right Ventricles
This (like the right) contains the internal muscular ridge like folds called Trabeculae Carneae.
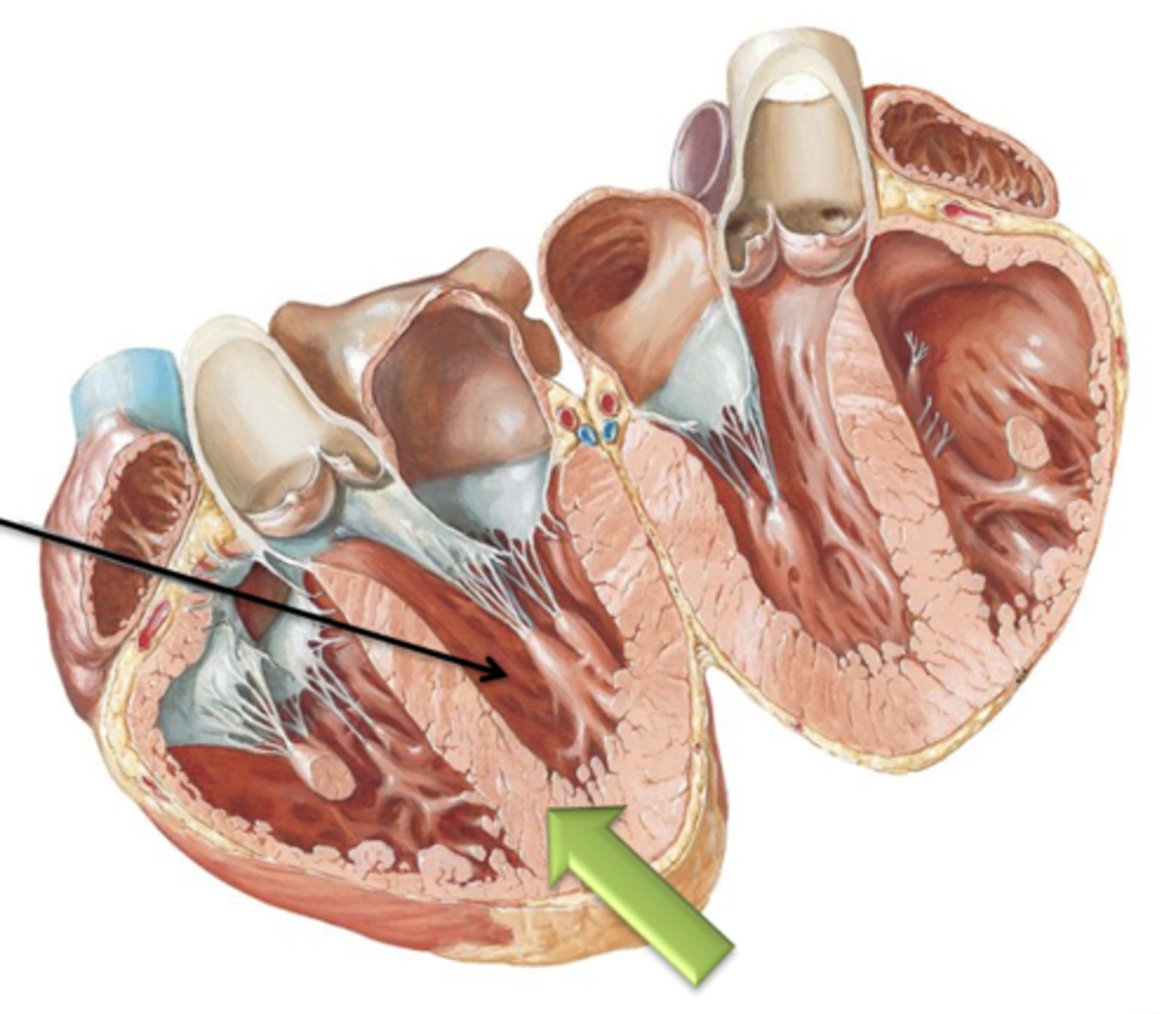
Interventricular Septum
Both ventricles are separated by the ___ ___.
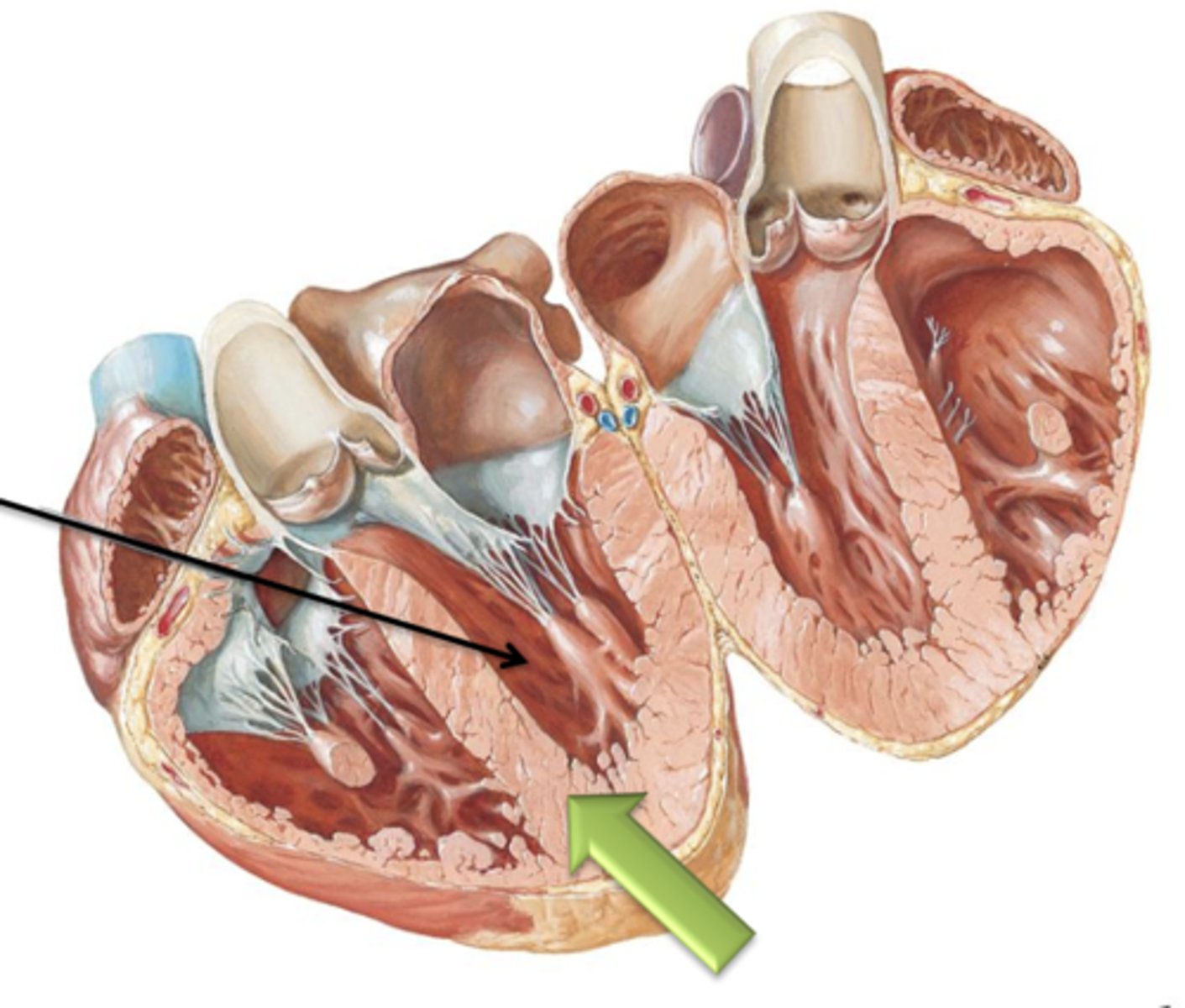
twice
The wall of the left ventricle is usually ___ as thick as that of the right.
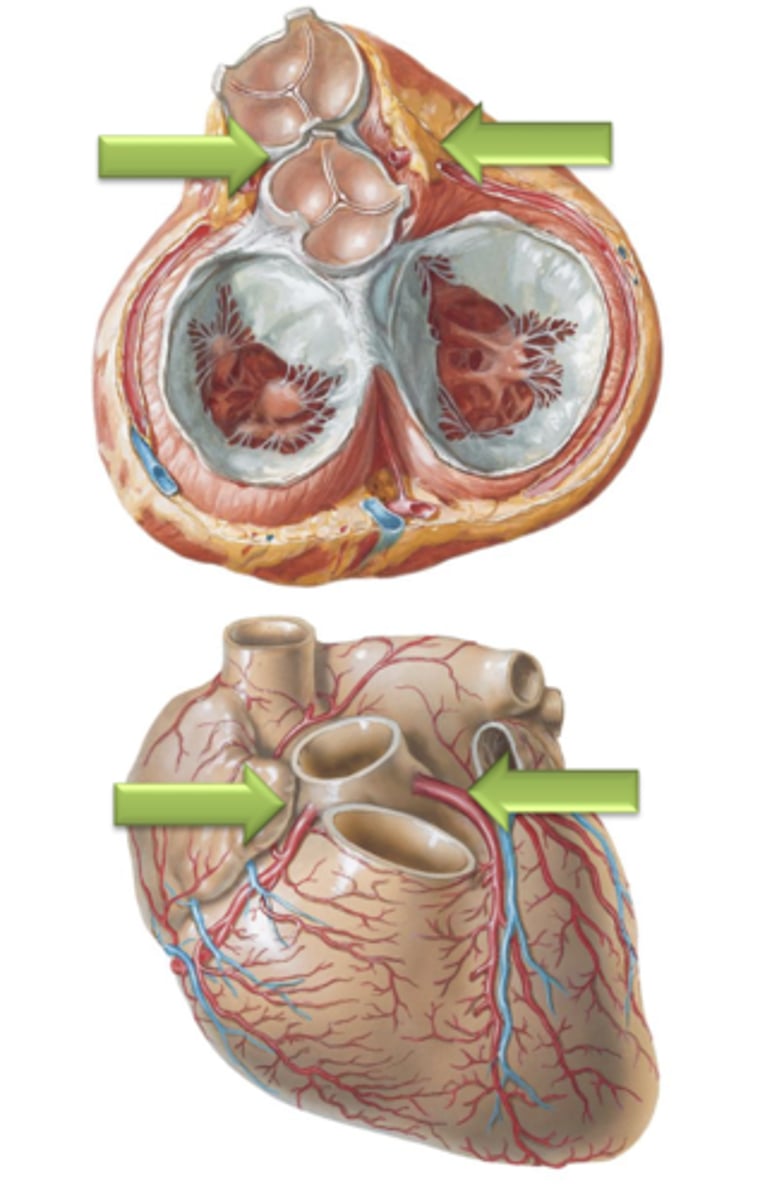
Aortic Semilunar Valve
The opening to the aorta is guarded by the ___ ___ ___.
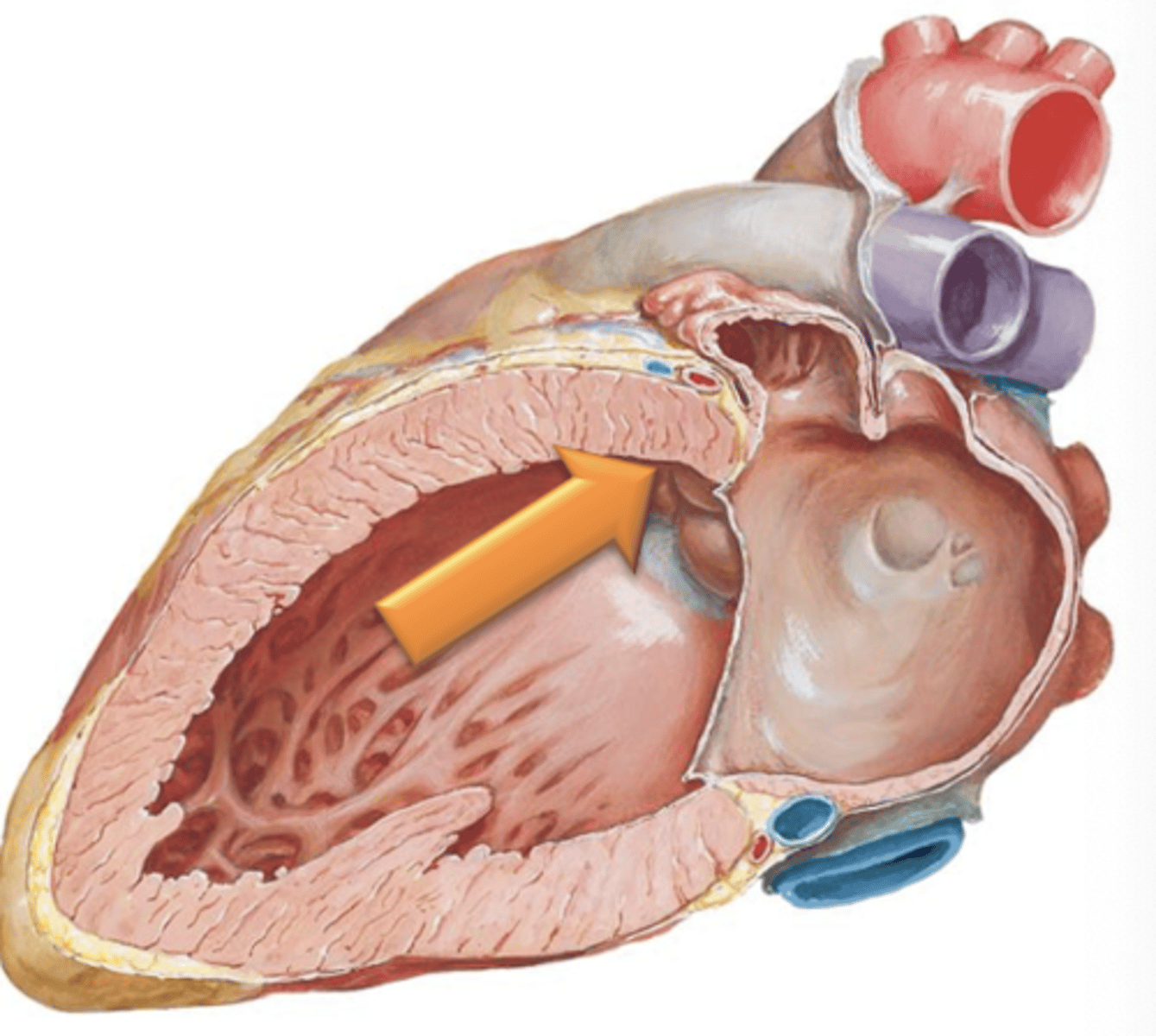
Aortic Sinuses
The spaces between the cusps of the aortic semilunar valve and the wall of the aorta. These are the sites of origin for the right and left coronary arteries which supply the myocardium in coronary circulation.
Right Atrium, Tricuspid Valve, Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Semilunar Valve, Pulmonary Trunk, Pulmonary Arteries, Pulmonary Veins, Left Atrium, Bicuspid Valve, Left Ventricle, Aortic Semilunar Valve, Aorta
What is the direction of blood flow through the heart (including pulmonary circulation)?
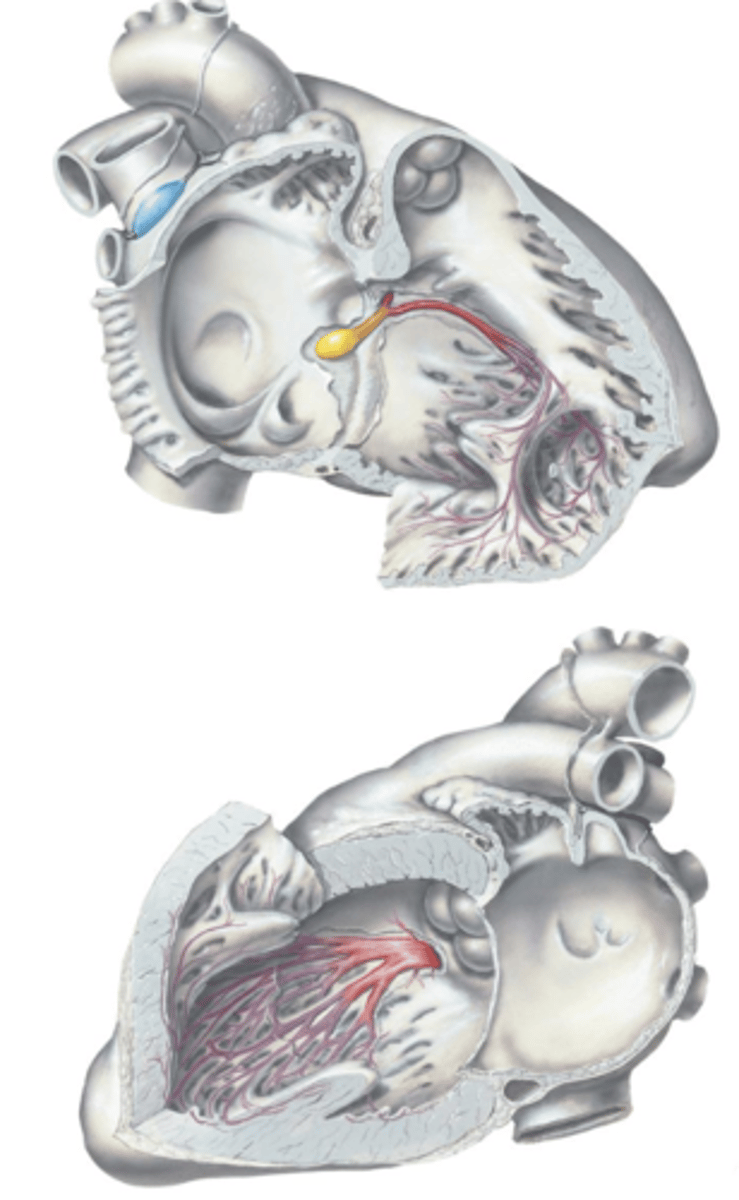
Sinuatrial (SA) Node
The nerve impulse initiates at the ___ ___ located at the base of the superior vena cava superior to the right atrium.
