Edexcel A-level Geography - Glaciers
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
variations in solar output
low sunspot activity causes cooler temperatures, e.g. maunder minimum(1650-1750)
volcanic emissions(short term causes of climate change)
volcanoes inject large amounts of sulphur dioxide(ghg) into the atmosphere, which consequently trap heat in the atmosphere
eccentricity
changed to the earth’s orbit over a 100,000 year cycle(circular to oval)
axial tilt(milankovitch)
changed to the earth’s tilt over a 41,000 yr cycle - changes how much solar energy is received at the earth’s poles
precession
‘wobbles’ in the earth’s axis over a 21,000 yr cycle
periglacial environments
surround glacial environments, feature permafrost(permanently frozen ground) e.g. siberia
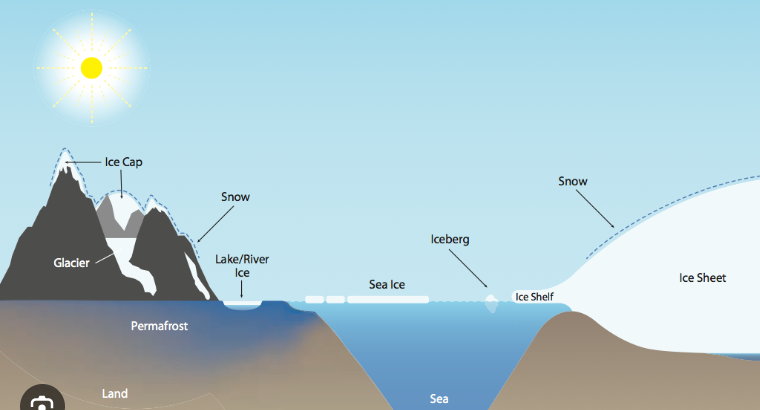
cryosphere
regions on earth where water turns into snow or ice

relict glacial landscape
no longer contains an active glacier, will still have distinct features left behind by its glacial past e.g. lake district, cumbria
freeze-thaw weathering
water enters cracks in the rock. when temperatures drop, the water freezes and expands causing the crack to widen
solifluction
mass movement of soil due to waterlogged conditions, causing it to flow downhill because of gravity
frost heave
the uplift of soil due to the expansion of groundwater when freezing
high winds(transportation)
due to limited vegetation cover, the wind is able to pick up and transport sediment
ice wedges
active layer freezes in winter(causes cracks), summer meltwater enters the cracks, widening them, meltwater freezes in winter to form ice wedges
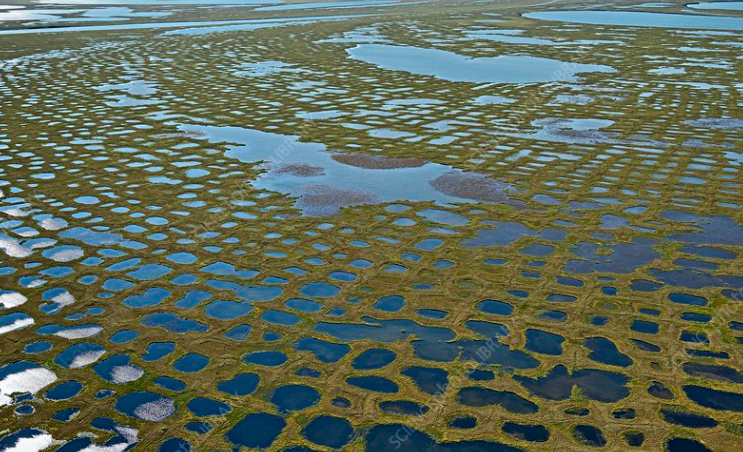

patterned ground
develops through repeated freezing and thawing of moist, frost-susceptible soil, typically forming circles, polygons, irregular nets and stripes

loess(depositional)
silt that’s picked up and transported by wind, can form extensive deposits of loess