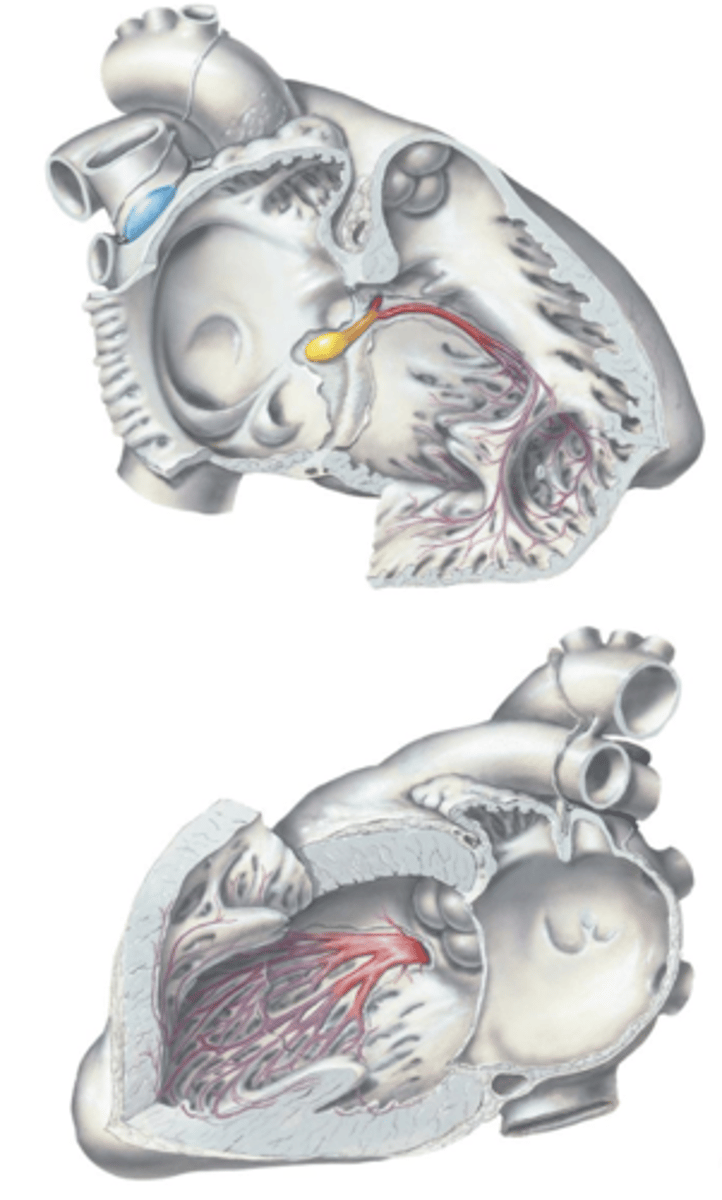
Atrioventricular (AV) Node, Atrioventricular (AV) Bundle (of His)
After the SA Node, the impulse is carried to the ___ ___ located within the membranous septum and is carried down the ___ ___.
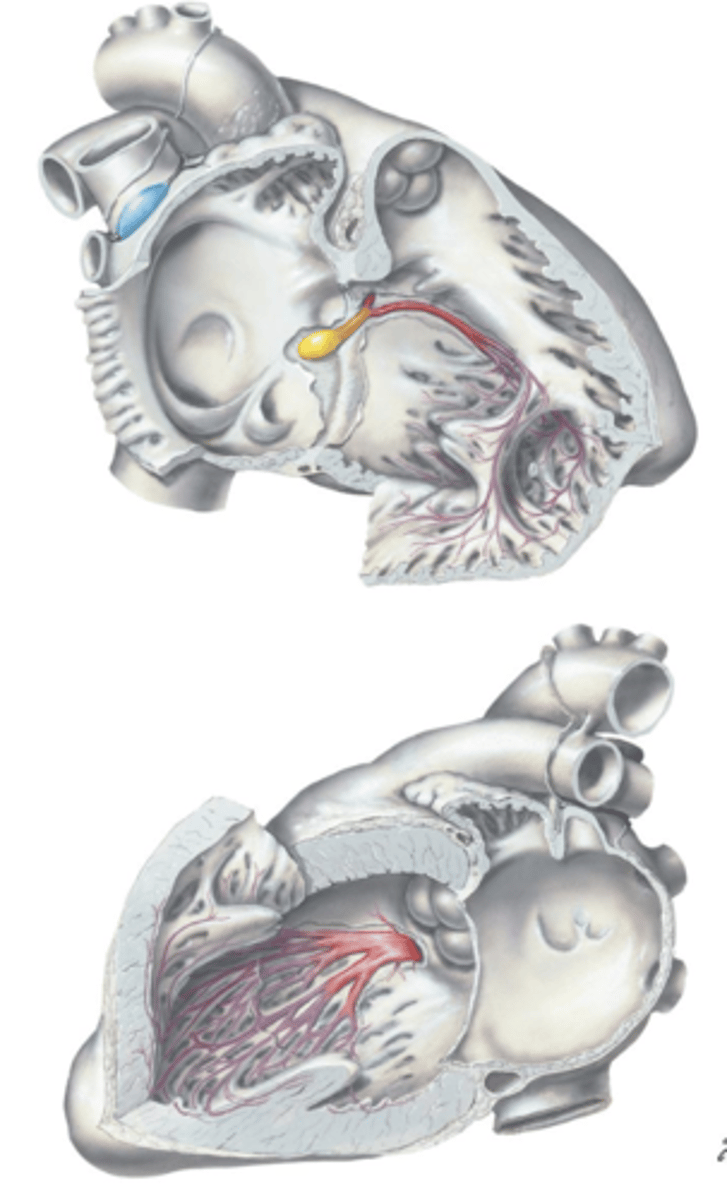
Left and Right Bundle Branches, Purkinje Fibers
From the Atrioventricular (AV) Bundle (of His), the impulse is carried down the ___ and ___ ___ ___ to the ___ ___ which radiate throughout the ventricles.
Vagus Nerve (CN X)
Parasympathetic innervation of the heart is supplied by what?
Acetylcholine (Ach), slowing
Release of the neurotransmitter ___ at the SA Node will act to decrease the rate and intensity of myocardial contractions, thus ___ the heart rate.
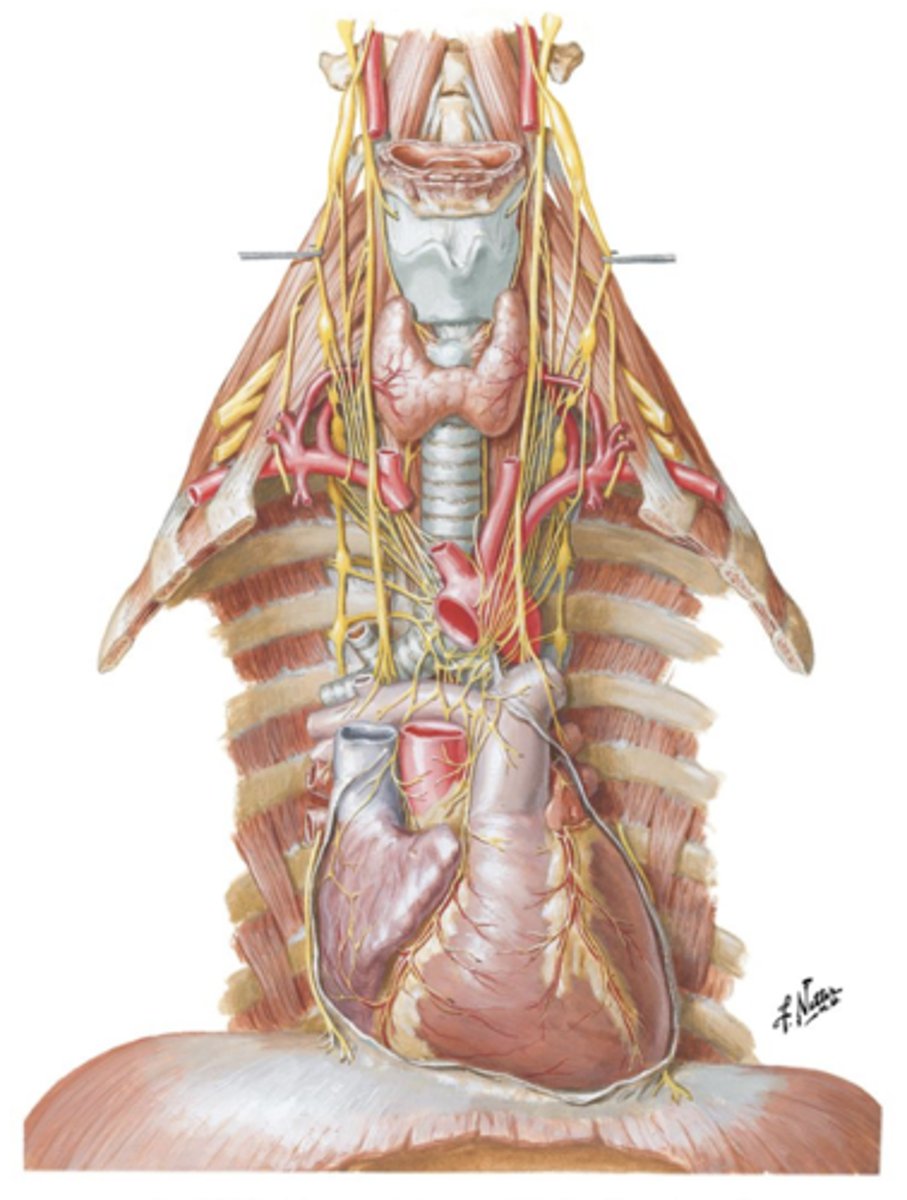
Sympathetic Chain Ganglion
Sympathetic innervation of the heart is derived from the ___ ___ ___ located on either side of the spinal column.
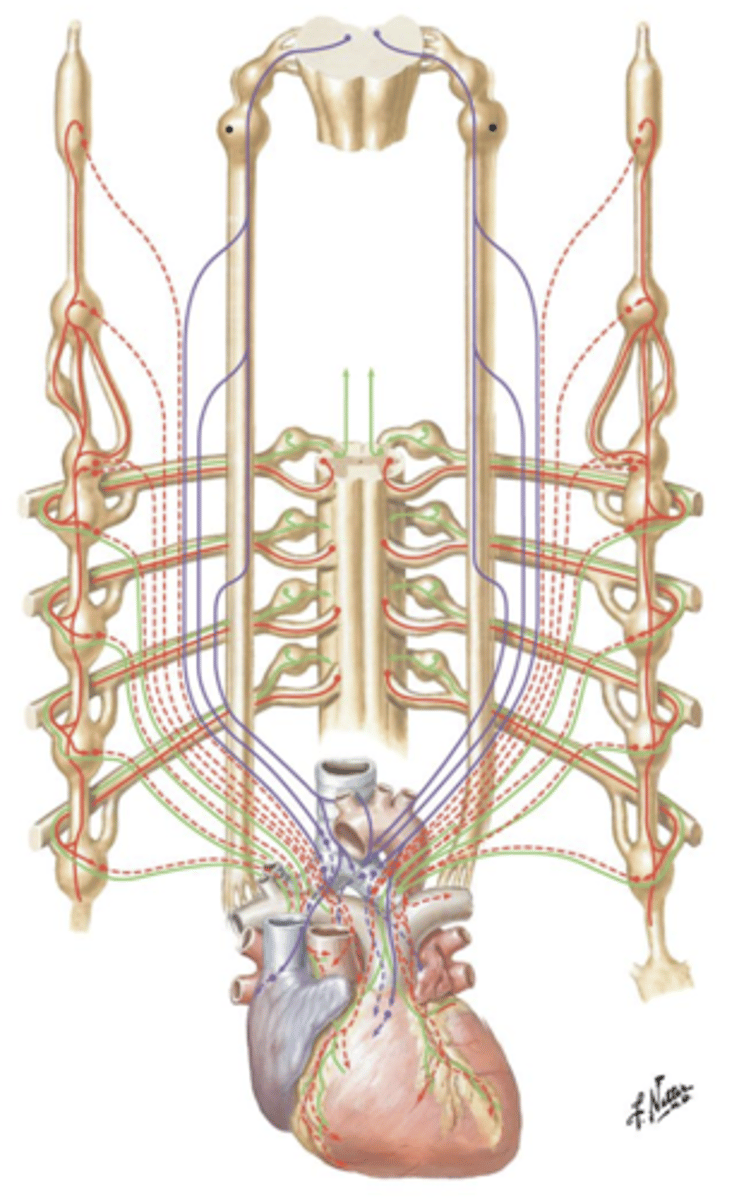
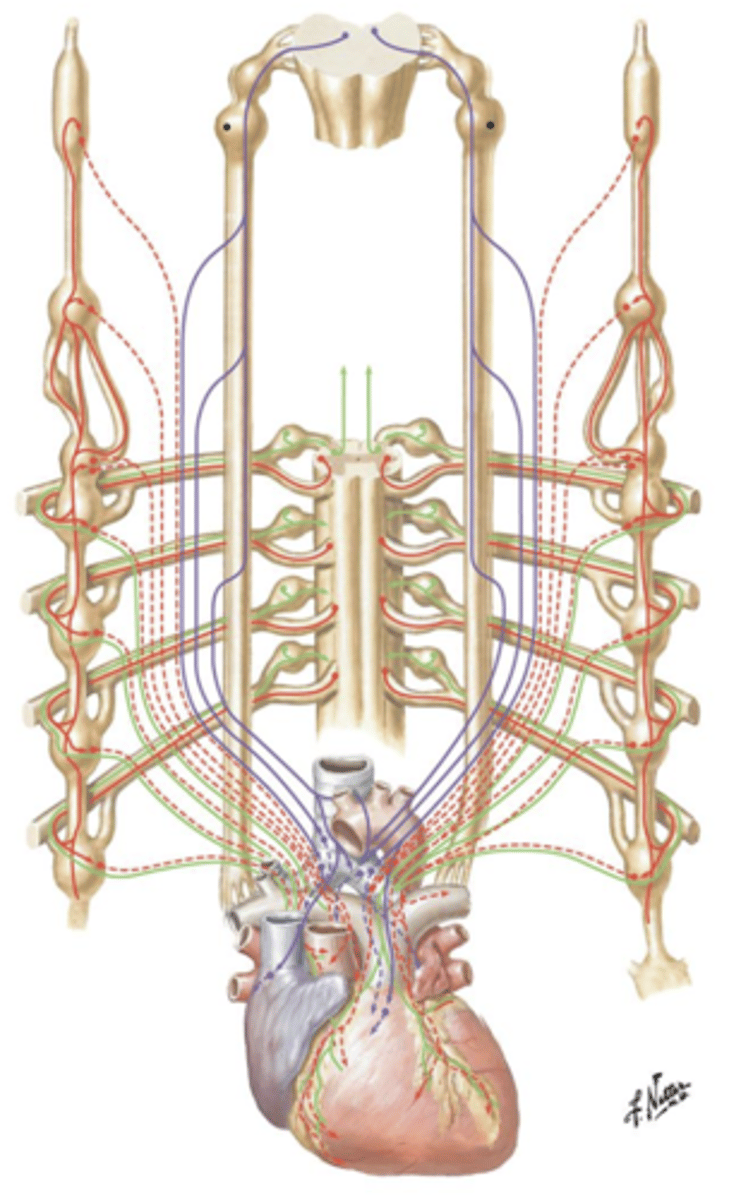
Norepinephrine, increased
Release of the neurotransmitter ___ directly to the myocardium of the ventricles will result in ___ heart rate.
Brachiocephalic Trunk
The first main branch off the aortic arch is what?
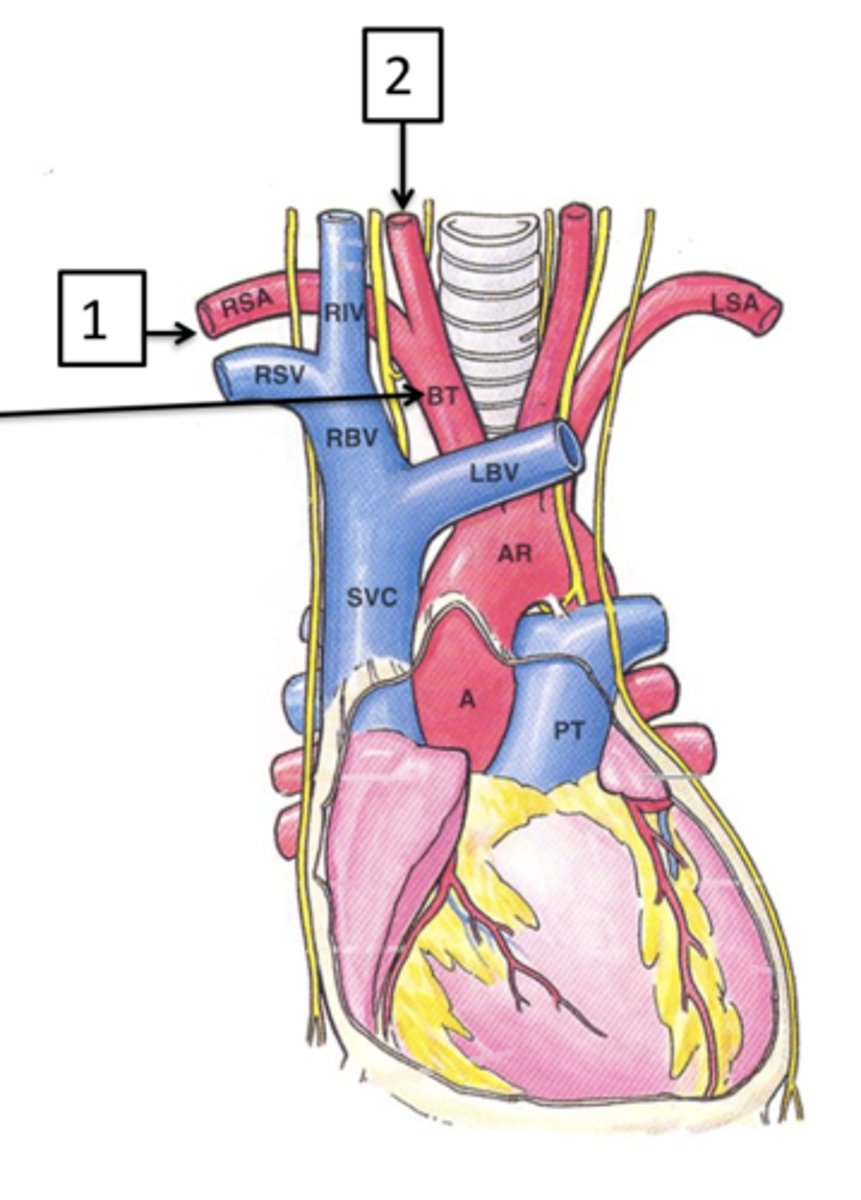
Right Subclavian Artery, Right Common Carotid Artery
The brachiocephalic trunk quickly branches into the ___ ___ ___ and the ___ ___ ___ which supply the right upper limb and right side of the head respectively.
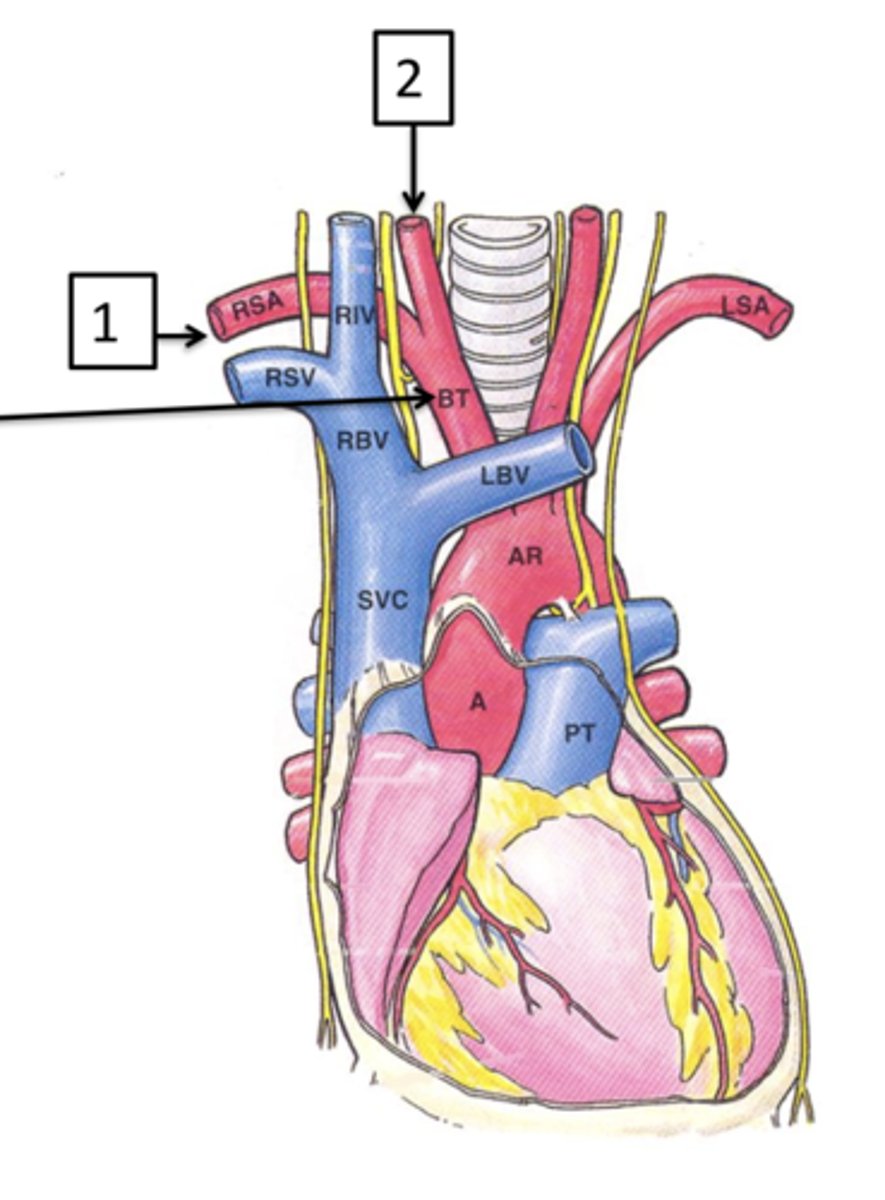
Left Common Carotid Artery
The next branch off the aortic arch is the ___ ___ ___ ___ which supplies the left side of the head.
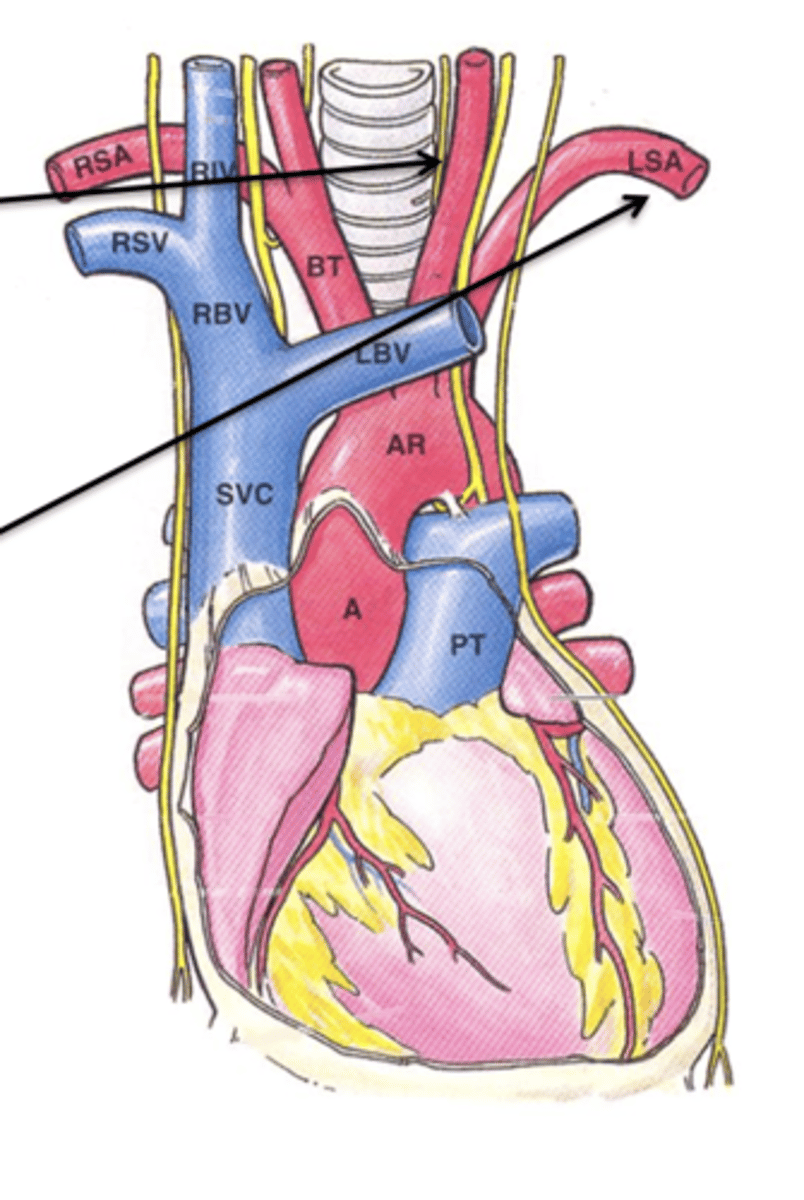
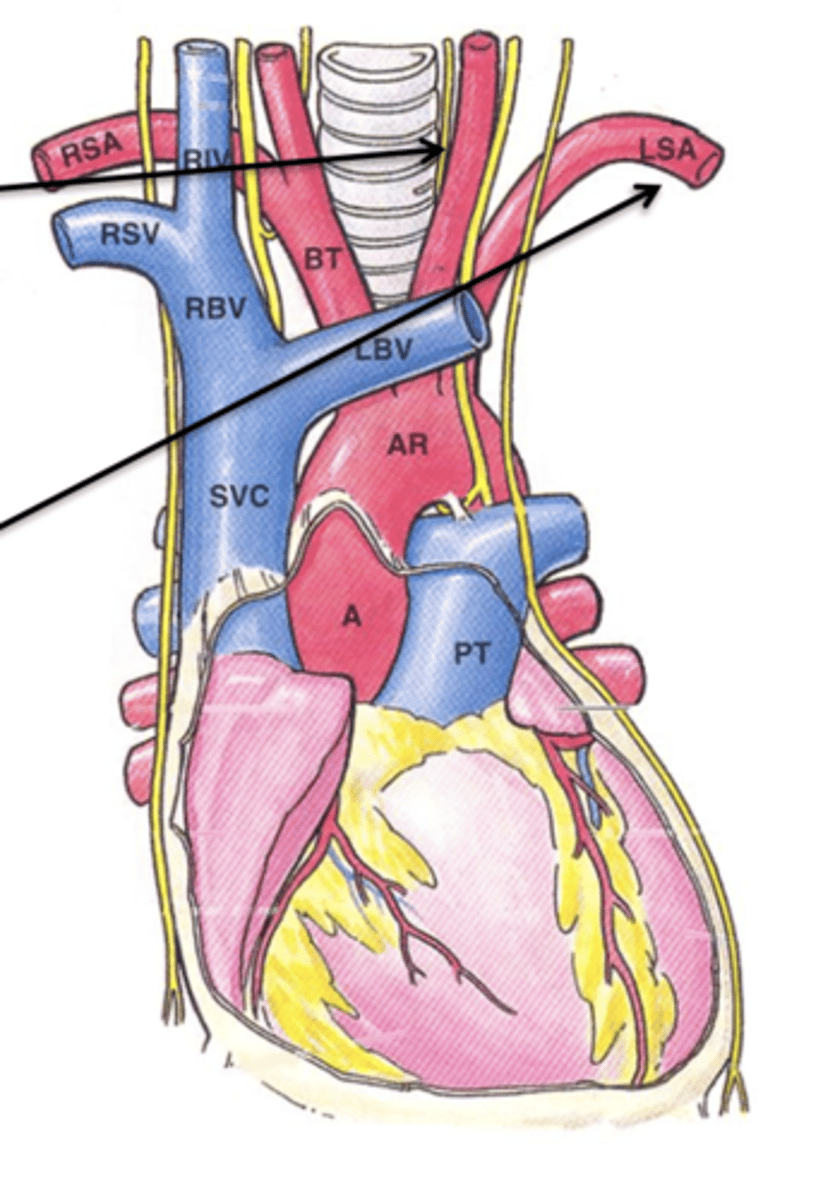
Left Subclavian Artery
The final branch off the aortic arch is the ___ ___ ___ which supplies the left upper limb.
Right Common Carotid Artery
The ___ ___ ___ ___ is a branch off of the brachiocephalic trunk that supplies the head and neck.
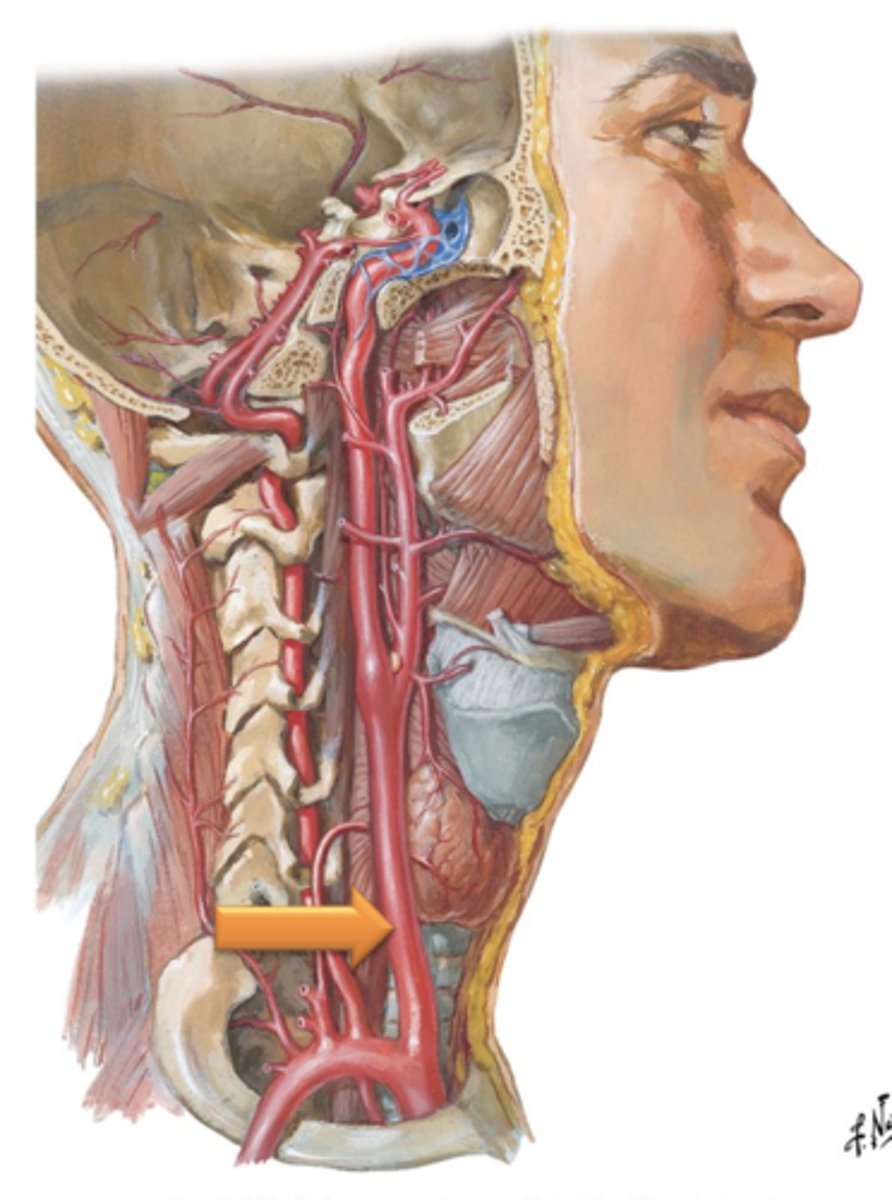
Left Common Carotid Artery
The ___ ___ ___ ___ is a branch off of the aortic arch that supplies the head and neck.
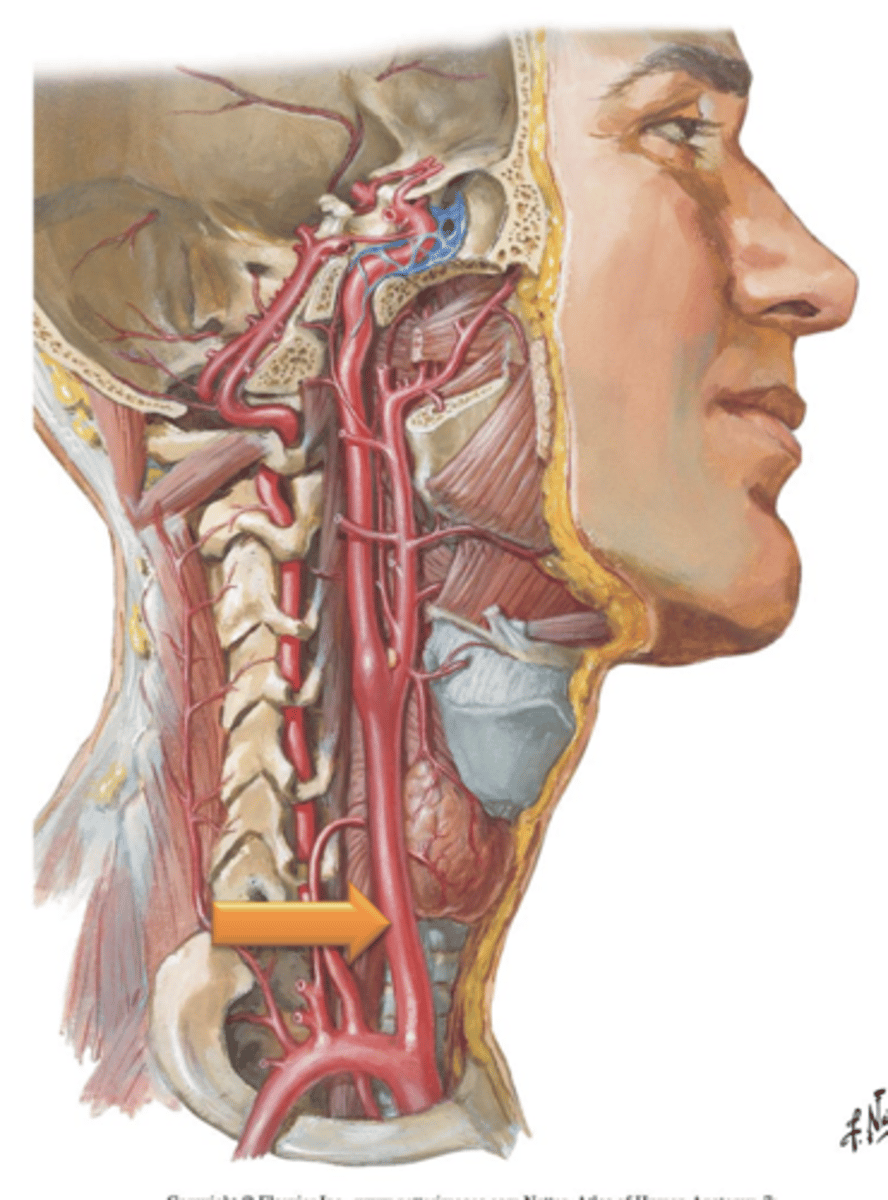
External Carotid Arteries
The left and right ___ ___ ___ branch from the common carotids and ascend through the neck posterior to the ramus of the mandible.