pingos
water filters down into the upper layers of the ground and freezes, the expansion of the ice causes the overlying sediments to heave upwards into a dome(pingo)
greenland case study:
avg rate of ice loss has gone up from 34gt a year in 92-01 to 215gt a year between 02-11
loss of ice cover is making the surface darker, accelerating melting(negative feedback loop)
melting of the ice sheet has contributed 0.33mm a yr to global sea rise between 02-11
how do warm based glaciers move
basal slippage(sliding) - glacier sliding over the bed due to the ice acting as a lubricant
movement of cold based glaciers
internal deformation - the weight of glacier ice and gravity causes ice crystals to deform, so the glacier very slowly moves down
factors controlling the rate of glacial movement
ice thickness - greater thickness creates more pressure in the ice, causing faster movement
slope
ice temperature
variations in mass balance - more ablation = more meltwater causing more basal slippage
altitude - high altitude = more snowfall so faster movement due to accumulation, low altitude = warmer so more meltwater, more basal slippage
how do glaciers alter landscapes
erosion
removal of weakened material by glacial ice
abrasion
glacier drags rocks, sediment and debris in its basal ice, grinding the bedrock beneath
plucking
rocks become frozen to the glacier and are plucked from the ground as the glacier moves forward
crushing(erosion)
as the glacier moves it causes erosion along the soil and rock it sits on, the weight may cause physical stress to the ground whilst picking up boulders
transport
rock debris is transported on the ice surface(supraglacial), within the ice(englacial) and at the base of the ice(sub-glacial)
deposition
till is sediment deposition directly by glacier ice, fluvio-glacial(erosion from meltwater) debris is deposited by glacial meltwater
glacial landforms
valley glacier landforms
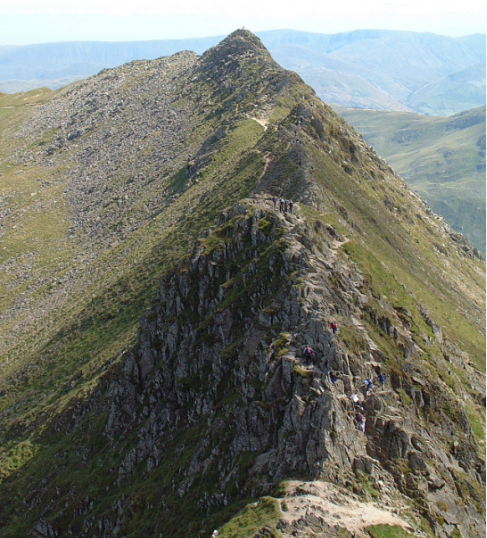

arete
develops through plucking and abrasion on the back wall of two cirques, this means they erode backwards towards each other, creating a narrow ridge
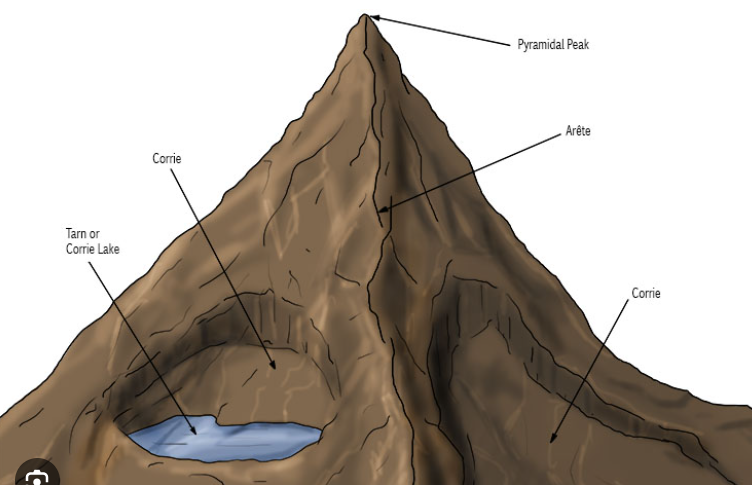
pyramidal peak
erosional processes within nearby cirques mean they erode backwards towards each other, creating a pointed mountain summit
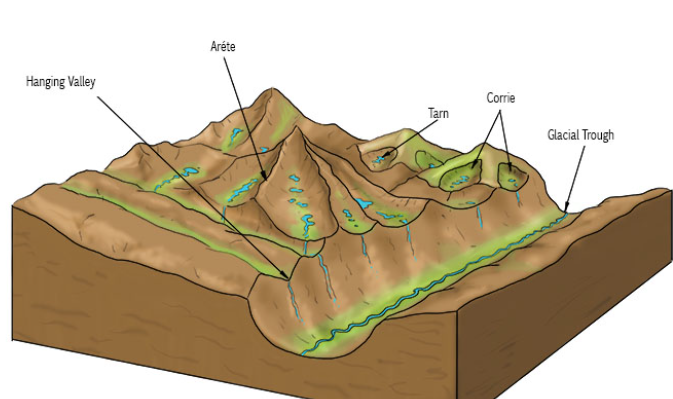
glacial trough(u-shaped valley)
v-shaped valley is widened and deepened as a result of plucking and abrasion by a valley glacier
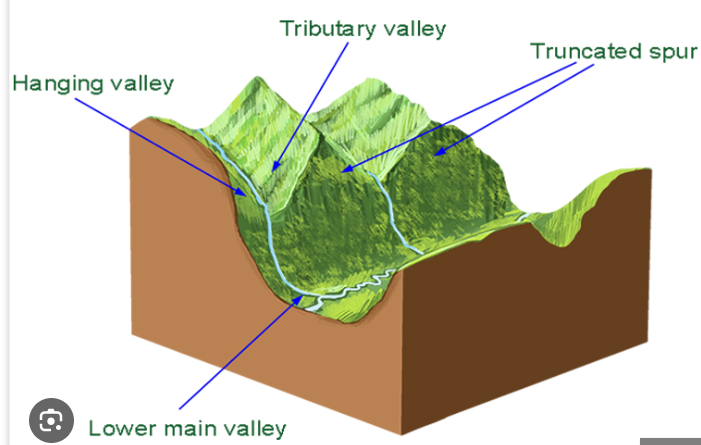
truncated spur
when a valley fills with a glacier, any land which is in the way of the moving glacier will be eroded away, causing a truncated spur
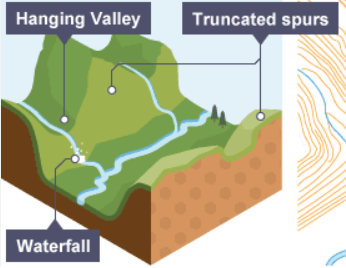
hanging valley
tributary glaciers entering a glacial trough
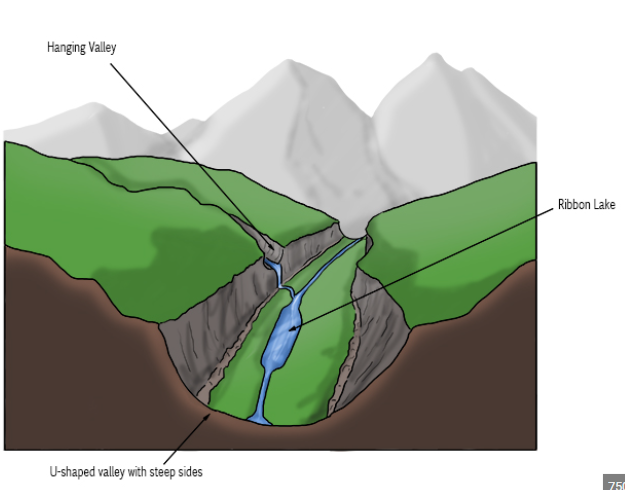
ribbon lake
areas of increasing plucking and abrasion by the valley glacier deepen part of the valley floor, usually because of weaker rocks, meltwater then fills this as the glacier retreats

cirque
snow accumulates in a sheltered location on a mountainside, nivation enlarges the hollow and more snow accumulates, a cirque glacier develops, plucking forms the back wall, abrasion scoops out the cirque hollow

roche moutonee
a more resistant rock causes ice movement, as the ice slides over the rock, it smooths the stoss(up-valley side) while refreezing on the lee(down-valley side) causes plucking resulting in jagged rock
dispositional features
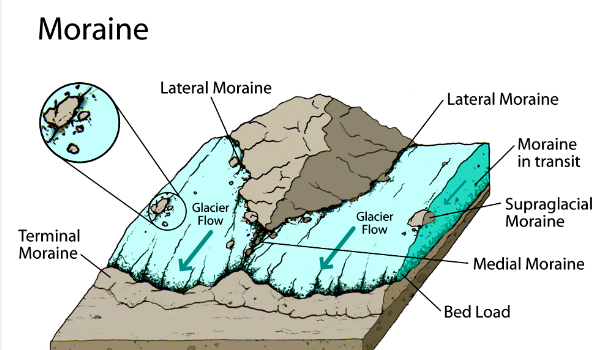
moraine
the material carried by a valley glacier and is deposited as till
terminal moraine
debris being deposited at the limit(end) of a glacier
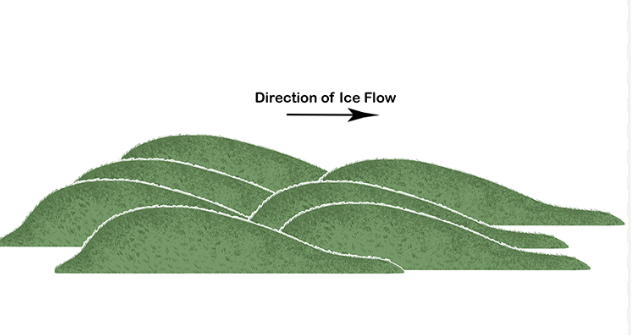
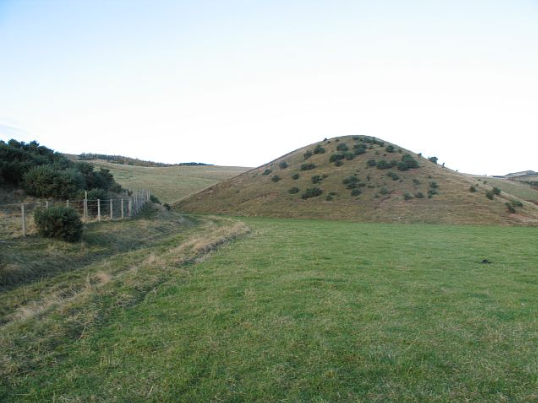
drumlins
theory: formed by deposition when glacier ice becomes overloaded with debris when exiting an upland area, the deposits are streamlined and shaped by moving ice
lowland depositions features
till plain
when a large ice sheet becomes detached from a glacier and melts, material is deposited over a sizeable area
lodgement till
when debris that was being transported gets lodged or pressed into the glacier bed
ablation till
ablation is the melting of the ice and the till is deposited as the glacier melts, includes supraglacial and englacial material
formation of fluvio-glacial landforms

kame
as meltwater streams emerge onto the outwash plain at the glacial snout, their velocity falls and the sediment is deposited
kame terrace
during summer, the valley sides radiate heat, melting the edge of the glacier, forming meltwater streams, which deposit sediment, the sediment forms a kame terrace as the glacier retreats
eskers