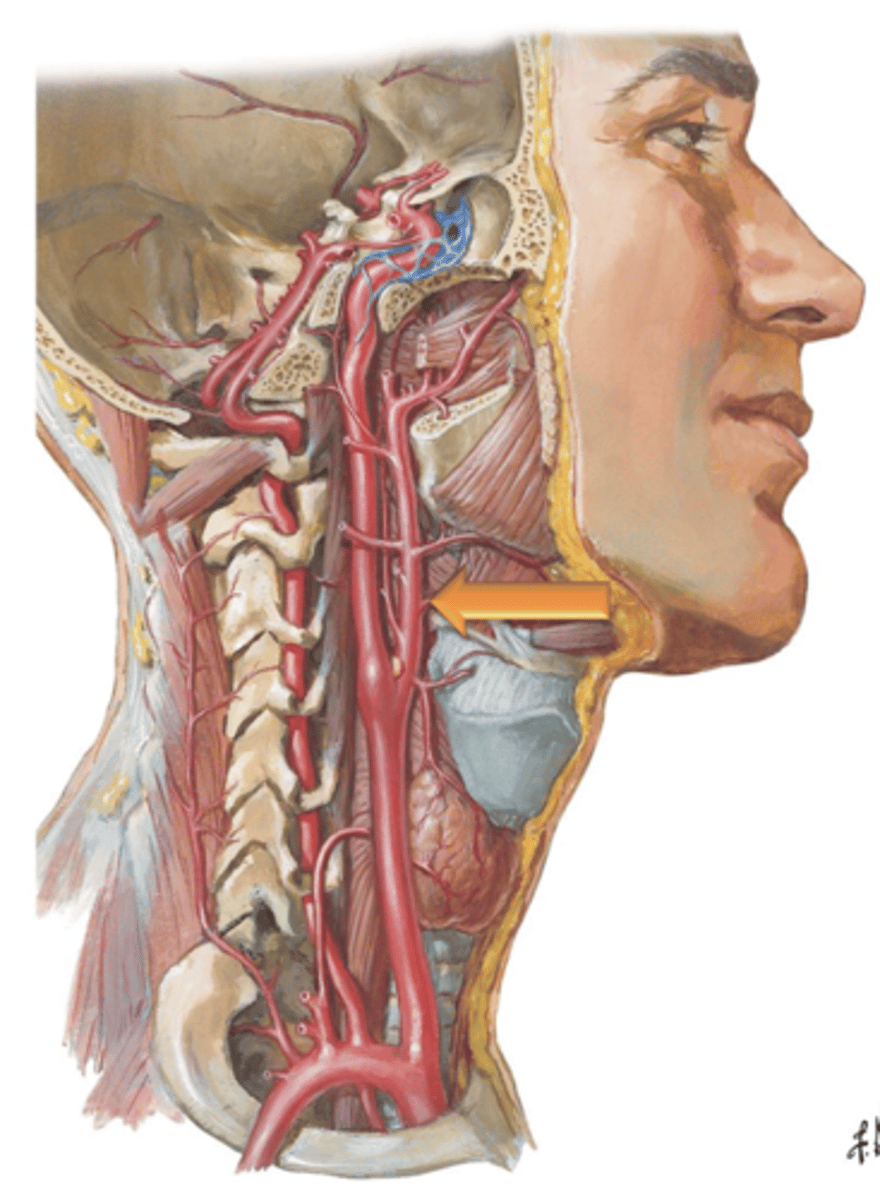
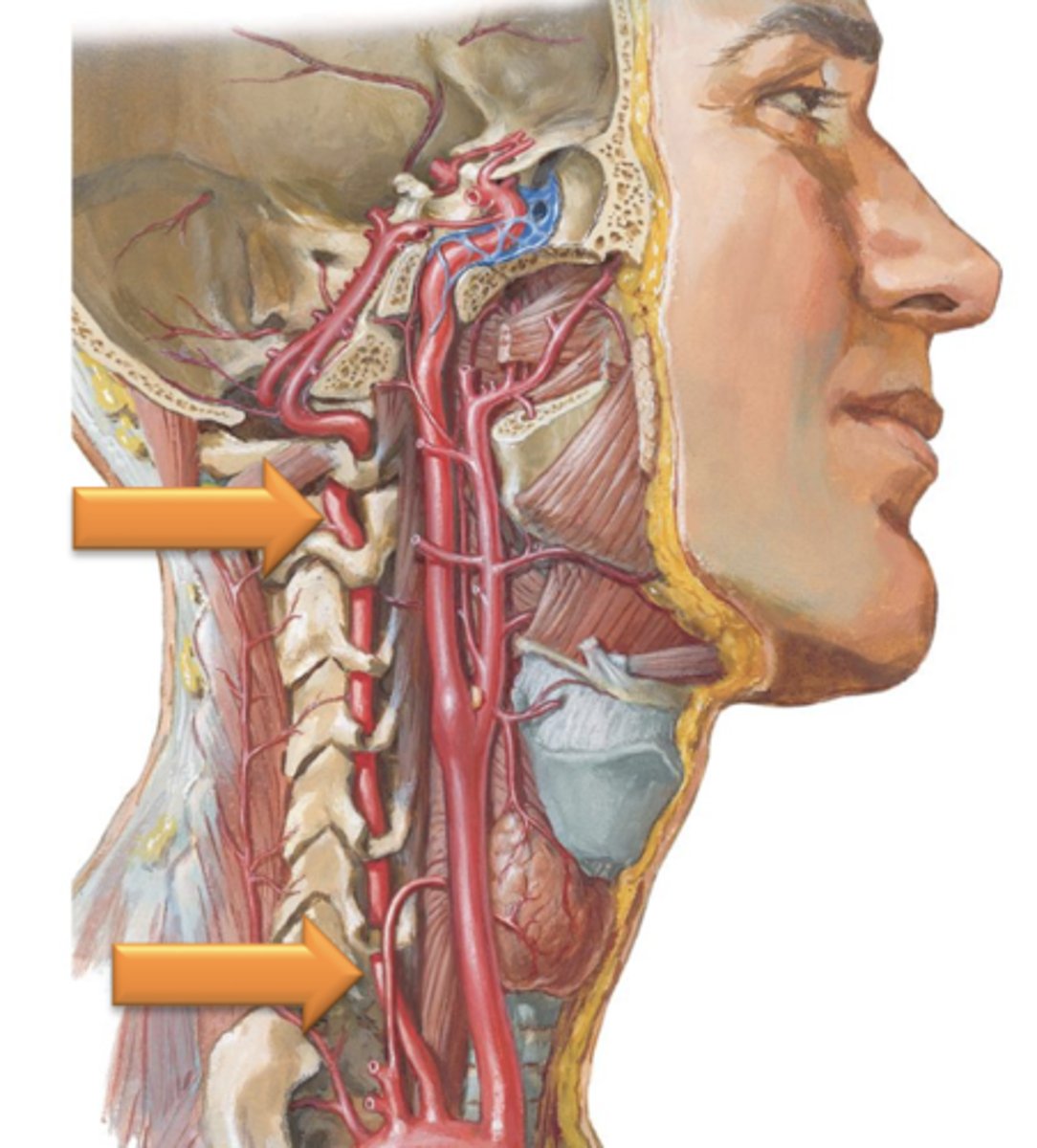
Internal Carotid Arteries, Carotid Canal
The ___ ___ ___ branch from the common carotid, ascend through the neck and enter the cranial cavity by traversing the ___ ___.
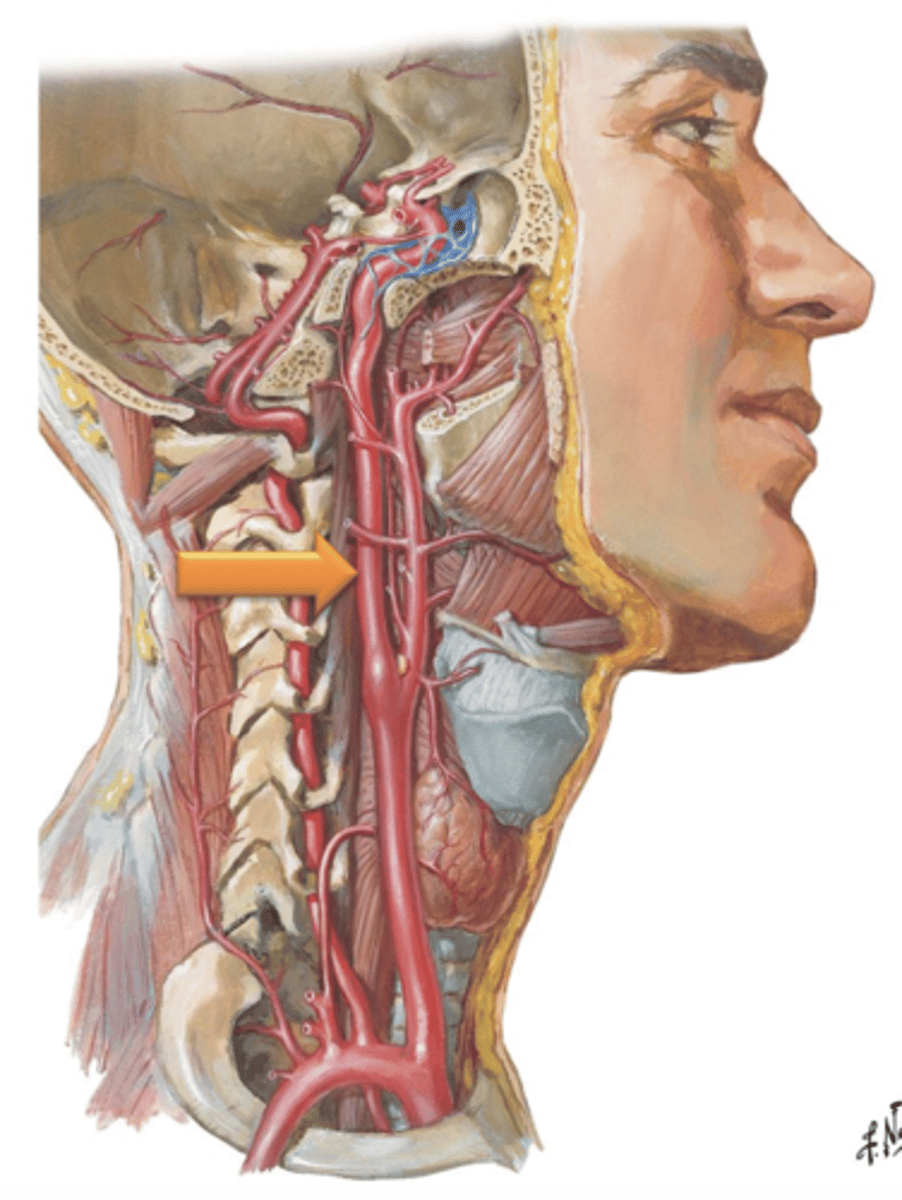
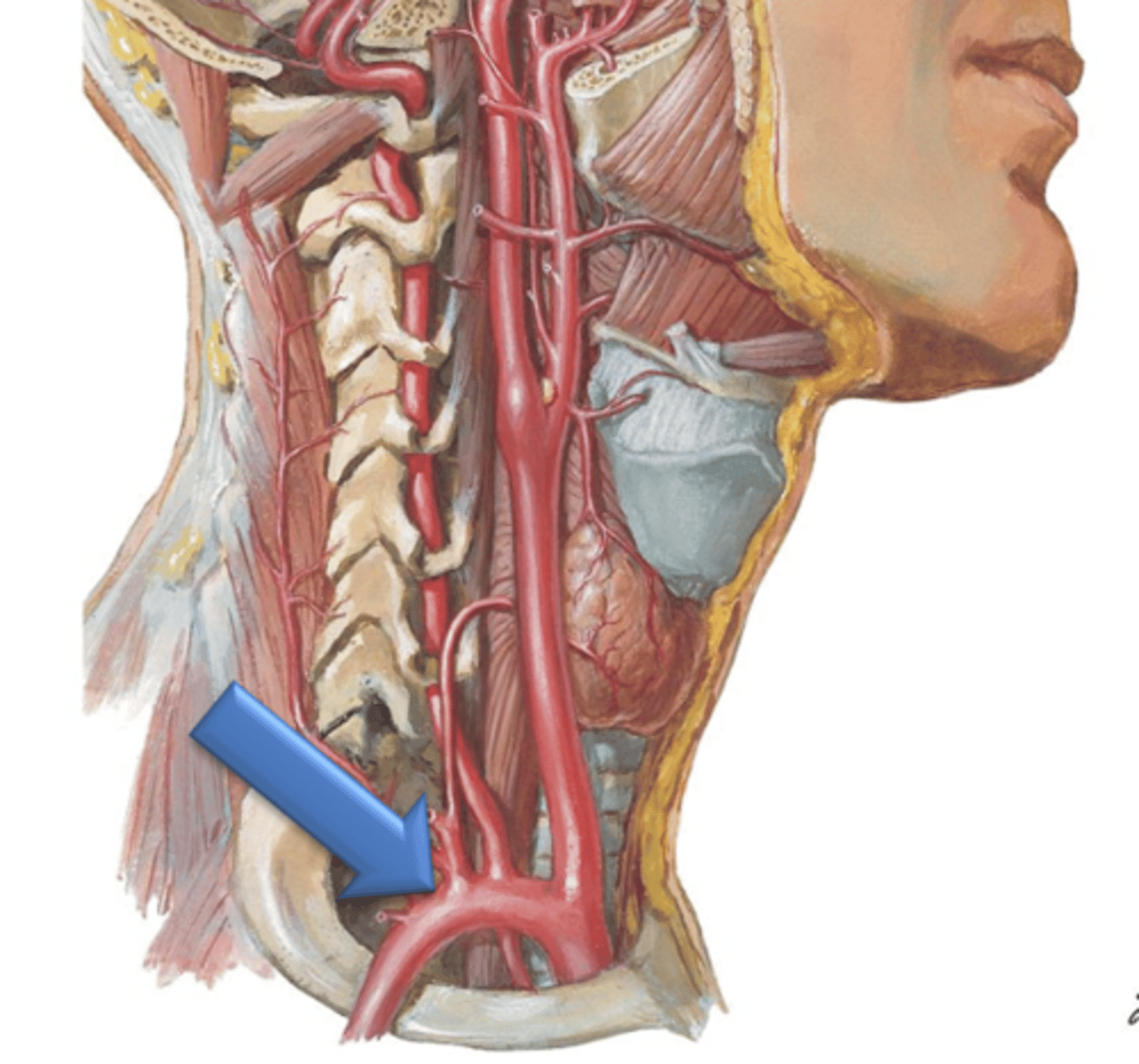
Vertebral Arteries, Transverse foramina
The ___ ___ branch from the subclavian arteries and ascend through the neck by coursing through the ___ ___ of the cervical vertebrae.
Subclavian Arteries
The left and right ___ ___ course between the clavicles and first ribs.
Axillary Arteries
As the Subclavian Arteries cross over the inferior border of the first rib they change their name to the ___ ___ which course through the axilla (armpit) and give off a total of 6 branches which supply the shoulder region.
Brachial Arteries
As the axillary arteries reach the inferior border of the teres major muscle, their name changes to the ___ ___ which course distally along the medial side of the arm.
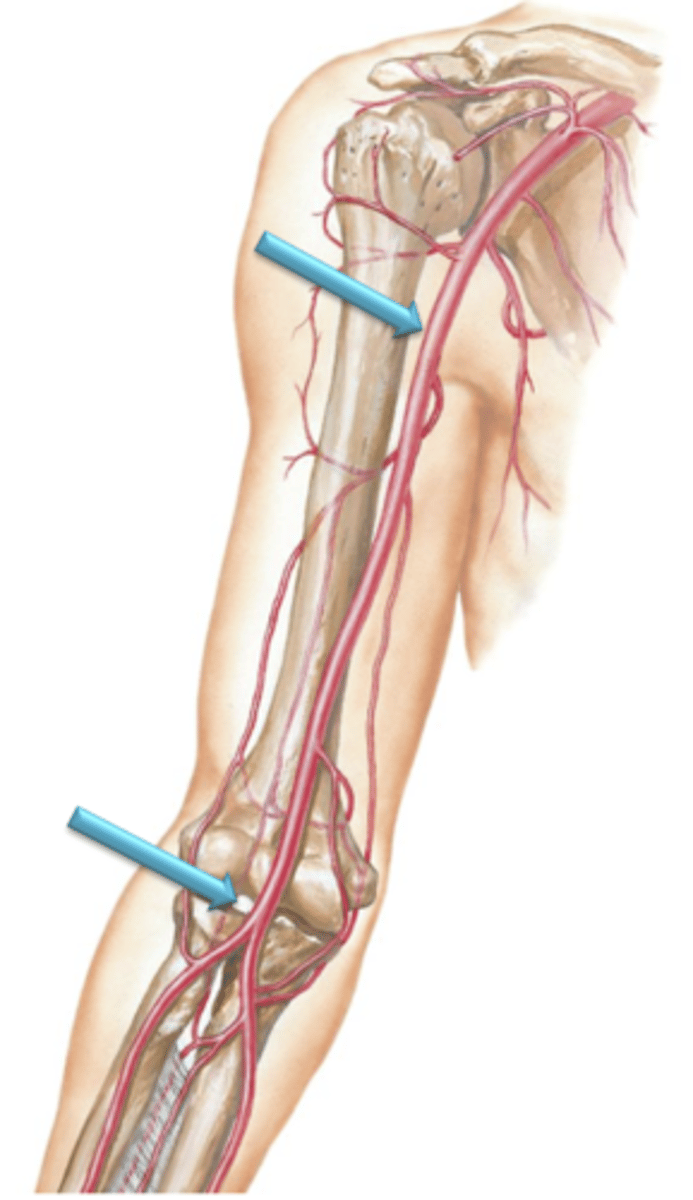
Profunda Brachii Artery
Arises as a large branch from the brachial artery and courses posterior to the humerus. It courses distally along the posterior surface of the arm between the medial and lateral heads of triceps brachii and supplies the posterior tissues of the arm.
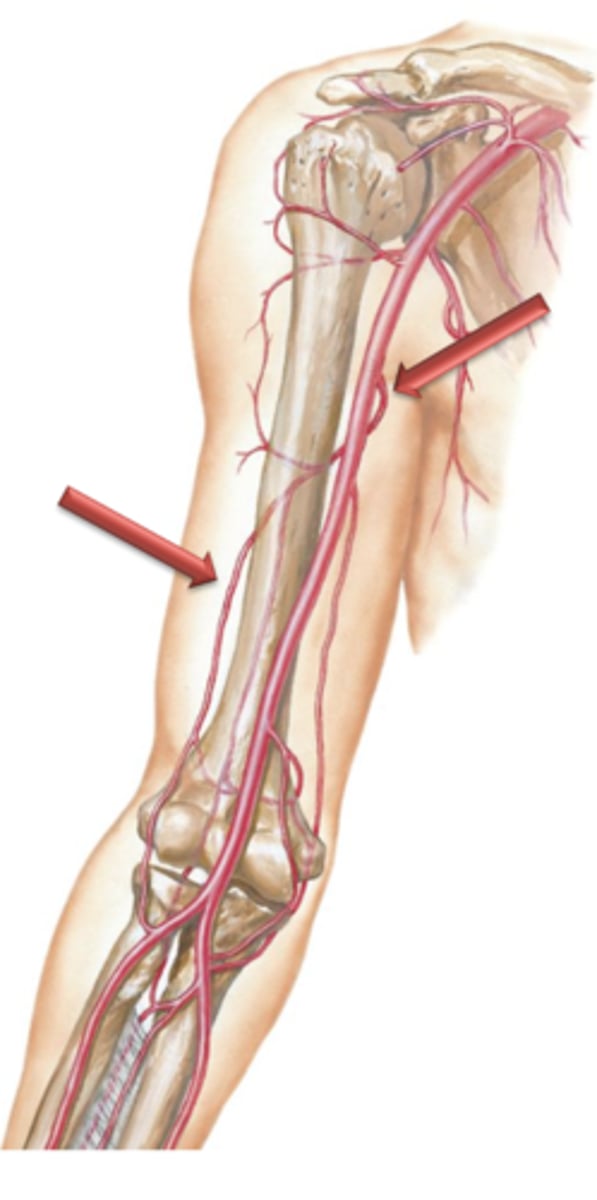
Radial Artery, Ulnary Artery
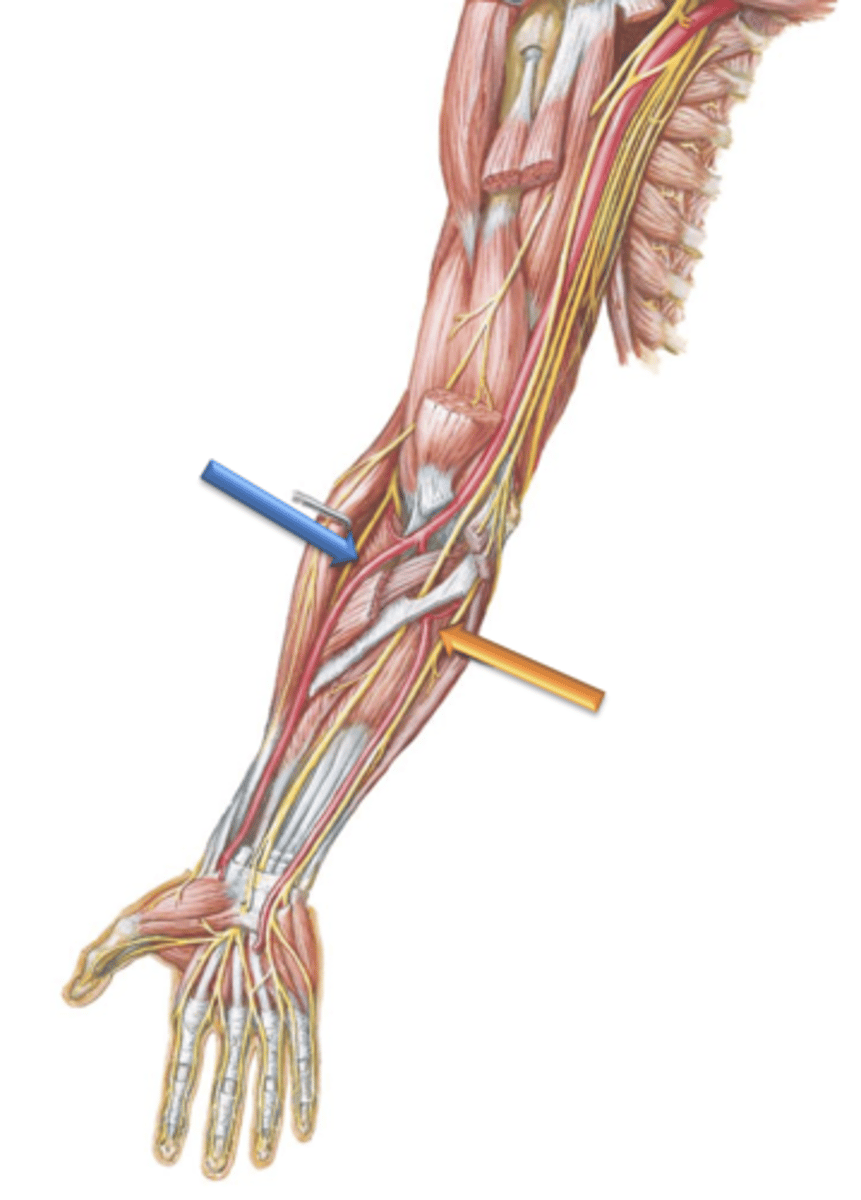
The brachial artery terminates anterior to the elbow by bifurcating into what?
Radial Artery
Artery that courses distally along the lateral surface of the forearm.
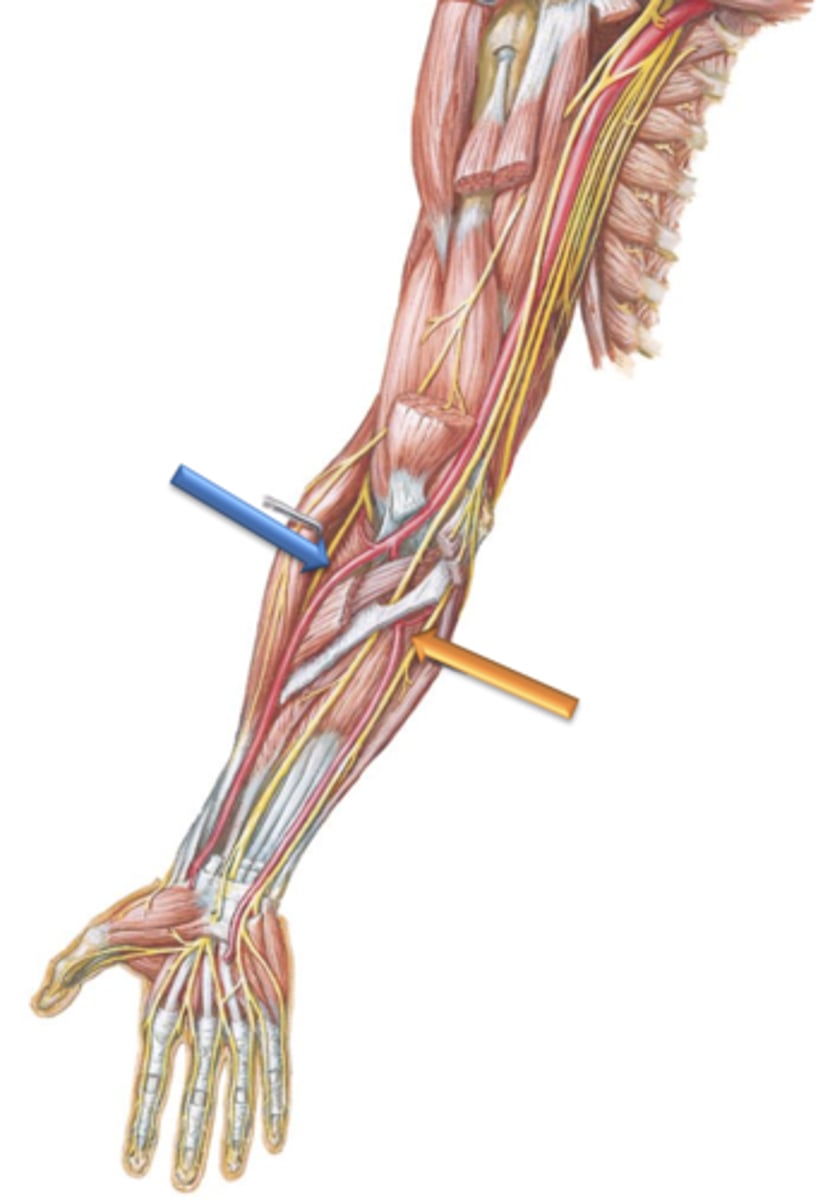
Ulnar Artery
Artery that courses distally along the medial surface of the forearm.
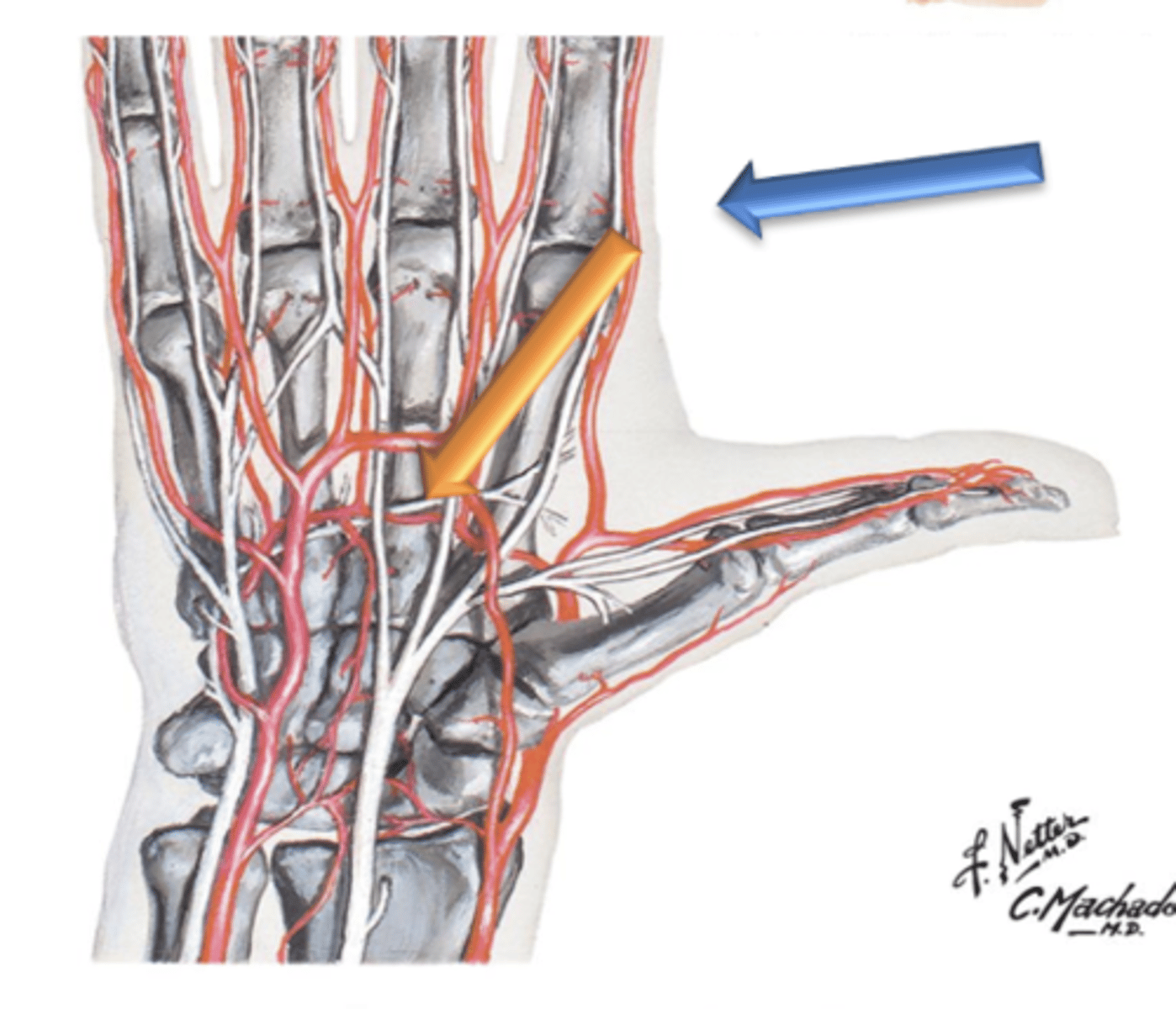
Superficial Palmar Arch
The Ulnar artery courses anterior to the wrist and terminates in the palm of the hand by forming what?
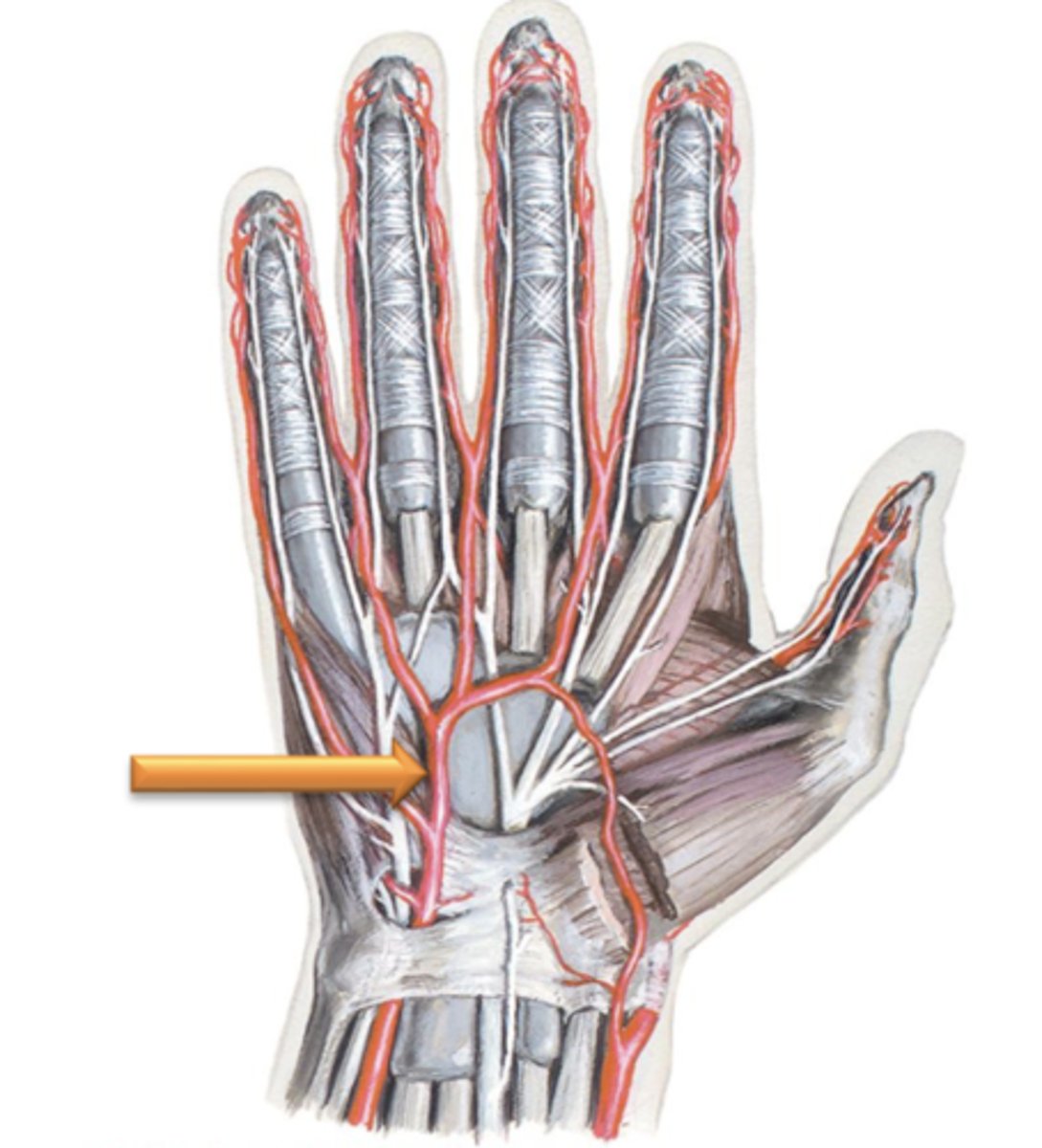
Deep Palmar Arch
The radial artery terminates in the palm of the hand by forming what?
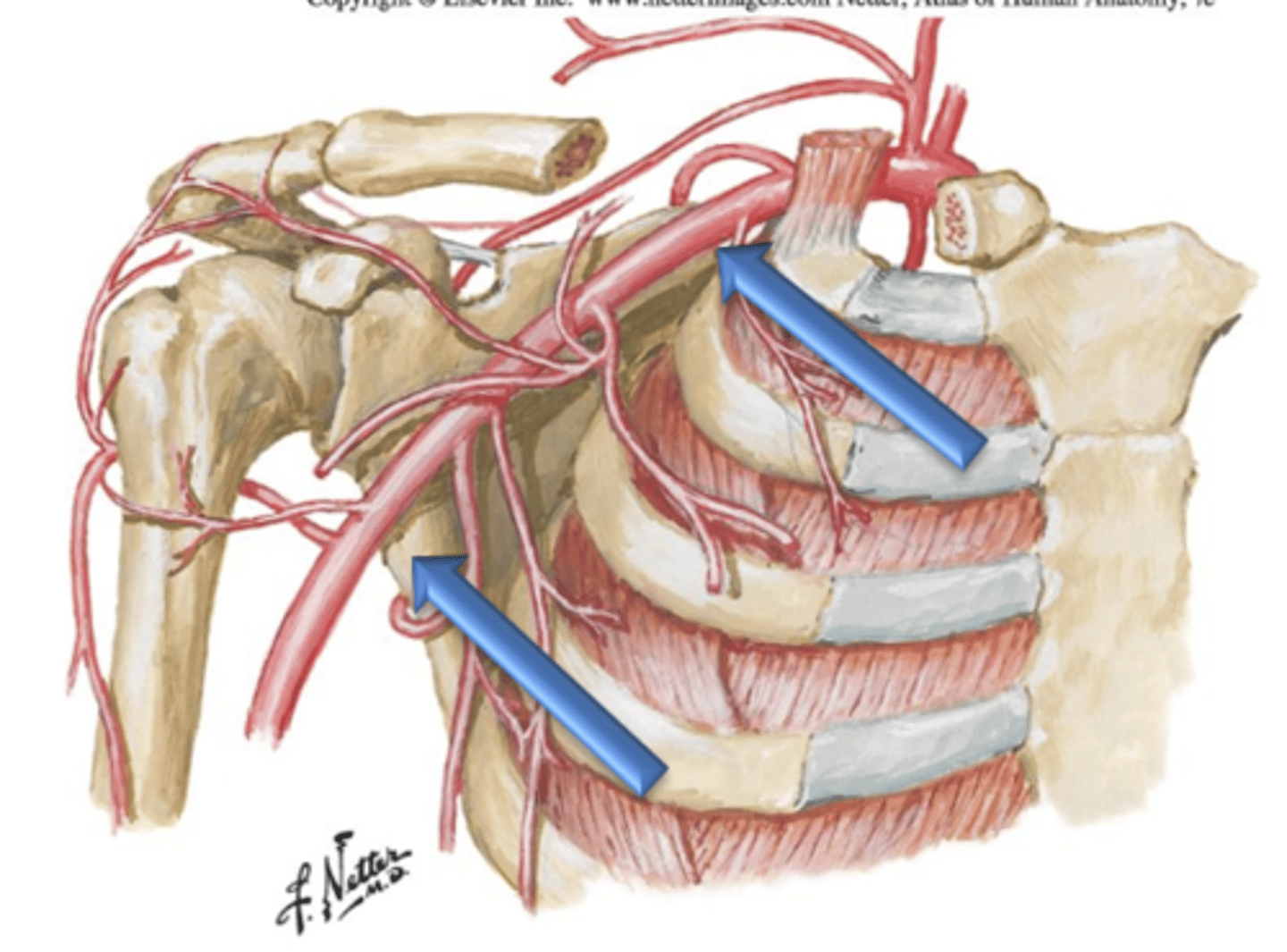
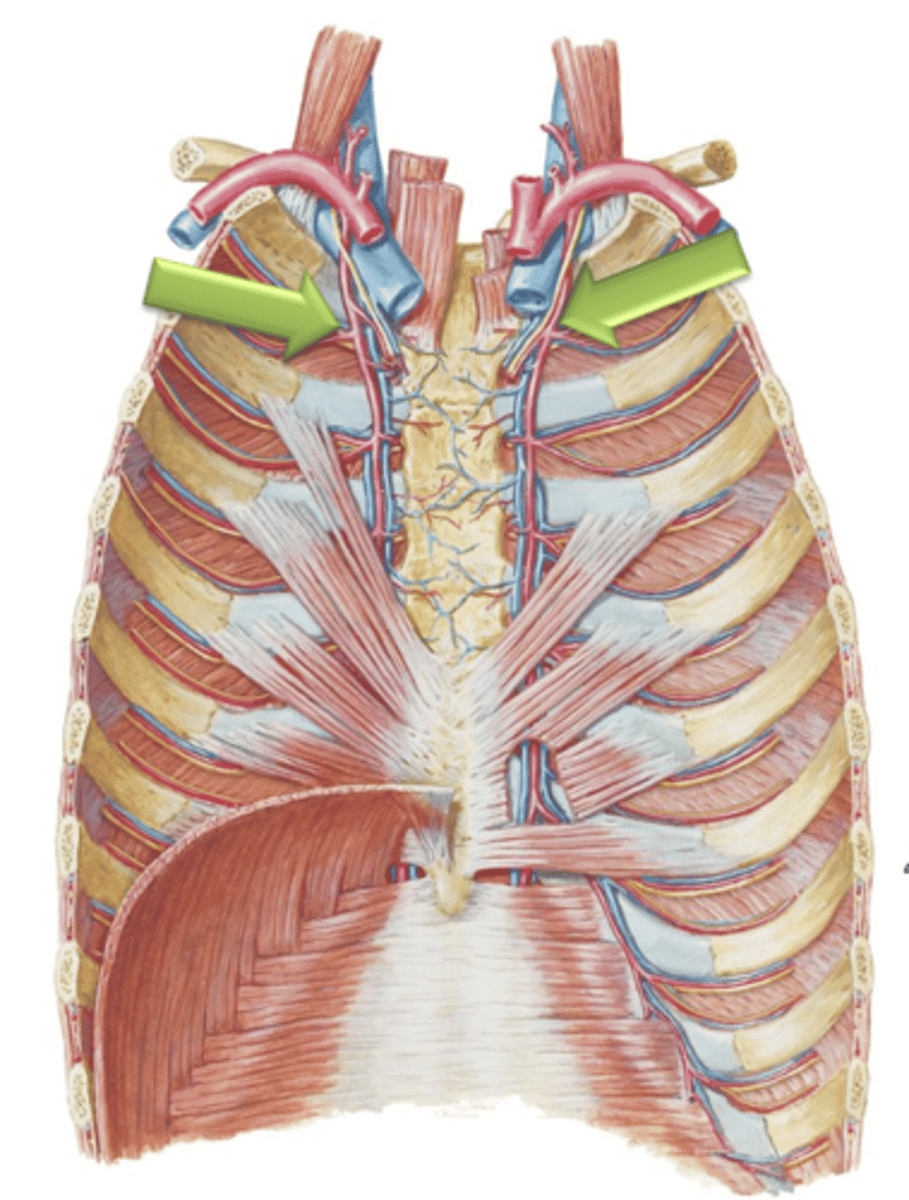
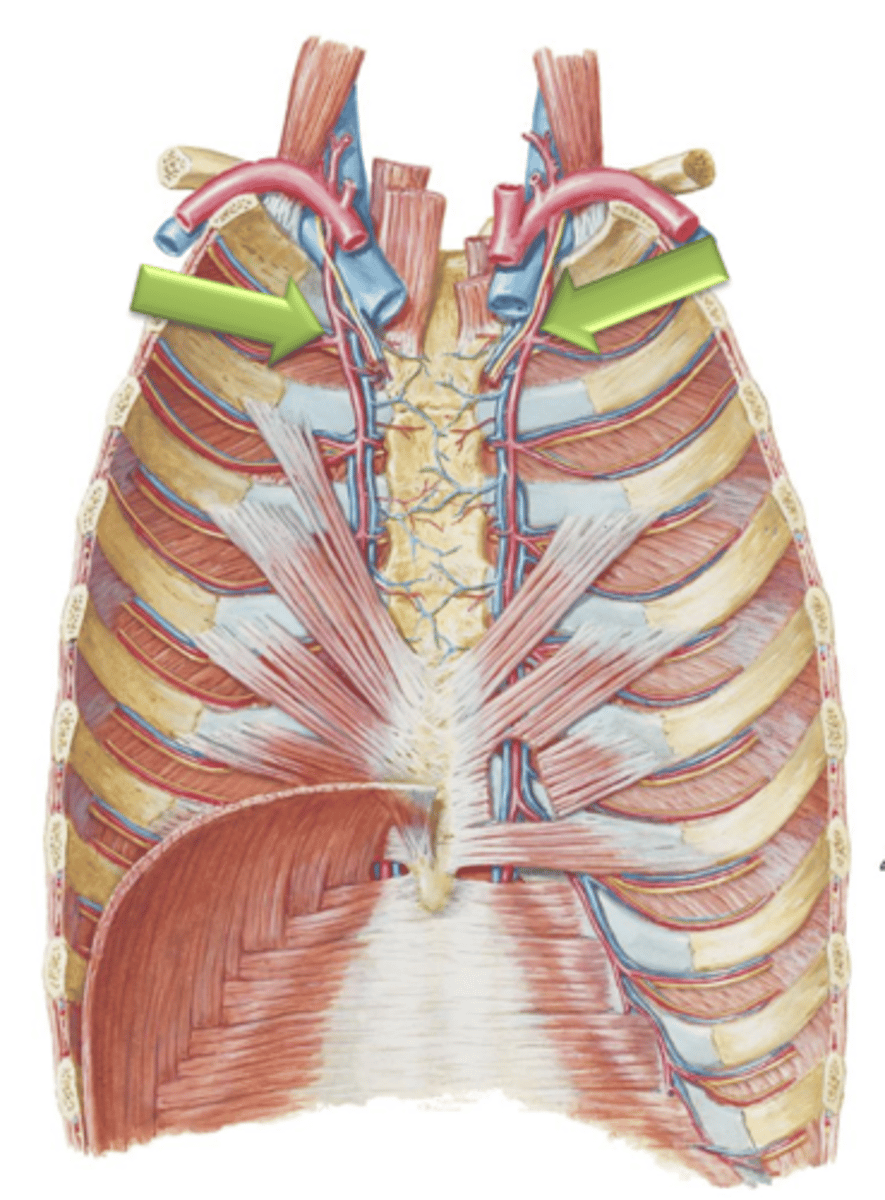
Internal Thoracic Arteries
Arteries that arise as branches from the left and right subclavian arteries.
Anterior Intercostal Arteries
The Internal Thoracic Arteries course distally along the internal thoracic wall just lateral to the sternum and give off ___ ___ ___ which supply internal thoracic tissues and intercostal muscles.
Posterior Intercostal Arteries
Arteries that arise as small branches from the descending aorta and course laterally between the ribs. These blood vessels supply the skin of the lateral and anterior chest wall as well as the intercostal muscles.
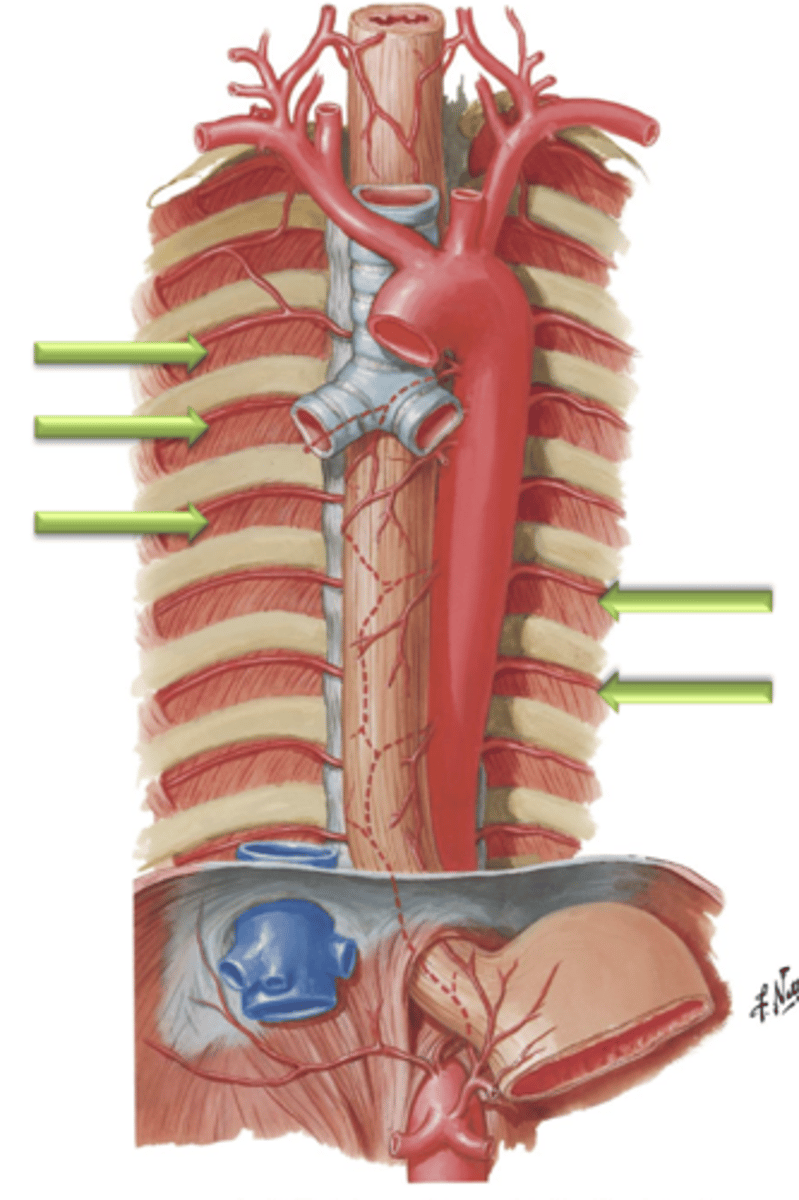
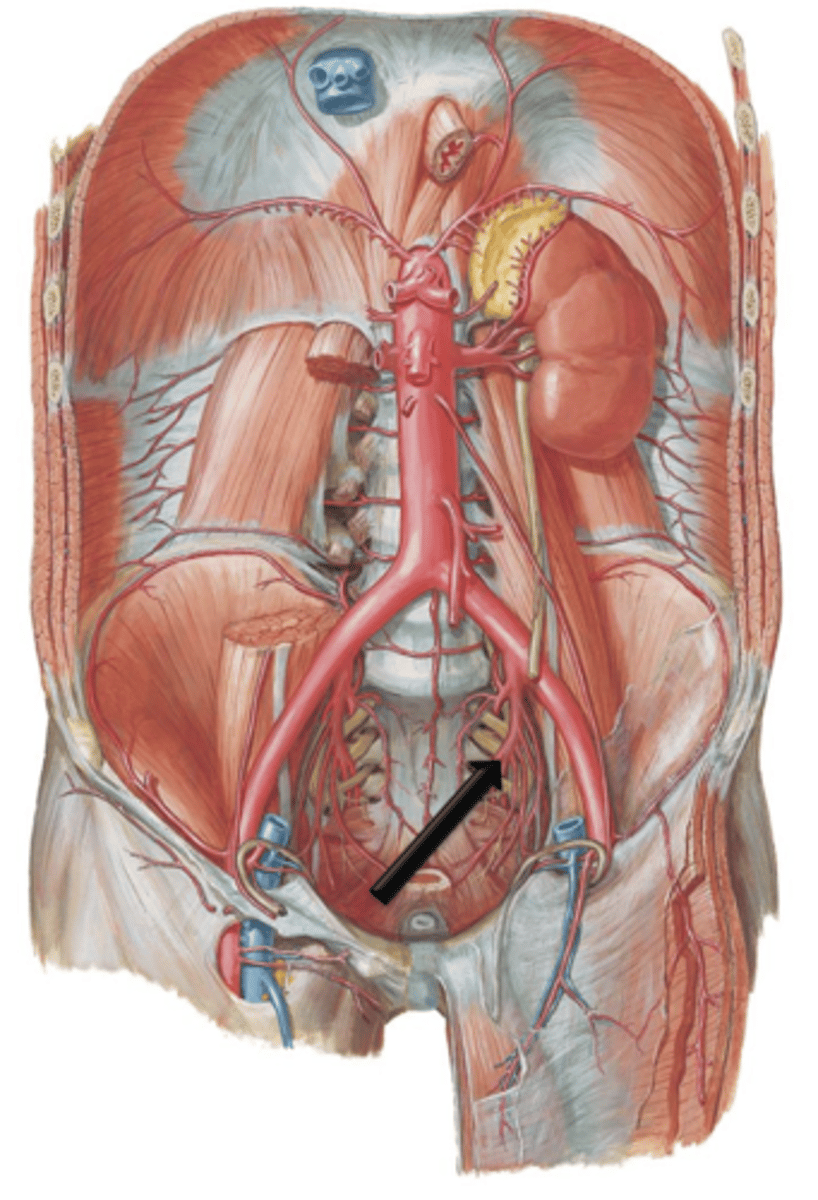
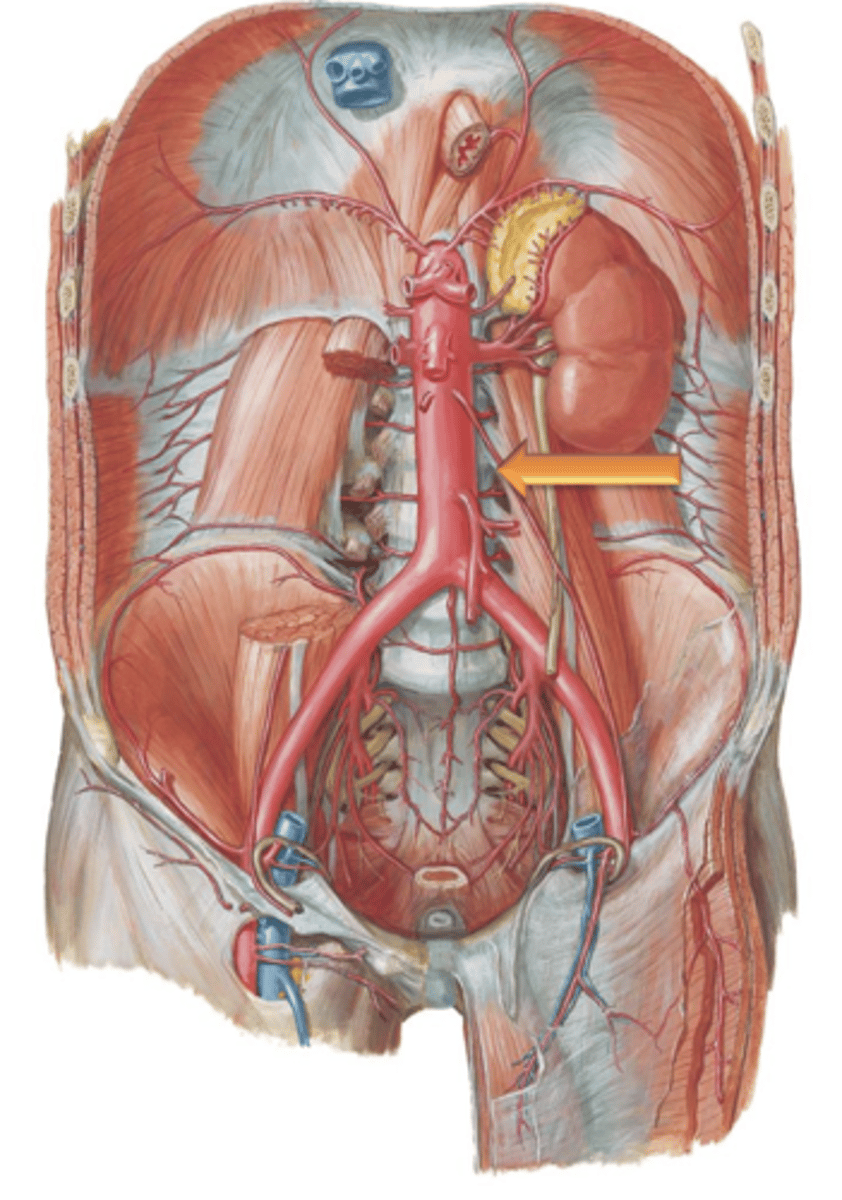
Descending (Abdominal) Aorta
The ___ ___ ___ enters the abdomen by traversing the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm at the level of T12.
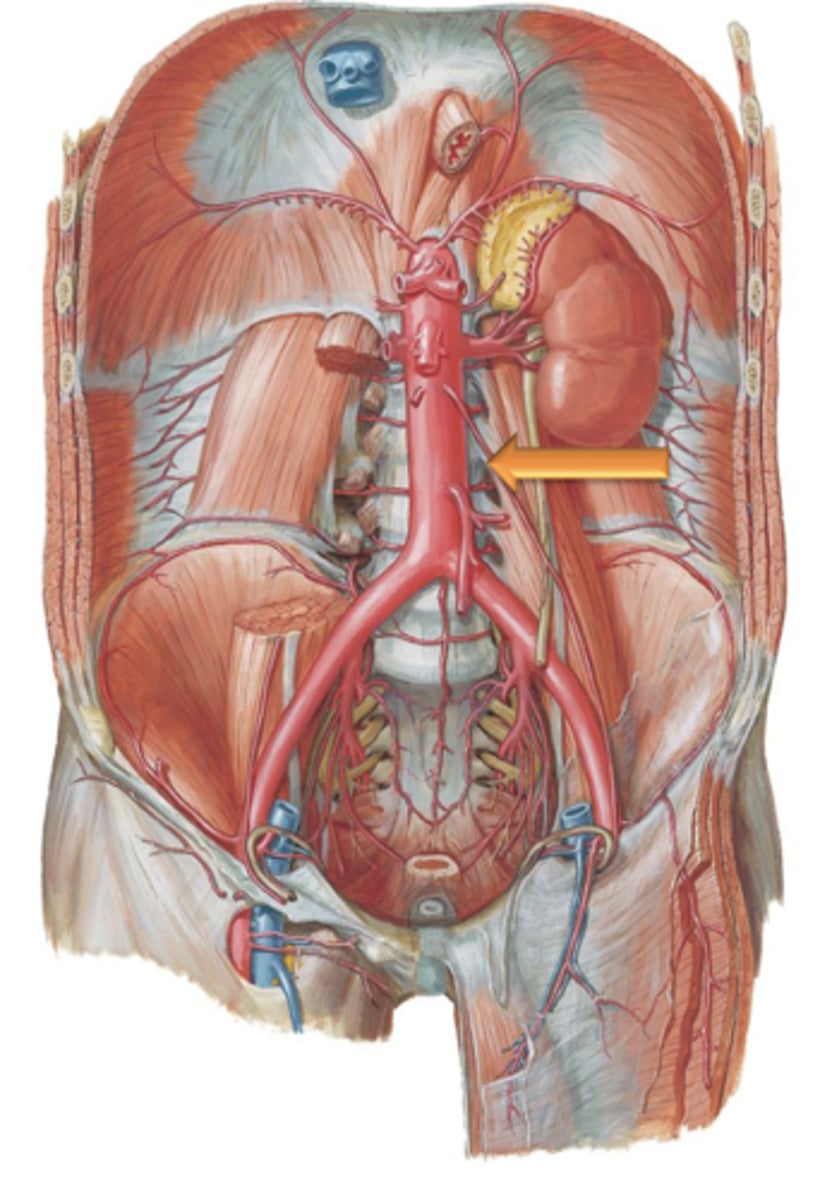
L4
The descending aorta gives off many branches that supply the organs and viscera of the abdomen before terminating at the level of ___.
Celiac Trunk
A short vessel that arises from the aorta immediately below the aortic opening of the diaphragm.
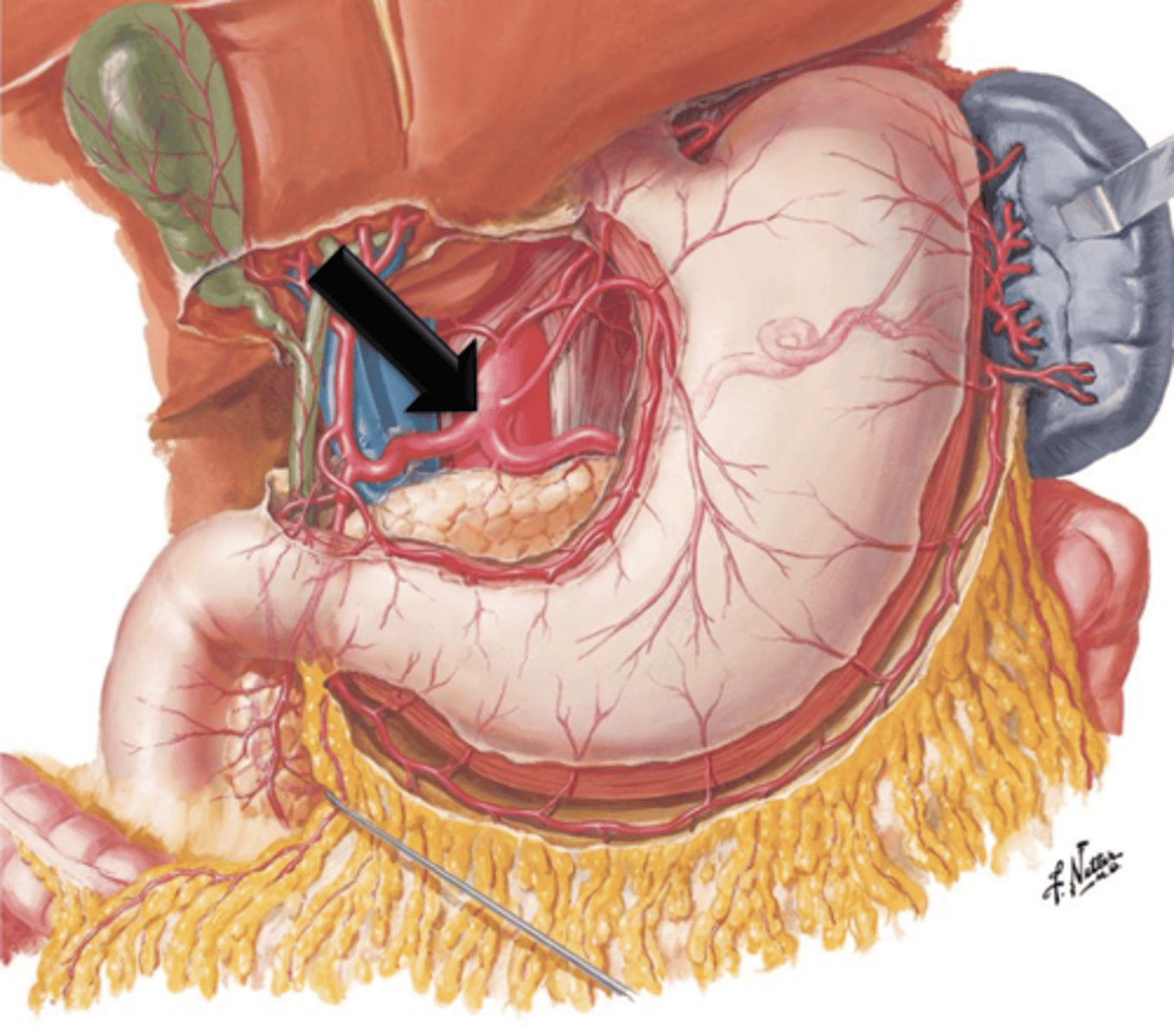
Left Gastric Artery, Splenic Artery, Common Hepatic Artery
What does the celiac trunk give off?
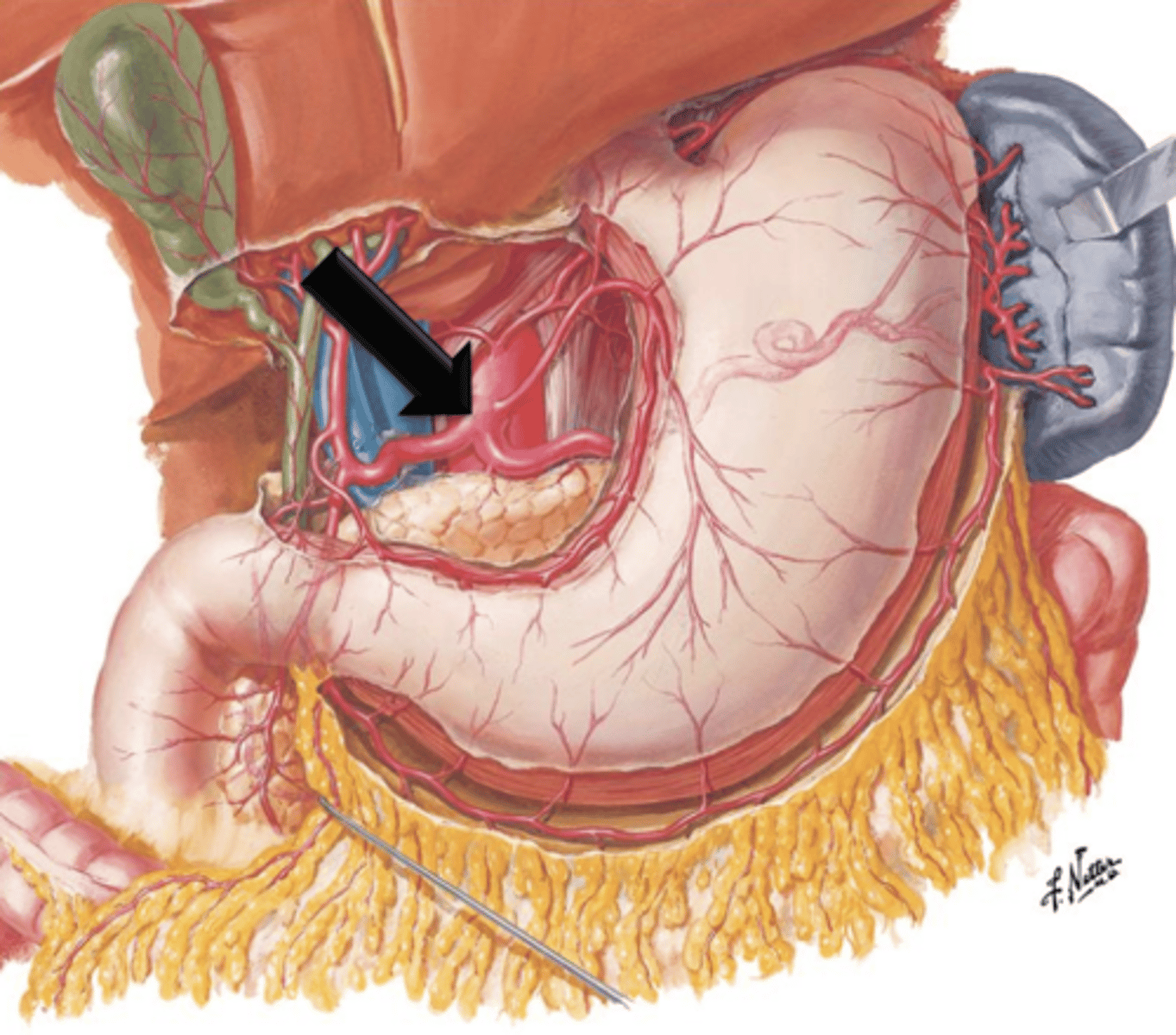
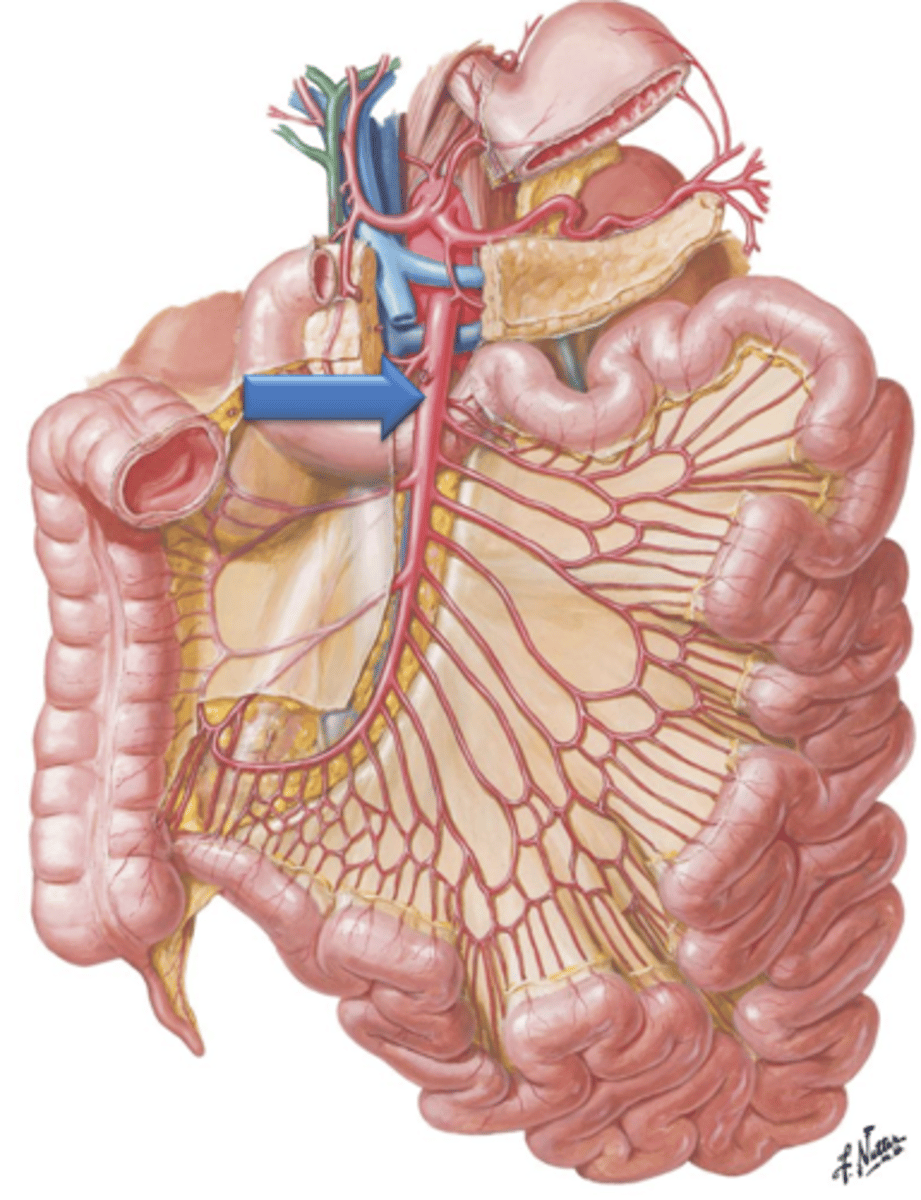
Superior Mesenteric Artery
Artery that arises from the aorta just below the celiac trunk. It descends in front of the lower part of the duodenum, enters the mesentery and supplies the small intestine and portions of the large intestine.
Renal Arteries
Arteries that branch from the descending abdominal aorta and course laterally where they enter into the kidneys.
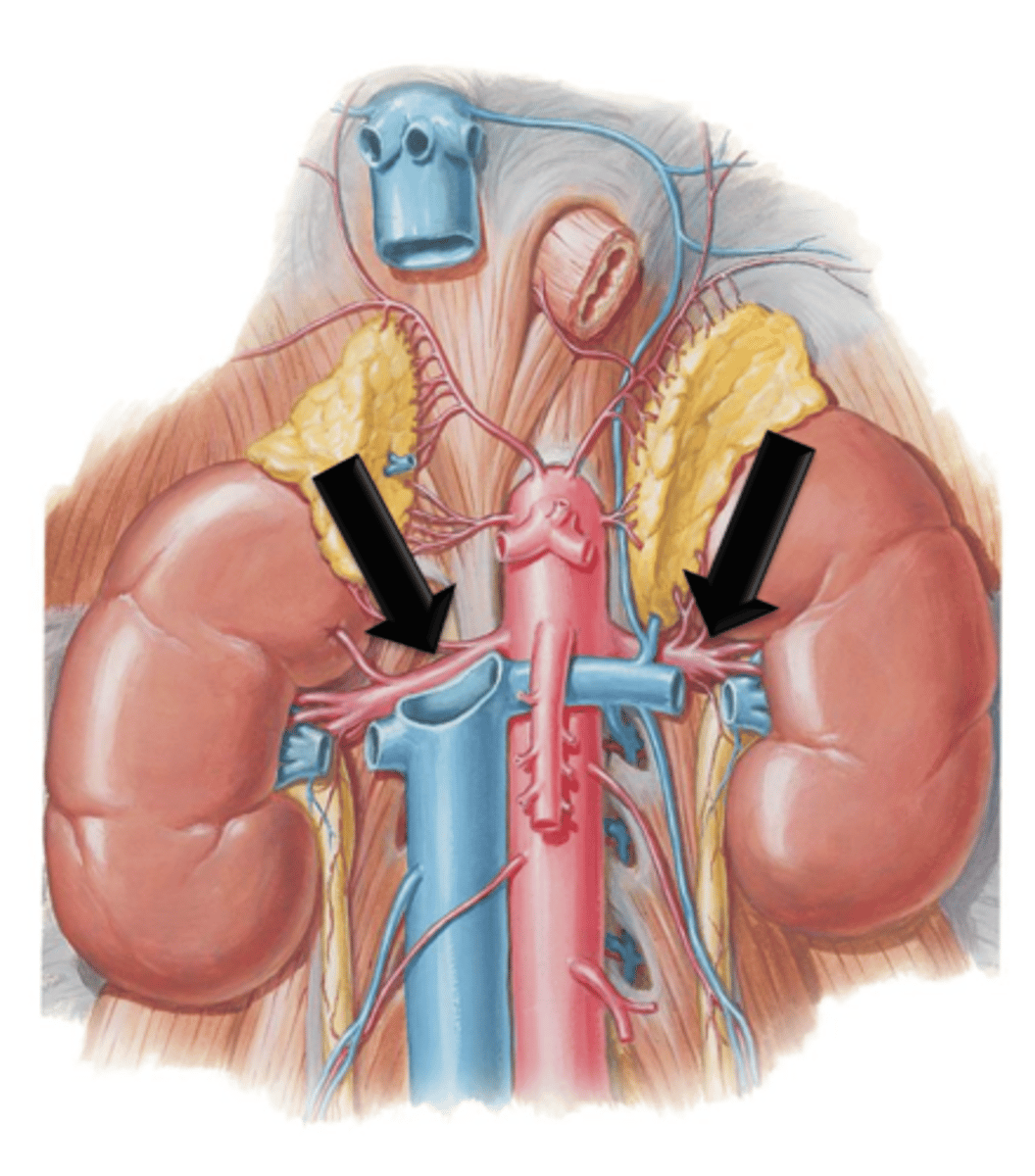
Renal Veins
Blood flowing into the kidneys through the renal arteries is filtered of impurities and returned to the circulatory system via what?
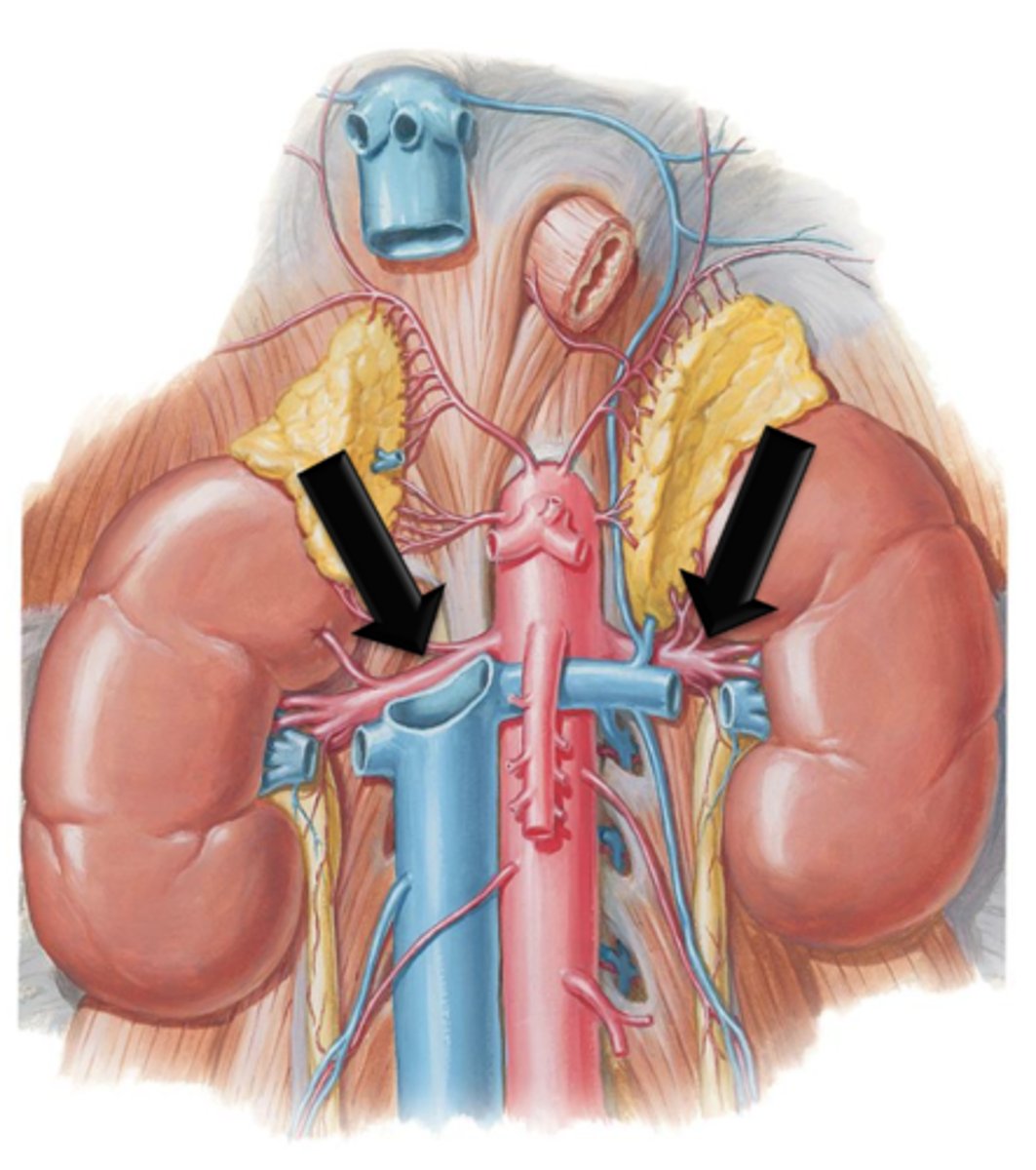
Gonadal Arteries
Arteries that are also known as the testicular or ovarian arteries depending on gender. They arise as small branches from the descending aorta and continue to course inferiorly to supply the reproductive organs.
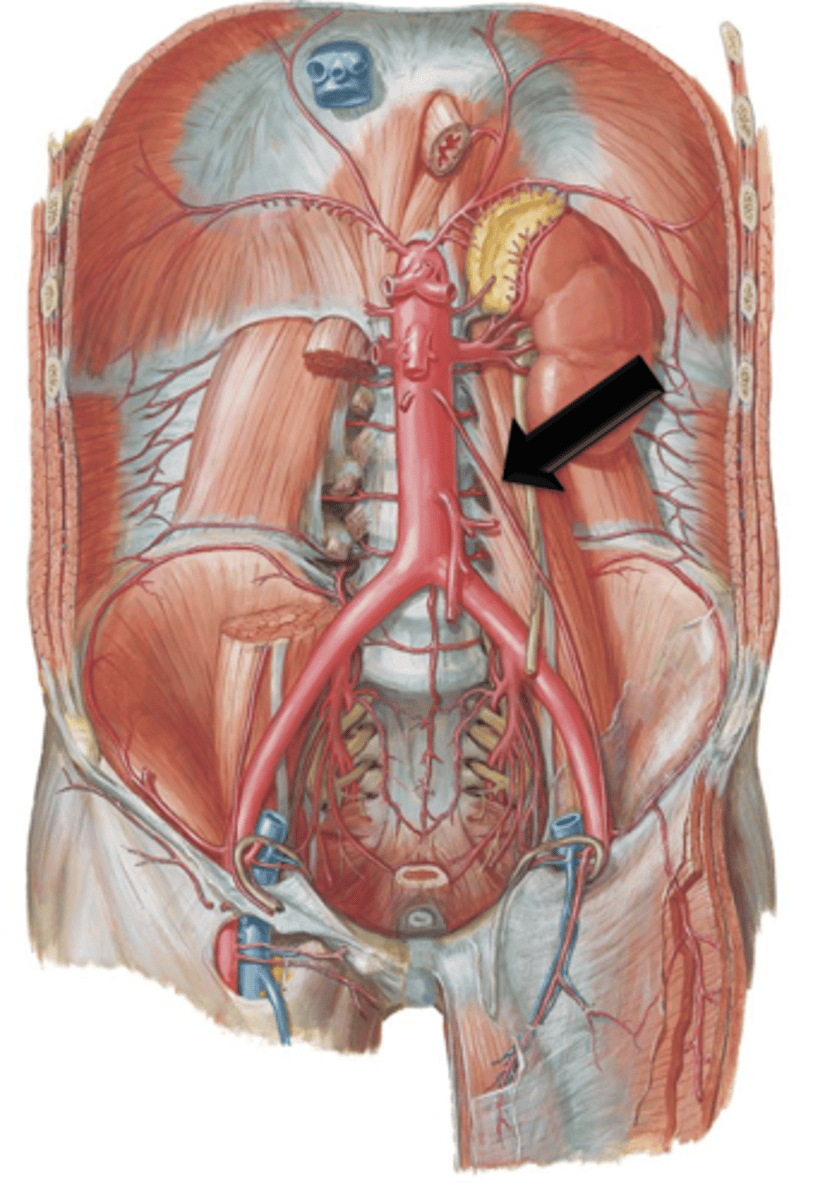
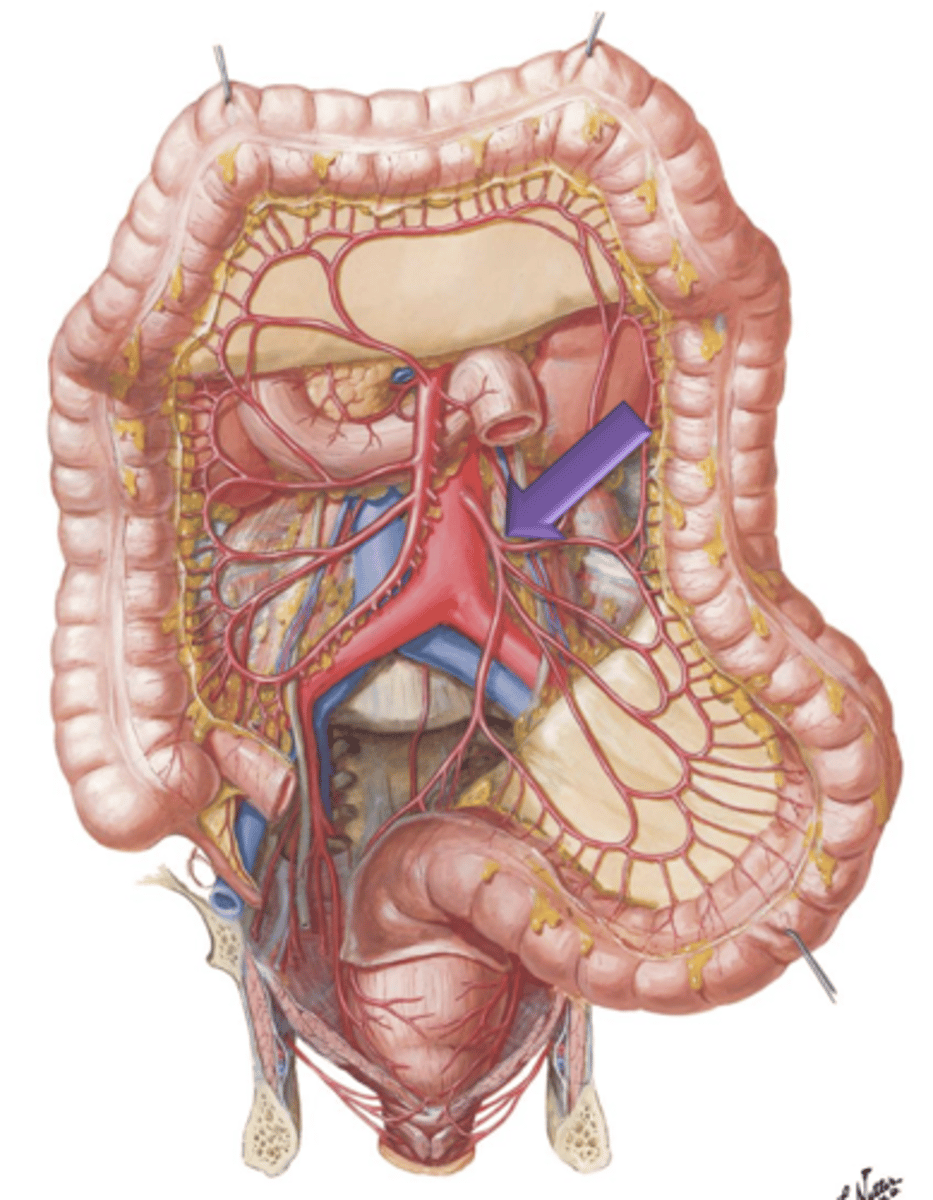
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
Artery that arises from the aorta a few centimeters above its bifurcation. It courses to and supplies areas of the descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum.
Common Iliac Arteries
The descending aorta terminates at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebrae by bifurcating into the left and right what?
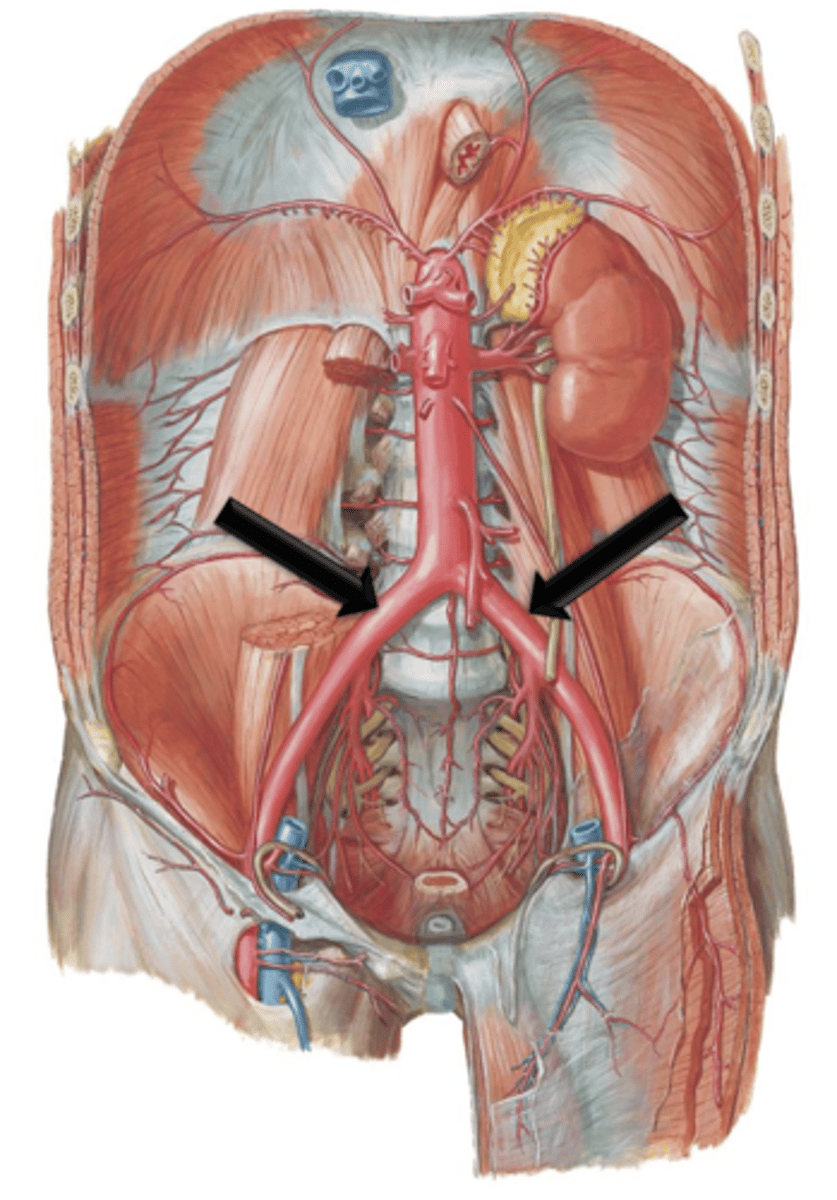
Internal and External Iliac Arteries
The common iliac arteries course for approximately 5 centimeters before bifurcating into what?
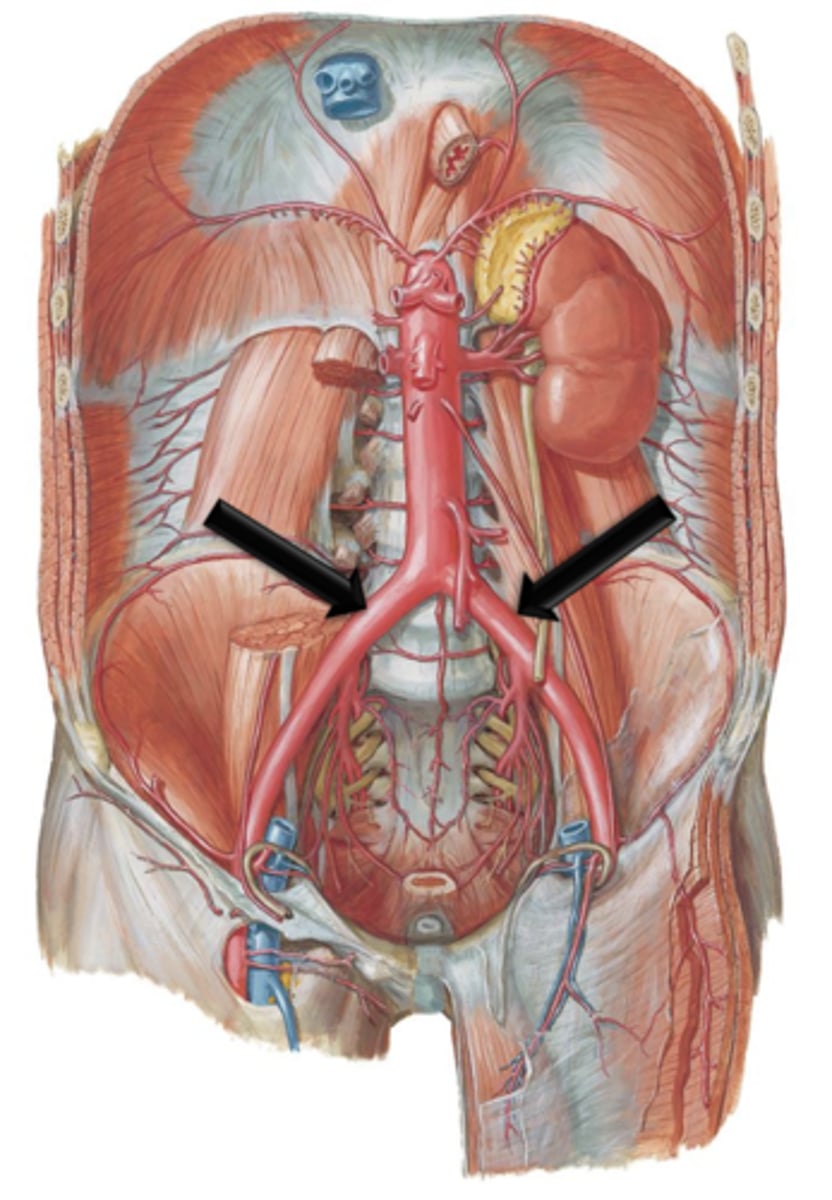
Internal Iliac Arteries
Small branches off the common iliac arteries. They course posteriorly along the pelvic wall. They give off many branches that supply the pelvic, genital and gluteal regions.